Module 3-Genotyping
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Genotyping
the process of determining differences in the genetic make-up (genotype) of an individual by examining the individual's DNA sequence using biological assays and comparing it to another individual's sequence or a reference sequence.
DNA polymorphisms
variations in DNA sequences; used as a basis for comparing genomes
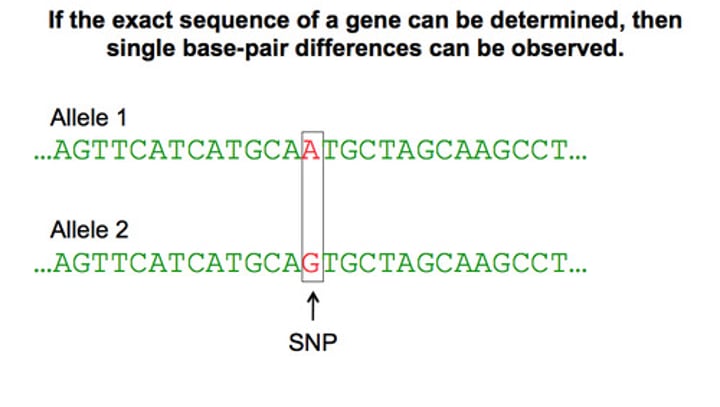
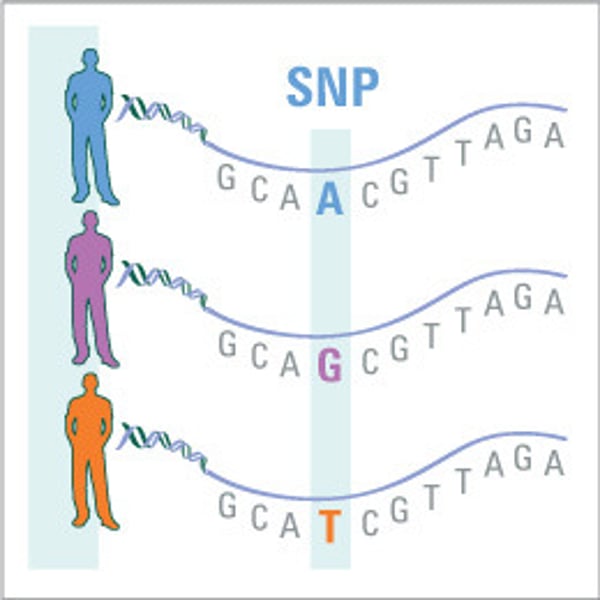
SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism)
Single nucleotide differences in sequences of DNA
-A common type of change in DNA (molecules inside cells that carry genetic information) sequences between individuals. Single nucleotide polymorphisms occur when a single nucleotide (building block of DNA) is replaced with another. These changes may cause disease, and may affect how a person reacts to bacteria, viruses, drugs, and other substances. Also called SNP.
Detected by PCR followed by ASO or primer extension
used in linkage mapping
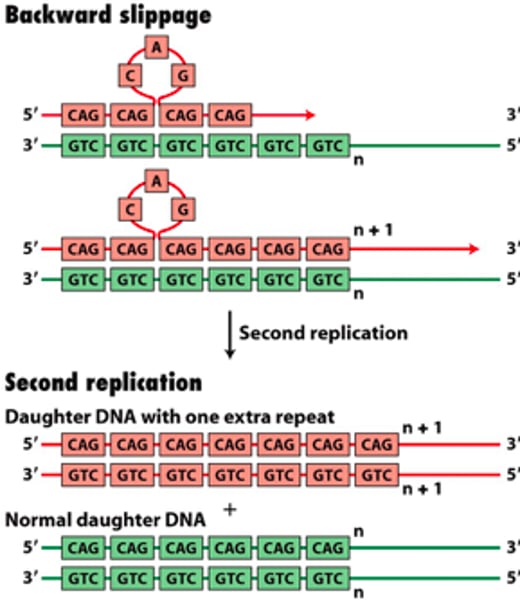
micro satellites
short tandem repeating sequences of base pairs of nuclear DNA; highly variable between individuals but similar between parents and offspring
30-300 bp
detected by PCR and gel eleltrophoresis
used in DNA fingerprinting
multilocus minisatellite
Nucleotide sequences 14 to 100 base pairs long, organized into clusters of varying lengths, on many different chromosomes; used in the construction of DNA fingerprints
1-20kb
detected by southern blot and hybridization
antibody
a protein (immunoglobulin) molecule, produced by the immune system, that recognizes a particular substance (antigen) and binds to it
detection tool in genotyping by marking and indentifiying specific proteins that are present
utilized in western blotting
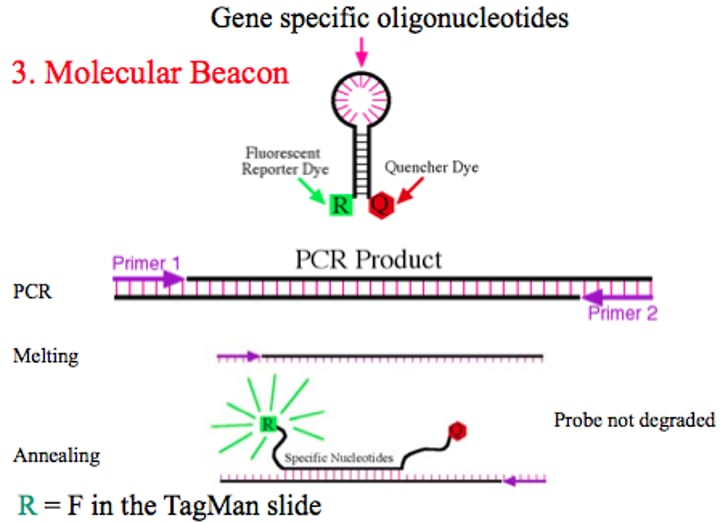
molecular probe (probe)
A single-stranded nucleic acid or antibody protein labeled with a detectable marker that attaches to a specific target molecule, allowing target molecule detection in subsequent analysis. Single-stranded nucleic acid probes detect target nucleic acids, and antibody probes bind specific target proteins.
