VCU DPT Neuro - Stuff that’s gotta be a test question
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
The pineal gland is found in what part of the diencephalon
Epithalamus
The thalamocortical/corticothalmic tracts take the ___, which is the bridge between the cerebral cortex and the internal capsule
Corona radiata
Epithalamus is made up of the ___ and the ___
Pineal gland and the habenula
T/F - Hypothalamus controls the INTERNAL environment
True
The hypothalamus modulates the ___
ANS
The satiety center is found in what part of the diencephalon
Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus sense and respond to ___, ___, and ___
Temperature, osmolality, and hormones
What is the general role of the ANS
HR, breathing, digestion, fight/flight
A pt with pusher syndrome is paretic in their right side. What side are they likely to fall towards?
Right side
What is the difference between rods and cones
Rods: Dim light/dark; contrast; motion, black/white; peripheral
Cones: Bright light/color; visual acuity; edges; central
what is the optic disc
Axons pierce choroid/sclera, forming the optic nerve; blind spot
What are the two horizontal movements of the eyeball? Vertical?
Abduction (away from nose) and adduction (towards nose)
Elevation (up) and depression (down)
What are the two pivotal movements of the eyeball?
Intorsion - eye rotates along itself; top of eye rotates TOWARDS nose
Extorsion - Eye rotates along itself; top of the eye rotates AWAY from nose
The superior oblique is innervated by CN ___, lateral rectus by CN ___, and the rest by CN ___
4 6 3
The only two extraocular muscles that act in the X axis are ___ (which ___ the eyeball) and ___ (which ___ the eyeball)
Medial rectus - adducts
Lateral rectus - abducts
The superior rectus ___ and ___ the eye, while the inferior oblique ___ and ___ the eye
Elevates and adducts
Elevates and abducts
Intraocular eye muscles control ___ accomodation and reaction to ___; the two in the iris are ___ and ___ and the one in the ciliary body is ___
Pupil accommodation and reaction to light
Sphincter pupillae and dilator pupillae
Ciliary muscle
Orbicularis oculi ___ the eye and is innervated by CN ___, while the lavatory palpebrae superioris ___ and ___ the superior eyelid and is innervated by CN ___
Closes; CN 7
Retracts and elevates; CN 3
When you turn your head left, the eyes move ___, the R eye moves ___ via the ___ ___, and L eye moves ___ via the ___ ___ (VOR)
Right
Lateral - lateral rectus
Medial - medial rectus
In the corneal reflex, the afferent portion is controlled by the ___ nerve, and the efferent portion is controlled by the ___ nerve
Trigeminal; facial
What are the three zones of the visual field
Binocular, right and left monocular zone
The temporal retina receives info from the ___ visual field, and the nasal retina receives infos from the ___ visual field
Conralateral
Ipsiilateral
Which retina goes through the optic chasm to the other side of the brain, and which stays ipsilateral and does NOT cross
Nasal retina - crosses
Temporal retina - ipsilateral q
If a pt has an oculomotor N palsy, what effects to their vision would you expect? What movements could they not do? Which eye muscles would still work?
