Lecture 1 - Functional groups and linkages
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What are the main functional organic compounds?
Alcohol, aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic acid, thiol, amines.
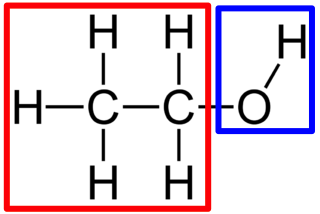
What is the functional group of an alcohol?
-OH (hydroxyl)
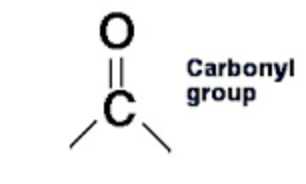
What is carbonyl?
A chemically organic functional group composed of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom.
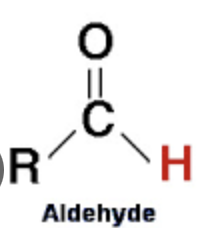
What is an aldehyde?
An organic compound in which the carbonyl group is attached to a carbon atom at the end of a carbon chain.
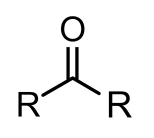
What is a ketone?
A chemical compound with a carbonyl bonded to two other carbon groups (R and R').
What is a carboxyl?
Broad term for either carboxylic acid (H) or carboxylate (ion).
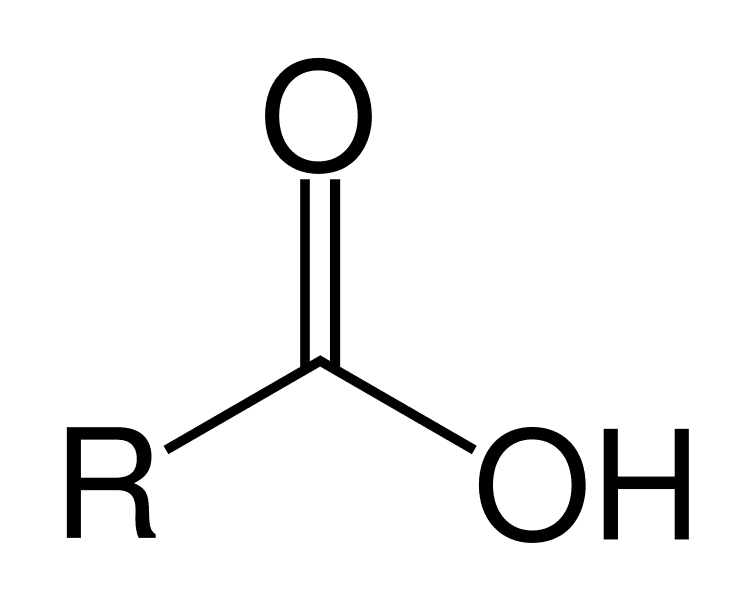
What is a a carboxylic acid?
An organic acid containing a neutral carboxyl group.
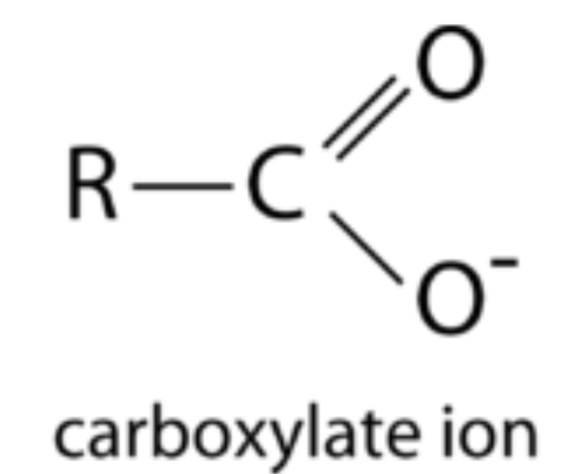
What is a carboxylate?
A compound containing a de-protonated carboxyl group (–COO⁻).
What is a thiol?
An organic compound containing the group (-SH).

What is an amine?
A nitrogen-containing functional group where the nitrogen atom is bonded to carbon atoms and/or hydrogen atoms.
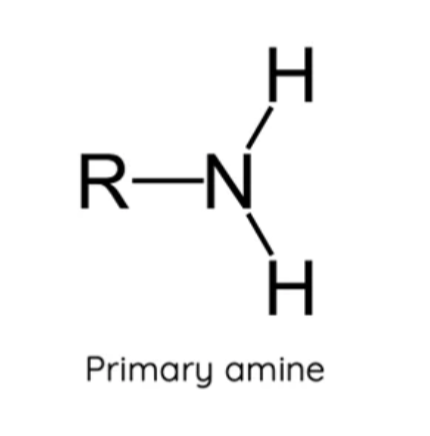
What is a primary amine?
