Electrical Transmission (Gow 1 )
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
the capacity of a cell to generate and propagate action potentials
this is fundamentally a ________ event\
most of what we know about this subject matter comes from the study of _______
cellular excitability
electrical
nerves
If the driving force is NEGATIVE does that mean the ion is pushed to go INTO the cell or LEAVE
INTO cell
+ direction means leaving cell
- direction is the reverse of entering cell so its leaving
KAHOOT:
If resting membrane pot'l is -70 mV and the Nernst pot'l for Na is +61 mV. What is the driving force on Na at rest?
electrochemical gradient (driving force) =
membrane potential (resting) - nernst
Ec= Vm -Vx
Ec = -70- (+61) = -131
-131
Driving force (Ec) = Vm - Vn
using this equation if
Vm>Vn will the ion come into or leave the cell?
Vm<Vn will the ion come into or leave the cell?
if Vm>Vn then driving force is POSITIVE meaning ion will LEAVE
if Vm < Vn then driving force is NEGATIVE then ion will come INTO cell
KAHOOT: TRUE/FALSE: Nernst Potential is the potential across the membrane at which there is no net flow of an individual ion
TRUE
KAHOOT: hERG channel dysfunction is associated with long-QT. The hERG channel primarily exhibits ____ flow.
INWARD
KAHOOT: Which component of an axon acts to enhance the speed of nerve impulses from the dendrite to the synaptic terminal?
myelin sheath
KAHOOT:
Which ion is most important for determining the resting membrane potential?
K+
KAHOOT: What channel or enzyme consumes up to 70% of energy for cellular activities in nerve cells?
Na+/K+ pump
KAHOOT: During which phase for action potential generation do K+ inward rectifying channels play an important role?
overshoot
K+ outward channels neccesary during repolarization BUT if you repolarize too much you need to ADD K+ to the cell through K+ INWARD channels
KAHOOT: which ions have the highest conductance?
K+
KAHOOT: do voltage-gated K channels begin to open as cells reach a threshold voltage?
YES
KAHOOT: true/false
Channels open rapidly at threshold for influx of K across the membrane
FALSE leaky K+ channels open SLOWLY
KAHOOT: When the voltage becomes more _______, the membrane is depolarized
positive
KAHOOT: What direction do ions flow across the membrane through Na+/K+ pump?
3 Na+ OUT
2 K+ IN
which cell types are excitable— have the ability to propagate action potentials?
neurons
cardiac
endocrine
skeletal
smooth muscle
what was the cable theory and what truth does it hold?
action potentials propagate through axons and dendrites like a long cable
is the nervous system a continuous network of interconnected nerve fibers, essentially a single, fused structure without distinct gaps between cells?
what theory believed this to be true?
reticular theory
DISPROVEN BY NEURON DOCTRINE
the nervous system is composed of discrete, individual cells called neurons, each functioning independently and separated by synapses
Neuron Doctrine
Golgi and the silver stains: silver nitrate where _______ were found
axons
received the 1906 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine for establishing the neuron, or nerve cell, as the basic unit of nervous structure.
Santiago Ramon y Cajal
do ALL excitable cells have a resting membrane potential?
who televised this discovery? what animal’s huge axon did they use to illustrate the resting membrane potential?
YES
Hodgkin + Huxley
giant squid axon
the resting potential is measured from inside to outside the cell
the inside is more positive/negative relative to the outside
negative
-70
inside -outside
(outside has more Na+ and positive charge)
so if outside is greater than inside then inside-outside is negative
can we record changes in the membrane potential?
Because of the position of the relative _______ the flow of __________ions into the cell is considered positive
YES
electrodes positive
the plasma membrane is permeable/impermiable to ions
impermeable NEED PUMPS and ION CHANNELS
what are the three types of channels?
voltage gates (a certain charge outside compared to inside) before ion can come in
ligand-gated
inward rectifier
how does the Na+/K+ channel work?
