Lab Practical - animal phylogeny
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Porifera - Metazoa
has spicules

ctenophora - metazoa
has complete, one way gut
placozoa - metazoa

cnidaria - metazoa
has cnidocytes, planula larva, radial symmetry, incomplete 2 way gut

Mollusca - lophotrochozoa
has mantle, shell, and radula
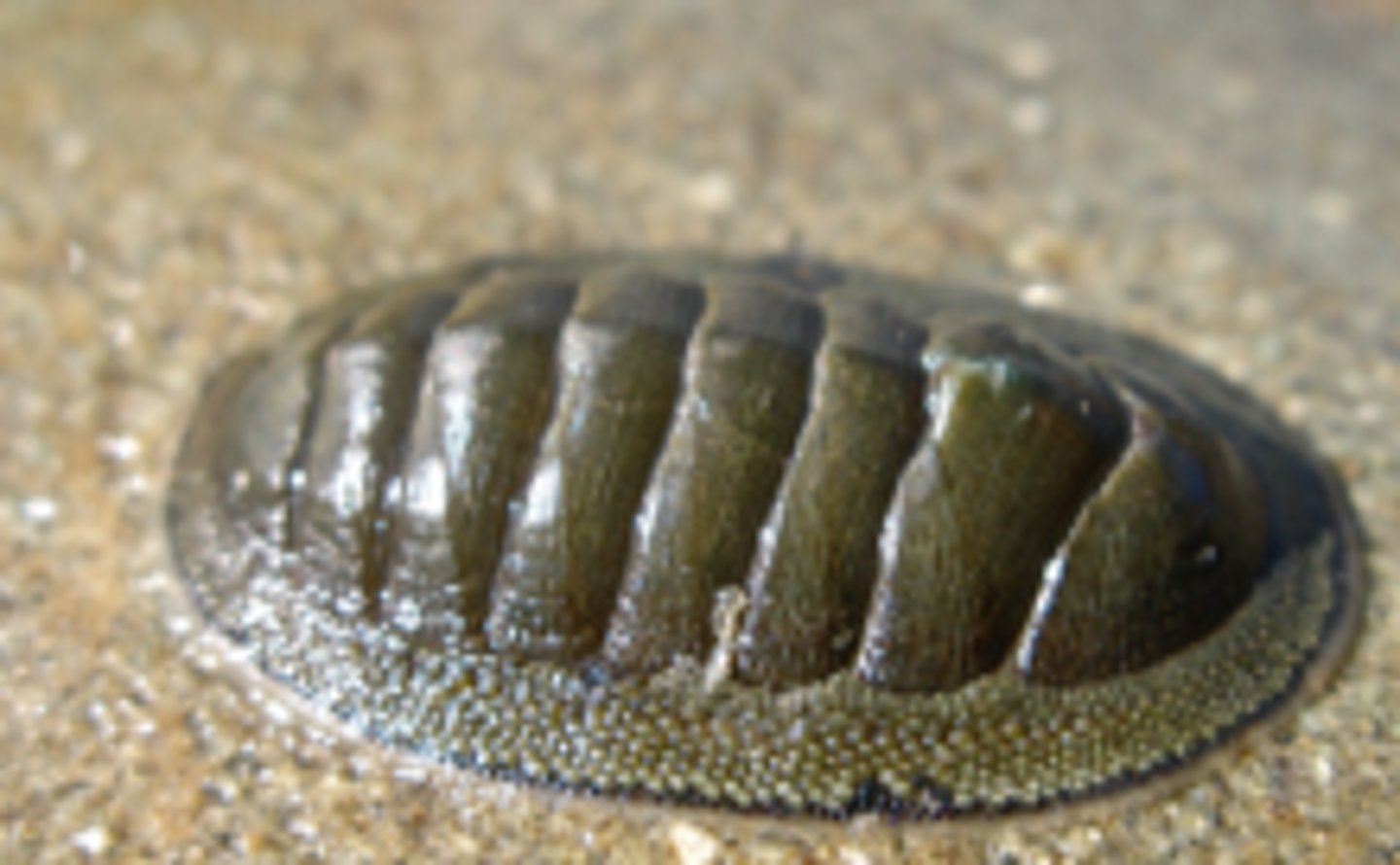

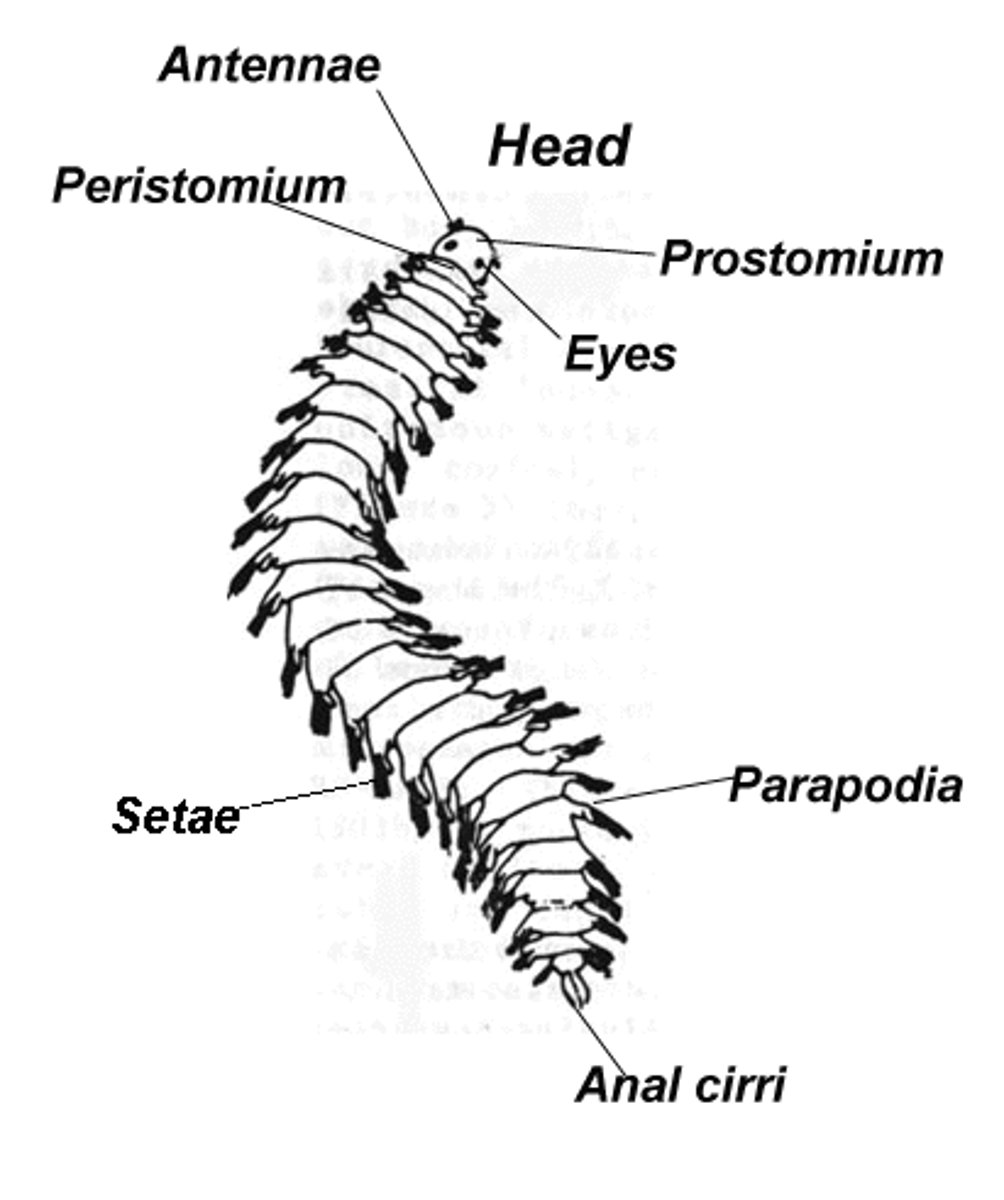
annelida- lophotrochozoa
has paired setae and segmentation