A nitrogen atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms and one carbon chain (R-group)
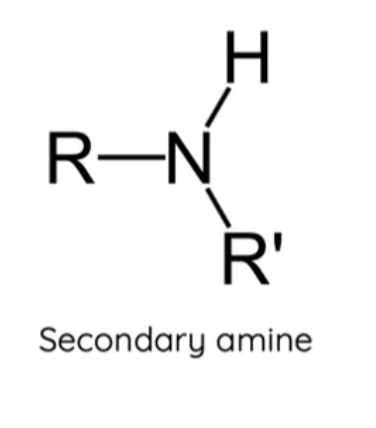
What is a secondary amine?
A nitrogen atom bonded to one hydrogen atom and two carbons.
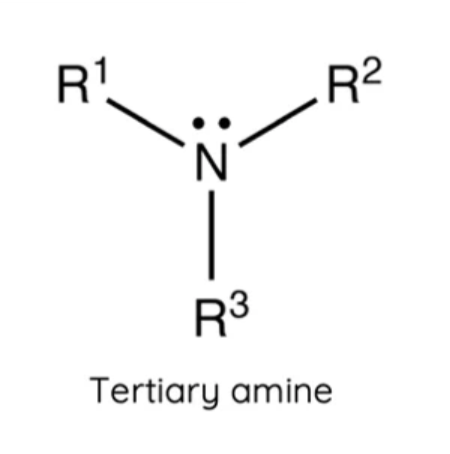
What is a tertiary amine?
A nitrogen atom bonded to three carbons.
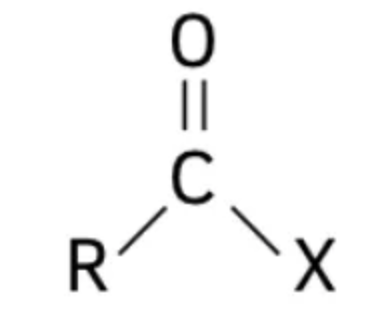
What is an acyl group?
(RCO-), formed by removing the -OH (hydroxyl) from a carboxylic acid, featuring a carbonyl and single-bonded to another alkyl group (R).