used for DNA (southern blot) and mRNA (northern blot)
DNA probes will stick to matching dna complemntarity, labeled to be detected later
Blot
a method of transferring proteins, DNA, or RNA onto a carrier
nucleic acid hybridization
the base pairing of one strand of a nucleic acid to a complementary sequence on another strand
used to identify specific DNA sequences
involves northern and southern blotting
Southern Blot
A DNA sample is electrophoresed on a gel and then transferred to a filter. The filter is then soaked in a denaturant and subsequently exposed to a labeled DNA probe that recognizes and anneals to its complementary strand. The resulting ds labeled piece of DNA is visualized when the filter is exposed to film.
Northern Blot
Similar technique [to Southern], except that Northern blotting involves radioactive DNA probe binding to sample RNA .
Western blot
probing for a specific protein, antibody based
a protein mizture extrated from cells is separated into bands of distinct proteins by electrophoresis and then blotted onto a membrane, the position of the protein is revealed by bathing the membrane in a solution of antibody where the position of the label is revealed at what the antibody caries
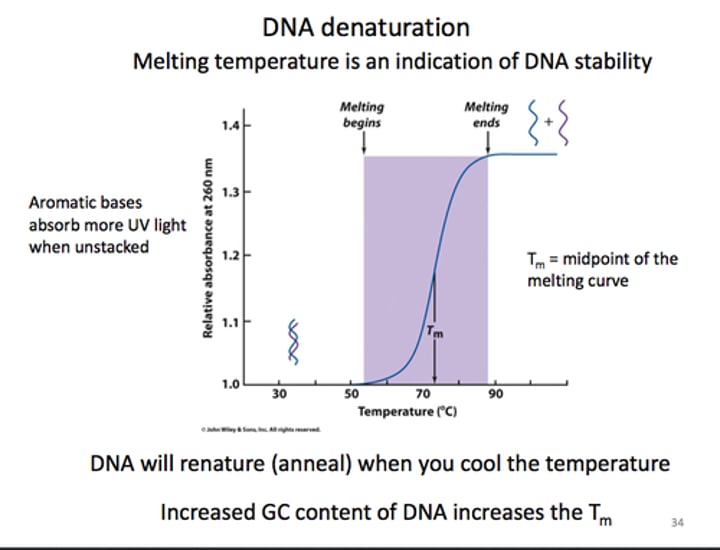
DNA melting
heating a DNA double helix gently until the hydrogen bonds are broken and one molecule separates from the complementary molecule; synonym: DNA denaturation
seperated by adding heat: ds->ss
DNA denaturation
The separation of a double-stranded DNA molecule into complementary single-stranded molecules.