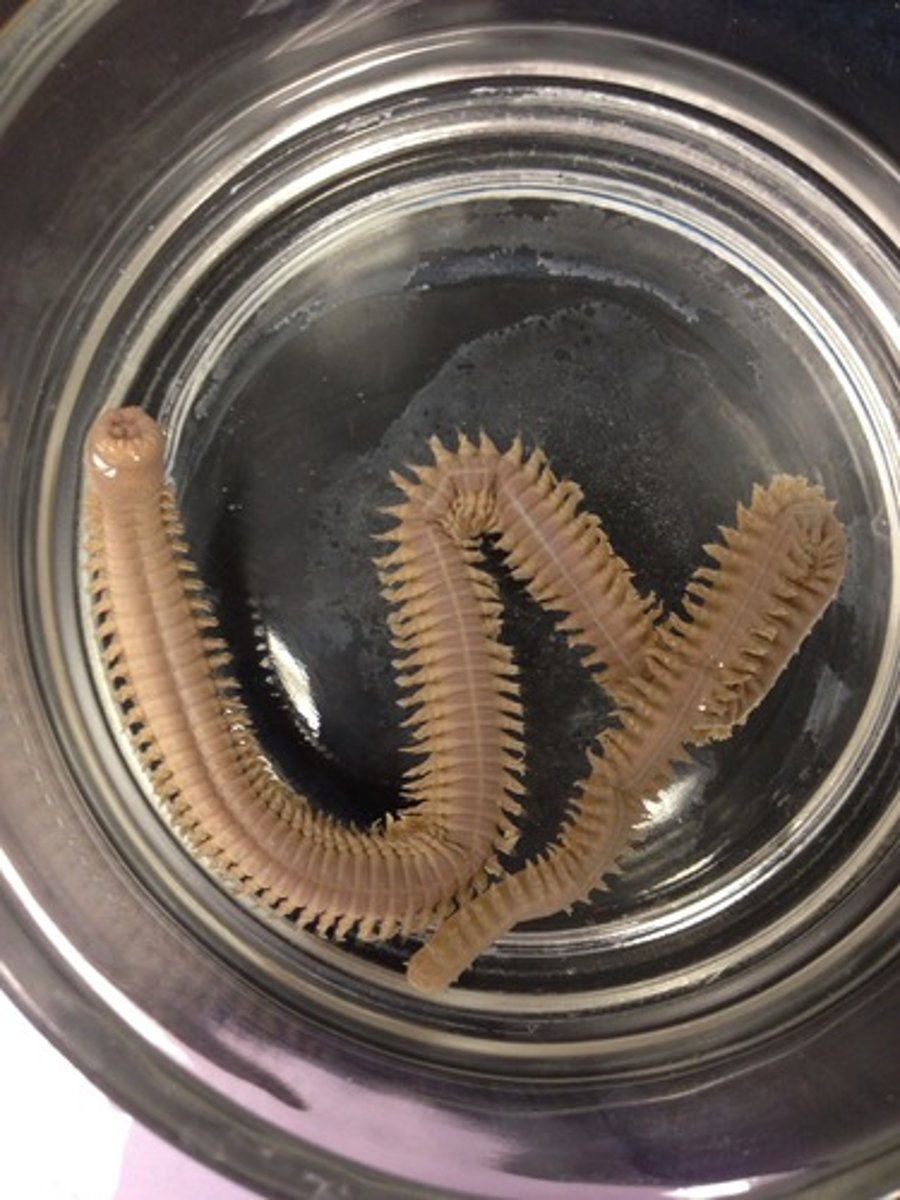

Nematoda - ecdysozoa

arthropoda - ecdysozoa
has exoskeleton and segmentation

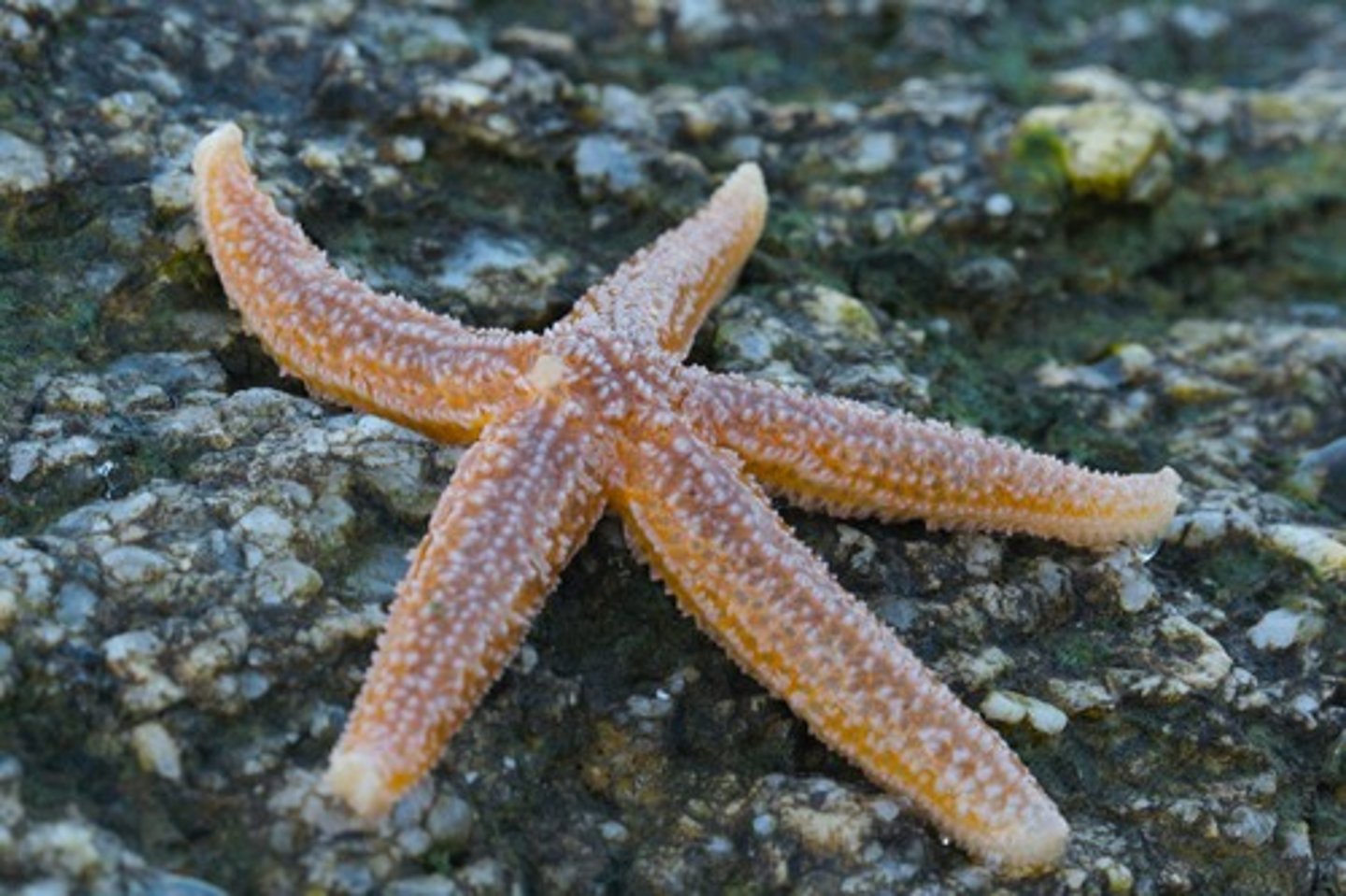
echinodermata - deuterstomes
has calcite endoskeleton, water vascular system, tube feet, pentaradial sym.