3 Na+ out 2 K+ in
there is differential permeability of ____, _____, and -____ ions via channels
Na+ K+ Cl-
are many neurological disorder the result of malfunctioning/mutated Na+/K+ pumps or channels?
channels
Ohm’s law states that there is a direct relationship between ________ and _________
meaning if there is an increase in one there is an increase in the other
if there is a decrease in one there is a decrease in the other
what is the equation?
current (I) and potential (V)
I=V/G
Ohm’s Law : I= V / G
what do the following stand for
current = potential /conductance
the slope of the relationship between current (X axis) and potential (Y axis) is ___________ which is the recipricol of __________
conductance (g)
reciprocal of resistance
by convention, the outward current is the flow of positive ions FROM _______ —→ ___________
inside the cell to outside
membrane potential (Vm) = V inside - Voutside
for most cells Vm is _______ beacuse there is more ____ outside than inside the cell
negative
positive charge inside
when Vm is negative the membrane is __________polarized and LESS likely to transmit signal
that means more positive outside than inside so hyperpolarization
when Vm is positive the membrane is ________polarozed and MORE likely to transmit signal
more positive inside the cell than outside =
depolarization
what is the difference between electrical and chemical force?
electrical force is the difference between how much + and - charges are in the cell
if there is more positive charge in the cell than there will be a force pushing positive out to reach equilibrium
chemical force is the difference between the amount of chemicals inside and out of the cell
if there is a higher concentration of the ion inside of the cell than there will be a force for it to leave the cell where it is less concentrated
when would the electrical force of potassium = 0
when would the chemical force of pottasium =0
when there is an equal amount of anions and cations (K+) inside the cell
when there is the same amount of potassium inside and out of the cell
Electrochemical Gradient =
chemical force + electric foce
if there are 7 anions and 7 pottasium ions inside the cell and no ions outside of the cell
what is the electric force?
what is the chemical force?
electrochemical force
electric = 0 (the amount of voltage inside the cell cancels out)
chemical = forward force for potassium to leave the cell because higher concentration inside than outside
chemical + electric = 0 + forward = forward force potassium OUT
if there are 7 anions and 5 pottasium ions inside the cell and 2 potassium ions outside
what is the electric force?
what is the chemical force?
electrochemical force
voltage = backwards force for the two potassium to go into the cell because inside the cell is more negative than positive
there is a forward chemical force for potassium to leave the cell because postassium inside the cell is more concentrated
——> (chemical) + ← (electric) = —>
as more and more K+ exits the cell what happens to the electrical vs chemical force?
electric force= increase because want positive inside to be equal to negative inside (as K+ leaves there will be a stronger push for them to come back in)
chemical force the concentration will become closer to equaling each other as more K+ exists the cell causing the force for K+ to leave to decrease as more K+ leaves
if there are 7 anions and 4 pottasium ions inside the cell and 3 K+ outside
what is the electric force?
what is the chemical force?
electrochemical force
backwards electric force since the inside of the cell is negative (want potasium to come back into the cell)
forward chemical force since there are more pottasium inside then out will want potassium to leave cell
forwards and backwards cancel each other out = 0
NERDS POTENTIAL - potasium will come in and out of the cell without having too much on either side of the cell unless triggered
what is Nerst Potential?
when the electrical and chemical force match (in opposite directions) and there is no net movement
what is the electrochemical gradient at Nerst Potential?
zero (electric + chemical force) evens out
what are the three factors that determine te Nernst Potential for individual ions?
charge of ion (z)
temperature (T)
intracellular and extracellular concentrations of ion
the electrochemical driving force is the difference between the __________ potential (___) and _________ potential (___)
membrane - nernst (Vm-Vx)
what are the two equations for Nernst Potential?
Vx= Vin -Vout
OR
RT / zF ln [out/in]
RT / zF ln [out/in]
what do the following stand for in the Nernst Equation?
of the following which are changed?
