Bio 103 Exam 3 (McMullen)
1/162
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
163 Terms
Interphase
cell grows, performs its normal functions, and prepares for division; consists of G1, S, and G2 phases
chromosomes are replicated, each consisting of 2 identical chromatids held together at the centromere
G1 phase
the cell grows in size and organelles double in number
S phase
DNA replication ("S"= synthesis)
G2 phase
cell growth, production of enzymes and other proteins
two categories of mitosis (eukaryotic cell division)
1. karyokinesis (division of cell nucleus)
2. cytokinesis (division of cytoplasm)
prophase
chromatin condenses to form chromosomes
centrosomes move apart and form polar spindle fibers (made of microtubules)
nuclear membrane and nucleoli disappear
kinetochore fibers attach to proteins called kinetochores within the centromere of each chromatid pair
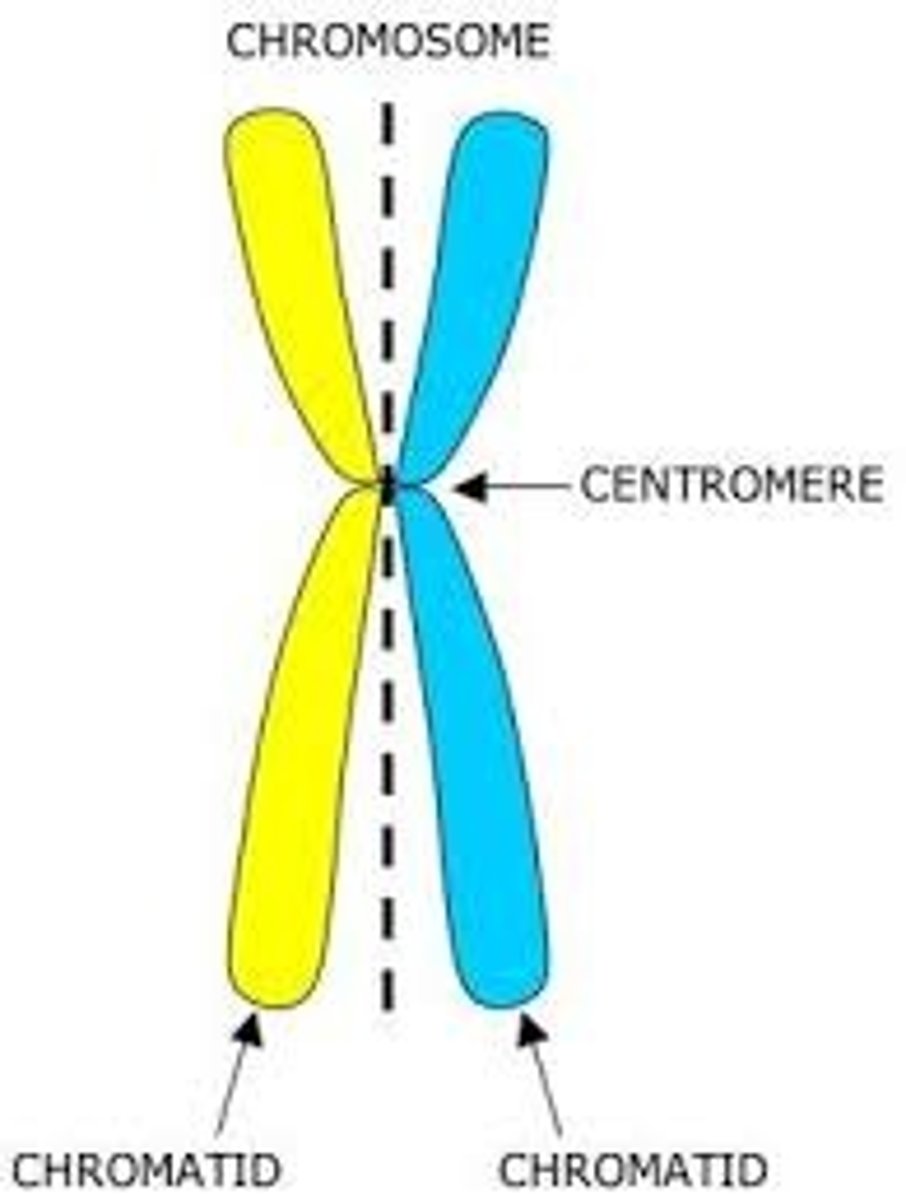
