Eyelids, Tears, & Eye Movements
1/175
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
176 Terms
what prompts eyelid closure
contraction of orbicularis oculi muscles
not the relaxation of the levator muscles
3 types of eyelid closure
blinking, winking, spasm
3 types of blinking
spontaneous, reflex, voluntary
most common type of blinking
spontaneous
rate of spontaneous blinking
12-15 blinks a minute
spontaneous blinking is a contraction of the palpebral orbicularis muscle in the absence of what
absence of external stimulus
role of spontaneous blinking
stabilizes the tear film
what happens to tears during a spontaneous blink
new tears are secreted and spread across the ocular surface
old tears are pushed towards the nasolacrimal drainage system
what happens when there is a decreased rate of spontaneous blinking
decreased tear secretion and increased tear evaporation
causes dry eye syndrome and secondary epiphora (tearing)
what causes a decreased blink rate
decreased corneal sensitivity
often when watching TV, reading, or after LASIK
what is a reflex blink
blink caused by sensory stimuli, including auditory, touch, bright light, or external threat
what cranial nerve mediates reflex blinking in response to loud sounds
CN VIII (auditory)
what CN mediates reflex blinking in response to touch
CN V (responsible for corneal sensitivity)
what does cotton swab testing check for, and what CN is it evaluating
checks for corneal sensitivity by assessing reflex blinking in response to irritation
assesses CN V1 (responsible for corneal sensitivity)
what 2 reflex blinks does CN II cause
dazzle & menace
dazzle
reflex blink in response to bright light detected by CN II
menace
reflex blink in response to an unexpected object threatening the eye detected by CN II
where does the efferent loop of reflex blinking in response to external stimuli begin
frontal lobe
what is the only reflex blink that does not involve the cortex
dazzle blink
afferent stimulus and efferent response loop remains in the eye
difference between reflex and spontaneous blinking
both are involuntary but reflex blinking is in response to an external stimulus, while spontaneous blinking is in the absence of external stimulus
the efferent loop of blinking involves stimulation of what CN
CN VII
stimulates palpebral orbicularis to close eye
