Comp 9.3
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
What is data transmission?
The process of sending data over a communication medium to one or more electronic devices.
What is a packet in data transmission?
A small piece of data that contains a header, payload, and trailer
List the three components of a data packet.
Packet header, payload (the actual data), trailer (info about error checking).
What does the packet header include?
Destination address, packet number, originator’s address.
Define packet switching.
The process of transmitting data packets where each packet could take a different route to the destination.
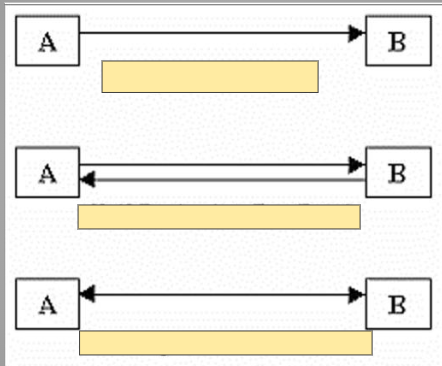
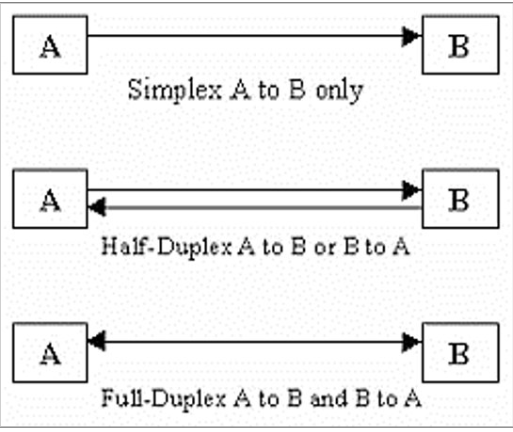
Name three types of data transmission.
Simplex, Half-Duplex, Full-Duplex.
Describe simplex data transmission.
Data transmission in one direction only (e.g., data from a computer to a printer).
Describe half-duplex data transmission.
Data transmission in both directions but not simultaneously (e.g., a two-way radio conversation).
Describe full-duplex data transmission.
Data transmission in both directions simultaneously (e.g., broadband internet).
What is serial data transmission?
Data sent one bit at a time in a single stream over a communication channel.
What is parallel data transmission?
Multiple bits are sent simultaneously along multiple channels or wires.
Why might serial transmission be preferred over parallel transmission?
Serial transmission is more reliable over longer distances and is cheaper.
What is an example of a device that uses serial transmission?
USB (Universal Serial Bus
What is USB short for?
Universal Serial Bus.
What are some advantages of USB?
Easy to use, robust connector system, low cost, and variety of connector types and sizes available.
What is a disadvantage of USB?
Limited capability and overall performance, and does not support broadcasting.
What is the payload in a data packet?
The actual data being transmitted
What is the purpose of a packet trailer?
Contains information about error checking.
What does a router do in data transmission?
Controls the route a packet takes to reach its destination.
Why is data transmission important?
Allows for the efficient and reliable transfer of information between devices.
What happens if packets arrive out of order?
They are reordered once the last packet has arrived
Name a scenario where full-duplex transmission is used.
Broadband internet connection on a phone line.
Name a scenario where half-duplex transmission is used.
A phone conversation where only one person speaks at a time.
Name a scenario where simplex transmission is used.
Data being sent from a computer to a printer.
What is the role of error checking in data transmission?
Ensures data integrity by detecting and correcting errors in the transmitted data
What type of data transmission is USB an example of?
Serial transmission.
What type of data transmission is used within a computer's motherboard?
Parallel transmission.
How does packet switching improve data transmission efficiency?
Allows packets to take multiple routes, balancing the load and reducing congestion.
What is a communication medium in data transmission?
The physical pathway through which data is transmitted, such as cables or wireless signals.
What is the difference between serial and parallel transmission?
Serial transmission sends one bit at a time over a single channel, while parallel transmission sends multiple bits simultaneously over multiple channels.
Which type of transmission is more expensive, serial or parallel?
Parallel transmission is more expensive.
Which type of transmission is more reliable over long distances, serial or parallel?
Serial transmission is more reliable over long distances.
Why might data packets arrive out of order?
Each packet can take a different route to the destination.
What is the function of the packet number in the packet header?
It helps in reordering packets when they arrive out of order.
What kind of information is typically found in the packet header?
Destination address, packet number, originator’s address.
What is the importance of the destination address in a packet?
It specifies the receiver's location for the packet to be delivered
Why is packet switching beneficial for data transmission?
It improves efficiency and reliability by allowing packets to take multiple routes to avoid congestion.
Describe an example where packet switching is used.
Internet data transfer, where data is broken into packets that travel independently across the network.
What is the difference between simplex and duplex transmission?
Simplex transmission is one-way, while duplex transmission is two-way.
What is a key advantage of using USB connections?
They are easy to use and have a robust connector system.
What does "plug and play" mean in the context of USB?
Devices can be connected and used without needing manual configuration
Why might USB not be suitable for all types of data transfer
It has limited capability and performance, and does not support broadcasting.
What is the significance of having a variety of USB connector types and sizes?
It allows USB to be used with a wide range of devices.
How does error checking contribute to data integrity?
It detects and corrects errors in the transmitted data, ensuring accurate communication.
exaples of serial tranimission
usb, printer,
example of paralle transmission
cpu, motherboard,
Benefits of packet switching
No need to tie up a single communication line,
it is possible to overcome failed, busy or faulty lines by simply re-routing
Relatively easy to expand package usage
a high data transmission rate is possible
Drawbacks of packet switching
packets can be lost and need to be re-sent
the method is more prone to errors with real-time streaming
there is a delay at the destiantion whilst the package is being re-ordered