T= temperature
z= charge of ion
F= Faraday’s constant
R= ideal gas constant
z and T change
what are the Nernst potentials for
Na+
K+
Cl-
Ca2+
+61
-95
-90
+159
if there is 145nM of Na+ ions outside the cell and 15nM inside the cell what is the nernst potential? (voltage of sodium when electrochemical force =0)
26.7 ln [145/15] =61mM
z= +1
RT/F(1) = 26.7
the nernst potential of Na+ is 61mM
if the membrane potential is greater than 61 does Na+ come in or out of the cell?
if the membrane potential is lower than 61 does Na+ come in or out of the cell?
if membrane potential greater than Nernst push ions out of cell
membrane potential lower than Nernst — bring ion into cell
how is Nernst potential related to electrochemical (driving force) and Membrane Potential
Np = Vm- Ec
the concentration differences in the Nernst potentials to the different ions can be attributed to
____ _______that utilize energy to maintain concentration gradients for ions
what are two examples?
variations in membrane permeability of ions
ion pumps
Na+/K+ (3:2) and Na/Ca2+ (1:3)
in most neuronal cells which ion is found in the highest concentration in the cell?
List in order from highest to lowest concentration
potassium
K> Cl > Na > Ca
how can you calculate the resting potential using Goldman- Hodgkin-Katz equation?
Vm = RT / F X ln permeability of ion [ion out] / permeablity of ions [ions in]
Vm = RT/ F ln (Pk * [Kout] + PNa * [Na out] + Pcl [Cl out] / Pk* [K in] + PNa [Na in] + PCl [Cl ] )
which ions are used to measure a membrane’s resting potential?
the nernst potential is closest to the permeability of which ion and why?
K, Na, and Cl
K because there are more potassium channels that any other ion
I = gv
current = conductance x potential
if g is the recipricol of resistance what is the equation of resistace?
r= v/I
g= I/v
I net is the sum of I __ + I __
resting membrane potential occurs when Inet = 0
resting membrane potential is closest to the membrane potential of which ion?
INa + IK
VR closest to Vpotassium
for all ions there is a difference between resting potential and nernst potential so there is ALWAYS an ion _________
the algebraic sum of these currents is balanced by the actions of ______ such that I net REMAINS 0
flux
pumps
How can we change the membrane potential?
use specific _______ called ION CHANNELS
_______ are __________ that allow ions to travel through the membrane
pores
pores proteins
ion channels are proteins made of pores that allow uins to travel through the membrane
pores are made up of ___ - _____
what does the neck of the poor control?
what determines whether or not an ion can enter through a pore?
do bidirectional ion channels require energy
what determines flow?
a helices
selectivity
size and density of ion
NO ions come in and out
electrochemical gradient (driving force)
what is another word for the driving force?
electrochemical gradient
takes into account the concentration of ion as well as its charge relative to outside
out of segments S1-S6 which voltage sensors were apart of the channel and which made up the pore?
which voltage sensor (helix) has the most charge to reach voltage-gated potential?
what happened once voltage to open voltage gated channel was reached?
S5 and S6 = pore
S4
S5 and S6 twist, rise to the top, and open pore allowing ions to come in
do voltage ion gated channels stay open for long period of time?
do voltage-gated Na+ channels work on a positive or negative feedback loop?
NO they open and close quickly
POSITIVE
opening Na+ channels stimulates the opening of MORE Na+ channels leading to increased excitability
Votlage gated ion channels function in the ______ and _______ (neurons + some glia) to create and propogate action potentials
Na+ channel inducers/blockers used to treat
arrhythmias (quinidine)
seizure disorders (phenytoin)
local anesthesia (lidocaine)
heart and brain
Na+ voltage gated channel BLOCKERS bc/ Na+ is stimulatory
a small change in G (conductance) leads to a BIG change in ___
why is this true?
I (current)
as you open more Na+ voltage gated channels (G) an INFLUX of Na+ rushes in as current (I)
explain the equation:
Ec = Vm -Vx
the driving force/ electrochemical gradient (Ec) of an ion =
the difference between the membrane potential and the Nernst potential of that ion (when driving force =0)
what is the electrochemical gradient (driving force) of sodium?