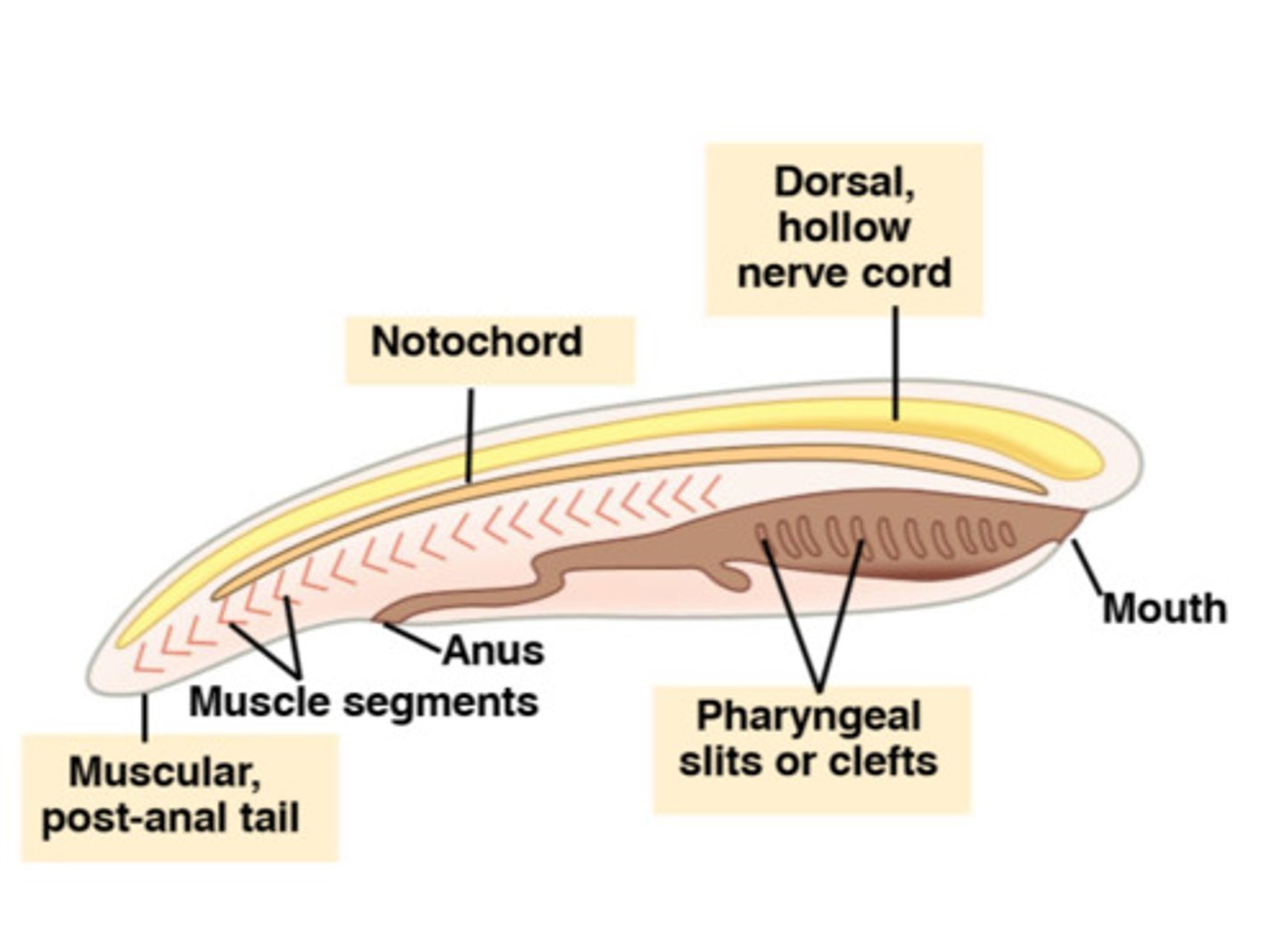
chordata - deuterstomes
has postanal tail, notochord, dorsal, hollow nerve cord, segmentation

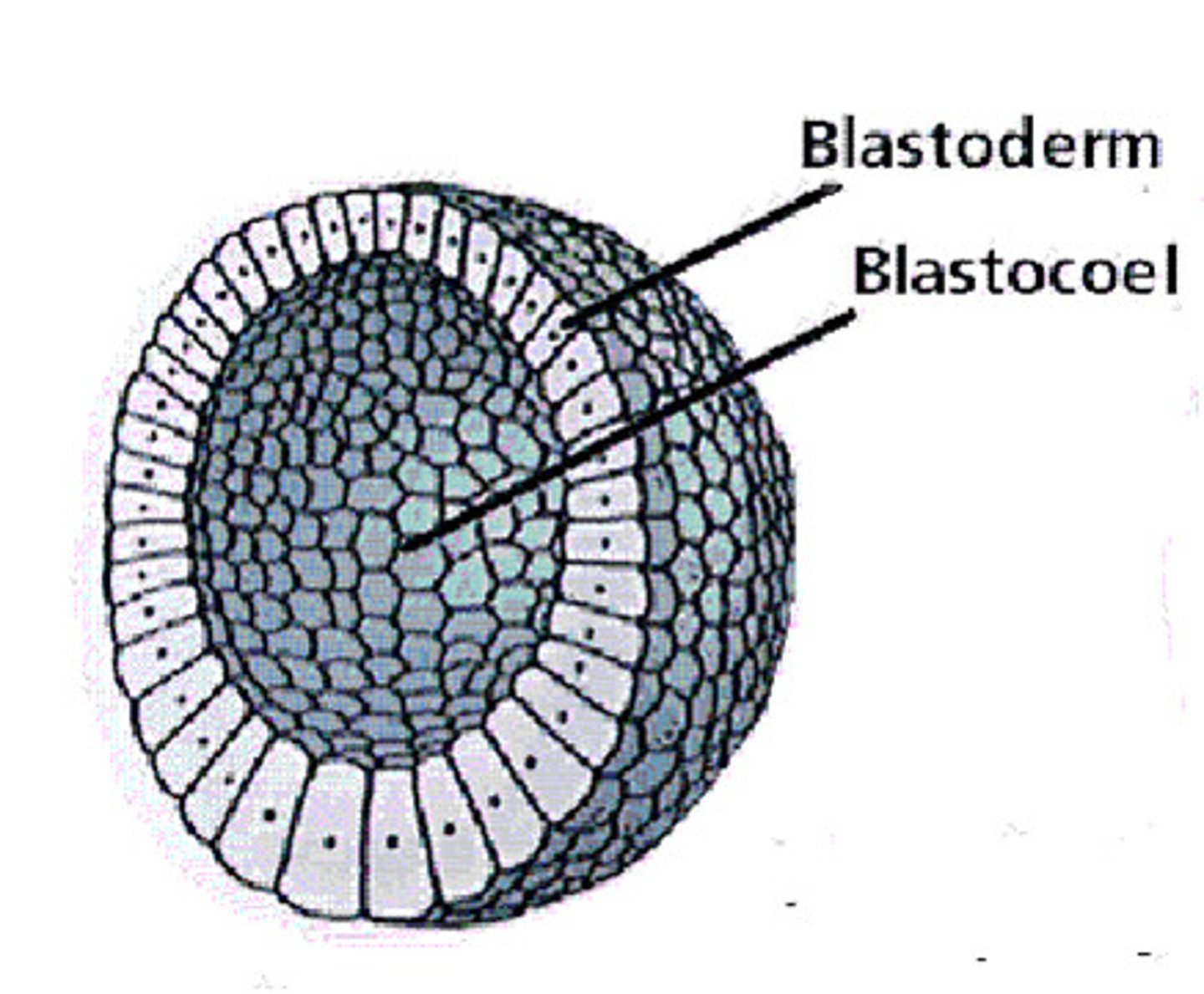
blastula - metazoa
Early animal embryo stage characterized by a hollow ball of cells formed after cleavage.
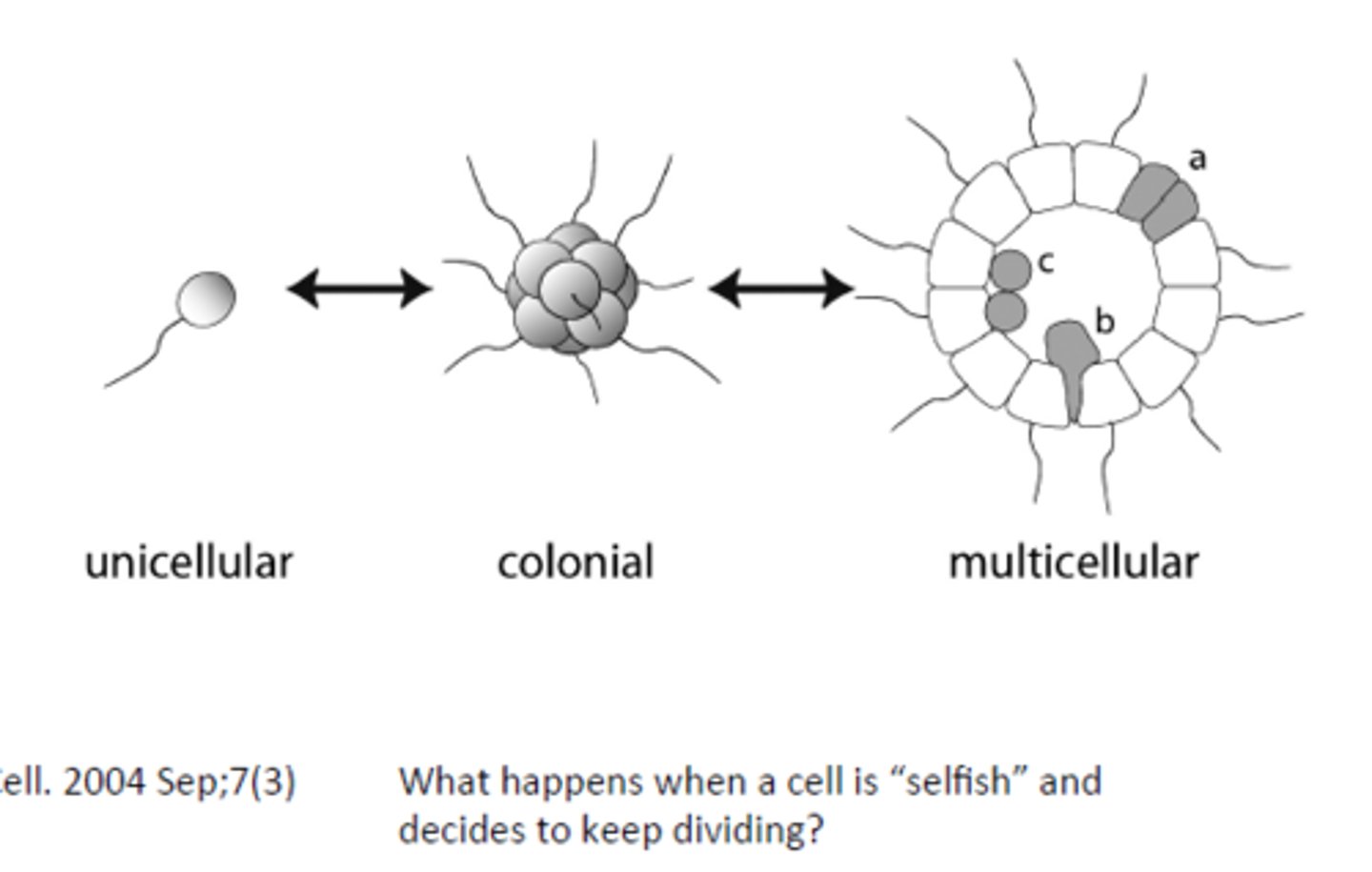
multicellularity - metazoa
Condition of an organism being composed of many cells that work together, allowing specialization and complex structures.