difference between voluntary blinking and spontaneous or reflex blinking
voluntary blinking has a more prolonged duration
what is winking
a form of voluntary blinking
what muscles are used to wink or forcefully close the eye
simultaneous contraction of orbital and palpebral orbicularis oculi
benign essential blepharospasm
condition characterized by bilateral, involuntary, sustained twitching of eyelids
what muscles cause benign essential blepharospasm
spasms of the orbicularis oculi, procerus, and corrugator muscles
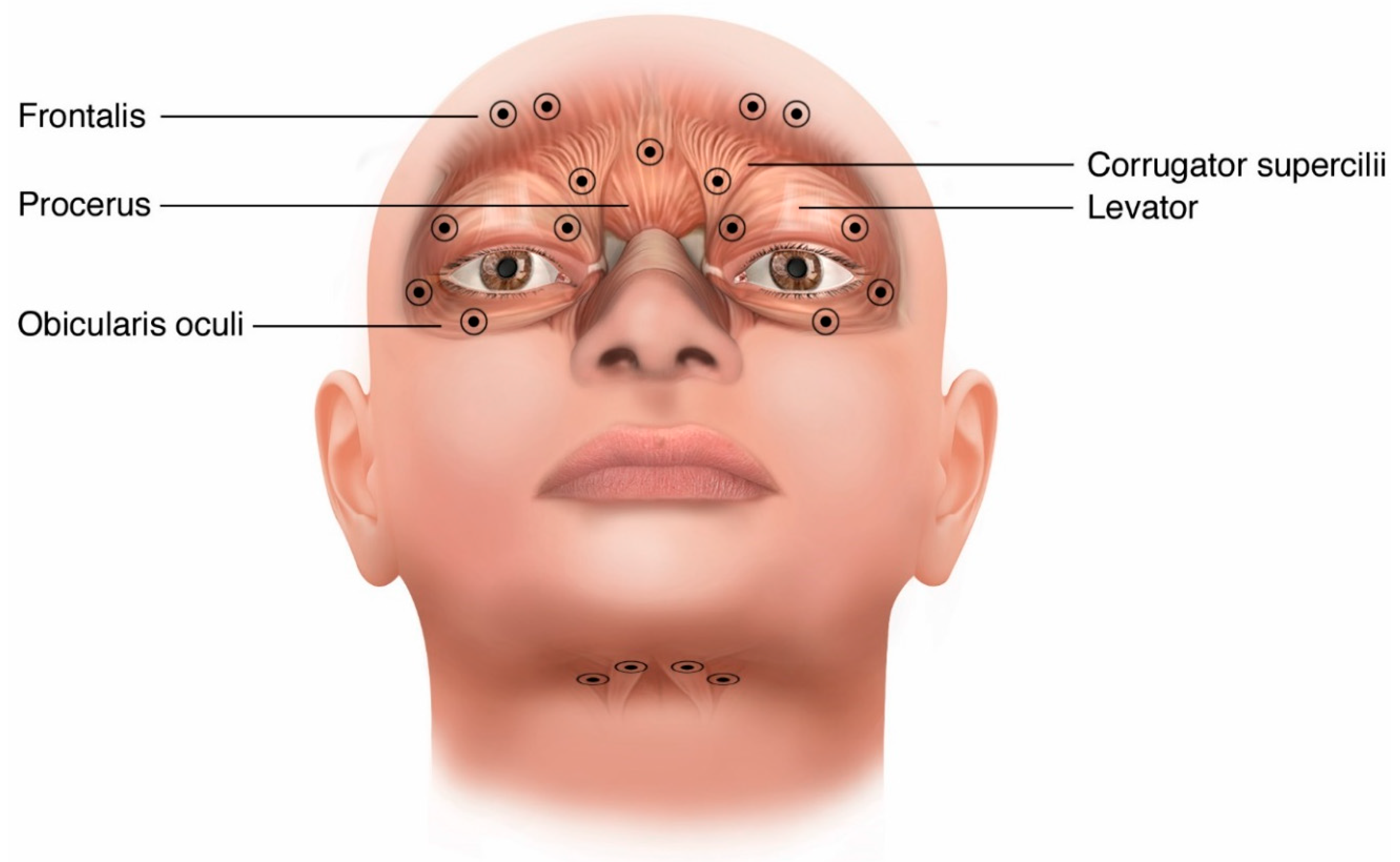
what muscle is used in tight or forced eyelid closure
requires contraction of the orbital orbicularis oculi
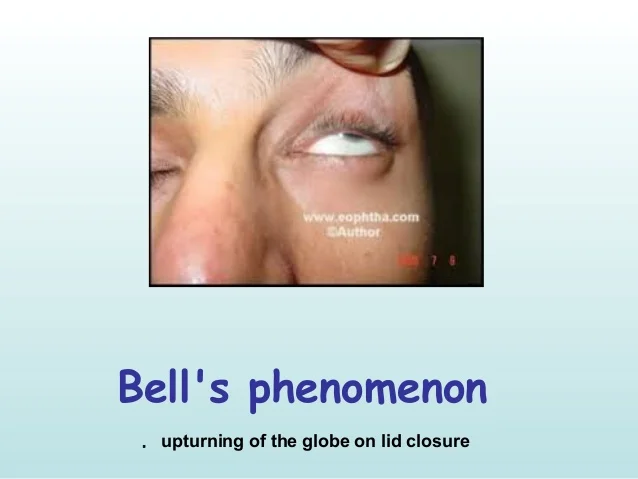
bell’s phenomenon
normal defense reflex in 75% of the population
upwards and outwards globe rotation after forced lid closure
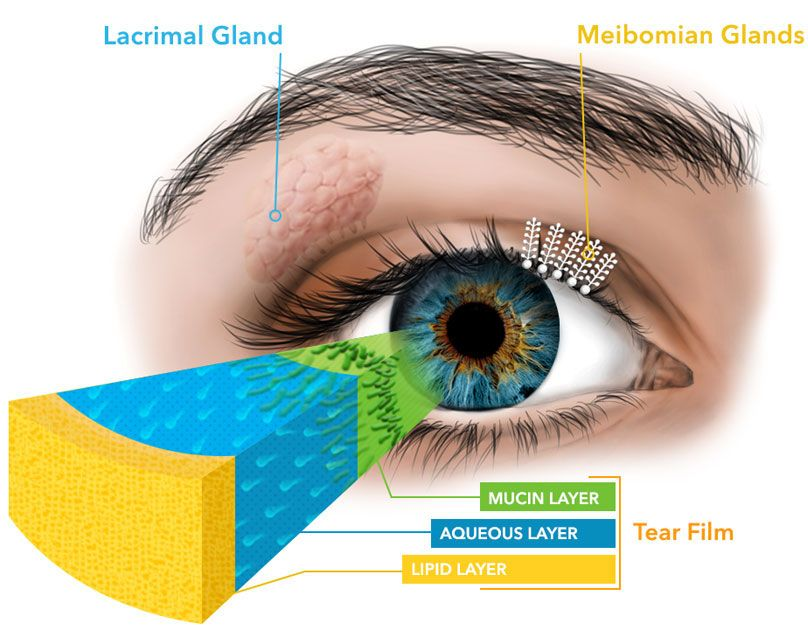
location of meibomian glands
upper and lower tarsal plates of the eyelids
role of meibomian glands
secrete anterior lipid layer of tear film
what kind of secretion do meibomian glands have
holocrine secretion (secrete their entire cell content as a product)
blinking stimulates release of what through holocrine secretion
release of lipids via the meibomian glands
what kind of glands are the accessory lacrimal glands
tubuloacinar exocrine glands
name and location of accessory lacrimal glands
glands of krause: fornices
glands of wolfring: tarsal conjunctiva
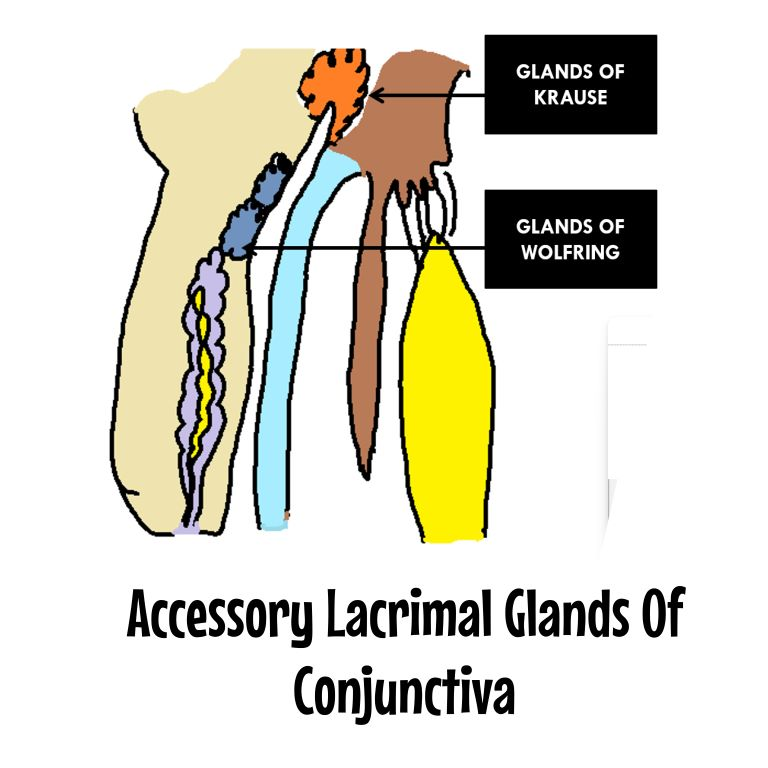
are there more glands of krause or wolfring
krause
in which direction does the eyelid close during a blink and why
laterally to medially
helps move tears toward puncta
what layer of the tear film is being spread evenly across the eye during a blink
mucin layer
how do tears drain when the eye is open
passive drainage into the puncta via capillary attraction
when the eyelids close, which 2 muscles contract to help with tear drainage
Horner’s and orbicularis oculi
how does the contraction of horner’s help with tear drainage
when horner’s contracts, the canaliculi shorten and move medially towards the lacrimal sac
this action pumps tears into the lacrimal sac
how does the contraction of the orbicularis help with tear drainage
when orbicularis contracts, temporal wall of the lacrimal sac is stretched away from the nose
