APH CH 14 lymphatic system and immunity
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
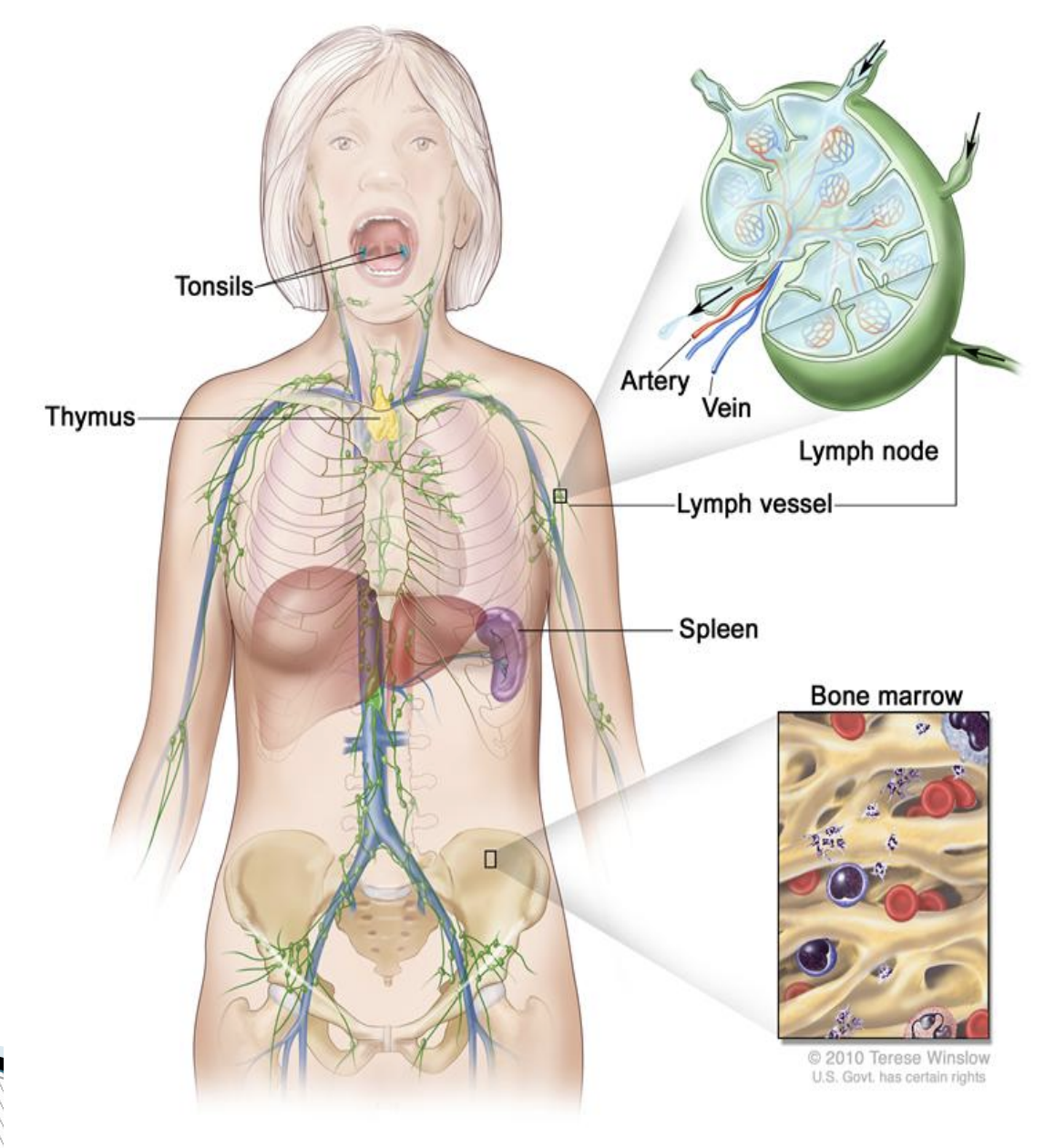
Lymphatic system
Network of vessels that…
• transport excess fluids
• absorbs fats
• helps protect against disease
Function
filtering potentially harmful particles from lymph before returning to the blood stream
Function
immune surveillance (occur singly or in groups)
Lymphocytes:
attack viruses and bacteria
Macrophages:
engulf and destroy foreign substances, damaged cells, cellular debris
Thymus and Spleen
functions similar to lymph nodes
Thymus
◦ larger during early childhood
◦ shrinks around puberty
◦ produce T cells that provide immunity
Spleen
◦ largest lymphatic organ
◦ filters blood (not lymph)
Pathogen:
disease-causing agent or infection.