DNA melting point (Tm)
temperature at which half of the DNA strands are in the ssDNA state, depends on lenght of and specific nucleotide sequence
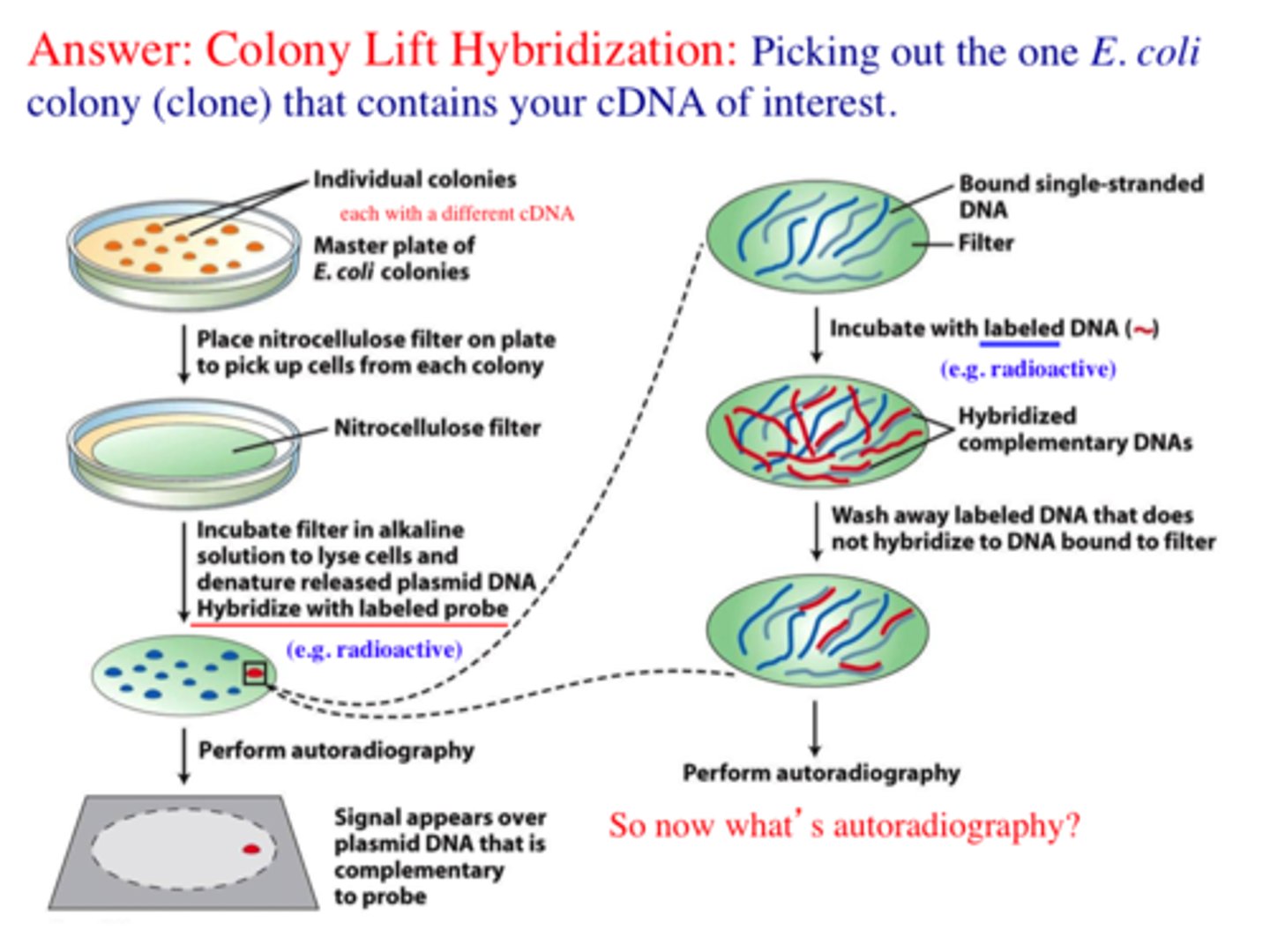
colony hybridization
Use DNA probes: short segments of single-stranded DNA complementary to the desired gene
hypervariable
describes a DNA segment that shows a high degree of variability