this creates a negative pressure that forces tears into the NLD
the orbicularis causes lacrimal sac (compression/dilation)
compression
forces tears into the NLD
role of blinking in tear drainage
moves the tears medially towards the puncta
lowers the canaliculi pressure, creating a pressure difference that promotes tear drainage
number of cilia on UL and LL
150 lashes on UL
75 lashes on LL
role of cilia
screen the environment and induce blinking when necessary to protect eyes
2 roles of eyelid glands
produce tear film
move debris away from cornea
5 functions of tears
optical, nutritional, mechanical, antibacterial, corneal transparency
optical function of tears
creates smooth optical surface for clear vision
primary role of tear film
largest change of refractive index of the eye
air/tear film interface
nutritional function of tears
primary source of oxygen for the corneal epithelium
from diffusion of atmospheric O2 from the tear film
mechanical function of tears
tear film collects debris during a blink and removes waste from corneal epithelial cells
antibacterial function of tears
aqueous layer has immune cells (lysozymes, lactoferrin, IgA, etc)
how tears help with corneal transparency
has specific osmolarity and pH that is maintained by secretory glands and corneal epithelial cells
helps prevent corneal edema
what is the tear film thickness (according to recent non-invasive techniques)
3 microns
what is the anterior lipid layer of the tear film composed of
fatty acids, cholesterol, waxy esters
what secrets the anterior lipid layer of the tear film
meibomian glands, zeis & moll glands
what is the main role of the anterior lipid layer of the tear film
to slow the evaporation of the aqueous layer of the tear film and maintain clarity
what is the main method of releasing lipids from the glands
blinking
what type of innervation is able to increase lipid secretion
PS innervation
increases lacrimation
3 functions of the aqueous layer of the tear film
protection through antibacterial proteins
nutrition by supplying glucose to the corneal epithelium
adding thickness to the tear film
what nutrient does the aqueous provide to the corneal epithelium
glucose
what is the main component of tears
water
components of the aqueous layer of the tear film
water, electrolytes, antimicrobials, lipocalins, vitamin A, enzyme cofactors, HCO3-, solutes, proteins