centromere
Area where the chromatids of a chromosome are attached
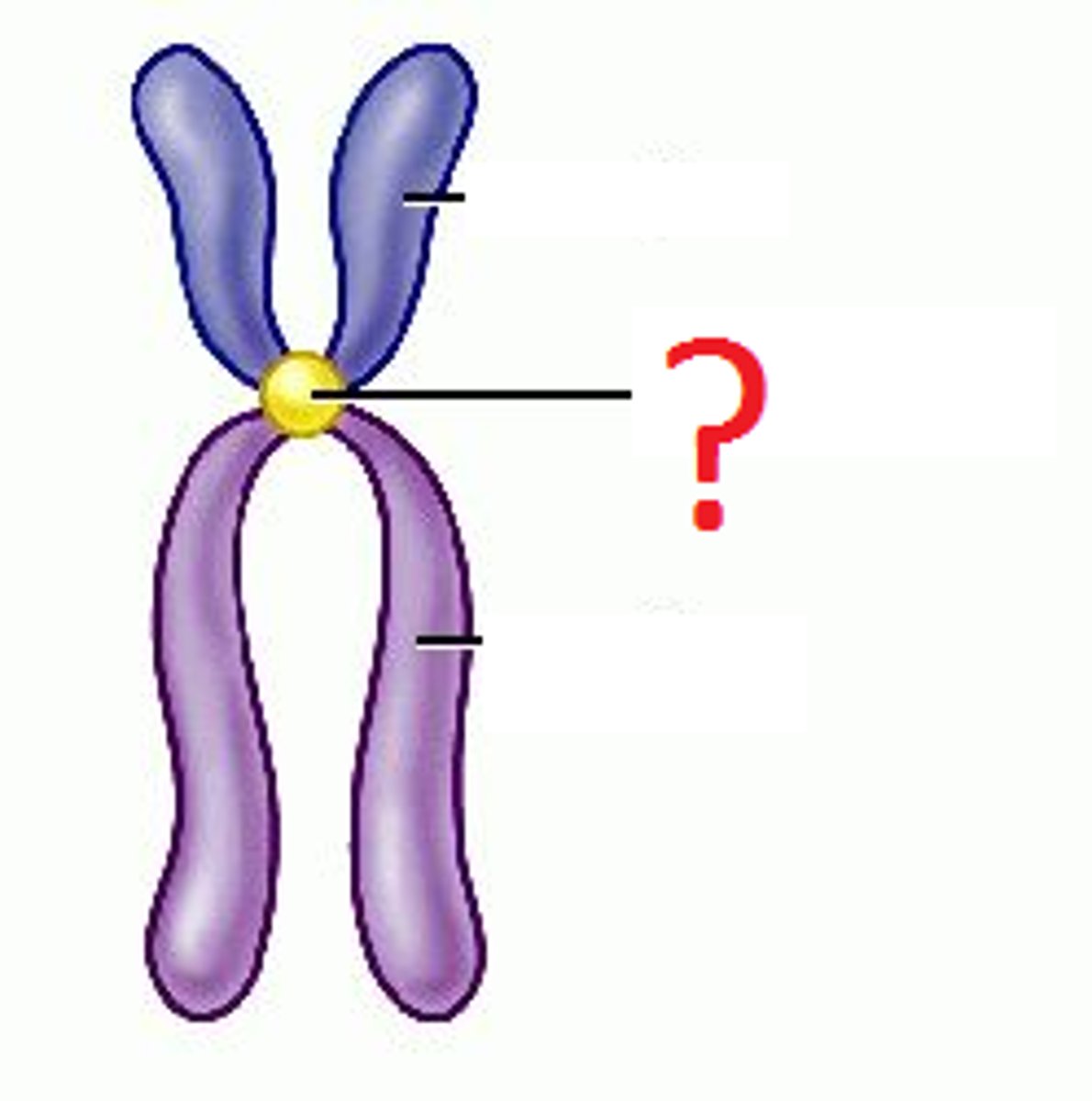
chromatid
one of two identical "sister" parts of a duplicated chromosome attached at the centromere
chromatin
the unorganized mass of DNA and histone proteins within the nucleus
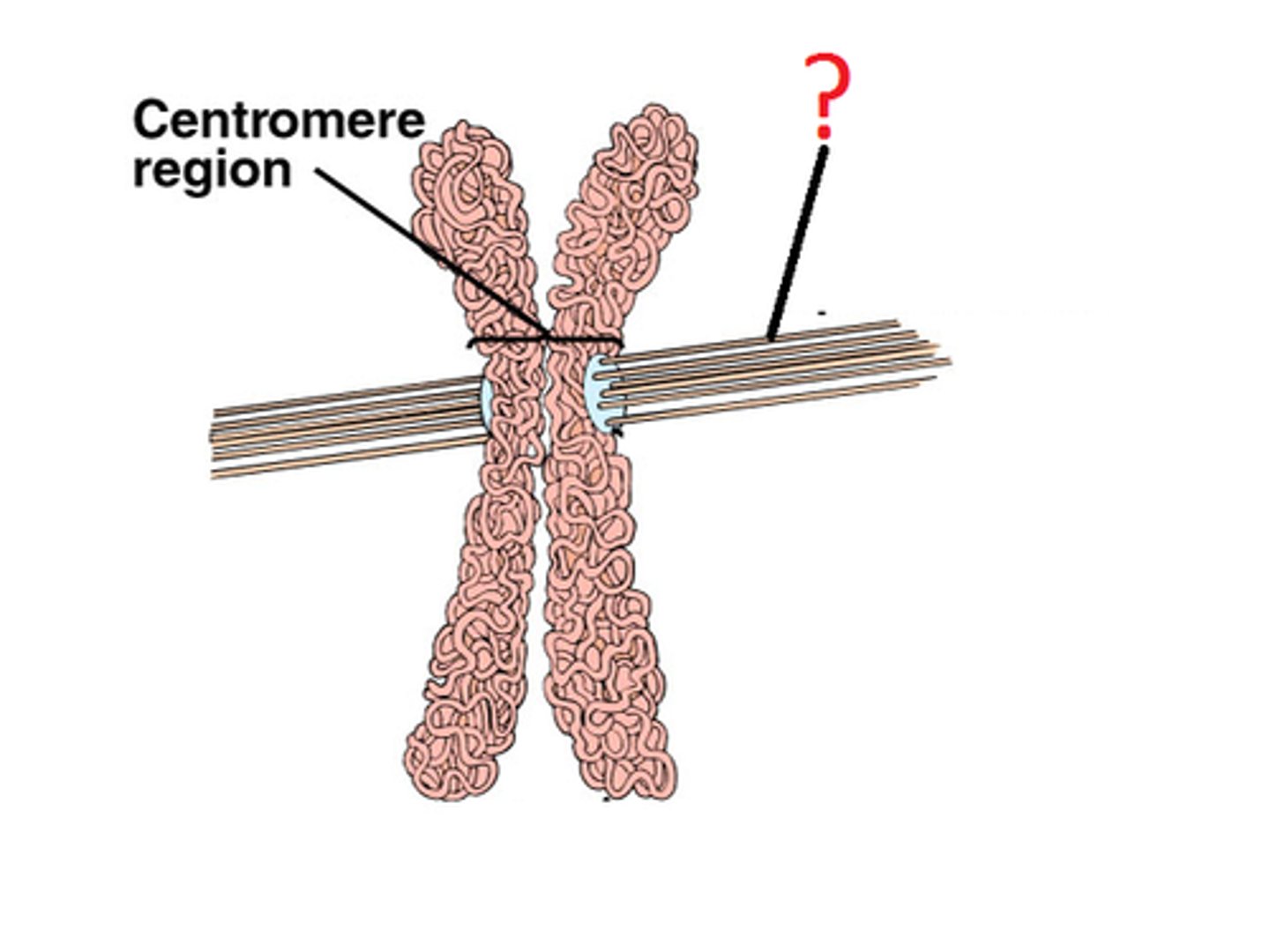
kinetochore
A specialized region on the centromere that links each sister chromatid to the mitotic spindle.