between members of a population, and that is expressed as a large number of alleles, as different base sequences, or as different numbers of tandem repeats
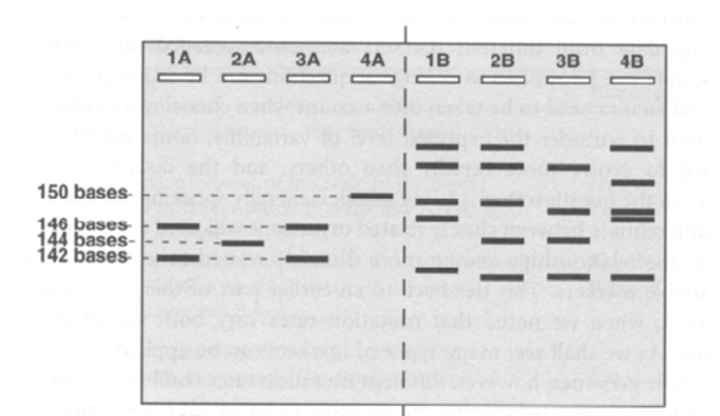
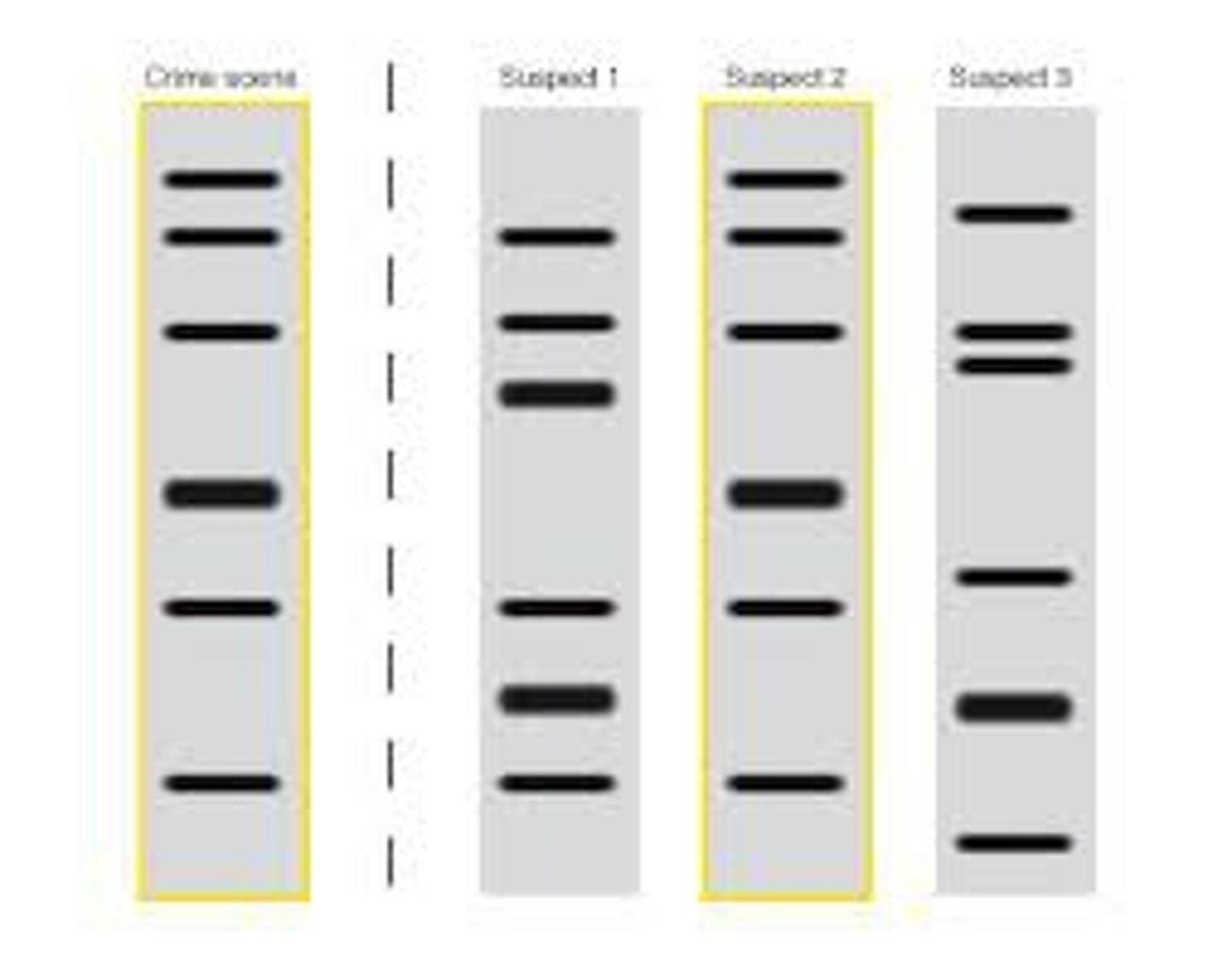
DNA fingerprint
Unique sequence of DNA base pairs that can be used to identify a person at the molecular level