Ex: virus, bacteria, fungi, protozoans
Mechanisms to protect the body are
a) nonspecific defenses or
b) specific defense (immunity)
Species resistance -
the fact that a given kind of organism or species develops a set of diseases that is unique to it
Ex: measles, mumps, gonorrhea, syphilis
infect humans, but not other animal species
Mechanical Barriers
First line of defense
ex: skin, respiratory pathway, digestive, mucous membrane, etc…
Chemical Barriers
enzymes in body fluid
ex: gastic juices (low pH), tears (lysozyme), perspiration (salt)
Fever
Elevated body temperature (average, is 98.6 F;
100 F or higher = fever)
Fever
Hypothalamus controls body temperature. Fever
caused by the actual resetting of the
hypothalamus's thermostat
Fever
High temp causes the liver and spleen to
remove iron from the blood. Bacteria and fungi
require more iron as temperature rises in order
to grow and reproduce
Fever
Phagocytic cells attack more vigorously the pathegen
Inflammation
tissue response to injury or infection
Inflammation
increased blood flow
Inflammation
results in ‘walling off’ the infected area so it won’t spread, attack and kill any invaders, dispose of dead and damaged tissue, and begin the process of repair
Inflammation
infected cells release chemical that attracts WBC (pus)
neutrophils-
engulfs and digest smaller particles
monocytes-
engulfs and digest larger particles
Antigen-
a chemical on the cell membrane of ALL cells
Foreign antigens stimulate the body to produce
antibodies
Lymphocyte -
Type of white blood cell that provides immunity. B cells or T cells
Lymphocyte
Originate in red bone marrow and are released into the blood before they differentiate
B Cells -
Produce and secretes antibodies to fight foreign substances in the body
B Cells mature in
red bone marrow
T Cells-
Interacts directly with antigens and
provides a cellular response (interacts directly
by cell-to-cell contact)
T Cells mature in
thymus
Lymphocytes must be activated before it can respond to an antigen
1. Antigen is present
2. Helper T cell contacts the foreign antigen (HIV attacks T cells- blue box p. 382)
3. If antigen fits and combines with the helper T cell than helper T becomes active
4. Once active, helper T cells stimulate the B cells to produce antibodies
5. Once B cells are active, they start to produce antibodies
HIV
Human Immunodeficiency Virus
HIV causes
AIDS
Reproduction
1) HIV attaches to cells with CD4 receptors on the cell membrane
2) Once in the host cell, HIV reproduces
3) Replicated HIV cells attack T-cell (AIDS)
(T-cells- Recognize cells with foreign antigens)
What do I need to know about HIV?
The first cases of AIDS were identified in the United States in 1981. In 1984 scientists proved that HIV causes AIDS.
Anyone can get HIV. The most important thing to know is how you can get the virus.
You can get HIV:
By having unprotected sex- sex without a condom- with someone who has HIV.
By sharing a needle and syringe to inject drugs or sharing drug equipment used to prepare drugs for injection with someone who has HIV.
From a blood transfusion or blood clotting factor that you got before 1985.
(But today it is unlikely you could get infected that way because all blood in the United States has been tested for HIV since 1985.)
Babies born to women with HIV also can become infected during pregnancy, birth, or breast-feeding.
You can NOT get HIV:
By working with or being around someone who has HIV.
From sweat, spit, tears, clothes, drinking fountains, phones, toilet seats, or through everyday things like sharing a meal.
From insect bites or stings.
From donating blood.
From a closed-mouth kiss (but there is a very small chance of getting it from open-mouthed or "French" kissing with an infected person because of possible blood contact).
