BIOL 3000 Translation
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Translation
Forming a polypeptide chain (protein)
Where: Cell cytoplasm (eukaryotes) associated with ribosomes. Out of the nucleus
When: Either G1 or G2 (the period where genes coding for cellular organelles are synthesized)
Why do transcription and translation mostly occur during G1 and G2?
There always has to be proteins being made
What ribosome does translation depend on?
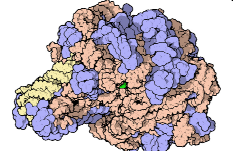
80S Ribosome
Ribosome
Highly complex cellular machine responsible for the synthesis of proteins from mRNA
Originally called “Palade Particles”
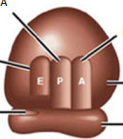
Contains the A, P, E sites, 60S, and 40S subunits
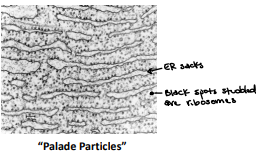
Function of ribosomes
Translates mRNA into peptide chains (protein biosynthesis)
80S Ribosome
A complex of proteins and ribosomal RNAs
The proteins bring the function, the ribosomes bring the structure
60S Ribosome
Large subunit that joins the amino acids together to form a peptide chain
x3 rRNA molecules and 46 proteins
40S Ribosome
Small subunit that is responsible for reading the mRNA 5’ → 3’
x1 rRNA molecules and 33 proteins
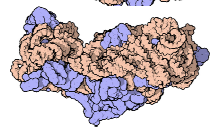
Function of 40S subunit
It will search for the mRNA by looking for the 5’ cap. Once recognized, the large subunit will be recruited.
A Site
Aminoacyl-tRNA binding site
The first site that tRNA goes into for translation
P Site
Peptidyl-tRNA binding site
Where the growing chain is held
E Site
Exit site
The site where tRNA leaves
tRNA
Transfer RNA
The RNA molecule that serves as the physical link between mRNA and amino acids
Outside in the cytoplasm associating with amino acids
Contains: Psi (T) arm, D arm, variable arm, and anticodon arm
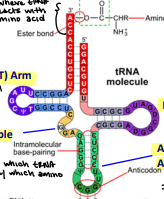
Psi (T) Arm
Provides structural purpose to the tRNA
Variable arm
Identifies which tRNA interacts with which amino acid
D Arm
Provides structural purpose to tRNA
Anticodon Arm
Interact with the complement mRNA
If GCC, then CGG
Codon
Three bases in an RNA molecule
3 nucleotides that are read at a time from 5’ to 3’
3 nucleotides = ?
1 codon
1 codon = ?
1 amino acid
Start Codon
AUG
Stop Codons
UAA
UGA
UAG
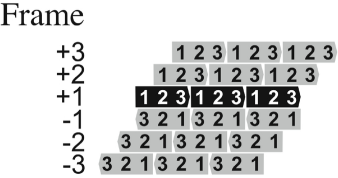
Reading frame
Refers to the one of three possible ways of reading a nucleotide sequence. It is identified based on where we start
We can change the reading frame because not ALL AUG are start codons; however, every stop codon is a stop codon.
Open reading frame
A sequence of DNA triplets, between the initiator and terminator codons, that can be transcribed into mRNA and later translated into protein
mRNA
Genetic code
Written in linear form
Comma-less (no pauses)
Coded in triplets (codons)
Unambiguous (1 codon = 1 amino acid)
Degenerate (1 amino acid can be coded by more than one codon)
Specific start and stop codons
Non-overlapping
Universal
Players in Translation
Ribosome (construction site)
mRNA (blueprint)
tRNA (delivery system)
Steps of Translation
Activation
Initiation
Elongation
Termination
Activation
The correct amino acid covalently bonds to the correct tRNA (charging)
tRNAs bring the correct amino acid to the ribosome to build polypeptide chains
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase catalyzes the reaction using ATP
Free amino acids are covalently attached to the 3’ end of the specific tRNAs (non-anti codon end)
Recognition features in the structure of tRNA determine which amino acid binds
Some tRNAs can bind multiple amino acids due to third position “wobble”
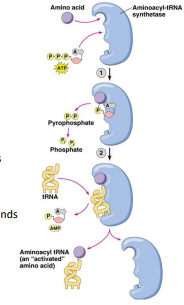
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase
Synthesizes amino acids onto tRNA
Initiation
Ribosome assembles and binds to mRNA molecule
The 40S subunit looks for mRNA with the 5’ guanine cap to associate with the mRNA molecule
The 40S subunit binds to an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase containing Met and UAC anticodon
It then recruits the 60S ribosome to form the 80S ribosome
The MET-tRNA occupies the P site of the 80S ribosome, only when the 60S is recruited
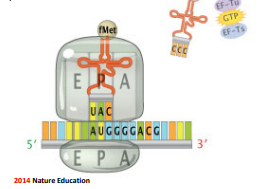
Elongation
Sequential binding of the aminoacyl-tRNA to the ribosome along with GTP and elongation factors (EF)
After charged tRNA is placed in the A site, phosphate is released from the GTP, providing energy.
The peptide bond forms between amino acids in P and A sites, then the amino acid in the P site is released from the tRNA
The ribosome moves down the mRNA strand (5’→3’) through translocation
The tRNA that was in the P site moves to the E site to be released into the cytoplasm; tRNA with growing peptide chain moves to the P site, then the A site is vacant and ready for the next charged tRNA allowed to enter
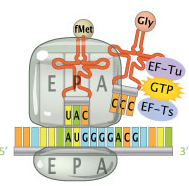
Elongation factors (EF)
Allows specific entry of an incoming tRNA molecule at the A site of the small ribosomal subunit with GTP (energy).
The cleavage of GTP to GDP releases elongation factors
EF-Ts (EF-1B in eukaryotes) acts as a Guanine Exchange Factor (GEF) to exchange GTP in place of the GDP on EF-Tu
Initiation factors (IF)
Associated with the A site to prevent the wrong charged tRNA from entering (like a bouncer)
Peptidyl-transferase
Forms a peptide in between the P and A site
What does the ribosome need for translocation?
GTP
Energy cost for Protein Synthesis
Charging of tRNA: 2 ATPs
Binding of tRNA to ribosome: 1 GTP
Translocation: 1 GTP
Total cost: 4 high energy phosphate bonds for each peptide bond formed
Termination
The A site of the ribosome recognizes a STOP codon
STOP codons (UGA, UAG, UAA) signal termination
There are no tRNAs for any of the STOP codons
Release factors bind to A site of ribosome
Facilitates the release of the peptide chain and dissociation of the ribosome and mRNA