Summer homework- miscellaneous active recall
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Define internalisation
Going along with the group because we accept their beliefs and attitudes into our own cognitions
Define compliance
Going along with the group, even if we do not really agree with what they are doing
Give two situational variables that can affect obedience
Proximity, location
Using your knowledge of psychology, explain why some people might resist pressures to conform
Some people may have an internal locus of control- meaning they believe they are in control of the events in their life. They tend to be less influenced by the opinions of others, and so therefore are less likely to conform, in comparison to those with an external locus of control
Explain how a minority can bring about social change
A minority group can bring about social change by firstly drawing attention to an issue. By being consistent and committed regarding their viewpoint, the snowball effect occurs, which is when some members of the majority join the minority, gathering momentum for the movement
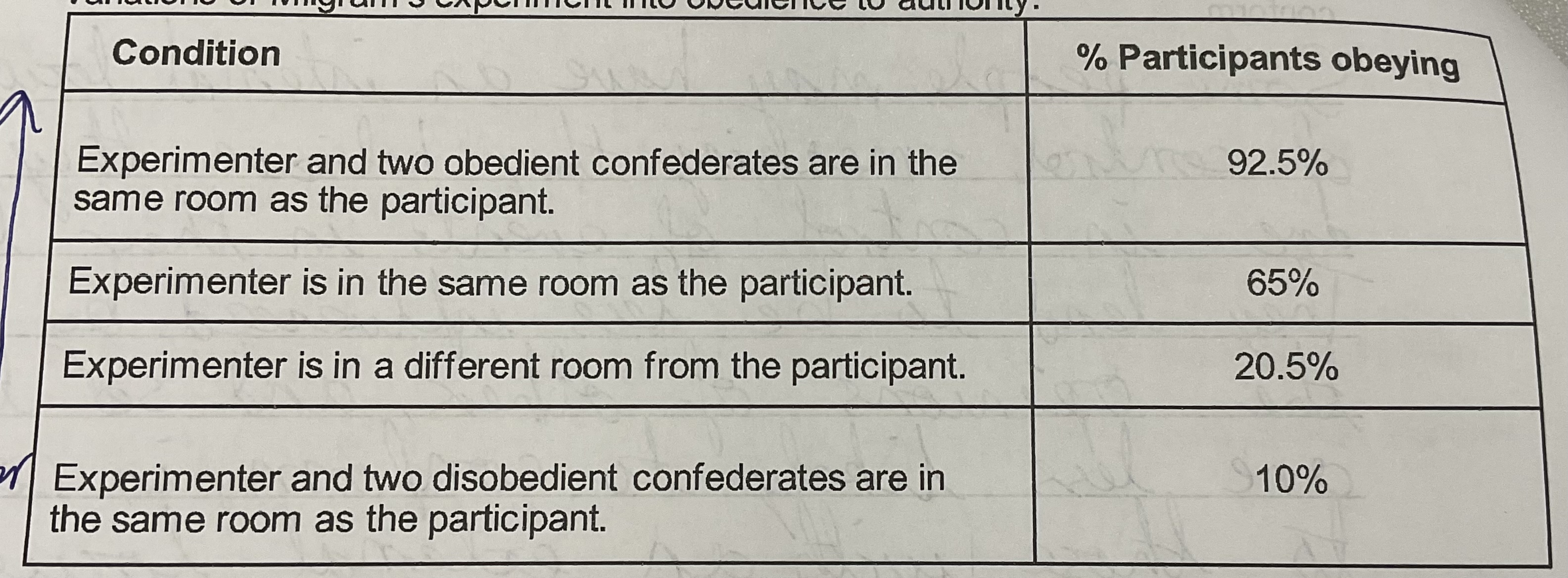
The following results are percentages of participants who gave the maximum shock, in variations of Milgram’s experiment into obedience to authority
What do these results suggest about the power of the confederates in variations of Milgram’s study
These results show that the confederates have a large power in altering obedience levels (an increase of 82.5%) by obeying or not obeying. They act as a dissenter when disobeying, which means participants are less likely to obey
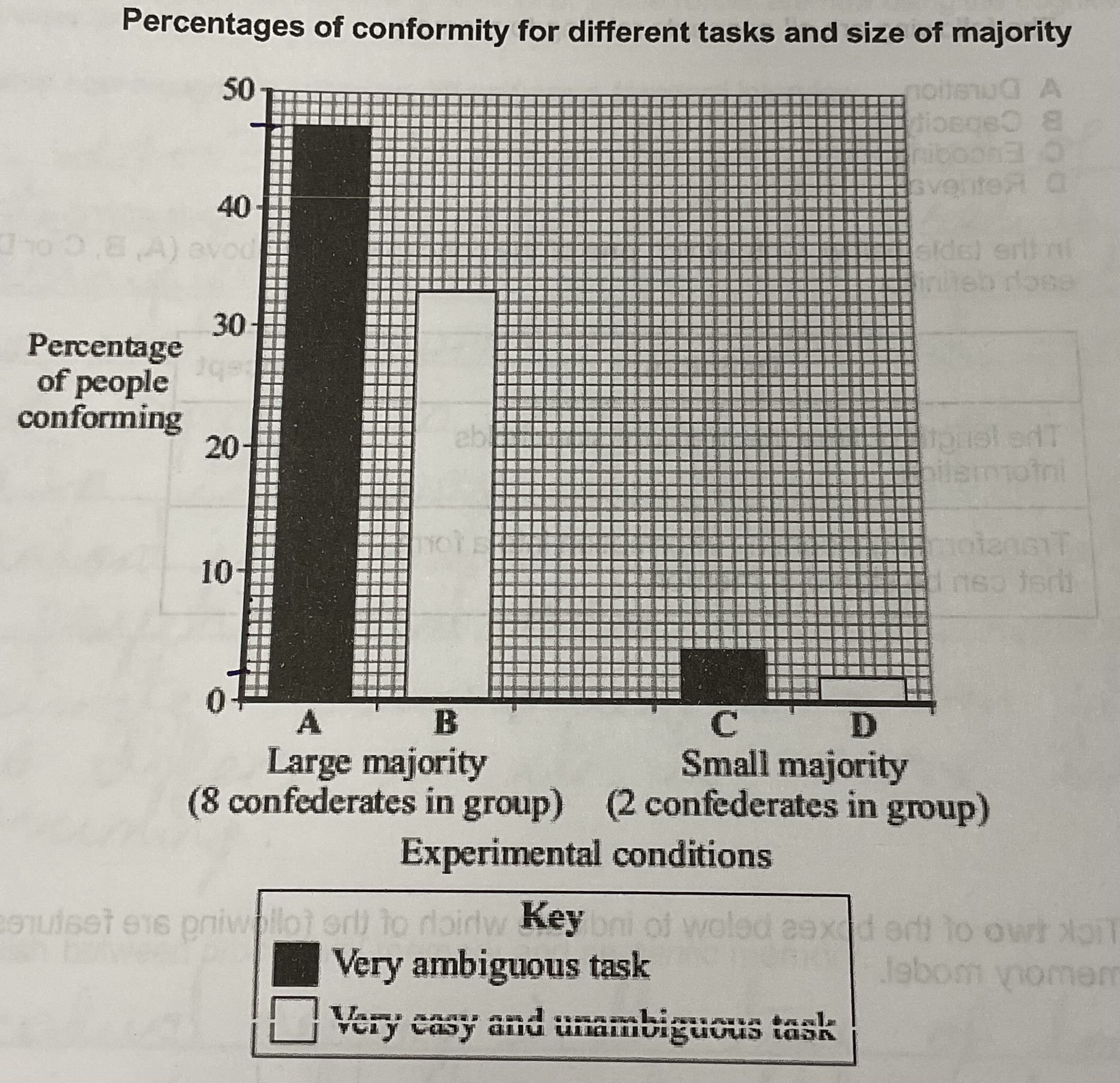
In an experiment into conformity, an experimenter varied both the number of confederates (stooges) and the ambiguity of the task. The bar chart below shows the findings.