unique cell cell junctions - metazoa
Specialized structures in animal cells that connect neighboring cells, including tight junctions, desmosomes, and gap junctions.
collagen & proteoglycan- metazoa
Key components of the extracellular matrix; collagen provides strength and structure, while proteoglycans provide cushioning and hydration.
bilateral symmetry - bilateria

triploblasty - bilateria
Having three primary germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm) during embryonic development.
complete one way gut - bilateria
A digestive system with two openings—mouth and anus—allowing food to move in one direction.
blastopore becomes mouth - protostomes
Developmental pattern where the first opening (blastopore) in the embryo forms the mouth; characteristic of protostomes.
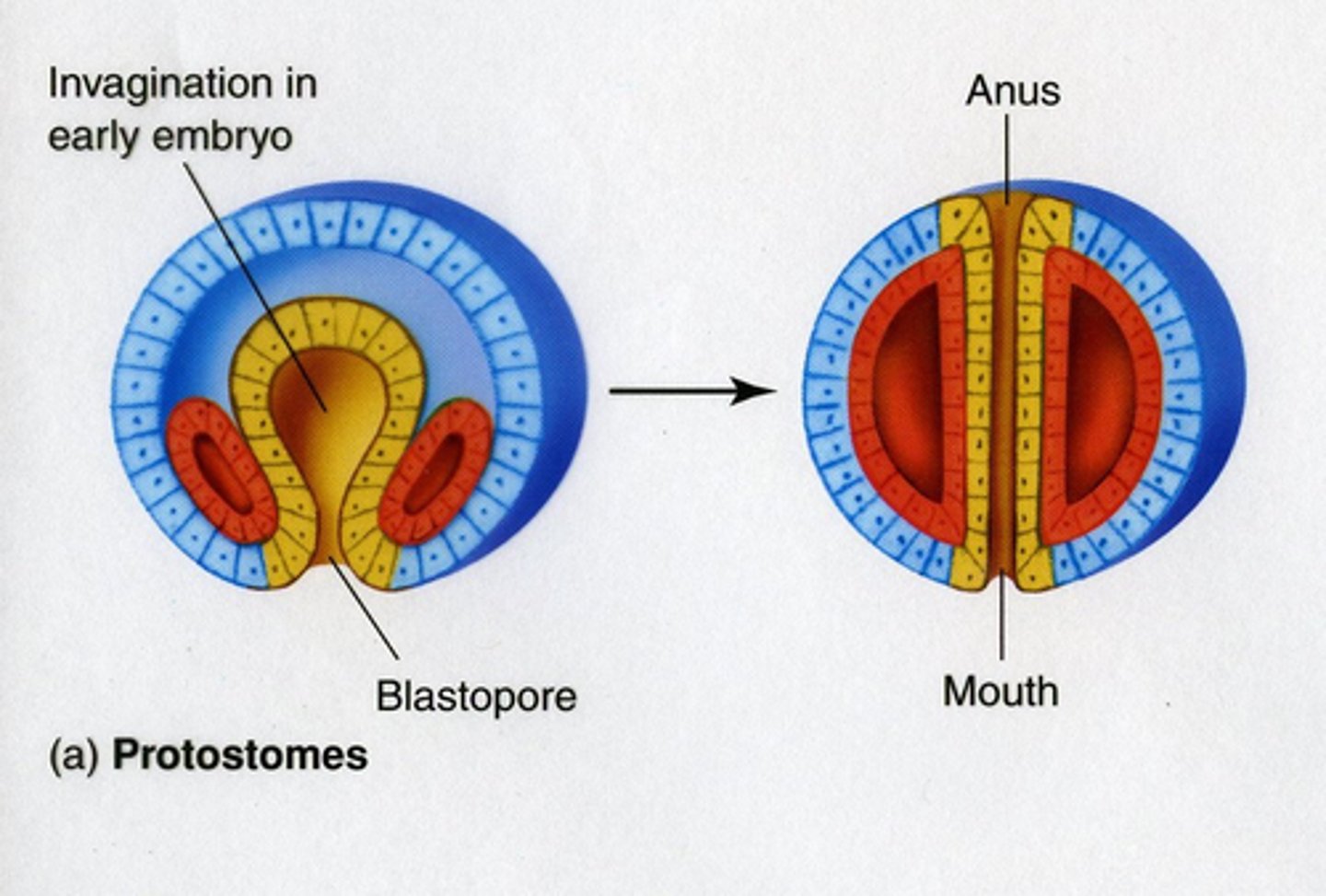
ecdysozoa - edysis
A group of animals that grow by molting their exoskeleton; includes arthropods and nematodes.
