Basic Histology(Cartilage and bone)
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Cartilage
Connective tissue that supports soft tissue and the development and growth of bones.
Chondrogenic cells
stem cells that differentiate into cartilage cells.
Chondroblast
building; immature cartilage cells that produce cartilage.
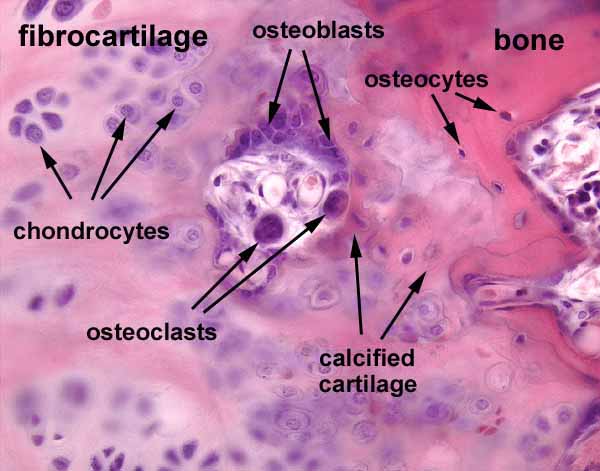
Chondrocytes
mature cells that maintain the cartilage matrix; embedded within lacunae.
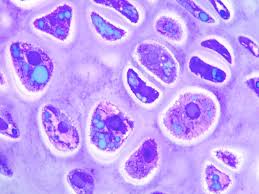
Matrix
the extracellular component that provides structural support and biochemical environment for cartilage and bone.
Strong and firm due to collagen fibrils and proteoglycans
Avascular
lacking blood vessels, which limits nutrient supply and healing in cartilage. diffusion
Cartilage types
Hyaline, fibrocartilage, elastic
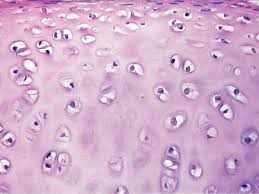
Hyaline cartilage
Cartilage that provides support with some flexibility. glassy, smooth appearance.
-ends of long bone in joint cavities, costal cartilage, nose traces, and larynx
-Surrounded by perichondrium.
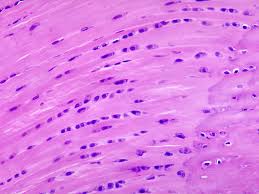
Fibrocartilage
A tough, dense cartilage; provides support and absorbs shock.
