Course Module 5 - Network
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
physical layer
represents the physical devices/hardware that connects to a computer
hardware includes:
fiber optic cables
twisted pair cables
network interface cards
purpose to transmit raw bits (1s and 0s) across a physical medium i.e cables. To determine if a bit is 1 or 0 you can look at the voltage level. And through a process call modulation which can access if a bit is a 1 or zero by the voltage of the electric charge
data link layer
deliver locally
responsible for traversing data on the same network. (ethernet, WIFI)
Network layer
the layer where all the networks communicate with each other
transport layer
target app
makes sure that data is getting to the right server (app)
two main category of cables
copper cables
made out of metal
slower but affordable
transmits electrical signals (1s and 0s)
fiber optic cables
made out of thin strains of plastic or glass
faster but more expensive
transmits light signals
crosstalk
a single transmitted from one wire interfers with a single from an adjacent wire
switch
a physical hardware that connects multiple devices in a network. (Data Link Layer) and it forwards data packets to its intended destination. Reduces collision domain
inspects ethernet data to determine where to send things
when a device is connected, the switch will store its physical address (MAC addresses) in the switch table. In this table that is how the switch knows the destination to route the data.
Collision Domain
When more that one device sends data packets simutanelously across a wire (For example computer A and computer C at the same time is transmitting a frame) so their signals can collide causing data corruption and collision of the electirc current sedning our ones and zeros
Hub
a hardware device that connects multiple device to an internal network. It ha multiple ports that accepts ethernet cables
Different from a switch because data packet is sent to all devices connected to the network not just the intended destination.
Physical layer
High risk for collision because if two devices are sending data on the same network it can cause collision and data corrupti
routers
A hardware that connects multiple devices to multiple networks by forwarding data packets to its intended destination by analysising the IP protocol
routers use routing tables
ISP have more sophsticated routers
duplex communication
data can travel in both directions simutaneously
socket programming
The process of connecting two nodes over a network to communicate with each other
CSMA/CD
Carrier Sense Multiple Access
A protocol that determines when communication channels are free and when devices are free to transport data. Listens for open lines of communication on a network segment.
Collision Detection
if a collision domain occurs (2 or more devices transmitting data on the same network segment) then in this protocol it will stop all communications of devices and make the devices wait a random interval of time (different times) to then resume transport
Ethernet broadcast
data that is sent to every device on a LAN
data packet
a container that contains a set of binary data that is being sent across a network segment
mac address
A unique 12 digit hexadecimal number used for communicating on LAN (local area networks)
more suitable on local networks when trying to send data packets because there is no system to know where a MAC address is geographically
MAC addresses will always be the same no matter where you are
dotted decimal notation
IP addresses are 32 bit long numbers. Made up of 4 octets
12.34.56.78
IP address
IP addresses belong to the network not devices so it will not always remain the same
a valid ip address is a number between 0 and 255
DHCP
Dynamic host configuration protocol
when a new devices is connected to the internet your router gives you an IP address using DHCP
these are dynamic IP addresses
dynamic ip address vs static IP address
dynamic IP addresses is when the DHCP give a devices an IP address
and static IP addresses is when you manually provide IP address to the node. usually reserved for networks and servers
what are data packets called on the ethernet layer
ethernet frames
what are data packets called in the network layer
IP datagrams
What is in a datagram
datagram consits of two things header and payload:
header has
- the source and destination IP
- the size of the datagram
- specifies the protcol that will be used in the next layer (TCP or UDP)
- TTL (Time To Live) prevents routing loop
payload:
- the actual contents/data of the datagram
- its job is the carry the contents to the next layer by using the contents from the header this process is called encapsulation
because once a datagram is fully formed it needs to be encapsulated into a ethernet frame
fragmentation
the process of breaking datagrams into smaller sizes if the payload exceed the max size specification that the network allows and apon arrival it is put back together
List the address classes
Class A: the first octet is the network ID the rest is the host ID: 9.100.100.100 (9 Net Id rest Host Id)
Class B: the first two octet is the network ID the rest is the host ID
Class C: the first three octet is the network ID the rest is the host ID
Think of the first octet (the first number) in an IP address like a label on a box:
Class A Box: Label range is 0-127.
ex: 10.100.50.1
Class B Box: Label range is 128-191.