Diplopia, ptosis, dilated pupil
Eye adduction and up/down gaze
SO4 and RL6
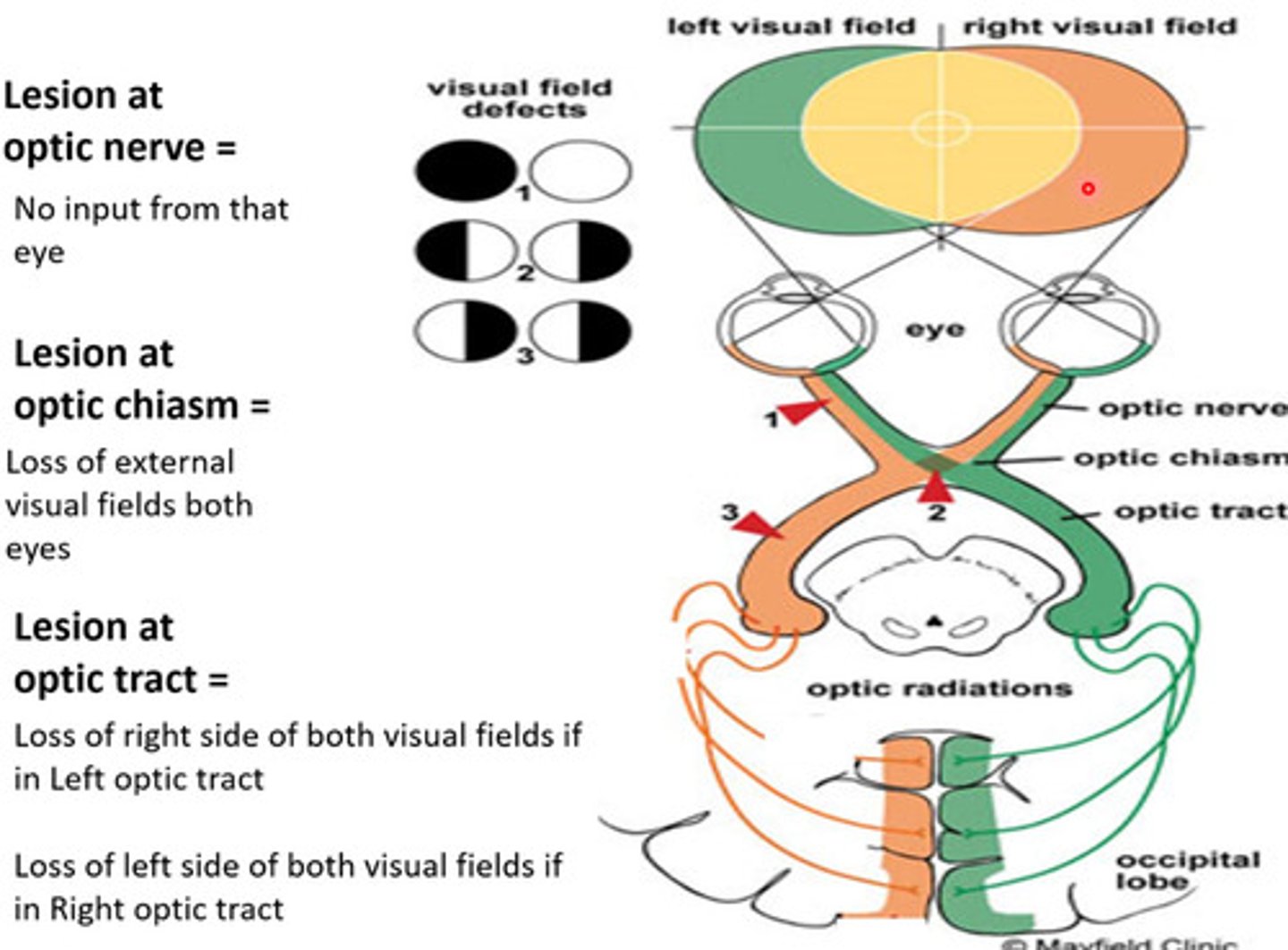
What would be the result of a lesion to the optic nerve? Optic chiasm? Optic tract?
Optic N: No input from that eye
Chiasm: Loss of external visual fields from both eyes (Nasal retina)
What three systems help to maintain balance
Vestibular, vision, somatosensory
The vestibular labyrinth consists of 3 semicircular canals and 2 otolith organs in the ___ portion of the ___ bone
Petrous; temporal
What are the three canals of the vestibular system? What motion does each detect?
Anterior: flex/ext
Horizontal: rot
Posterior: side bending w ext
Describe the relationship between the ant and post semi circular canals working as functional pairs
Right ant works with left post
Left ant works with right post
The semicircular canals expand in an area called the ___. In this area, hair cells (sensory) stick up into an area called the ___
Ampulla
Cupula
Describe the activity of the vestibular system at rest
There is a constant tonic activation
What is the name of the longest hair cell on the cupula? What happens if the movement is going to towards it? Away?
Kinocilium
Depolarization (more afferent)
Hyper polarization (decr afferent)
If you're rotating your head right, the kinocilium on the right side becomes ___ and the left side becomes ___
Depolarized
Hyperpolarized
In teh macula of the utricle and saccule, the ___ cause the ___ membrane to move, moving the hair cells, which send signals out
Otoliths x 2
The utricle detects linear acceleration in teh ___ plane while the saccule detects linear acceleration in the ___ plane
Horizontal
Vertical
Which nuclei(s) promote the vestibulo-oculomotor reflexes (VOR)
Superior/medial
When your head is moving, the ___ reflex activates the muscles in the neck to help keep you upright against gravity
Vestibulocollic reflex (VCR)
the vestibulcollic reflex travels through CN ___ to what spinal nerve levels? What is the purpose of the reflex?