Antibodies- reacts with specific foreign antigens (5 types)
◦Causes antigens (pathogen) to clump together in
order for phagocytic cells to engulf them
or
◦Covers antigen and neutralizes their effect
Immune Response
Primary response-
Release of antibodies into lymph, which is then transferred into the blood
Immune Response
Secondary Response -
forming new antibodies
Vaccine -
consists of killed or weakened bacteria or viruses that stimulates a response but doesn’t produce the disease
Allergen -
Antigen that triggers and allergic response
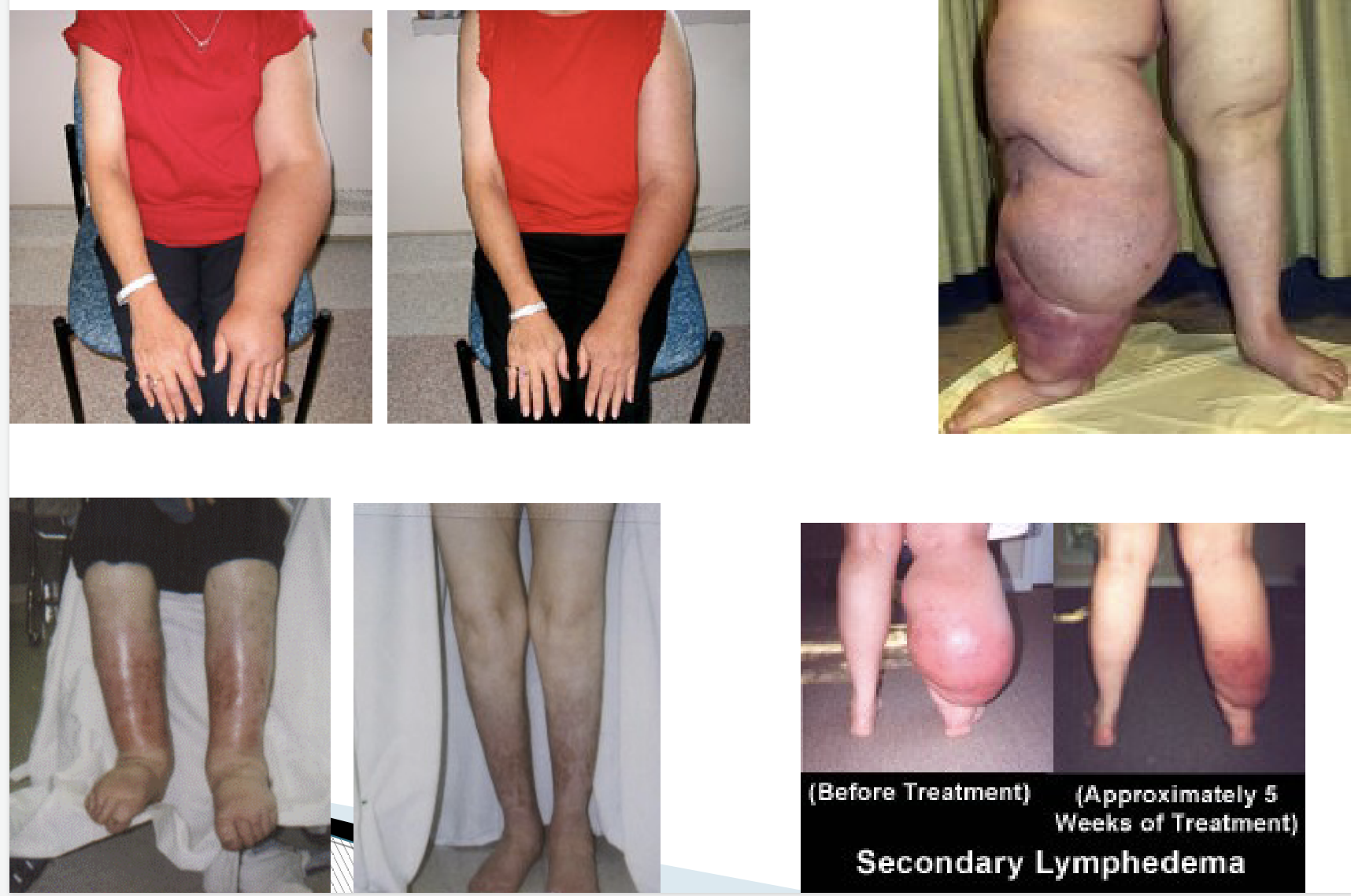
Lymphedema