What does the bar chart show about conformity
The larger the majority, the higher the levels of conformity
The more ambiguous the task, the more people will conform
In a situation with an unambiguous task and a small majority, only 2% of people conformed, in comparison to 47% in an ambiguous task with a large majority- suggesting that these things strongly affect conformity rates
Define duration
The length of time the memory store holds information
Define encoding
Transforming incoming information into a form that can be stored in memory
Give two features of the working memory model
Central executive, phonological loop
Traditionally, police have questioned eye witnesses using the standard interview procedure. This involves a period of free recall about an event , followed by specific questions. However, an increasing number of police forces are now using the cognitive interview technique
Explain how a cognitive interview differs from a standard interview
A cognitive interview is a method of interviewing eyewitnesses which uses 4 techniques- report everything, reinstate the context, report in reversed order, and report in changes perspective. In this way it differs demo a standard interview, as it is supported by psychological research to enable accurate testimonies, however it also differs as it is more time consuming
Distinguish between procedural memory and semantic memory
Procedural memory is the type of long term memory for how to perform motor actions, it is not time stamped and does not require conscious effort to recall. On the other hand semantic memory is the memory store for facts about the world, which is also not time stamped, but does require conscious effort to recall
In the context of explanations of forgetting, what is meant by interference
Interference is when two similar memories compete, resulting in one of both of them being distorted or forgotten
Choose one study in which the effects of interference were investigated. Briefly outline what participants had to do in the study
Baddely and Hitch (1977)- rugby players were asked to remember the names of the teams they had played in the season, week by week
Briefly discuss one limitation of interference as an explanation of forgetting
One limitation of interference as an explanation of forgetting is that it is limited in that it can only be used to explain forgetting of similar memories, not those that are different
One technique used in cognitive interviews is report everything. When using this technique, the police officer in this investigation read the following instructions to the participants
“Please tell me everything that you can remember about what you saw in the film. Do not leave anything out, even the small details you think may be unimportant”
Identify one other technique which could have been used by the police officer in this cognitive interviews. Write down the instructions that he could have read out to the participants
Technique- report in reversed order
“Please tell me everything in the opposite order than it happened in. Start with the events that happened last, and end with what happened first”
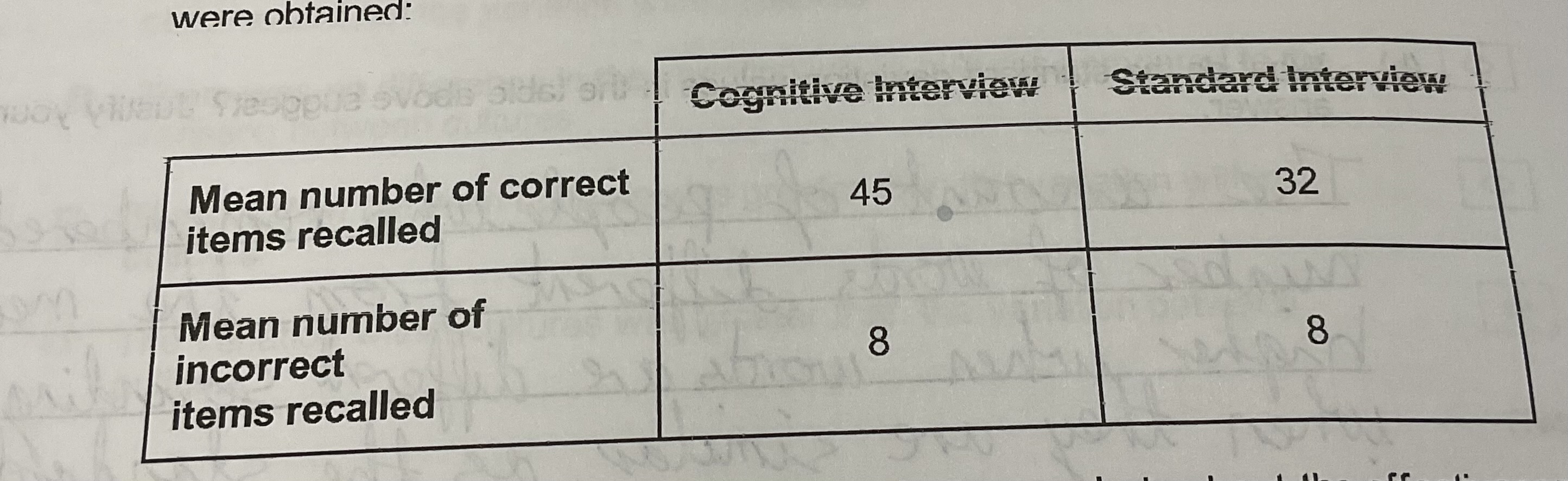
The psychologist also recorded the number of correct items recalled and the number of incorrect items recalled in each type of interview. The following results were recorded
From these results, what might the psychologist conclude about the effectiveness of cognitive interviews
Cognitive interviews draw out not only a larger amount of information from a person, but a larger amount of information overall
Explain how counterbalancing might improve the design of a study
Counterbalancing removes order effects, as if the study is a repeated measures design. Thus avoiding the skewing of results from fatigue or learning the material
Give two examples of behaviour of a securely attached child in the strange situation
The infant goes to the caregiver when she returns and is easily soothed
The infant explores a strange environment, plays happily with toys and uses the caregiver as a safe base
In Van Ijzendoorn’s cross-cultural investigations of attachment, which one of the following statements is correct
The variation within cultures was greater than the variation between cultures