metaphase
the kinetochore and its fibers move the chromosomes to the equatorial plate where they form a line
anaphase
1. chromatids separate and move to opposite poles
2. the centromeres move first and the arms drag behindonce the chromatids have separated, they are called daughter chromosomes
what are the longest and shortest phases of mitosis
prophase is the longest; anaphase is the quickest
telophase
1. the spindle fibers break down
2. nuclear membranes, nucleoli, and chromatin reappear
cytokinesis in plant cells
1. cell plate forms from inside out by vesicles produced by dictyosomes
2. cell plate becomes middle lamella
3. cell wall is laid down
the result of mitosis or duplication division
daughter cells that are identical to one another genetically
what allows plants to reproduce asexually?
rhizomes, stolons, and plantlets
rhizomes
horizontal underground stems (grasses, irises) ex. crabgrass
stolons “runners”
horizontal above ground stems (ex. strawberries)
plantlets
miniature plants on special leaves that produce new plants at a later time (formed at the margins of leaves) (ex. mother of thousands)
what allows animals to reproduce asexually
fragmentation, budding, and fission
fragmentation
a portion of an individual can break free and regenerate an entire organism (ex. sponge)
budding
a miniature offspring forms on the parent and then breaks off (ex. hydra)
fission
the separation of a parent into two or more individuals of roughly equal size (ex. sea anemone)
what are some animals that reproduce asexually
sponge, sea anemone, hydra
advantages of asexually reproduction
1. create numerous offsprings quickly
2. quickly colonize a new habitat
3. can reproduce in isolation (no mate)
4. perpetuates successful combinations of genes
*most advantageous in a stable, favorable environment
meiosis
the process of cell division in which the chromosome number is reduced from the diploid number (2n) to the haploid number (n)**reduction division
sexual reproduction (EUKARYOTES)
gamete formation (meiosis) and syngamy (fertilization)
syngamy (fertilization)
The fusion of two gametes to form a diploid zygote in fertilization.
meiosis i
separates homologous chromosomes
meiosis ii
sister chromatids separate
prophase i
1. the chromosomes become visible and group in pairs (separate)
2. the nuclear envelope breaks down and pairs synapse into tetrads
3. crossing-over occurs (recombination)
tetrads
synapse of homologous pairs; four chromatids from homologous chromosomes
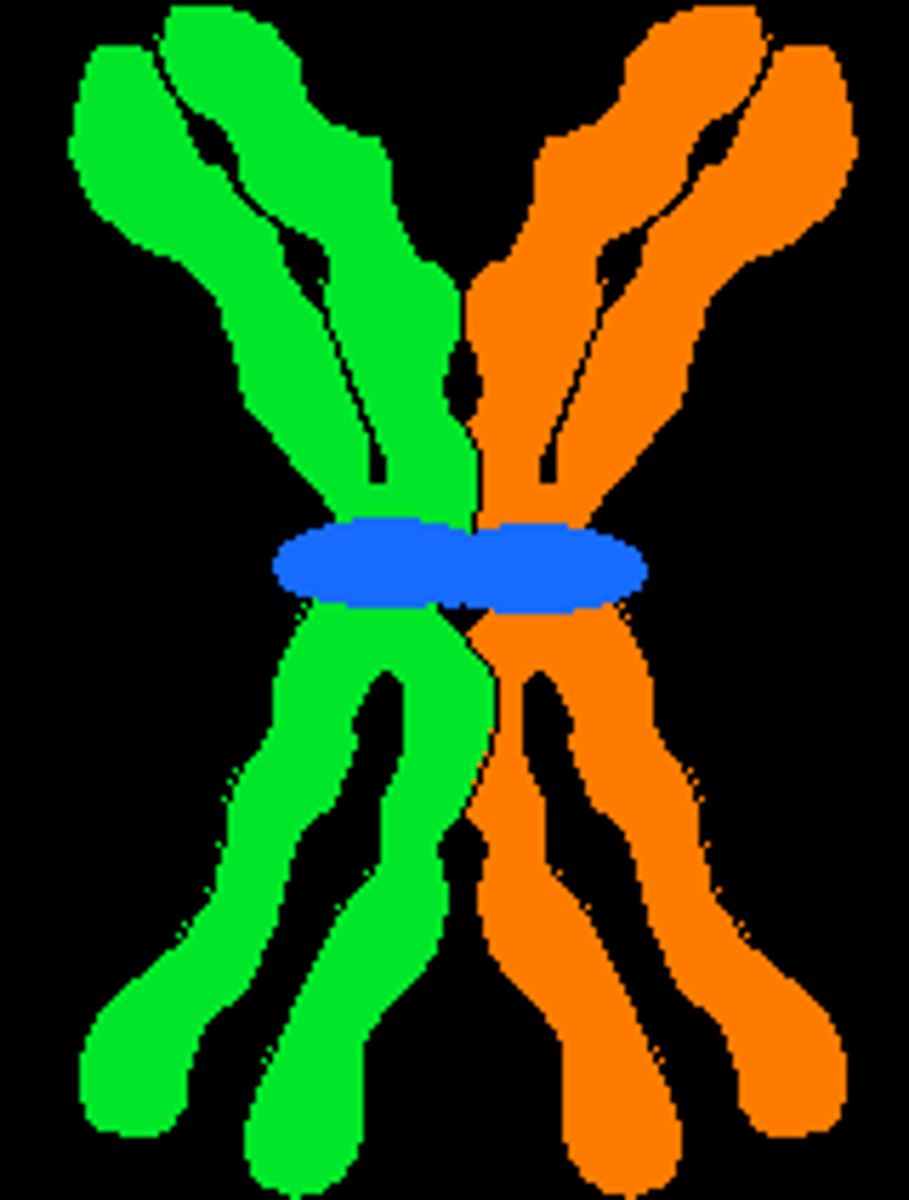
metaphase i
tetrads line up in the middle of the cell
anaphase i
homologues separate and move to opposite poles ; sister chromatids stay together
telophase i
1. homologous chromosomes have reached the poles; nuclear envelopes may/not form and cytokinesis may/not occur
2. newly forming cells are haploid; each chromosome has two non-identical sister chromatids
interkinesis
period of time between meiosis I and meiosis II during which no DNA replication takes place.
prophase ii
1. the nuclear envelope breaks down and spindle fibers reform
2. starting cells are the haploid cells made from meiosis i
metaphase ii
the chromosomes line up on the equatorial plane
anaphase ii
sister chromatids separate and new daughter chromosomes move to opposite poles
telophase ii
1. the spindle fibers disappear, and a nuclear membrane forms around each set of chromosomes
