Electromagnetism
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Mdefine magnetic flux
A measurement of the total magnetic field that passes through a given area; a measure of the number of magnetic field lines passing through the given area (symbol 𝜙; SI unit, Wb).
define magnetic flux density
The strength of a magnetic field or the number of magnetic field lines per unit area (symbol, 𝐵; SI unit, Wb m-2 or T).
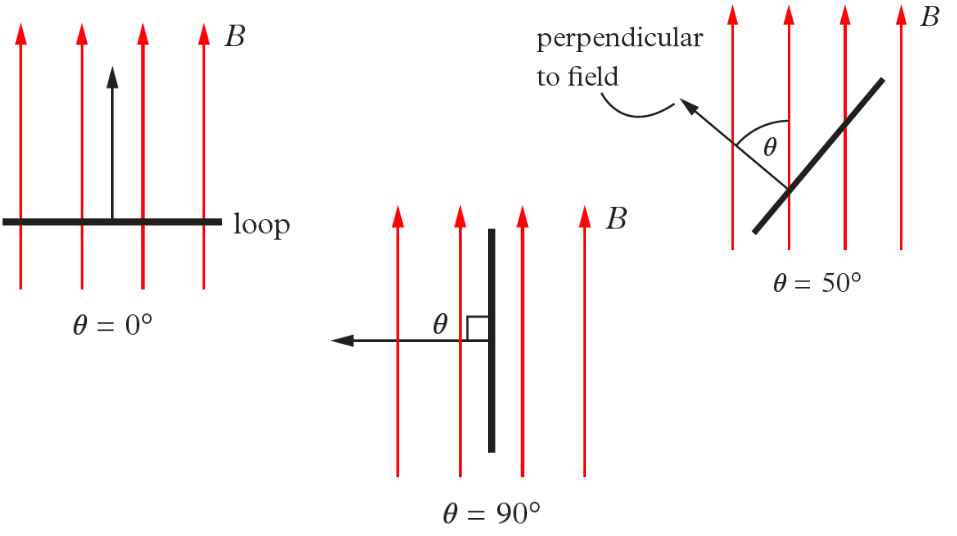
flux angle
the angle between the perpendicular to the loop and the field
define electromagnetic induction
The production of an electromotive force (EMF) or voltage across an electrical conductor due to its dynamic interaction with a magnetic field.
process of inducing an EMF
Electromagnetic induction occurs when an electromotive force is produced across a conductor due to its dynamic (i.e., moving) interaction with a magnetic field. For example, when a bar magnet is moved towards or away from a coil of wire, an EMF will be induced by the changing magnetic field.
explain how Lenz’s Law is consistent with the principle of conservation of energy
The conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed. Lenz's law indicates that work needs to be done (i.e., energy needs to be expended) in order to induce a current in a coil.
explain how transformers work in terms of Faraday’s Law and electromagnetic induction
An alternating current flows through the primary coil, creating a constantly changing magnetic field that induces a current in the secondary coil.
define and explain electromagnetic radiation in terms of electric fields and magnetic fields
Radiant energy that consists of synchronised oscillations of electric and magnetic fields, or electromagnetic waves, that travel at the speed of light in a vacuum. The fields are perpendicular to each other and the direction of travel. The changing electric field creates a magnetic field, and vice versa, allowing the electromagnetic wave to self-sustain its motion.
define magnetic field
A region of space near a magnet, electric current or moving electrically charged particle in which a magnetic force acts on any other magnet, electric current or moving electrically charged particle.
Moving charges
Moving charges produce magnetic fields. This is most commonly observed in the magnetic field around a current-carrying wire, which can be seen by placing a compass or iron filings near the wire.
what happens when you place electric current-carrying conductors or moving electric charges in a magnetic field
they experience a force
define Coulomb’s Law
A law stating that like electric charges repel and opposite electric charges attract: F=(kQq)/r²
electric fields
Regions around an electrically charged particle or object within which a force would be exerted on other electrically charged particles or objects.
electric field strength
The intensity of an electric field at a particular location.
electrical potential energy
The capacity of electric charge carriers to do work due to their position in an electric circuit