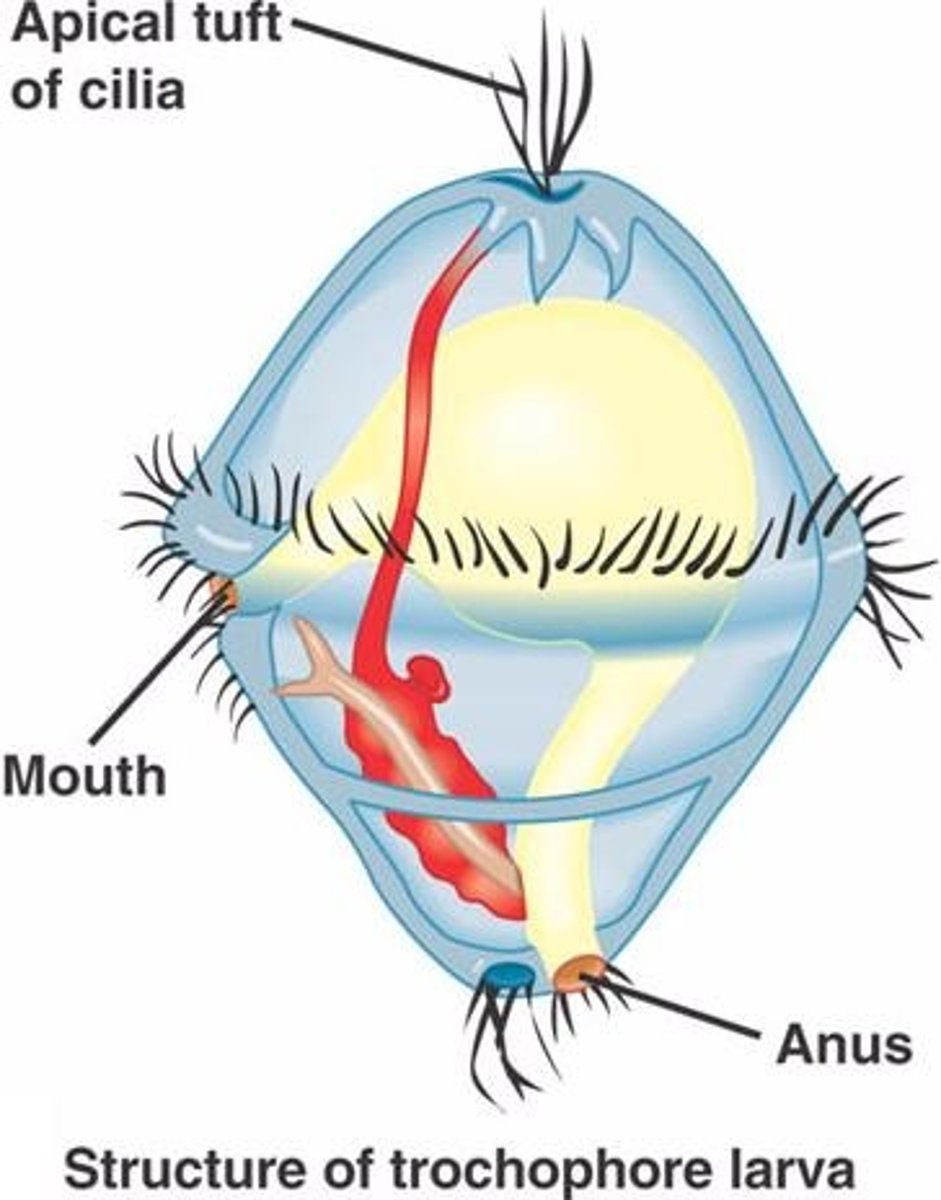
trochophore larva- lophotrochozoa
A free-swimming, ciliated larval stage found in some marine invertebrates like mollusks and annelids.
spiral, mosaic cleavage - lophotrochozoa
A pattern of embryonic cell division where cells divide at oblique angles (spiral) and each cell's fate is determined early (mosaic).
blastopore becomes anus - deuterstomes
Developmental pattern where the first opening (blastopore) in the embryo forms the anus; characteristic of deuterostomes.
radial, regulative cleavage - deuterstomes
Embryonic cell division where cells divide parallel or perpendicular to the axis (radial) and early cells can regulate to form any cell type (regulative).
spicules - poridera
Small, spike-like structures made of silica or calcium carbonate that provide support and protection in sponges.