2. newly forming gametes are haploid
3. cytokinesis takes place
results of meiosis
4 haploid daughter cells; each has 25% of DNA and half the amount of chromosomes
fertilization of egg and sperm result in...
diploid offspring with 50% of DNA and homologous pair of chromosomes
importance of meiosis
genetic variation in species
** in humans: over 64 trillion different combinations w/o considering crossing over
green plants
green algae
nonvascular plants
seedless vascular plants
gymnosperms (seed vascular plants)
angiosperms (seed vascular plants)
land plants
nonvascular plants, vascular seedless plants, gymnosperms (seed vascular), angiosperms (seed vascular)
most primitive green plant
green algae
green plant synapomorphies
chlorophyll b, grana in chloroplasts, cellulose & hemicellulose are major cell wall components, plasmodesmata, and starch is the food storage product
plasmodesmata
channels through cell walls that connect the cytoplasms of adjacent cells
differences between land plants and green algae
gametangia, diploid embryo, and cuticle
gametangia
outer, sterile layer of protective plants
diploid embryo
grows into a multicellular, sporophyte generation
cuticle
outer, waxy covering which prevents them from losing water since they have to live on land
most primitive LAND plants
nonvascular plants: liverwort, hornwort, moss
once thought to cure liver disease
liverwort (according to the Doctrine of Signatures)
hornworts
1. mature sporangium releases spores
2. spores become gametophyte
moss
most advanced nonvascular plant due to stomata; has hydroids and leptoids (similar to xylem and phloem)
stomata are often present on the sporophytes
haploid generation
gametophyte
diploid generation
sporophyte
sporic meiosis (sexual reproduction in land plants)
alternation of generations between haploid and diploid generations (produces spores)
vascular plants
have organs (roots, stems, and leaves)
vascular tissue system (xylem and phloem)
dominant sporophyte generation
lignin comprises the secondary cell walls of certain cells
seed plants
have seed = embryo, nutritive tissue, seed coat
2 types: gymnosperms and angiosperms
gymnosperms
A plant that produces seeds that are exposed; no fruits, no flowers
ex: pine, conifers, male cones, pollen grains, female cones
pine
males cone (pollen grains), female cone (ovule)
angiosperms (vessel seed)
1. flowers
2. fruits
3. double fertilization (endosperm)
4. 3 nucleate
largest angiosperm
eucalyptus
smallest angiosperm
wolffia (duckweed)
two classes in phylum anthophyta
monocotyledones and eudicotyledones
characteristics of moncots
1. one cotyledon apart of each embryo
2. flower parts in 3's or multiples of 3
3. parallel leaf venation
4. scattered stem vascular bundles
monocot examples
coconut palm, trillium, rice, wheat, corn
characteristics of dicots
1. 2 cotyledons apart of each embryo
2. flowers in 4's or 5's
3. distinct ring of stem vascular bundles
4. net leaf venation
examples of dicots
cinquefoil, daisy, strawberry, poppy, cactus, lima beans
typical flower parts
ovule, receptacle, sepal, stamen (anther/ filament), petal, pistol (stigma, style, ovary)
ovule
female reproductive structure of a seed plant where the haploid egg develops; becomes seeds
receptacle
The base of a flower; the part of the stem that is the site of attachment of the floral organs.
