endocardium, myocardium,epicardium
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What is the epicardium?
The visceral layer of the serous pericardium.
What does the epicardium consist of?
Mesothelial cells, connective-adipose tissue.
What happens at the base of the large vessels in the epicardium?
The epicardial mesothelium continues with the parietal mesothelium of the serous pericardium.
What is the pericardial cavity?
A virtual cavity between the epicardial mesothelium and parietal mesothelium.
Contains a fine layer of fluid called pericardial fluid.
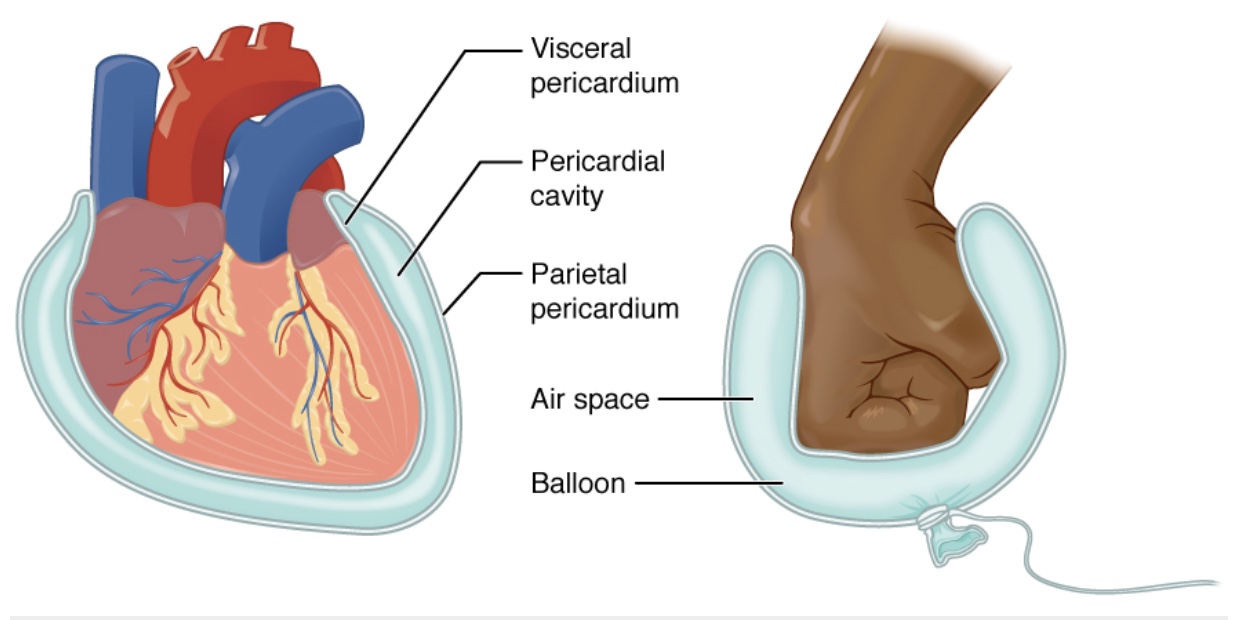
What is the role of pericardial fluid?
Adhesion of the pericardial layers. Allows them to slip during heart movement.
What are the layers of the myocardium?
Superficial, middle, and deep layers.
What is the myocardium composed of?
Cardiac muscle, connective tissue.
What are the components of the myocardium?
Working myocytes,
excitoconductive myocytes,
myoendocrine cells,
Cajal-type interstitial cells,
→ fibroconnective network, to which blood vessels, lymph, nerve fibers and interstitial fluid are added.
What was the myocardium considered in the classic view?
A functional syncytium.
How are cardiomyocytes organized in the myocardium?
Organized to form muscle fibers,
covered by endomysium (wraps around each muscle fiber and cell).
What covers more muscle fibers in the myocardium?
Perimysium.
What makes up the extracellular matrix in the myocardium?
Cardiac cell fixation support.
Components: connective tissue, blood vessels, nerve fibers, interstitial cells, migrated blood cells.
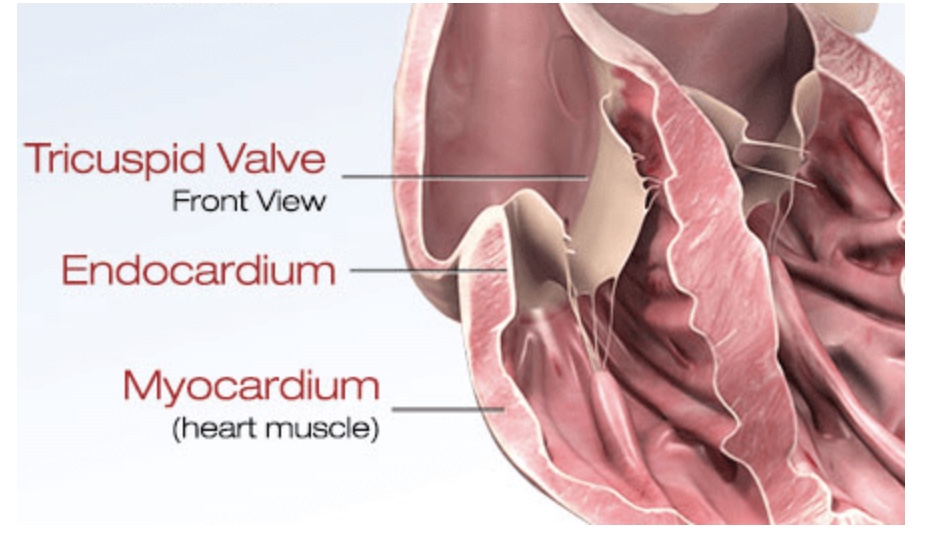
What is the endocardium made of?
A single layer of squamous endothelial cells.
What is the subendothelial layer in the endocardium made of?
Elastic fibers, collagen, and smooth muscle cells.
What connects the subendothelial layer to the myocardium?
The subendocardial layer, which contains vessels, nerves, and Purkinje cells.
Is the endocardium well-innervated?
Yes, it is well-innervated, similar to the epicardium.