Ec = Vm - Vx
Ec = resting potential - nernst potential
Ec = -70 -40 (for sodium) = -110mV
-110 so it has a very large driving force into the
Voltage Gated Na+ Channels:
what is the difference between the m and h gate of voltage-gated Na+ channels?
which twists up and makes the pore?
m= activation gate = allows room for ion to come in or makes narrow if voltage not reached— within channel
h= inactivation gate (intracellular gate that blocks entry into cell) — outside channel
m (activation) gates twist up as pore (S5+ S6)
what are the states of the m and h Na+ voltage gates in the following states?
Resting (R)
Open (O)
Inactivated (I)
resting = h open m closed (intracellular entry open but can’t get through pore)
open = h open m open
inactivated = h close m open (can get through transport protein but can’t come in due to blockage with h)
Voltage gated K+ channels:
most channels influx/ efflux potassium from the cell
the function of the heart and brain to __polarize the membrane and terminate action potentials
do potassium channels work on negative or positive feedback? are they slow or fast?
eeflux TAKE OUT
RE polarize
NEGATIVE can be both slow or fast allowing for acute AND longterm response to signals
hERG (human ether a go-go) plays a role in ______ QT syndrome
does stimulation or inhibition of hERG cause Torsades Pointes which can lead to fatal VENTRICULAR FIBRILATION
which channels are used to help with overshoot?
long
inhibition of hERG
Potassium inward rectifying channels allow K+ to come back in if repolarization to rectify torsades is too much
what is hERG (human ether a go-go) responsible for?
repolarization of cardiac cells after depolarization
if hERG is blocked then action potential will be prolonged and not return back to resting potential (prolonged QT interval)
what are the different types of Ca2+ channels that exist?
L
N
T
P/Q
R
which type of voltage gated ion channel involves the trasnmission of electrical to chemical energy
Ca2+
within muscle fibers Ca2+ stimulates __________
entry of Ca2+ into a cell can lead to
excitation in _________
release of _________
gene _______
contractions
neurons
neurotransmitters
induction
are Ca2+ channel blockers or agonists used to treat hypertension?
blockers
prevent the contraction of smooth muscle of the blood vessels
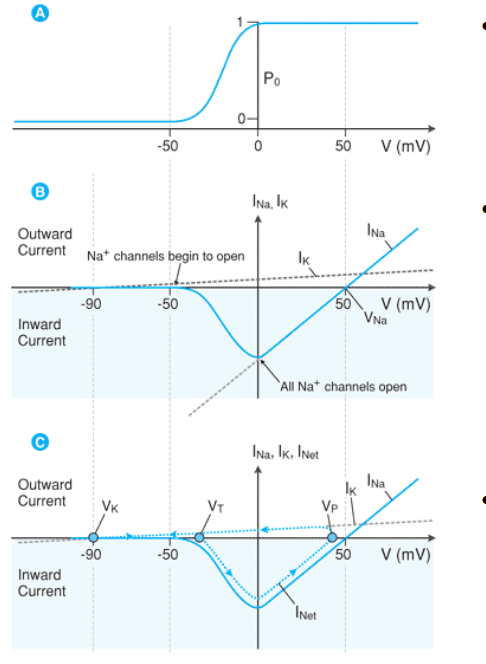
what does Po represent?
the probability of the channel opening
between which two voltages is the probability of opening sodium channels (Po) the greatest?