what 3 electrolytes are in the tear film aqueous
Na+, K+, Cl-
5 antimicrobial components in aqueous tear film
IgA, lactoferrin, lysozyme, beta-lysin, interferon
role of lysozyme in aqueous tear film
cleaves peptidoglycan in bacterial cell wall, killing bacterial
antimicrobial
role of lactoferrin in aqueous tear film
chelates Fe2+, which is an essential nutrient for bacterial cell wall growth and metabolism
antimicrobial
role of beta-lysin in aqueous tear film
destroys bacterial cytoplasmic membrane and works together with lysozyme
antimicrobial
role of lipocalins in aqueous tear film
decrease surface tension of tears to enhance spreadability
role of vitamin A in aqueous tear film
development of goblet cells of the conjunctiva
in what form is vitamin A present in aqueous tear film
all-trans retinol
role of enzyme cofactors in aqueous tear film
maintain membrane permeability of corneal epithelial cells
how does the composition of the aqueous layer of the tear film change with increasing age
decrease in levels of lysozyme and lactoferrin proteins (antimicrobials) in the tears
overall decrease in aqueous secretion
how does contact lens wear change the aqueous composition of the tear film
increase in electrolyte and protein concentrations because of increased tear evaporation
how do closed eye conditions change the aqueous composition of the tear film
increased concentration of IgA and albumin
lysozyme and lactoferrin levels remain the same
what secretes the aqueous layer of the tears
main lacrimal gland
accessory lacrimal glands of krause and wolfring
what innervates the main lacrimal gland
PS fibers of CN VII
sympathetic fibers
sensory nerves of V1
what innervates the accessory lacrimal glands
PS nerves
role of main vs accessory lacrimal glands
main: reflex and emotional tearing
accessory: maintenance/basal tearing
recent theories that both glands are responsible for basal tearing
reflex arc of corneal CN V1
when a reflex stimulates CN V1, it causes lacrimation, miosis, and a protective bling
the dazzle reflex also causes lacrimal gland secretion
innermost layer of the tear film
mucous layer
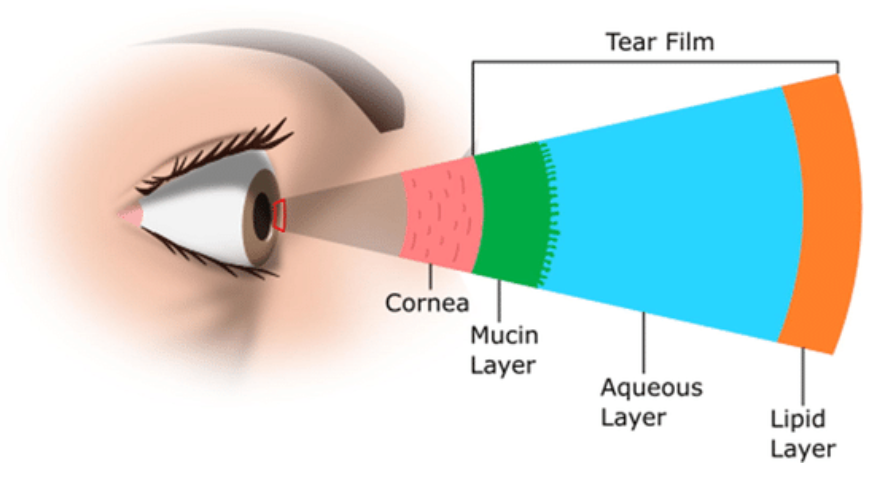
outer layer of the mucous layer
mucin layer
role of mucin layer
interacts with glycocalyx of corneal epithelium to spread tears across the corneal surface