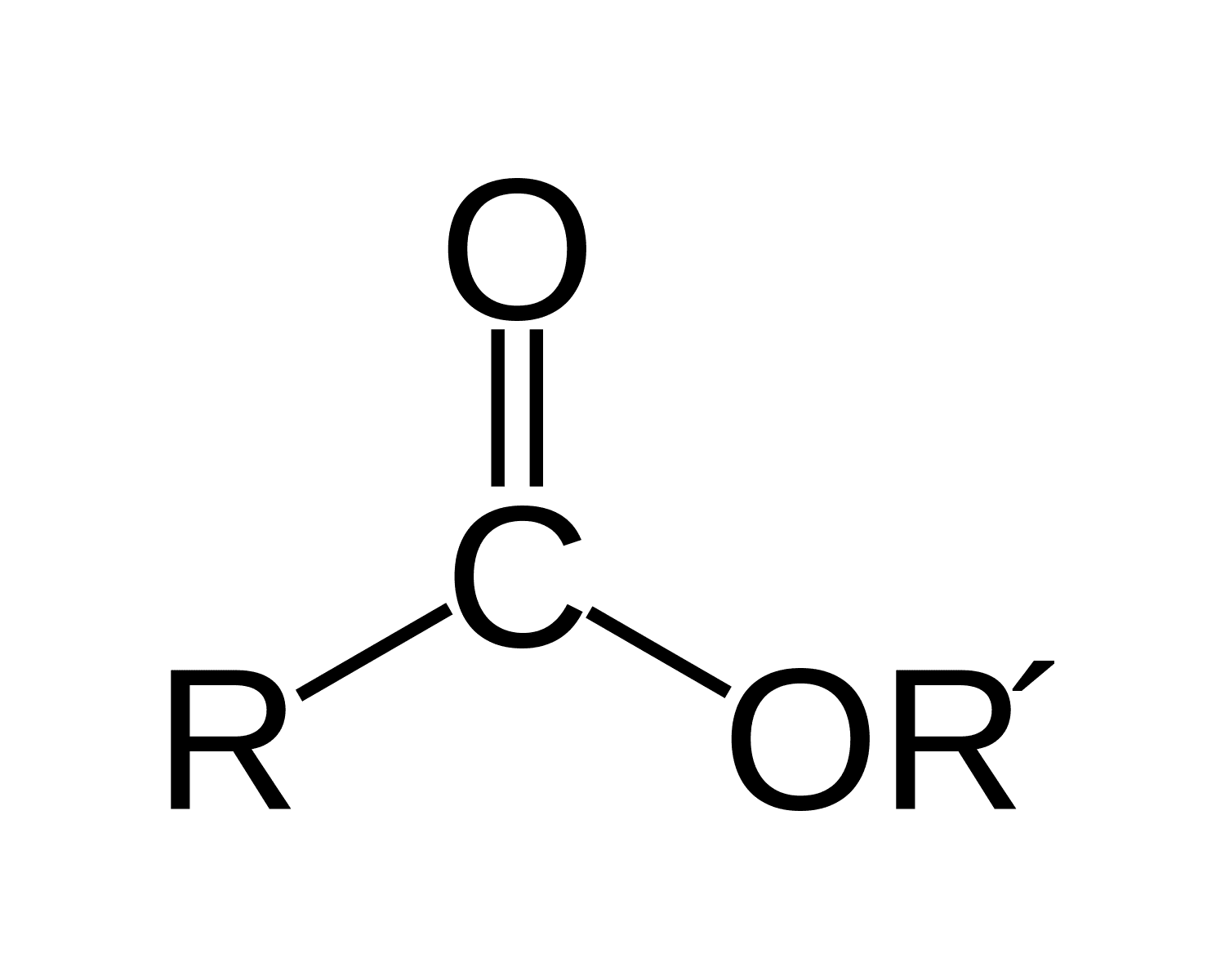
What is an ester?
C-O-C=O
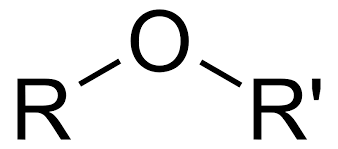
What is an ether?
oxygen single bonded to two carbon groups.
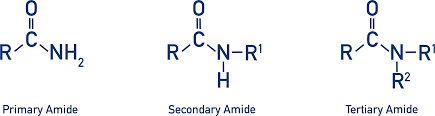
What is an amide?
a carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to a nitrogen atom, forming the structure R−C(=O)−NR′R″
What is the difference in structure between primary, secondary and tertiary amides?
Primary amide, nitrogen is bonded to one carbon.
Secondary amide, nitrogen is bonded to two carbons.
Tertiary amide, nitrogen is bonded to three carbons.
