a&p ii | exam 1 blood and hemostasis
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
blood
only fluid tissue in the body
classified as a connective tissue
functions of blood
transports (nutrients, wastes, and hormones)
regulates (homeostasis)
protects (against infections)
composition of blood
plasma
formed elements
erthrocytes (RBC)
leukocytes (WBC)
platelets
erythrocytes
red blood cells
transports oxygen and carbon dioxide
leukocytes
white blood cells
make up our immune system that protects us from infection and cancer
platelets
cell fragments that function in hemostasis
produced by a type of leukocyte found in red bone marrow (megakaryocytes)
contain granules loaded with Ca 2+ and enzymes that aid in hemostasis
plasma
fluid that surrounds formed elements
consists of water, electrolytes, plasma proteins, nutrients, hormones, respiratory gases, and metabolic waste
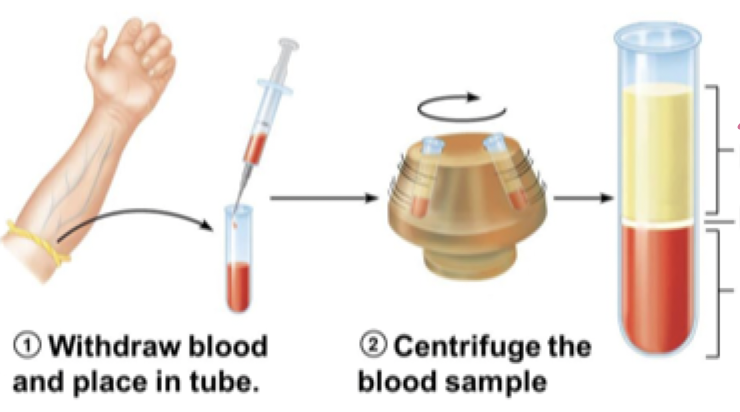
hematocrit
percent of blood volume occupied by erythrocytes
plasma = 55%
leukocytes and platelets
erythrocytes = 45% (hematocrit)
normal hematocrit
men = 47 ± 5%
women = 42 ± 5%
erythrocyte structure
biconcave disc
no nucleus or membrane-bound organelles
lots of hemoglobin (efficient oxygen and respiratory gas carrier)
erythrocyte function
transports oxygen and carbon dioxide
hemoglobin
a protein that transports O2
consists of globin and 4 heme groups that allows it to carry 4 oxygen molecules
iron-containing heme pigment plays a role in its transport
hematopoiesis
process of blood cell formation
occurs in red bone marrow
driven by hematopoietic stem cells
erythropoiesis
formation of erythrocytes