used via PCR analysis from a southern blot and hybridization, multilocus minisatellite
STR/VNTR
Short tandem repeat/ Variable number tandem repeat
there is a number of repeats in a row
used as DNA markers
paternity inclusion/exclusion
determining familial relationships, if child matches parents=inclusion, no match=exclusion
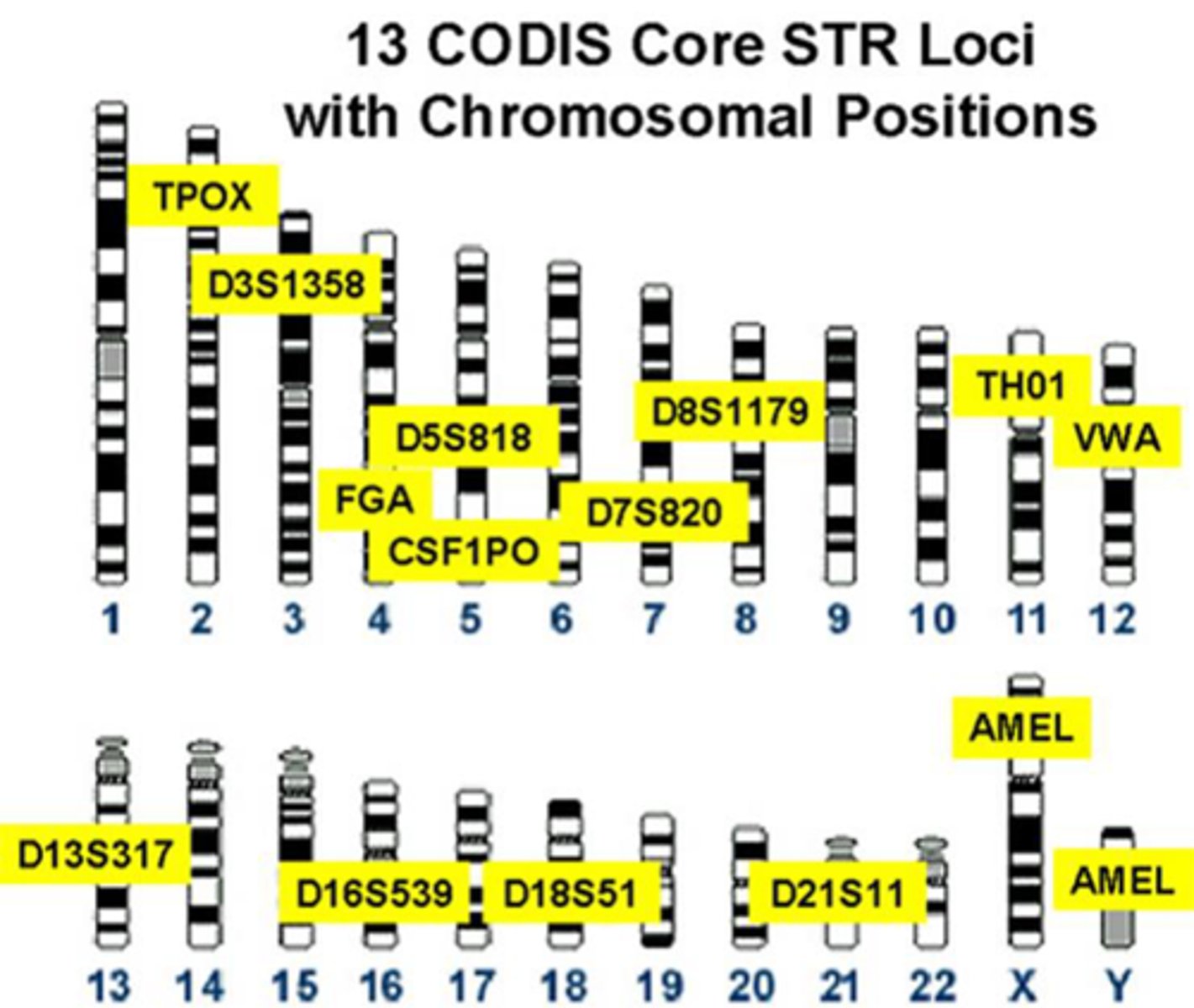
CODIS