ex: 176.16.0.10
Class C Box: Label range is 192-223
ex: 198.168.1.1
What is the ARP
Address Resolution Protocol
the ability to find the MAC address by using an IP address. It will most likely use the ARP table. Howver if the IP address does not exsit on the ARP table then the node will broadcast an ARP message to all devices on the LAN.
the device with the IP address will send back a response with the MAC address and add it to the ARP table for future use
ARP tables do have an expiration date
subnetting
sub-pizza: dividing a large pizza (network) into small slices (subnets) to make it more manageable
submasking
It is used to determine the network id and host id in an IP address
First you need to convert the IP address and the sub mask IP address into binary
whatever is a ‘1’ it is reserved for the network id and the rest for the host
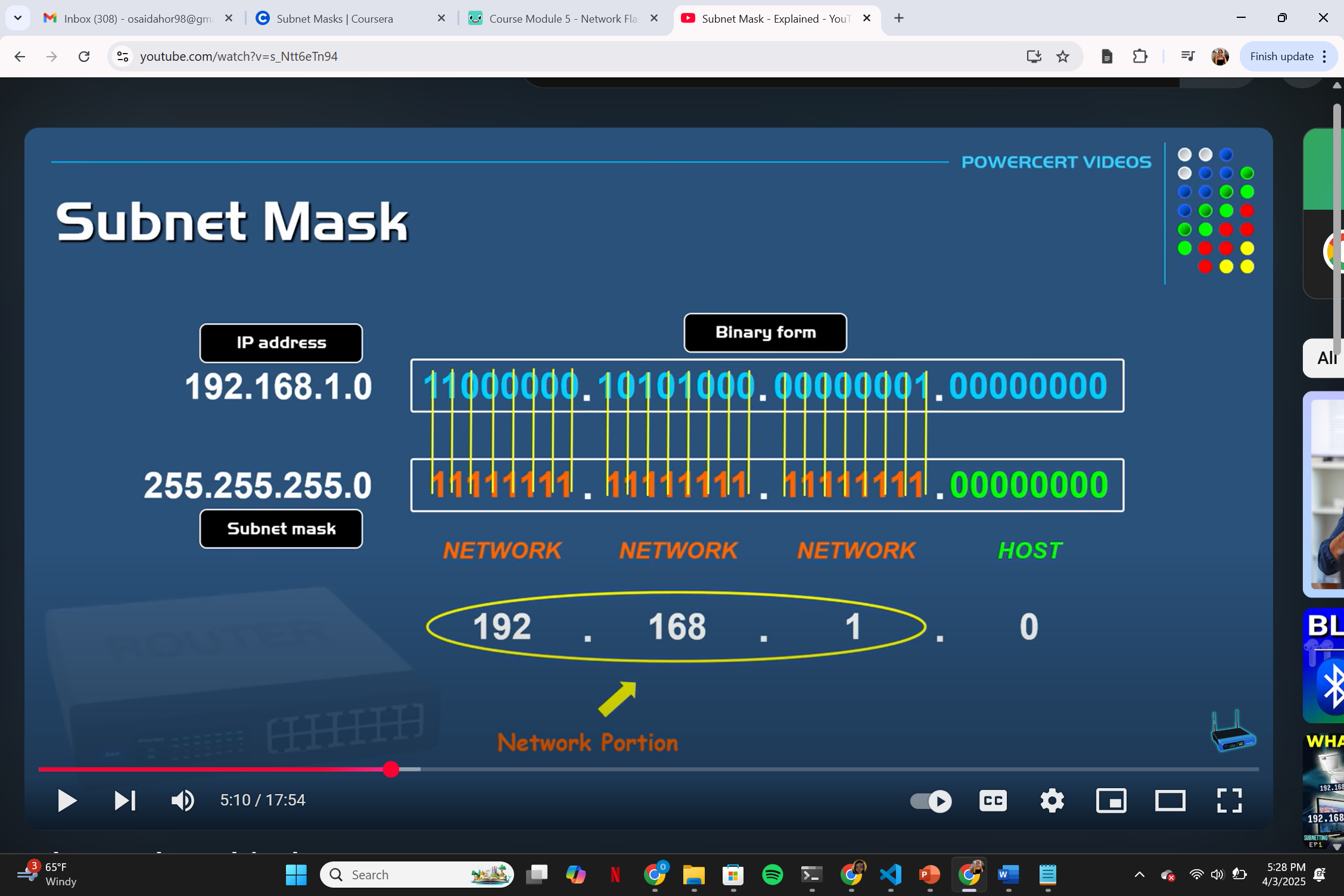
submasking example
example shown in image
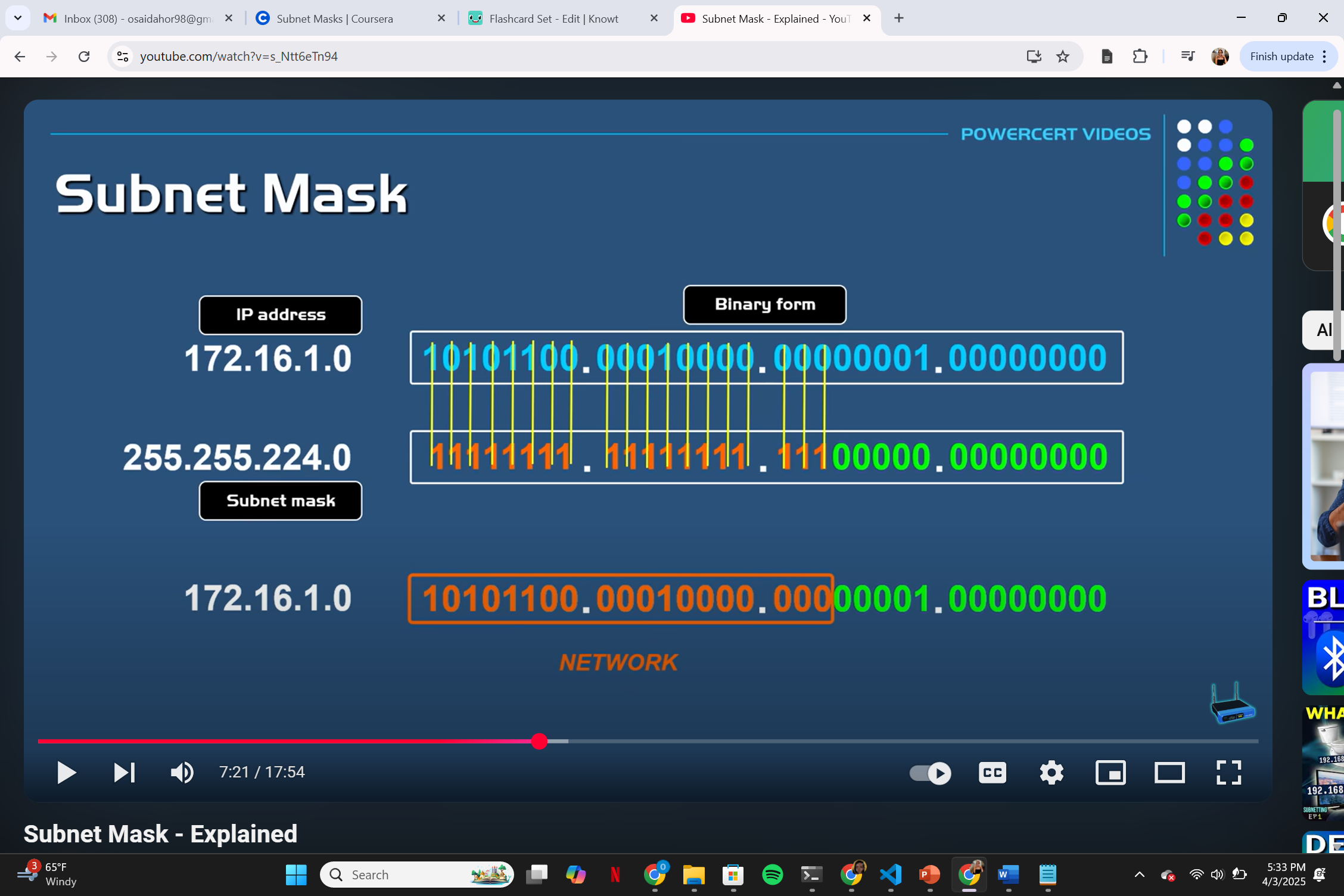
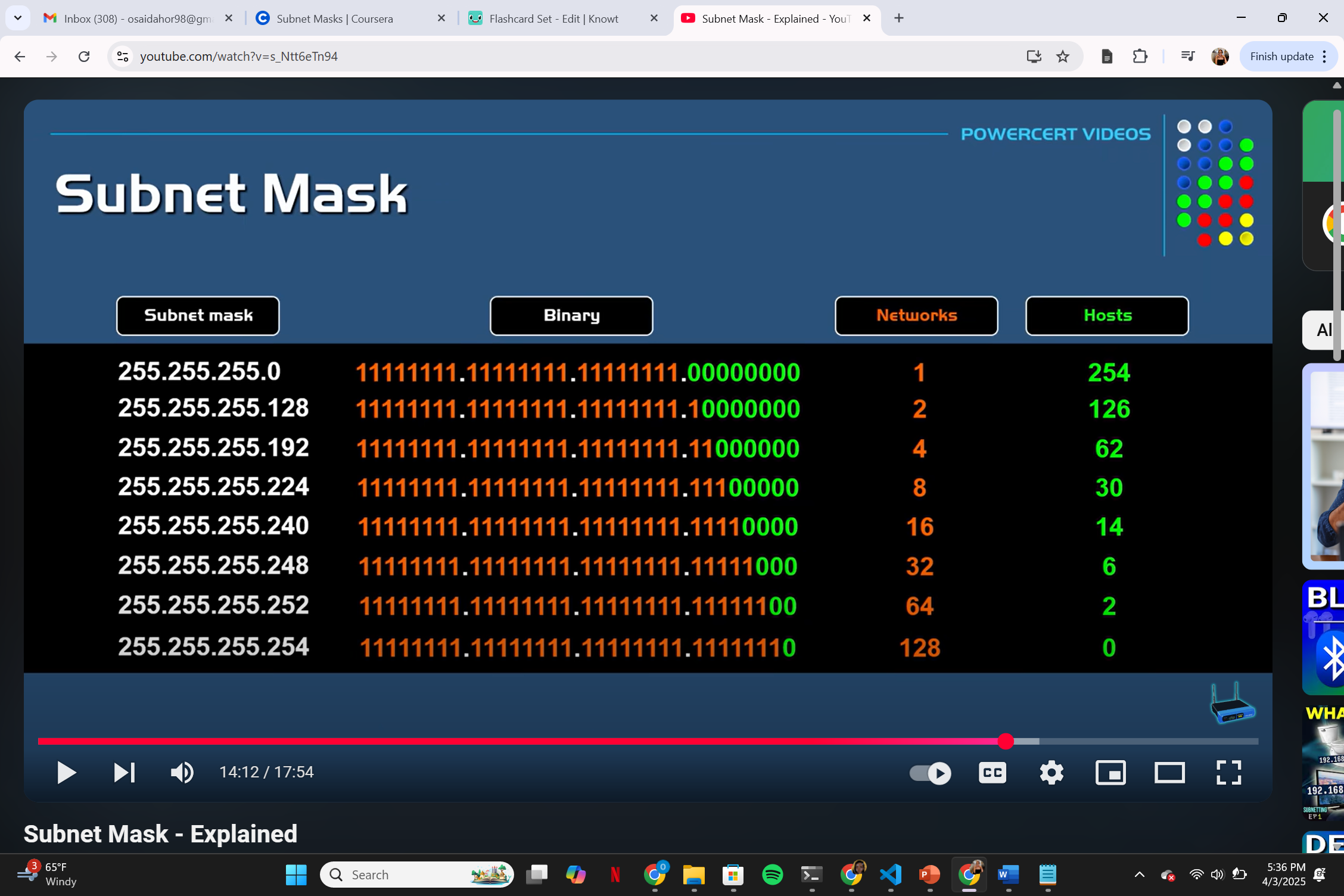
the number of networks and host submasking example (image)
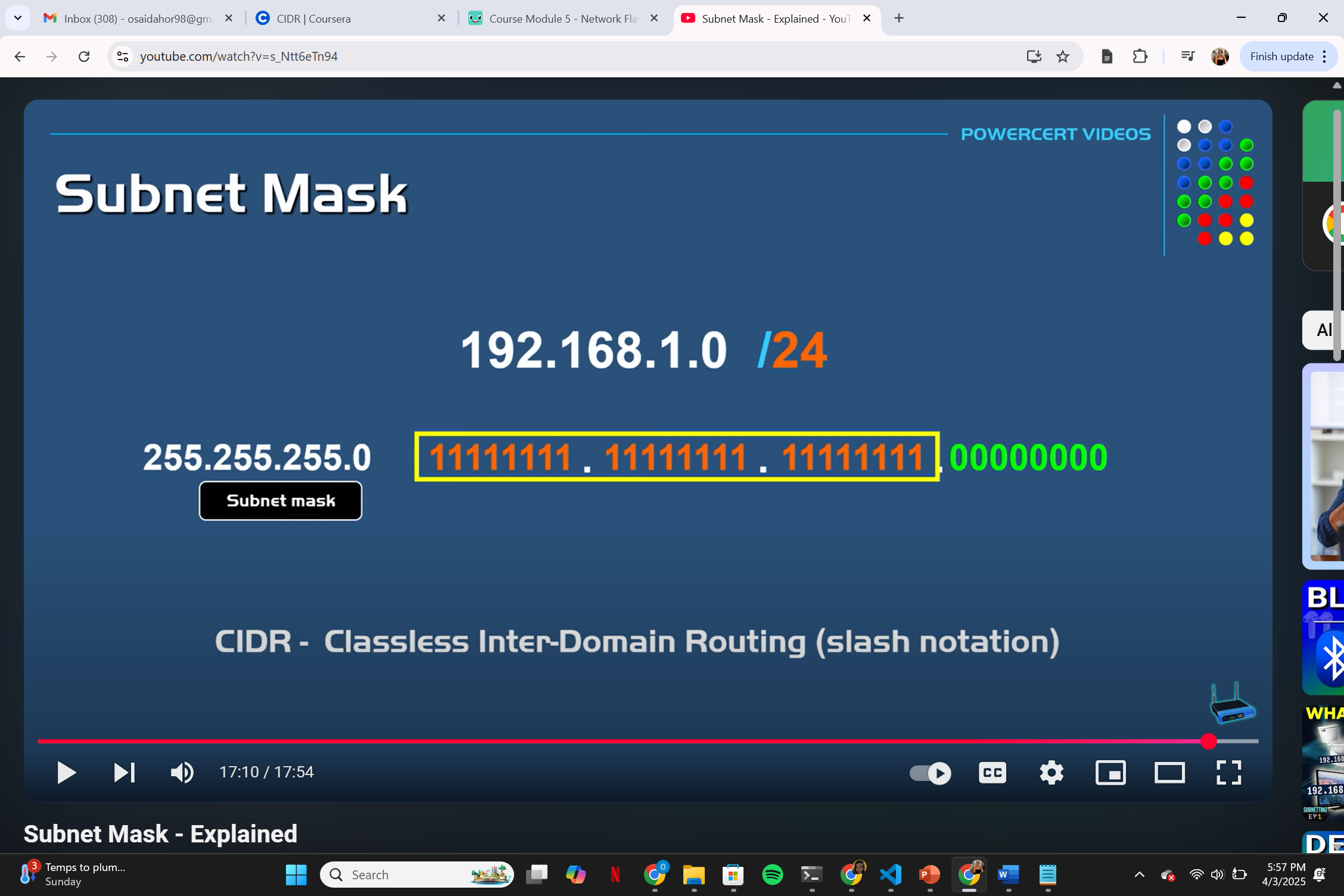
CIDR Notation
something like this 9.100.100.100/24 just means there at 24 1s in front leaving the last 8 digits to be hsot
the steps in a router when sending a data packet
recieve the data packet
take apart the encaspulation of the ethernet frame and turn to datagram
examine the IP address
look up the destination IP through the routing table
send the IP address to its intended destination
steps in a router
recieves data packet
examine ip address destination
look up ip destination in routing table
forward traffic to appropriate router
whats in a routing table
ip address destination title
next hop (the immediate next router that the data packet will go towards)
total hops (the total number of routers to get to the ip address destination
interface ip address
What are the protocols for routers
interior gateway protocol and exterior gateway protocol
Define interior gateway protocol and its protocol
This functions as a way for routers to share their information (tables,etc) with routers within their single autonomous network. A large company can have multiple networks so the routers are communicated withthin this network
distance vector protocol: routers can share the routing infromation with neighboring routers
link-state protocol: routers can share their information with all routers within their network
define exterior gateway protocol
This allows for rotuers to communicated with other routers in different organization’s networks
What is MDF?
Main Distribution Frame
It is is the the heart of an internal network. It houses equipment like routers, switches, and patch panels and helps route data to and from the internal to external network
TTL
time to live ->every packet has a value and its given a certain lifespan before terminated. It helps packets not to endlessly circulate the network. (That could happen if there are routing or network errors)
64 is the recommended standard