takes 2-15 days to complete development
2 million erythrocytes are made every second
nutrients essential for erythrocyte production
iron
folic acid
vitamin B12
iron
required for hemoglobin synthesis
bound to ferratin in the liver and transports in the blood via transferrin
Fe must be replaced through a diet
folic acid
vitamine obtained from leafy plants
used to make thymine
required for DNA synthesis
vitamin B12
obtained from animal products
supports the function of folic acid
erythropoietin (EPO)
glycoprotein that regulates erythrocyte production
stored in the kidney
stimulated by a
decreased erythrocyte count
decreased amount of hemoglobin
decreased availability of O2
anemia
decrease O2 in the blood due to loss of erythrocytes or hemoglobin
anemia due to blood loss
acute hemorrhagic anemia
chronic hemorrhagic anemia
anemia due to deficiency in erythrocyte production
iron-deficiency anemia
pernicious anemia (destruction of stomach mucous lining)
renal anemia (lack of EPO)
aplastic anemia (destruction/inhibition of red marrow)
anemia due to excessive erythrocyte destruction
thalassemias (absense of globin chain)
sickle-cell anemia (abnormal hemoglobin)
hemostasis
processes that stop blood from escaping a damaged blood vessel
3 components
vascular spasm (transient)
platelet plug formation (rapid)
blood clot formation (slow)
vascular spasm
first response to bleeding
triggered the damage and contractions of smooth muscles (vasoconstricition)
minimizes blood flow long enough for a platelet plug to form
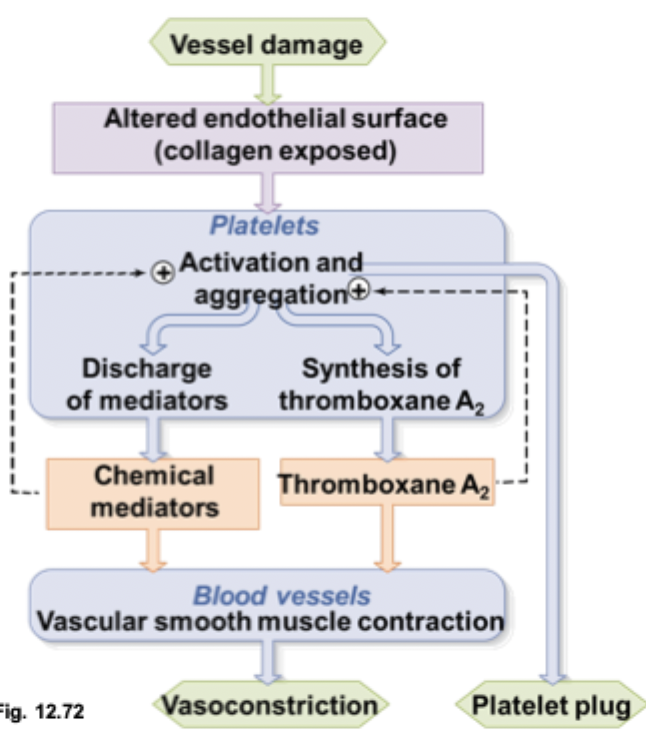
step 1 of a platelet plug
platelets adhere to a damaged endothelium and exposes of collagen