-It is found in intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis, and menisci of the knee.
-No perichondrium.
Elastic cartilage
Highly flexible and resilient, containing numerous elastic fibers.
-It is found in structures such as the ear and epiglottis.
-Includes perichondrium.
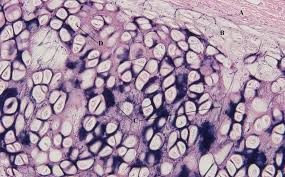
type of bone tissue
Compact(dense) bone, spongy(cancellous) bone
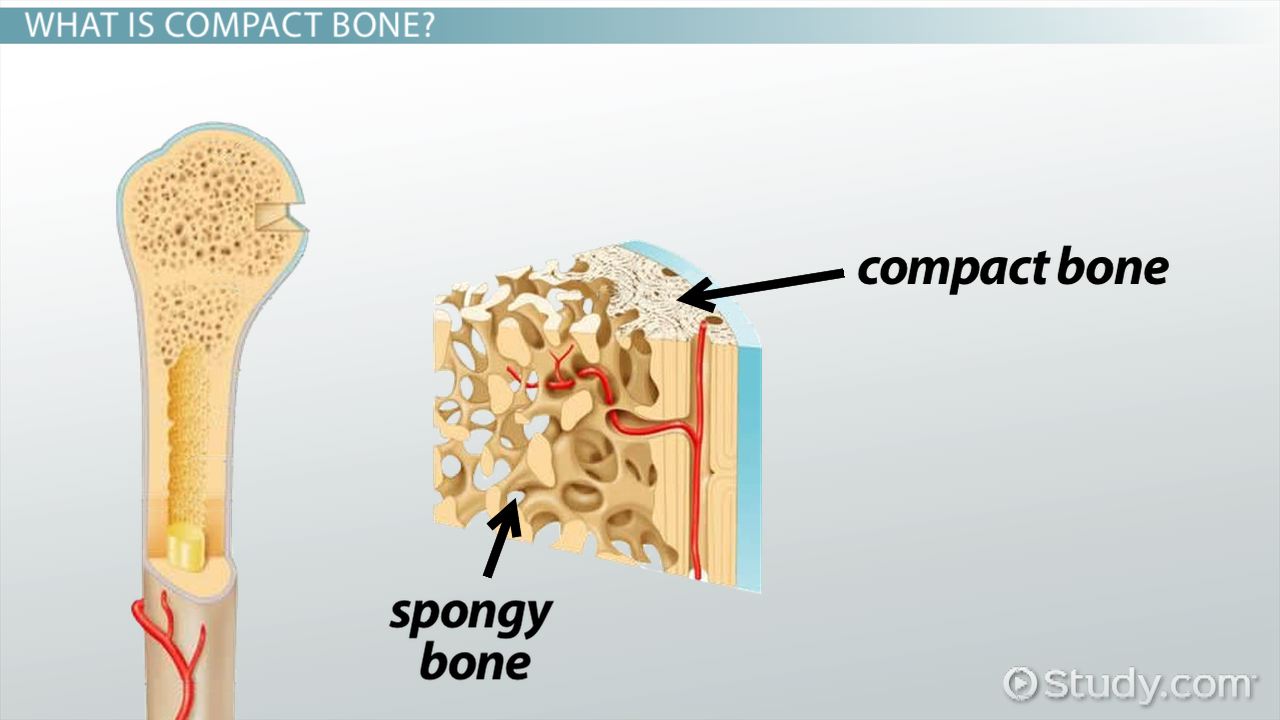
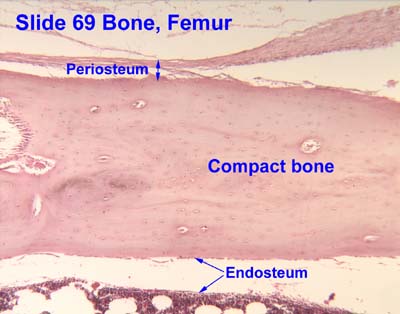
Compact(dense) bone
Provides protection and support, resisting the stresses of weight and movement. Matrix is arranged into lamellae.
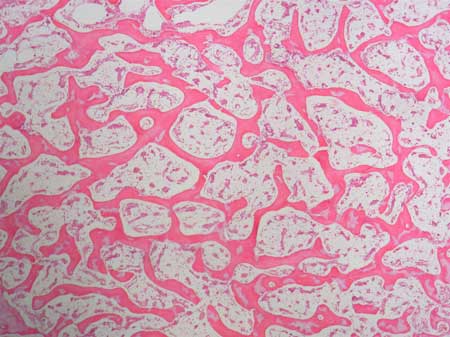
Sponge(cancellous) bone
Resist stresses and transfer force, reduce bone weight, support and protects bone marrow. Less matrix.
Osteogenic cells
-Bone-forming stem cells that develop into osteoblasts, responsible for bone growth and repair.
-stem cells
-located in inner layer of periosteum and endosteum
-spindle shaped
Osteoblast
Building cells that produce and release bone matrix & initiate mineralization
-cuboidal shaped
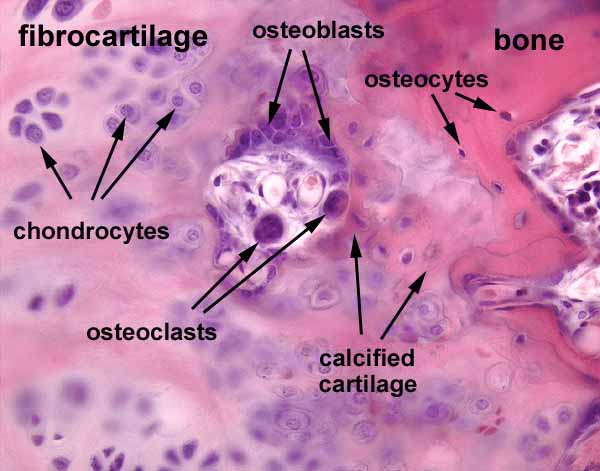
Osteocytes
Mature cells that maintains bone tissue and regulates mineral control.
