Test 3 (deuterostomes, evolution, animal behavior, physiology)
1/117
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
Which one of the following is not a coelomate?
a. lamprey
b. shark
c. fluke
d. clam
c. fluke
Which one of the following is a fish?
a. sea horse
b. crayfish
c. jellyfish
d. star fish
a. sea horse
Which one of the following is the biggest fish?
a. blue whale
b. whale shark
c. dolphin
d. giant squid
b. whale shark
Vertebrate should have the following except:
a. ventral nerve chord
b. notochord
c. pharyngeal slits
d. postanal tail
a. ventral nerve chord
Which of the following animals have the bony vertebrae?
a. lamprey
b. shark
c. ray
d. frog
d. frog
Jaw is evolved from:
a. gill arches
b. operculum
c. swim bladder
d. fins
a. gill arches
Which one of the following is not a vertebrate?
a. lamprey
b. human
c. turtle
d. grasshopper
d. grasshopper
Reptiles have the following general features except for:
a. amniote egg
b. more concentrated urine than the amphibians
c. four-chambered heart
d. jaws
c. four-chambered heart
What phrase best describes natural selection?
differential survival and reproduction of individuals
Black wolves got their coat color from exchanging genes with dogs. This is an example of:
a. genetic drift
b. gene pools
c. gene flow
d. founder’s effect
c. gene flow
deuterostomes
trploblastic animals, bilateral symmetry, blastopore —> anus, coelomates, pharyngeal slits
echinoderms
spiny-skinned animals, mostly penta-radially symmetrical, coelomate
What is the general body plan of chordates?
bilateral symmetry, pharyngeal slits, notochord, dorsal hollow nerve chord, postanal tail
notochord
dorsal supporting rod
What are the three clades of chordates?
urochordates (tunicates), cephalochordates (lancelets), vertebrates
What are the traits of urochordates (tunicates)?
tadpole-like larvae: notochord, postanal tail
as an adult: no notochord, visible pharyngeal slits, sessile, surrounded by a layer of tunic (cellulose)
What are the traits of cephalochordates (lancelets)?
dorsal notochord that extends to tip of head & stays throughout adulthood, dorsal hollow nerve chord, pharyngeal slits for filter-feeding, no fins or jaws or brain, small heart enlargements of the vessels
What are the traits of vertebrates?
dorsal vertebral column, anterior skull that accommodates brain growth, internal skeleton, coelomate, well-developed closed circulatory system
What are the taxons of vertebrates?
jawless fish (outgroup), chondrichthyans (cartilaginous fish), ray-finned fish, amphibians, amniotes (birds, reptiles, mammals)
What is a lamprey?
jawless fish —> vertebrate —> chordate —> deuterostome
mostly parasitic, cylinder-shaped fish, single fins, primitive cartilaginous skeleton, prominent notochord as primary support structure
What are examples of chondrichthyans (cartilaginous fish)?
rays, sharks, whale sharks
What did jaws evolve from?
gill arches
Chondrichthyans have _____ gill slits.
uncovered/visible
What is the structure of a chondrichthyans (cartilaginous fish) heart?
2-chambered (atrium —> ventricle —> gill —> body —> atrium)
What are examples of ray-finned fish?
sea dragon, angler fish
What distinguishes ray-finned fish from chondrichthyans?
ray-finned fish have bony skeletons, operculum, & swim bladder
chondrichthyans have cartilaginous skeletons & lack operculum & swim bladder (why they have to constantly swim to stay afloat)
operculum
gill covers that can open & close to generate water flow into the gills, help fish stay afloat w/o having to swim
swim bladder
gas-filled sac that helps regulate buoyancy, outgrowth from pharynx
What are examples of amphibians?
anurans (frogs), coelocanths, caecilians, tailed slamanders
How do amphibians reproduce?
reproduction and beginning of life in an aquatic environment, jelly-covered eggs —> larva —> metamorphosis (lose gills and develop longs and leg limbs)
What are examples of amniotes?
birds, reptiles, mammals
What allows amniotes to start life on land?
amniotic egg = “pond w/ the shell” for an aquatic environment on land
What are the extraembryonic membranes of the amniotic egg?
chorion —> amniotic membrane —> yolk sac —> allatois
chorion
membrane of amniotic egg that encloses everything w/n the shell
amniotic membrane
encloses the embryo and amniotic fluids in an amniote egg
yolk sac
contains the nutrients for the amniotic embryo
allatois
carries the amniote embryo waste products
_____ are the first to become fully terrestrial.
Reptiles
What adaptions allowed reptiles to become full terrestrial?
amniotic egg, internal fertilization, scaly skin, kidneys can excrete more concentrated urine, impermeable skin to water
internal fertilization
non-reliant on water for survival of an egg, fertilization of an egg inside the organism
What are examples of reptiles?
tuatara, squamates (snakes), turtles, crocodilians
ectothermic
reliance on external heat source to maintain body temperature
What is the difference between crocodiles and alligators?
crocodiles have V-shaped snouts, visible teeth
alligators have U-shaped snouts, wider upper jaw hiding the teeth
What adaptions allowed birds to fly?
hollow bones & no teeth for lighter weight, modified forelimbs as wings, bipedalism, sternum, air sacs, light feathers
endothermic
non-reliance on an external heat source to maintain body temperature
What is the general digestive system of birds?