-50 to 0mV
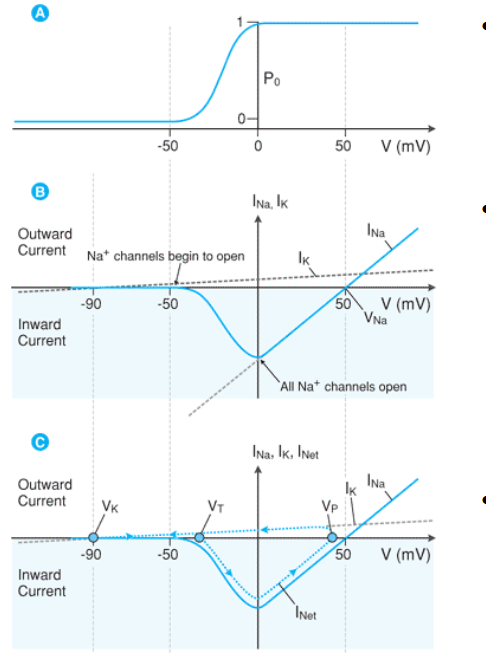
the current relationship to potential is altered by the _________ _____________channels
the max current occurs at ____ as all channels are OPEN but No opposing electrical force is generated (AT THIS POINT CONDUCTANCE CANNOT GET ANY HIGHER)
current is _________ as sodium ion flow is INWARD
voltage gated
0 mV
negative
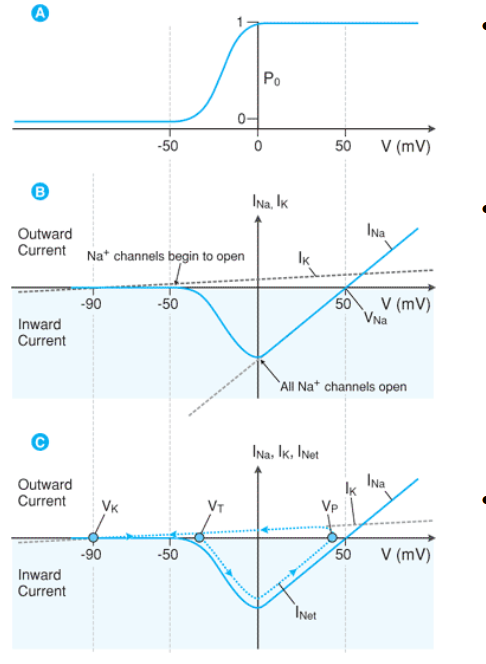
Voltage-Probability relationship:
As Po increases, the relative conductance (G) of Na+ __________
increases
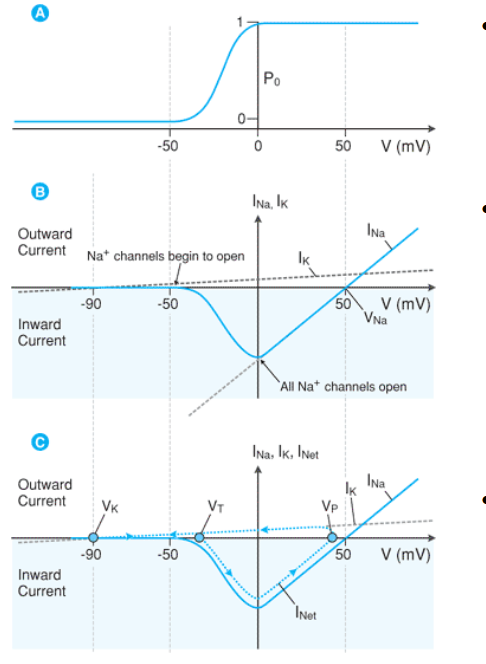
Voltage - Current (I) Relationship:
As voltage increases —> conduction increases
what happens to the current?