-each occupies lacuna
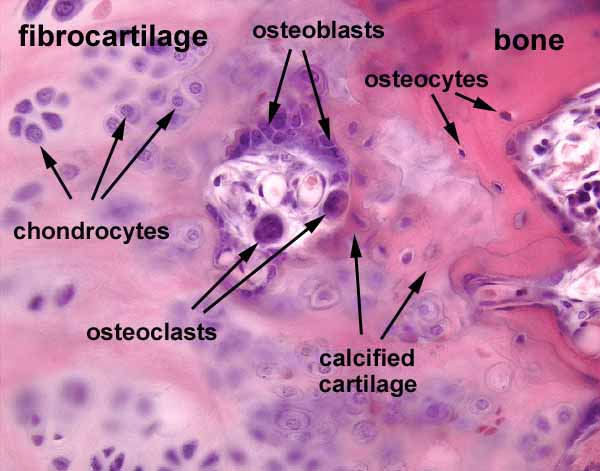
Osteoclast
Multinucleated cells that break down the bone into minerals. Resorption and remodeling of bone.
-concetrated in endosperm
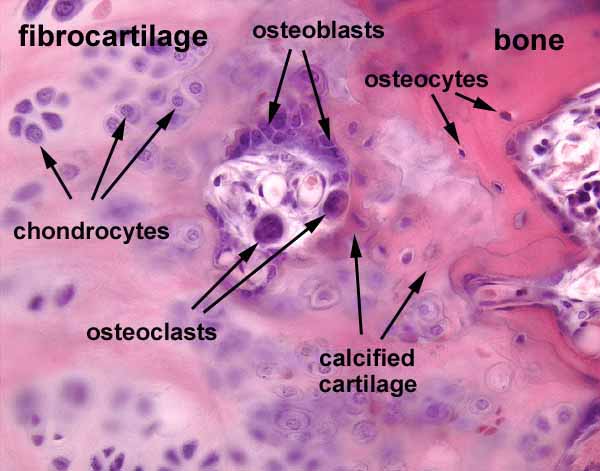
Periosteum
A thin, tough layer of tissue that covers the outside of bones. It protect the bone, provides nutrients, and supports bone growth and repair.
-outer layer: fibrous layer
-inner layer: cellular layer
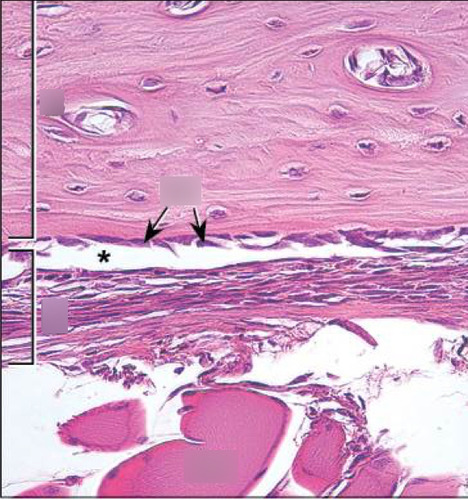
Endosteum
A thin membrane that lines the inner the medullar cavity. Helps with bone remodeling and formation of new bone tissue from the inside.
-contains osteogenic cells
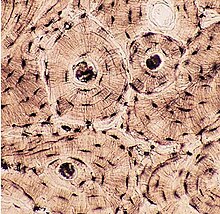
Osteon/Haversian canal
Tiny tubes that make up compact bone. Made of rings of bone tissue with a small tunnel in the middle that carries blood vessels and nerves.
Osteogenesis
The process of bone formation or bone development. It's how your body makes new bone tissue, either during growth
Membranous osteogenesis
The process where bone forms directly from a connective tissue membrane, without first forming cartilage. e.g. flat bones
Chondral osteogenesis
the process where bone forms by replacing a cartilage template. e.g. long bones
epithelial tissue
Tissue that covers outside of the body and lines organs and cavities.
Connective tissue
tissue that protects and supports the body and its organs; binds organs together;
Msucular tissue
tissue that generates physical force for movement and thereby generates body heat.