8 (vestibulocochlear)
C1-4
Maintain upright head
What vestibular nucleus does the vestibulocollic reflex use? What neural tract?
Medial
Medial vestibulospinal tract
The vestibulospinal reflex travels through CN ___ to what spinal nerve levels? What is its purpose?
8
Lower half of C, thoracic, and lumbar
Hip/step strategy to maintain balance by activating (mostly) extensors
What vestibular nucleus does the vestibulospinal reflex use? What tract?
Lateral vestibular nucleus
Lateral vestibulospinal tract
What are the efferent motor nerves in the vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR)
CN 3, 4 (kind of), 6
When your head turns left, the eyes move ___, the R eye moves ___ via the ___ ___, and the L eye moves ___ via the ___ ___
Right
Lateral - lateral rectus
Medial - medial rectus
Sound travels through the cochlea, through the spiral ganglion and vestibulocochlear nerve, to the ___ ___ nucleus and ___ ___ nucleus. It's then transmitted to the ___ ___ nucleus in the thalamus and to ___ area in the auditory cortex
Post cochlear and ant cochlear
Medial geniculate
Wernicke's area
Before reaching the middle ear, sound travels through the ___ and the ___ ___ meatus
Auricle
External auditory meatus
In the middle ear, sound hits the ___ membrane, which vibrates and causes the ___, ___, and the ___ to vibrate. The stapes then "taps" on the ___ ___
Tympanic
Malleus, incus, and stapes
Oval window
When the oval window is "tapped," there are vibrations through the ___ vestibuli, and the wave travels to the apex, through the ___, and down through the ___ ___
Scala
Helicotrema
Scala tympani
If there's enough amplitude of vibration, the ___ membrane moves, and the Scala tympani eventually ends at the ___ window
Basilar
Round
What is the difference between wernicke's and Brock's area
Wernicke: interpretation of language
Broca: expression of language
During the middle ear reflex arc, a loud sound stimulates the hair cells and the ___ nuclei which can activate efferent axons from the ___ ___ nucleus to type 2 cells. From the cochlear nucleus, the impulse travels to the ipsilateral facial motor nucleus that innervates the ___ via CN ___
Cochlear
Superior olviary
Stapedius - CN7
The ___ artery branches from the ___ ___ ___ artery, supplying the nerve, ganglia, and vestibular/cochlear receptors
Labyrinthine
Ant inf cerebellar
The semicircular canals and cochlea are located in what bone
Temporal
What is the name of the fluid in the semicircular duct
Endolymph
What deficits would you expect if the vestibulocochlear nerve was severed
Hearing loss, deficit in balance/equilibrium (vertigo)
What are the contents of the neostriatum? What additional structure is included in the striatum?
Putamen and caudate
Nucleus accumbens
What separates the caudate and putamen
anterior limb of internal capsule
What artery supplies the putamen, nucleus accumbens, and globes pallidus
Lenticulostriate A from MCA
What artery supplies the caudate nucleus
Medial striate A
If there was an aneurysm to the lenticulostriate A, which of these structures would not be affected
Putamen, caudate, nucleus accumbens, and globus pallidus
Caudate nucleus
What is the function of the caudate
Cognitive control of movement, planning, and execution of voluntary movement, learning and memory, occulomotor control
What is the function of the putamen
Motor control (habitual and automatic movements); regulation of movement amplitude and velocity
What is the function of the nucleus accumbens
Reward and motivation ; involved in reinforcement learning, pleasure, addiction, and emotional behavior
Most of the neurons in the neostriatum are ___ ___ neurons that release ___ for an inhibitory effect and ___ ___ for a neuromodulatory effect
Medium spiny
GABA
Neuroactive peptides
What are the efferent targets of the striatal complex? Which receives the most information?
Pallidum (striatopallidal fibers), nigral complex (striatonigral fibers), and subthalamic nuclei
Pallidum receives the most
The globus pallidus internus is a ___ pathway to the thalamus while the globus pallidus externus is a ___ pathway to the subthalamic nucleus and substantia nigra; they both release what neurotransmitter
Direct
Indirect
GABA
What are the efferents of the subthalamic nucleus? What kind of pathway is it? What neurotransmitter does it release?