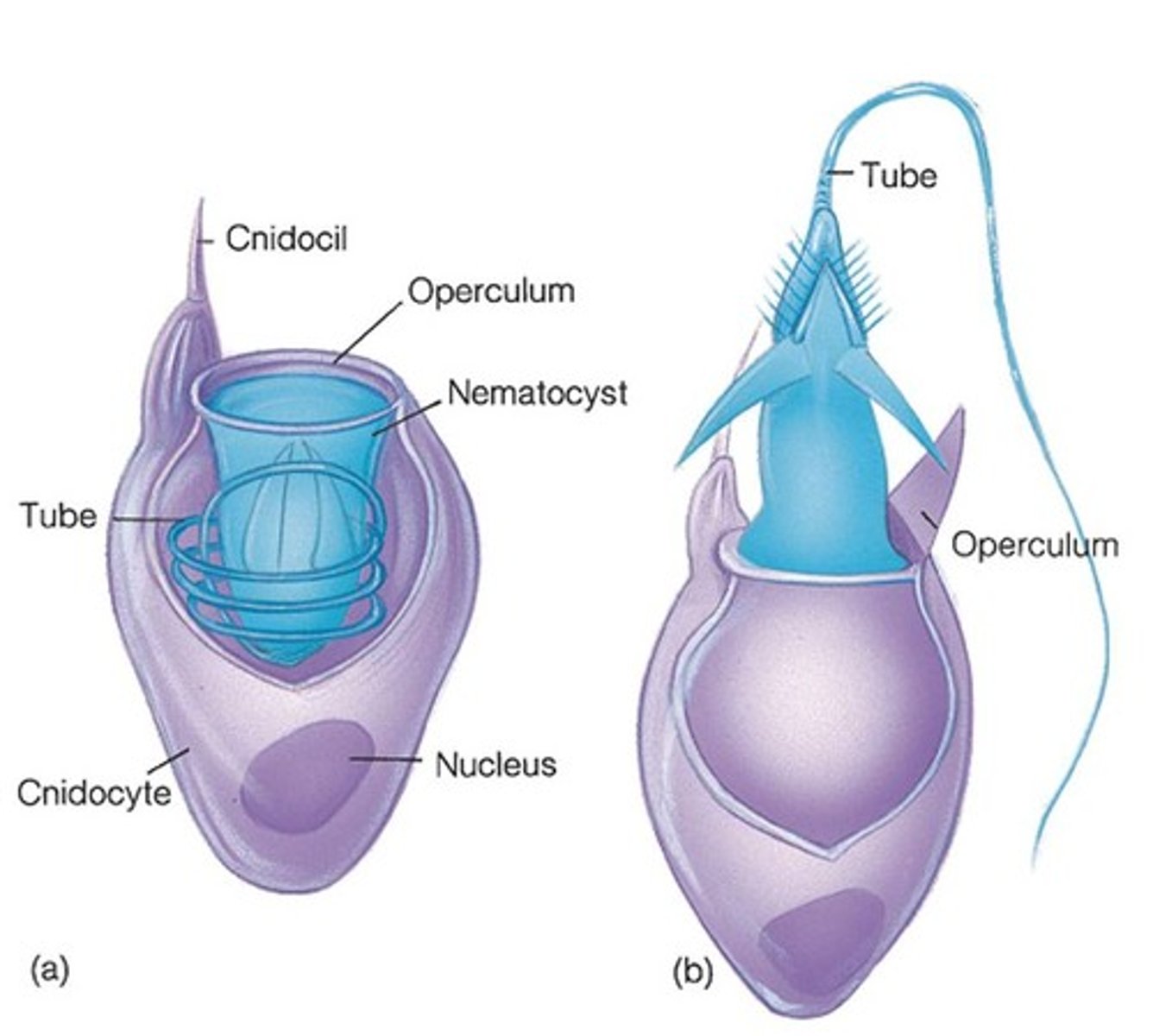
cnidocytes - cnidaria
Specialized stinging cells in cnidarians used for defense and capturing prey.
planula larva - cnidaria
Free-swimming, ciliated larval stage of cnidarians that eventually settles to form a polyp.
radula - mollusca
A ribbon-like, toothed feeding organ found in most mollusks used to scrape or cut food.

paired setae - annelida
Bristle-like structures found in pairs on each segment of annelid worms, helping in movement and anchorage.
tube feet - echinodermata
Small, flexible, hollow appendages in echinoderms used for movement, feeding, and respiration.

notochord - chordata
A flexible, rod-like structure in chordate embryos that provides support and signals development.

dorsal, hollow nerve cord - chordata
A tube-like nerve cord located along the back (dorsal side) of chordates, which develops into the central nervous system.