Nervous tissue
tissue that detects changes in a variety of conditions and responds by initiating and transmitting nerve impulse
Squamous
cells are flattened
Cuboidal
cells are usually cube-shaped or hexagons
Columnar
Tall and cylindric cells shapes
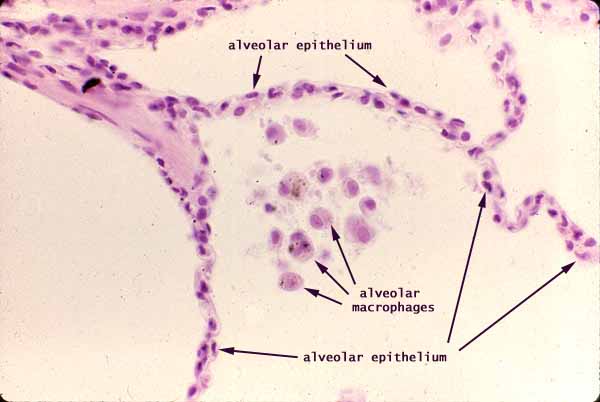
Simple squamous epithelium
Single layer of flattened cells with disc-shaped central nuclei
-Allows passage of materials by diffusion and filtration in sites where protection is not important e.g lining of the heart
-Air sacs of the lungs, lungs of the heart, blood vessel and lymphatic vessels
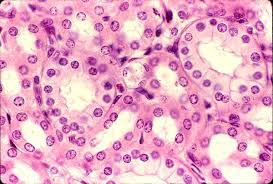
Simple cuboidal epithelium
Single layer of cube-like cells with large, spherical central nuclei
-Secretion and absorption
-Ducts and secretory portions of small glands; ovary surface
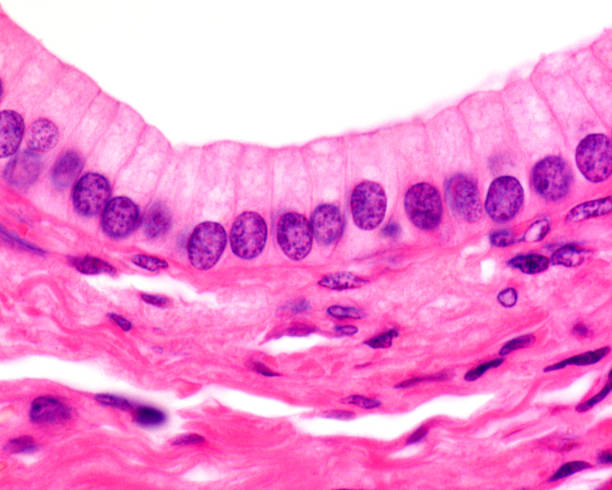
Simple columnar epithelium
Single layer of tall cells with oval nuclei
-Absorption; secretion of mucus, enzymes, and
other substances
-digestive tract, small bronchi, gallbladder
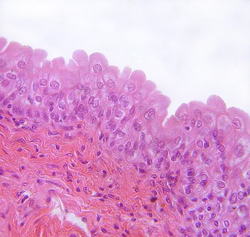
Stratified squamous epithelium