beak —> mouth —> pharynx —> esophagus —> crop —> gizzard —> stomach —> intestines —> anus
What is the purpose of feathers for birds?
thermoregulation (trap or release warm air), waterproofing, mating signals, camouflage
What are the key features of mammals?
mammary glands, hair, sweat glands, 4-chambered heart
What are the major taxons of mammals?
prototherians, marsupials, eutherians
What is the purpose of hair for mammals?
heat insulation, sensory functions camouflage, protection
prototherians
close to reptiles,lay eggs w/o placenta, have mammary glands
What are examples of prototherians?
spring ant-eater, duck-billed platypus
marsupials
short gestation —> ventral pouch development
What are examples of marsupials?
kangaroo, opossum, banded ant-eater
eutherians
true placental mammals, much more developed baby at birth
What are examples of eutherians?
bats, primates, beavers, dophins, humans
What is the Genus species of the first human to appear on Earth 3.5 mya?
Lucy the Australopithecus afarensis
What advancements evolved primates to humans?
bipedalism, smaller jaws, larger brains, complex language & culture
wet-nosed primates
mostly smaller, nocturnal, arboreal monkeys
found in Africa, tropical Asia, Madagascar
What are examples of wet-nosed primates?
lemur, loris
dry-nosed primates
generally larger, diurnal, bigger brain
new world & old world monkeys
What is the difference between the dry-nosed new world monkeys and old world monkeys?
new world monkeys are arboreal, have a long prehensile tail, and their nostrils open to the side
old world monkeys are aboreal/ground-dwelling, lack a prehensile tail, and their nostrils open downward
What are examples of new world monkeys?
spider monkeys, squirrel monkeys
What are examples of old world monkeys?
mandrils, orangutans, gibbons
Which primate are humans most closely related to?
chimpanzees
evolution
accumulation of inheritable changes w/n a population over time
natural selection/fitness
differential survival & reproductive success of an individual
phenotype
physical expression of genes, observable traits
genotype
genetic information of a trait
gene
unit of heredity, the specific section of DNA that can be transcribed to RNA
alleles
different forms of a gene
gene pool
sum of all alleles in a population
allele frequency
= # of a specific allele in the population/sum of all alleles in the population
genotype frequency
= # of individuals w/ a specific genotype/total # of individuals in the population
Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
deviations from the following five show that evolution is occurring
mating is random
very large population size
no gene flow
no mutation
no natural selection/natural selection that doesn’t affect reproductive success
mutation
any change in the organism DNA resulting in genetic variation
germline mutation
mutation that is passed onto offspring genes
artificial selection
selection of traits from organisms through evolution
gene flow
movement of genes into or out of a population, which may change allele frequencies
genetic drift
can cause large changes in populations
bottleneck effect
change in allele frequency by random chance, a period in which only a small # of individuals survive due to external pressure
founders effect
when a few pioneering individuals colonize a new region and there aren’t enough to produce a population w/ all alleles found among the members of the same population
sexual selection
struggle between the individuals of one sex for the possession of the other sex
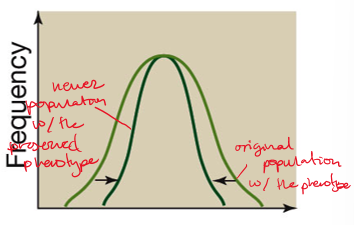
stabilizing selection
reduces variation in a population (preserves average)
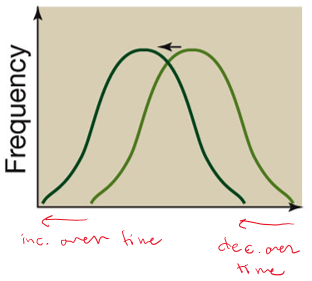
directional selection
one extrema is favored/preserved
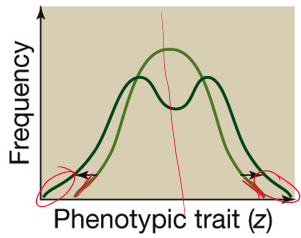
disruptive selection
extremes are favored over the averagee
ethology
examination of animals in a natural habitat w/o treatments
innate behavior
“born to do it”, behavior that doesn’t need to be learned
What are examples of experiments that studied innate behaviors?
deprivation & interbreeding/courtship
habituation
learned behavior, diminishing response to repeated stimuli
conditioning
learned behavior, conditioned reflex/response to a stimuli
imprinting
learned behavior, parent-offspring recognition
tissues
cells groups w/ the same characteristics, make up organs
What are the four types of tissues?
epithelial, muscle, connective, nervous
What is the function of epithelial tissues?
line the external & internal body cavities (protection), chemoreceptors (smell, taste), secretion (mucous, sweat, milk), absorption, filtration, transportation
What are the shapes of epithelial tissue?
squamous (thin, flat), cuboidal (short cylinders), columnar (column or cylinders)
What are the classifications of epithelial tissue based on the number of layers?
simple (one), stratified (2 or more), pseudostratified (one layer, appears stratified)
What is the function of muscle tissues?
elongated cells capable of contractity & causing involuntary movement (movement of internal organs, heartbeat) & voluntary movements (skeletons)
What are the types of muscle tisses?
smooth (motility to internal organs), skeletal (voluntary movements), cardiac (heart contractions)
What is the outline of a muscle?
muscle —> muscle fibers —> myofibrils —> repeating sarcomere