increases (but value is negative because Na+ is + and it is leaving the cell
greater current in the negative direction
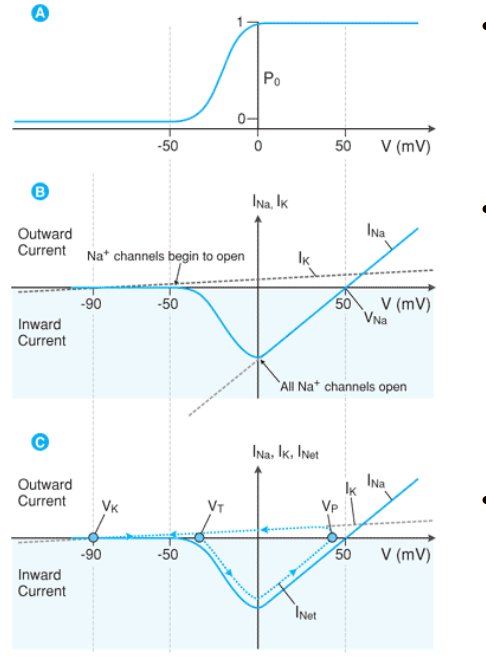
By combining the voltage gated behavior of sodium channels with potassium leak _______ we can follow the net change in _________
CURRENT
CURRENT
After reaching 0 mV what happens to conductance (G) and current (I) as you continue to increase voltage
after reaching 0mV conductance cannot be any greater so as the voltage continues to increase the conductance and therefor current decreases
SEQ Action Potential
resting state
threshold— initial depolarization (ex. glutamate—>nueron)
depolatization (highest Na+ conductance)
Action Potential (Na+ close K+ open)
Repolarization
Refractory Period/ overshoot
Resting State
when voltage becomes more positive the membrane is ___________
when the voltage becomes more negative the membrane is __________
depolarized
repolarized
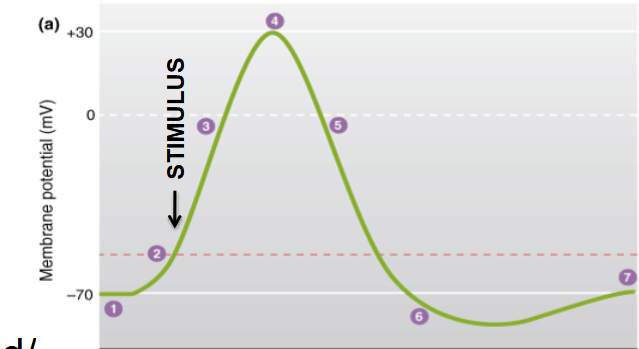
at which stage is Na+ conductance (G) greatest?
3= depolarization
the ability for Na+ to move into the cell increases as more and more channels open
Action Potentials:
Na+ channels open quickly to initiate INFLUX of Na+ leading to large change in ____
After Na+ channels open the K+ channels begin to open more slowly and EFFLUX K+ from the cells
as the permeability of _____ rises and the permeability of _____ falls the membrane potential is influenced by ______
while ____ channels remain open it is harder to generate another action potential
Vm (membrane voltage)
K+ Na+ K+
K+
synaptic transmission:
neuron synthesizes _______
action potential arrives
_______ activates calcium channels
activation of _______ _______ ________
neurotransmitter diffuses across the ______
Bind directly to channel receptor (ligand gated)
OR bind to indirect _____ _______ system
signal termination by removal of the transmitter through ________ _________ or ________ ________
neurotransmitter
depolarization
synaptic vesicle fusion
second messenger
enzymatic degradation or reuptake transporter
Neuronal Transmission:
Despite being an I/O (on or off) system, output is __________
MULTIPLE inputs received by __________
_______ ________ is where action potential can fire or not
_____ speeds transmission
can have MULTIPLE targets of the output due to ______ _______
integrated
dendrite
axon hillock
myelin
axon terminal
are monoamines, catecholamines, and amino acids considered small or large neurotransmitters?
small
acytelcholine
seretonin
histamine
the following are ____________ which are considered small neuerotrasnmitters
monoamines
dopamine
norepinephrine
epinephrine
(all GPCR linked)
the following are ____________ which are considered small neuerotrasnmitters
catecholamines
glutamate
GABA
glycine
the following are ____________ which are considered small neuerotrasnmitters
amino acids
substance P
Enkephalines
Vasopressins
the following are considered _________ neurotrasmitters
LARGE
substance P
Enkephalines
Vasopressins
are LARGE neuropeptides that take alot of effort to create. what does this say about their release?
they are released only in areas where they can change regulation (not just any old place)