Combined DNA Index System used by law enforcement to identify DNA samples from a crime scene
The FBI maintains a database for 13 loci for STR analysis
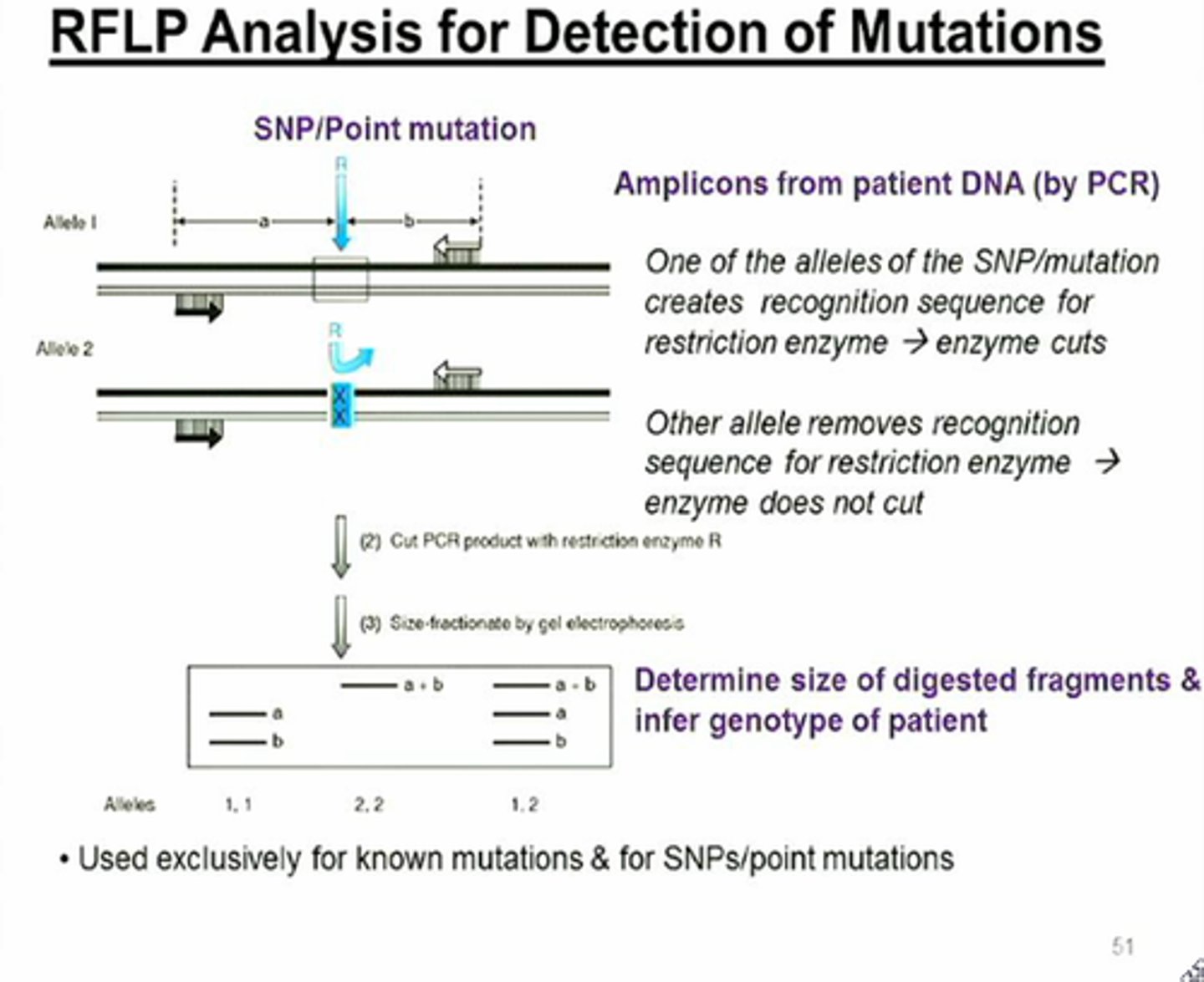
RFLP (restriction fragment length polymorphism)
Differences in DNA sequence on homologous chromosomes that can result in different patterns of restriction fragment lengths (DNA segments resulting from