What is sulfhydryl?
-SH
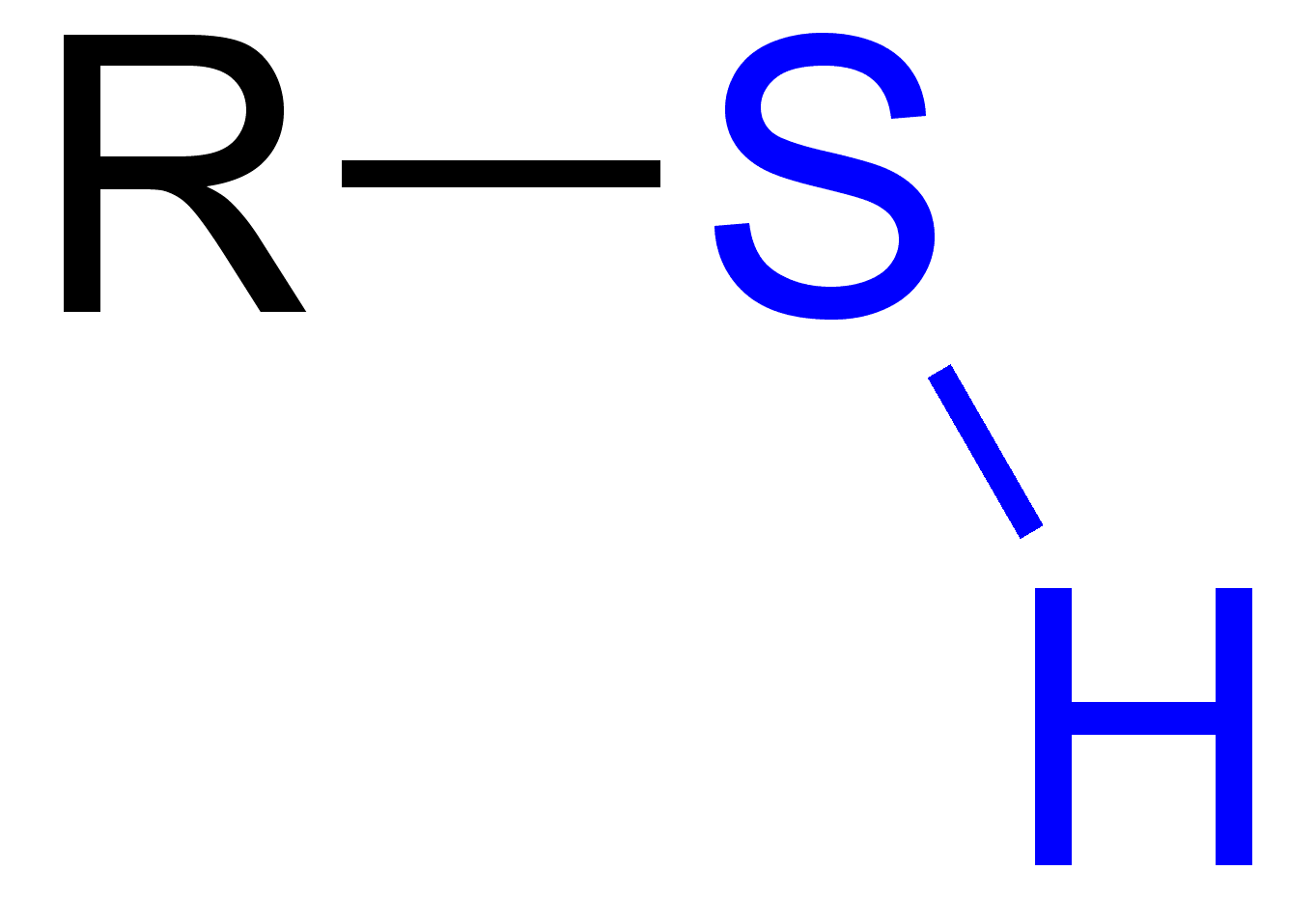
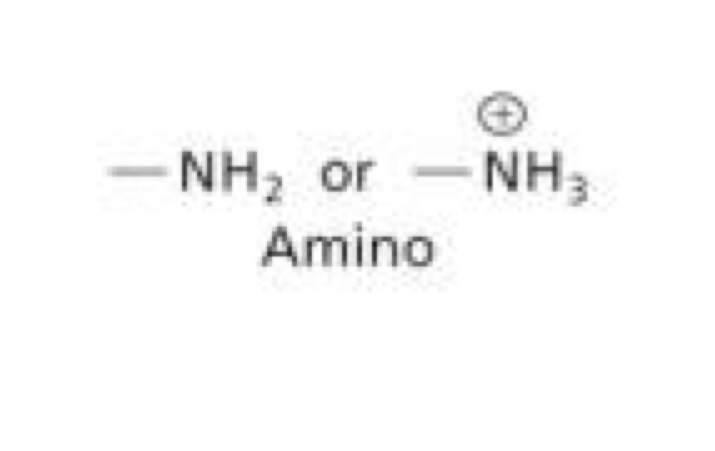
What is an amino functional group?
-NH2 or NH3+
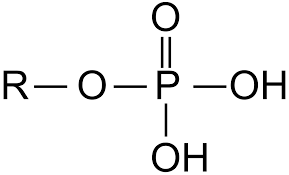
What is the structure of a phosphate group?
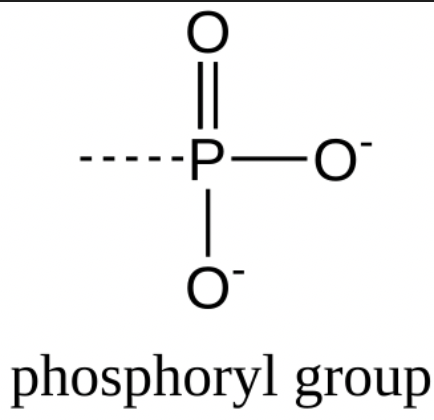
What is the structure of a phosphoryl group?
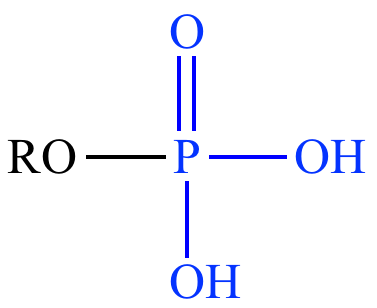
What is the structure of a phosphate ester?
What is phosphoanhydride linkage?
a high-energy linkage between two phosphate groups (P-O-P) in molecules like ATP
What is a thioester?