Learning theory provides one explanation of attachment. It suggests that attachment will be between an infant and the person who feeds it. However, some findings of research studies do not support this explanation
Outline research findings that challenge the learning theory of attachment
Harlows research on monkeys showed that when scared, they go to the cloth ‘mother’ that cannot feed them instead of the wire ‘mother’ that can. This means that they develop attachment based on comfort, rather than the ability to obtain food, which contradicts the learning theory
Some researchers believe that caregiver-infant interactions influence the development of attachment
Explain one reason why it is difficult to draw conclusions about the role of caregiver-infant interactions in the development of attachment
It may be difficult to draw conclusions based on caregiver-infant interactions as babies may complete movements or make noises unconsciously, and so it may be hard to draw conclusions
Briefly evaluate learning theory as an explanation of attachment
One strength of learning theory is that it provides a valuable insight into how an infant form attachment to its main caregiver. However, an issue is that many infants form attachments to people who do not feed them, which contradicts learning theory, and a lack of support from animal studies
Give two statements that describe the deviation from ideal mental health definition of abnormality
Not achieving self actualisation, not being able to resist stress
Define statistical infrequency
Behaviour which is rare and not exhibited by many people
Define deviation from social norms
Behaviour which does not fit the rules of expected behaviour
Define failure to function adequately
Behaviour which shows an inability to cope with everyday life
Outline the characteristics of obsessive compulsive disorder
The behavioural characteristics of OCD include compulsive behaviours and avoidance
The emotional characteristics of OCD include feelings of anxiety, distress, shame and disgust
The cognitive characteristics of OCD include persistent obsessions and awareness of excessive anxiety
Outline cognitive behaviour therapy as a treatment for depression
Cognitive behaviour therapy helps treat depression by changing negative thought and behaviours. The therapist works with the patient to spot unhelpful thinking patterns and challenge them. Patients also do activities that improve their mood, called behavioural activation activation.CBT is usually a short-term structured therapy where the patient and therapist works together
What are the elements of Beck’s negative triad
Negative views about the self, the future and the world
Briefly discuss one reason why systematic desensitisation might be a more successful treatment for phobias than flooding
Systematic desensitisation may be less traumatic than flooding which reduces the number of people who will drop out of the therapy (making it more successful overall)
Is negative schema best described as measuring a cognitive, emotional or behavioural characteristic of depression
Cognitive
What is Wundt’s method of introspection
Introspection involves reporting present experience
What best describes the aim of cognitive neuroscience
To relate mental processes to brain structures
Briefly explain what social learning theorists mean by modelling in relation to gender development
Modelling is someone who influences another person by being imitated. Someone is more likely to act as a model for someone if they are able to identify with them
Explain how reinforcement might be used to encourage primary school children to pick up litter in the playground
Positive reinforcement can be used by rewarding children for picking up litter. Vicarious reinforcement will then encourage more children to pick up more litter, as they will see that the other children were being rewarded, and they want that reward
Explain what is meant by an inference
An inference is making a conclusion based on a set of data
Describe the structure of the personality according to the psychodynamic approach
According to the psychodynamic approach, the personality is made of the id, which is purely selfish and fuelled by wants, the superego, which contains the conscience and morals, and the ego, which tries to find a balance between the two