sepal
A leaflike structure that encloses the bud of a flower; for protection
stamen
the male reproductive organ of a flower
anther
the part of a stamen that contains the pollen.
filament
the stalk of a stamen; supports the anther
petal
attracts pollinators
pistil
female reproductive organ of a flower
stigma
where pollen lands
style
The stalk of a flower's carpel, with the ovary at the base and the stigma at the top; "pollen tube"
inflorescence
cluster of flowers on a plant
(panicle, spike, raceme, head, catkin)
panicle
a branched, indeterminate inflorescence with flowers on short stalks along the axis (most complex)
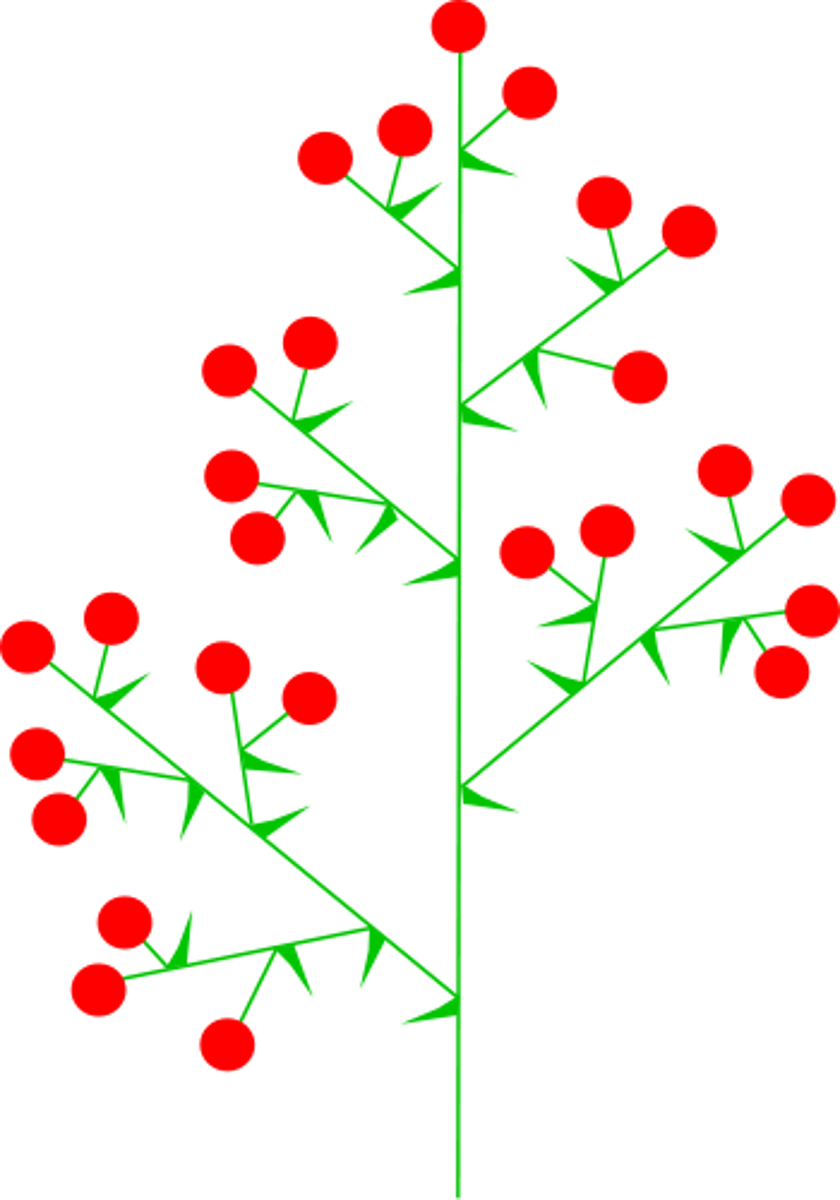

spike
single stalk with flowers directly on the stalk (simplest)
ex: corn