Thick membrane composed of several cell layers;
surface cells are flattened.
-Protects underlying tissue in area subjected to abrasions
-kreatinied: skin; -nonkeratinized: mouth, vagina, lining of esophagus
Stratified cuboidal epithelium
Generally two layers of cube-like cells
-Protection
-largest ducts of sweat, mammary, and salivary glands
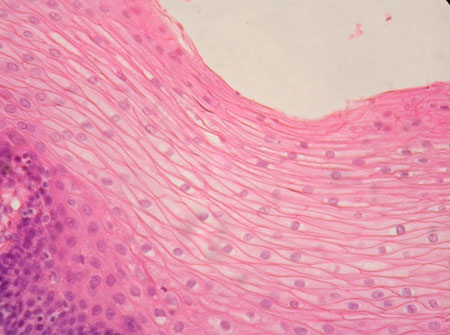
Stratified columnar epithelium
Several cell layers; base cells usually cuboidal;
superficial cells elongated and columnar
-Protection; secretion
-small amounts in male urethra and large ducts of some glands
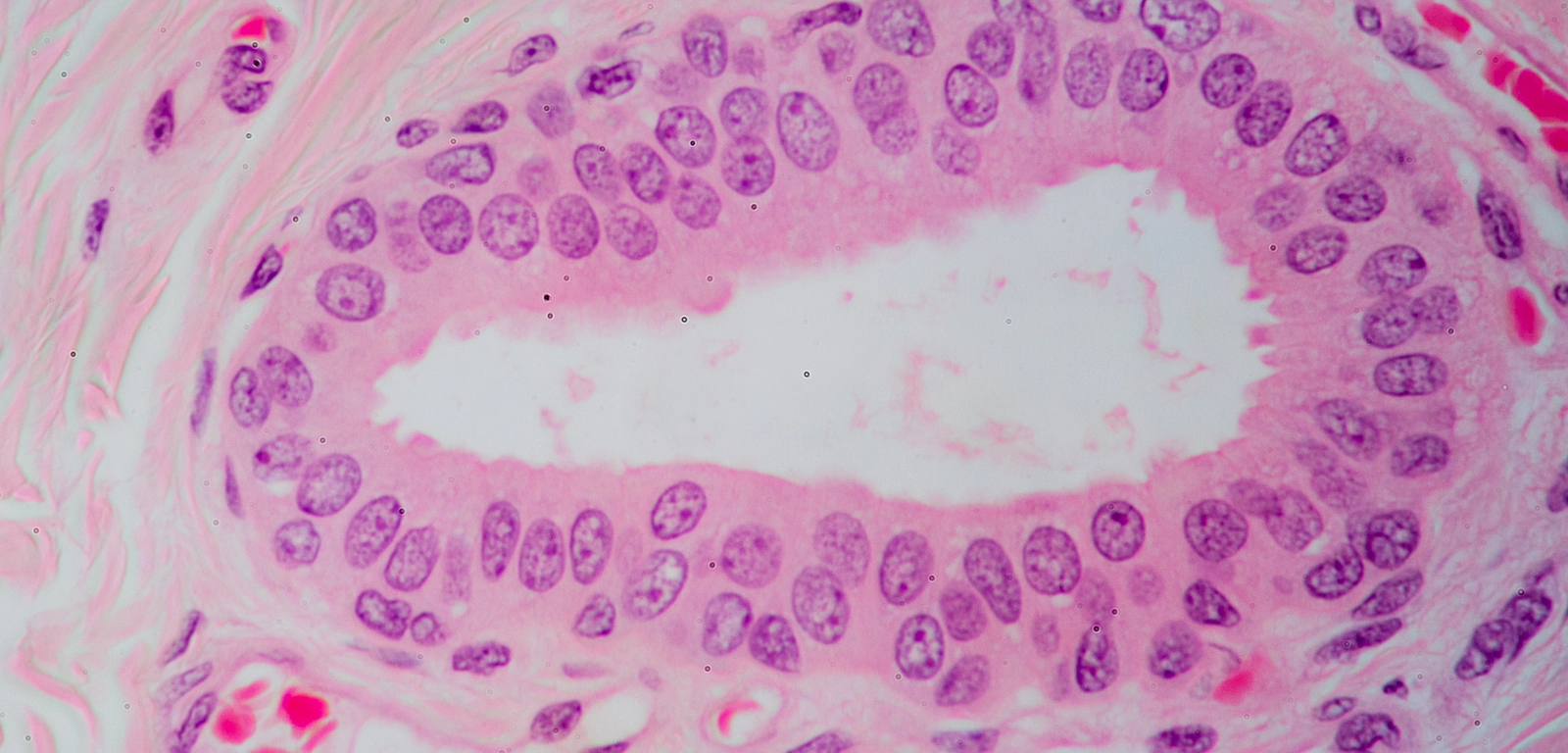
Transitional epithelium
Surface cells dome-shaped or squamous-like
depending on the organ stretch
-Stretches readily and permits distension of urinary
organ by contained urine
-urinary bladder, part of urethra
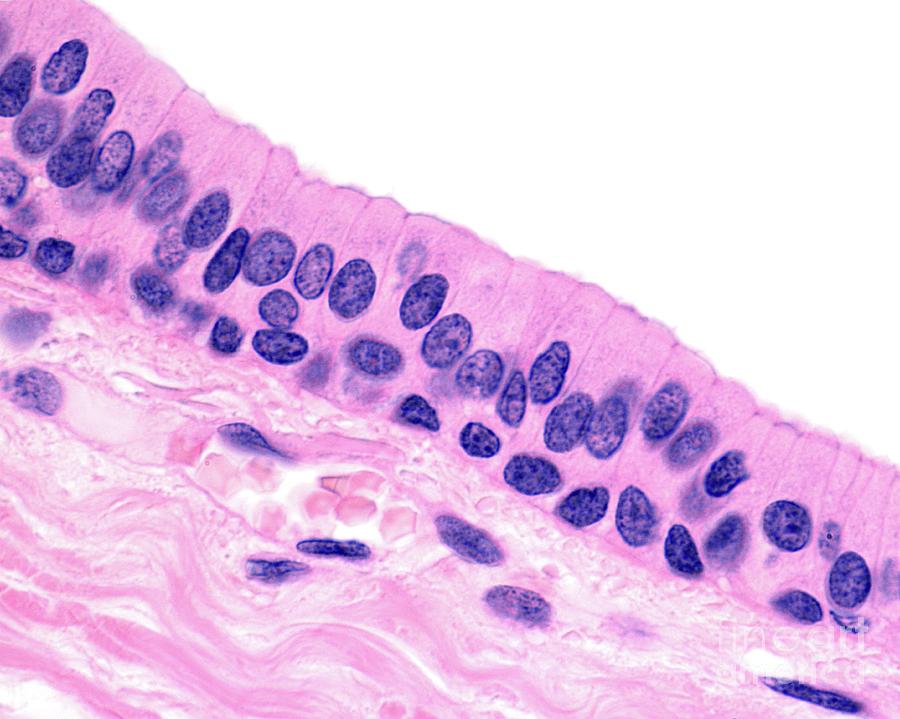
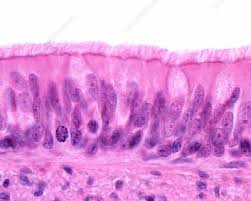
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
Single layer of cells of different heights; some not
reaching the free surface; nuclei seen at different
levels; may bear cilia
-Secretion, particularly of mucus; propulsion of mucus