GPi/GPe and substantia nigra
Indirect
Glutamate
In the substantia nigra, the pars compacta releases ___ and the pars reticulata releases ___
Dopamine
GABA
What is the function of the pedunculopontine nucleus in the parabranchial pontine reticular formation? Does it release excitatory or inhibitory signals?
Gait, posture, motor control
Excitatory
The direct pathway ___ activity and the indirect pathway ___ activity
Facilitates (GO)
Inhibits (STOP)
T/F - dopamine FACILITATES movement by suppressing GPi input through both direct/indirect pathways
True
The motor loop in the basal nuclei can be found in the posterolateral ___ and its relative position is ___
The executive loop can be found in the dorsomedial ___ and its relative position is ___
Putamen - lateral
Caudate - mid
The visuomotor loop of the basal nuclei can be found in the body of the ___ and its relative position is ___
The motivational loop can be found in the ventral ___/nucleus ___ and its relative position is ___/___
Caudate - mid
Striatum/nucleus accumbens - medial/ventral
The two main classes of dysfunction of the basal nuclei are ___ disturbances and ___ disturbances
Hypokinetic
Hyperkinetic
Akinesia, bradykinesia, and dystonia are all impairments you may see in a pt with a ___ disturbance of the basal nuclei
Hypokinetic
Ballismus/hemiballismus, chorea, and athetosis are all impairments you may see in a pt with a ___ disturbance of the basal nuclei
Hyperkinetic
In Parkinson's, the pt will have decr activity in the (direct or indirect) pathway, inc activity in the (direct or indirect) pathway, both of which enhance the output of ___ and ___
direct
Indirect
GPi and SNr
T/F - PD can be described as the "same amount in and more out", while Huntington's is the "Same amount in but less out"
False
PD: same in less out
Huntingtons: same in more out
Huntington's disease is primarily caused by ___ degeneration
Striatal
Huntington's disease is often associated with the impairment ___, which can be characterized by by slow/writhing movements (mostly in hands/fingers), so the pt is unable to keep the limb in a fixed position
Athetosis
What is the primary role of the hypothalamus
Homeostasis
What is the rostral border of the hypothalamus? Superior?
Rostral: Laminal terminalis
Superior: Hypothalamic sulcus
T/F - the posterior pituitary is closest to the optic chiasm
False - anterior
The preoptic, supraoptic, and rostral portions of the lateral hypothalamic area aer supplied by what arteries? What about the tuberal, mammillary, and middle/caudal parts of the lateral hypothalamic area
Ant comm and A1 segment of ACA
Post comm and P1 segment of ACA
What is the blood supply of the pituitary gland? What does it drain into?
Superior and inferior hypophyseal A
Cavernous sinus
What nucleus contains neurons that manufacture gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)
Medial preoptic
What nucleus is known as the feeding center
Lateral hypothalamic nucleus
What nucleus receives input from the retina and may mediate circadian rhythm
Suprachiasmatic nuclei
The supraoptic/paraventricular nuclei send projections to the post pituitary and release what hormones
Oxytocin and anti diuretics (ADH/vasopressin)
What is the role of the anterior nuclei of the supraoptic region
Maintain body temp
What are the four nuclei found within the supraoptic region
Supraoptic, paraventriular, suprachiasmatic, and the anterior nuclei
What are the three nuclei found in the tuberal region
Ventromedial, dorsomedial, and arcuate
What is the function of teh ventromedial nucleus
Satiety center
What is the function of the dorsomedial nucleus
Behavior and SHAM RAGE
Which part of the tuberal region contains neurons that contain releasing hormones to teh anterior pituitary
Arcuate nucleus
What si the function of the mamillary region of the medial zone of the hypothalamus
Long term memory formation
Whta is korsakoff syndrome? It's the result of a lesion to what part of the hypothalamus
Decreased ability to make long term memories out of short term memories
Mamillary region
What ar the three regions of the medial zone of the hypothalamus
Supraoptic (chiasmatic), tuberal, and mamillary
Which hypothalamic nuclei is the most associated with the ANS
Paraventricular nuclei
What is the role fo the amygdala
Emotional modulation
What is the function of the septal area and basal forebrain
Motivation and arousal