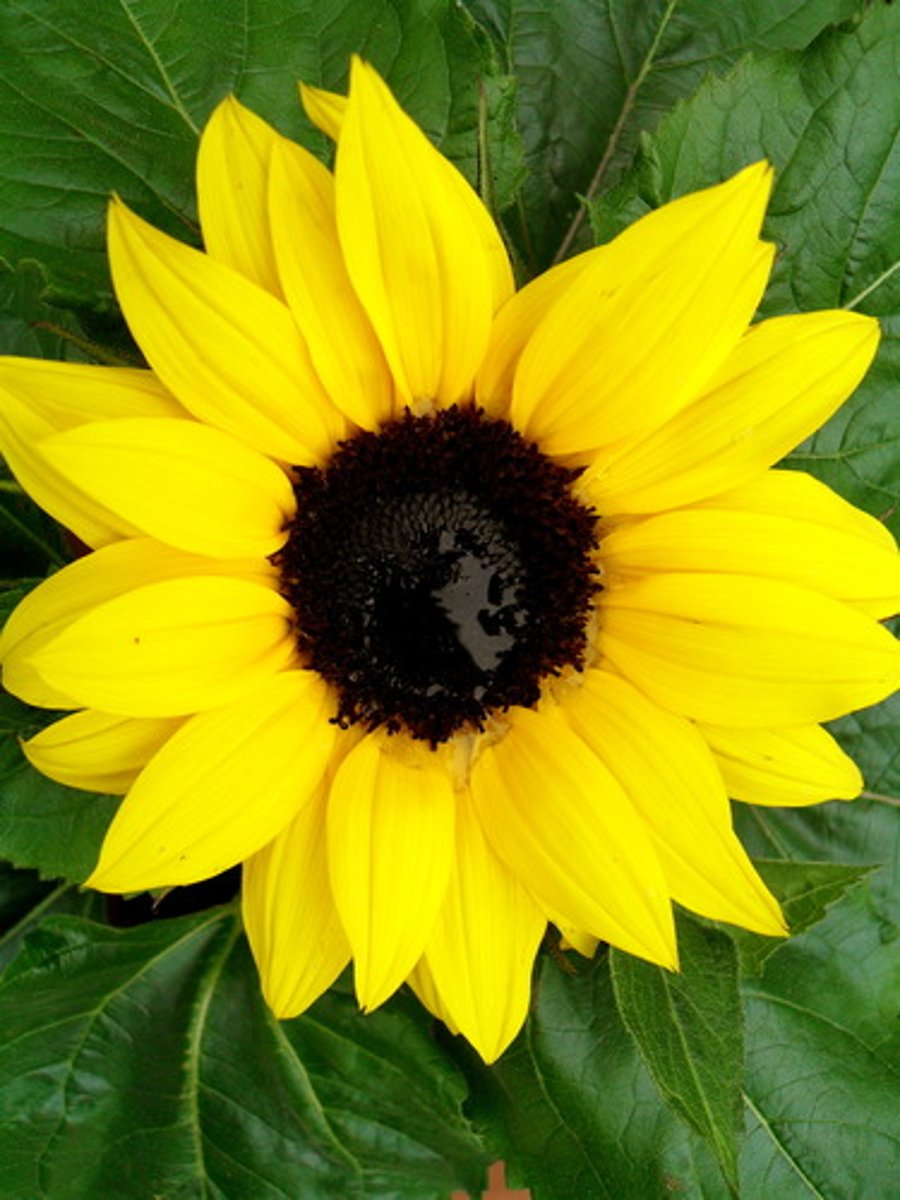
head
outer (ray) and disc (inside) flowers

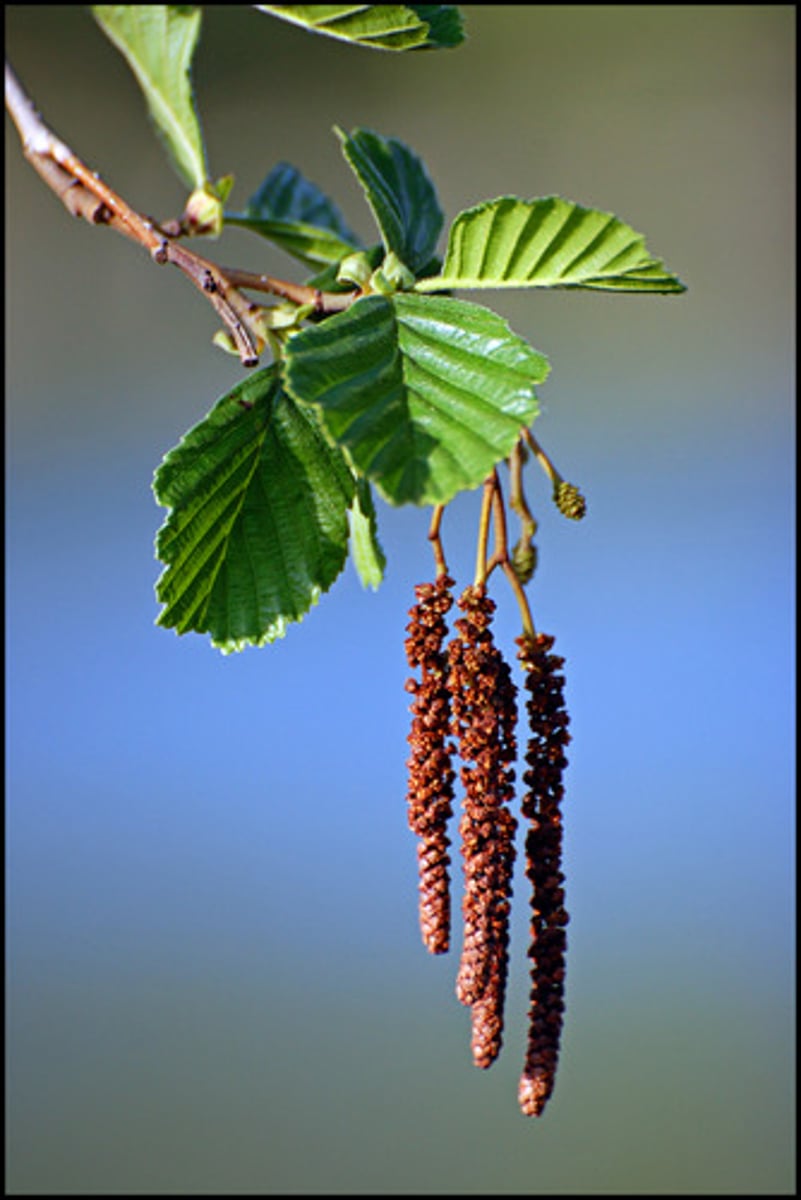
catkin
slim cylindrical flower cluster with few or no petals; hanging arrangements

pollination syndrome
pollinators and flowers coevolve; flowers and their pollinators have adapted to each other
beetle pollination
eat their way through petal with their jaws (so ovules are found deeper)
pollinate one large flower (magnolia or dogwood) or inflorence
clumsy, primitive, unsophisticated
bee pollination
white or yellow flowers
nectar guides
some orchid flowers resemble female bees that male bees copulate with them
nectar robbing: no pollination occurs but bees get nectar
adult bees eat nectar larvae feed on pollen
fly pollination
1. foul odor
2. pollen sticks to body
moth pollination
1. active at night
2. pale flowers; strong odor
butterfly pollination
1. attractants: brightly colored flowers
2. rewards: abundant nectar (head flowers like sunflowers)
bird pollination
1. bright colors (reds); no odor, more nectar
2. pollen attaches to beak and feathers
bat pollination
fermented or musty smell
mostly in tropics
more nectar
pale or white flowers
petals or tear resistant
wind pollination (abiotic- nonliving pollination)
1. pollination of plants by means of pollen carried on the wind
2. no odor, no petals, no nectar
ex: corn
water pollination
pollen floats on water between flowers
three types of fruits
aggregate, multiple, simple