plasma (vWF) binds to exposed collagen
vWF bind to platelets to anchor them to the damaged site
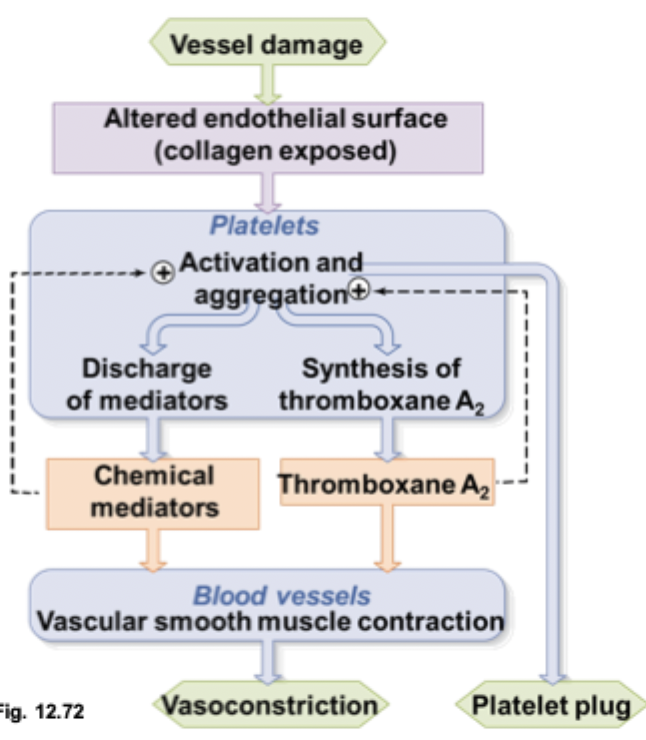
step 2 of a platelet plug
platelets are triggered when binded to vWF and secrete chemical mediators and thromboxane A2
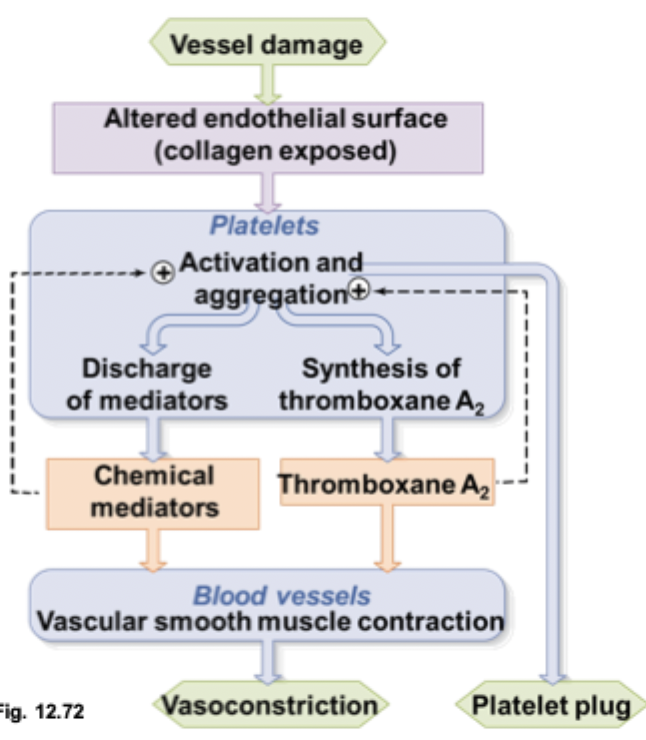
step 3 of a platelet plug
chemical mediators and thromboxane A2 direct changes to platelet surfaces causing them to adhere to each other
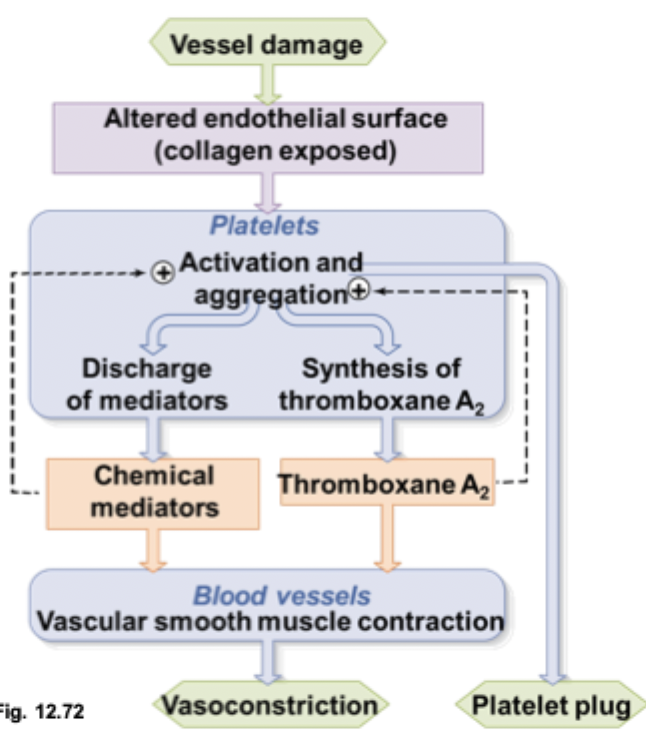
step 4 of platelet plug
positive feedback results in rapid formation of a platelet plug
blood coagulation
transforming blood into a solid gel (forming a clot)
occurs around platelet plug
involves fibrin to act as a glue to strongly reinforce the platelet plug
process is divided into 3 phases
phase 1 of blood coagulation
can occur via the intrinsic or extrinsic pathway
phase 2 and 3 of blood coagulation
prothrombin activator formed by one of the pathways turn into an active enzyme that catalyses the creation of cross-linked fibrin mesh
agents that limit the growth of a blood clot
heparin and antithrombin III
heparin
an extracellular matrix molecule found on the surface of intact endothelial cells
antithrombin III
plasma protein made by the liver
binds to heparin, causing its own activation which inactivates clotting factors
fibrinolytic system
dissolves blood clots
requires plasminogen and tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA)
t-PA
activates when it binds to firbin
activated t-PA converts plasminogen into plasmin
plasminogen
activated t-PA turns this into plasmin which cutes the fibrin mesh tissue formed from the clot into small, soluble fragments