treatment with restriction enzymes); useful as genetic markers for making linkage maps.
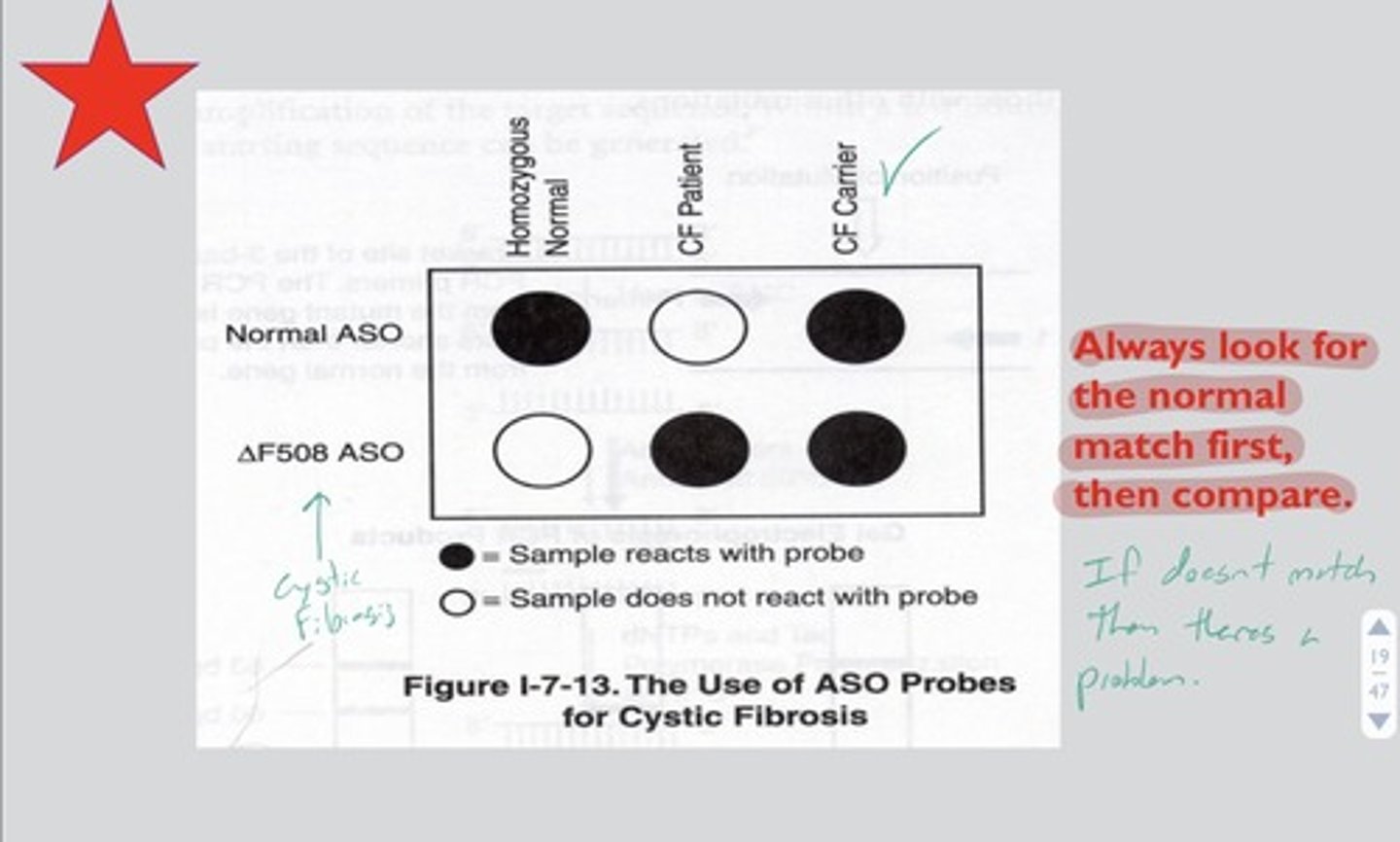
ASO (allele-specific oligonucleotide)
a short (usually < 50 nt) molecule of single-stranded DNA used to genotype a SNP locus within a DNA sample
SNP detection
Microarray
a grid of DNA segments of known sequence that is used to test and map DNA fragments, antibodies, or proteins.