by ciliary action
-trachea, upper respiratory tract
Loose connective tissue, areolar
Gel-like matrix with all three fiber types;
cells: fibroblasts, macrophages, mast cells, and some
white blood cells.
-Wraps and cushions organs; its
macrophages phagocytize bacteria; plays important
role in inflammation; holds and conveys tissue fluid
-any epithelia tissue area
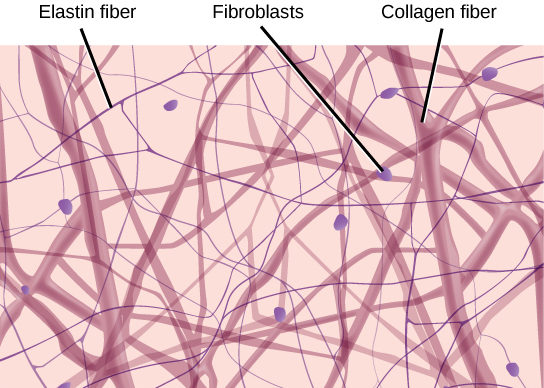
Dense connective tissue, dense irregular
Primarily irregularly arranged collagen
fibers; some elastic fibers; major cell type is the
fibroblast
-Able to withstand tension exerted in
many directions; provides structural strength.
-dermis of skin, fibrous capsule of organs and joints
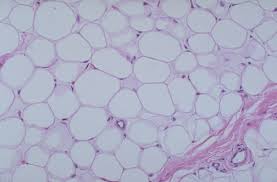
Adipose tissue(fat)
Matrix as in areolar, but very sparse; closely packed adipocytes, or fat cells, have
nucleus pushed to the side by large fat droplet.
-Provides reserved food fuel; insulates against heat loss; supports and protects organs.
-under skin, within abdomin, breast
Collagen fiber
fibers appear as pink, wavy fibers of different sizes
when stained with H&E.