traps debris, bacteria, and sloughed corneal epithelial cells
what is unique about mucin molecules
can mix with lipid and water
allows mucous layer to mix with the aqueous layer and spread it evenly across hydrophobic corneal surface
what produces the mucous layer of the tear film
goblet cells of the conjunctiva
squamous cells of the cornea and conjunctiva
where are goblet cells mostly found
inferonasal fornix
nasal bulbar conjunctiva
what do goblet cells need for development and where is it found
vitamin A
found in the tears in the aqueous layer as all-trans retinol
what does vitamin A deficiency cause in the conjunctiva and why
causes keratinization of the conjunctiva and cornea because without vitamin A goblet cells cannot develop
can cause bitot’s spots
bitot’s spots and what cause them
foamy build up of keratin on the conjunctiva
caused by vitamin A deficiency
innervation of corneal and conjunctival mucous secretion
sensory nerves in the corneal and conjunctival epithelium stimulate sympathetic and PS nerve endings surrounding goblet cells
PS stimulation causes an increase in mucous secretion
what kind of innervation causes increased mucous secretion
PS
disease process of mucous fishing syndrome
when patients fish for mucous, they further damage conjunctival epithelium
this further increases mucous production and creates a cycle that worsens the mucous
most common cause of mucous fishing syndrome
dry eye syndrome
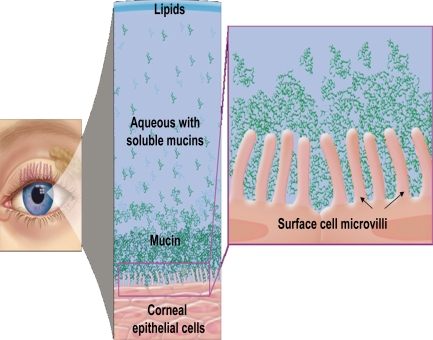
new research suggests that the tear film has what kind of composition
instead of 3 separate layers, aqueous and mucin layers are intermixed
there is a greater mucin concentration towards the corneal surface of the tears
how does TBUT work
once the anterior lipid layer becomes insufficient, the aqueous layer evaporates and the tears break up
with a blink, the anterior lipid layer is secreted again and restores the tear film
a TBUT of less than _____ seconds is considered abnormal
10
how are 25% of tears eliminated
evaporation
how are 75% of tears eliminated
drain through the nasolacrimal system or into systemic circulation by absorbing into conjunctival or nasolacrimal vessels
total tear volume of ocular surface
7-9 microns
max amount of fluid the eye can hold in the tear film
20-30 microns