can analyze the expression of tens of thousands of genes simultaneously, very good at detecing SNPs
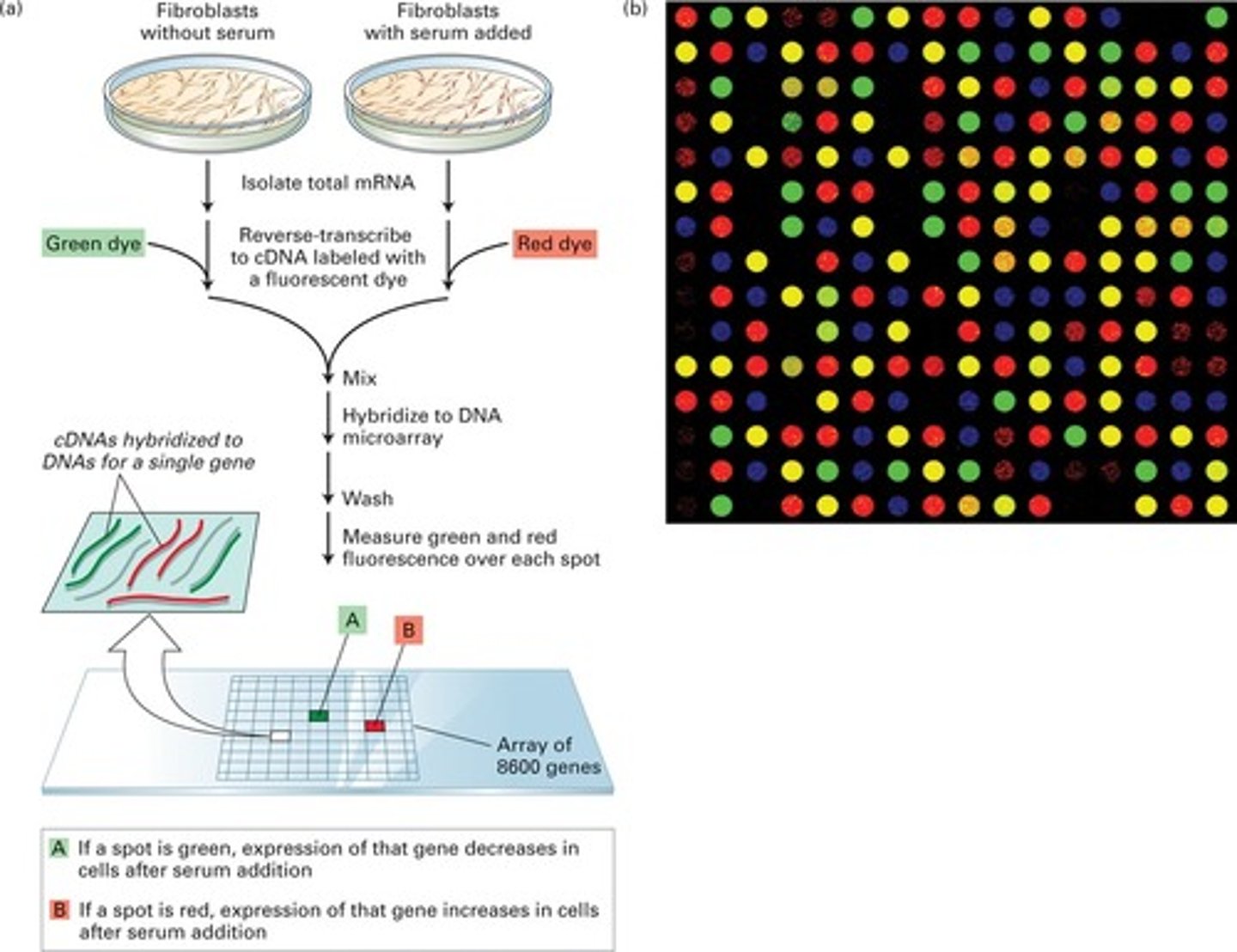
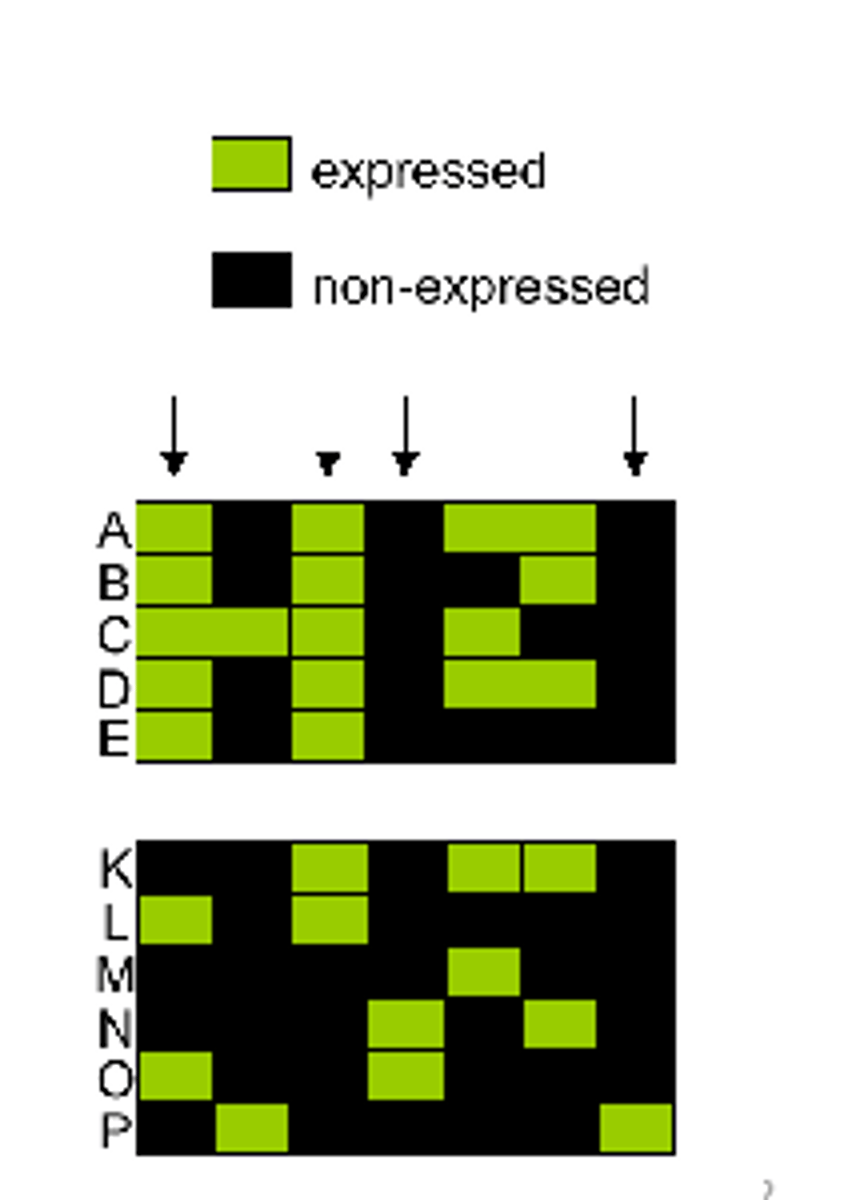
differential gene expression
The expression of different sets of genes by cells with the same genome.
microarrays can detect differences in gene expression