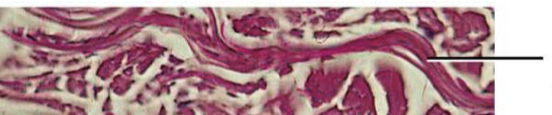
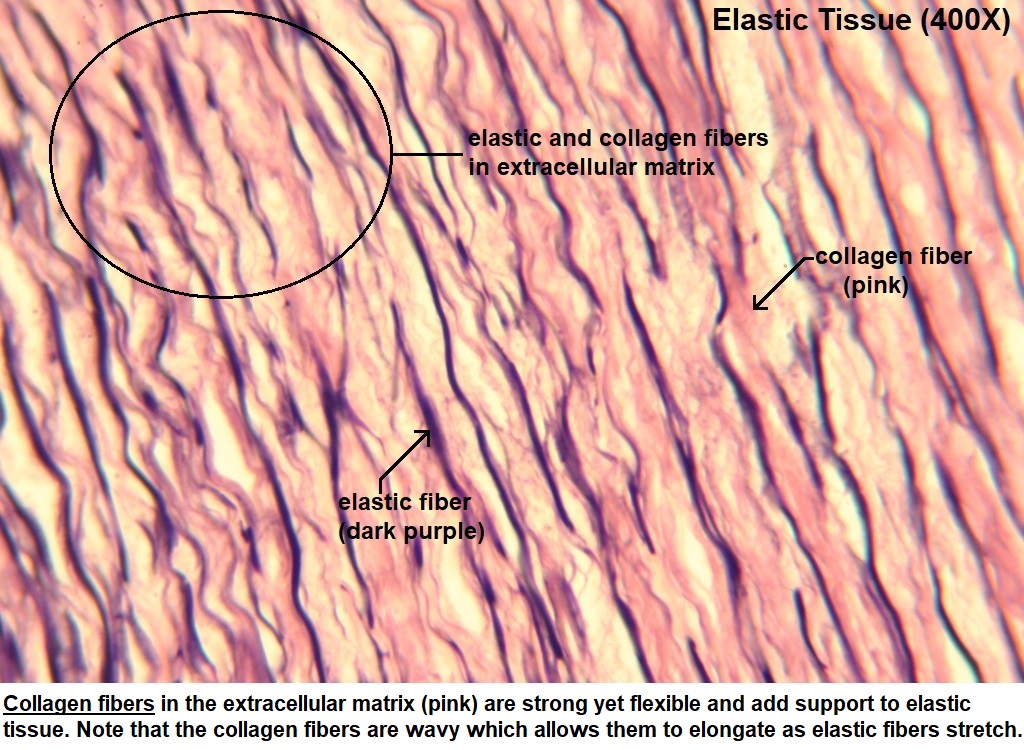
Elastic fiber
fibers have a very resilient nature, which is important in areas like the lungs, aorta, and skin.
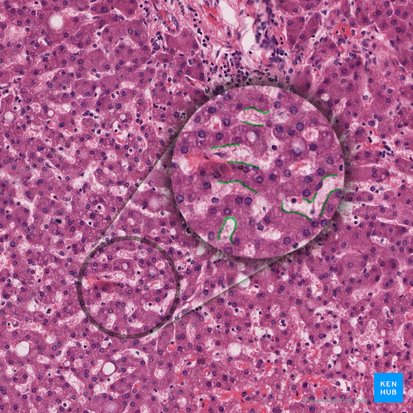
Reticular fiber
These small, dark-staining fibers form a supportive, meshlike framework for organs that are composed mostly of cells
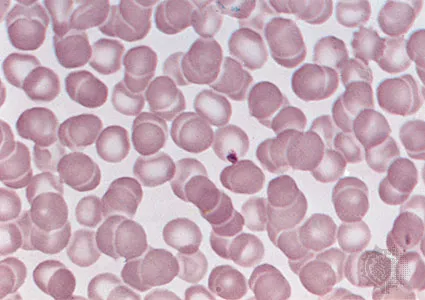
Blood cells
Red and white blood cells in a
fluid matrix (plasma).
-Transport of respiratory gases, nutrients, wastes and other substances.
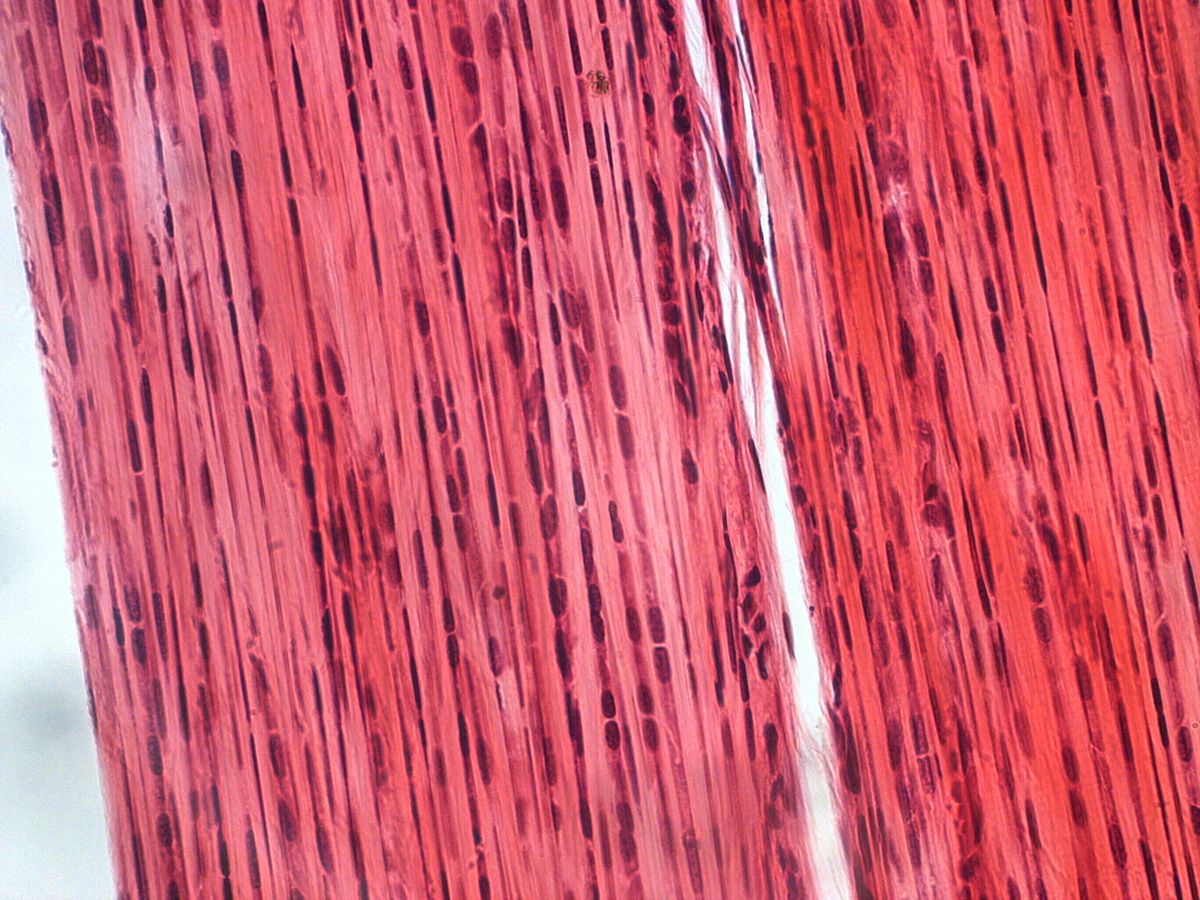
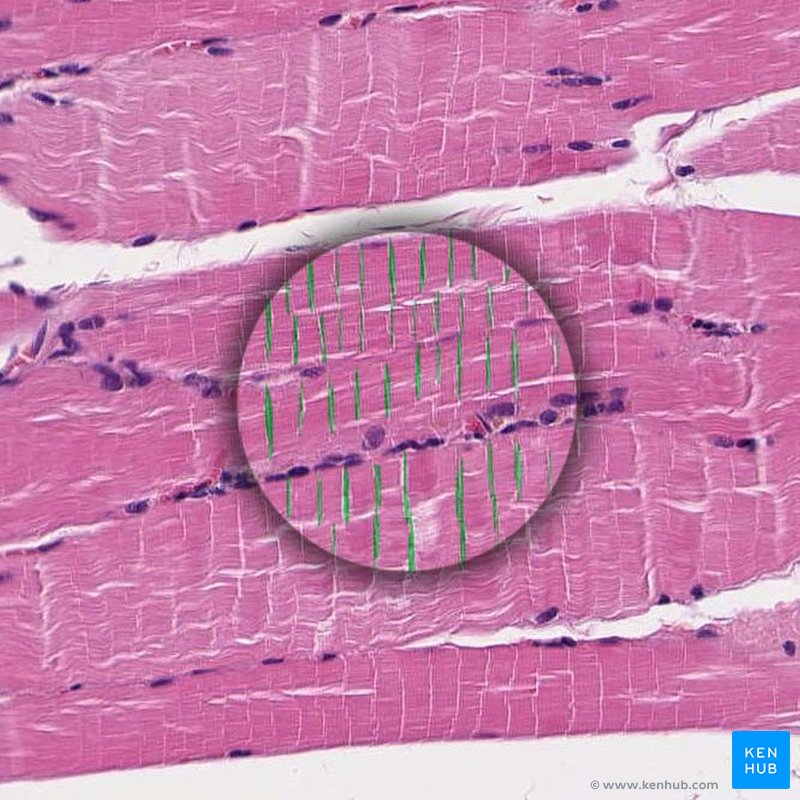
Skeletal muscle
muscle that’s long, cylindrical multinucleate cells; obvious striations
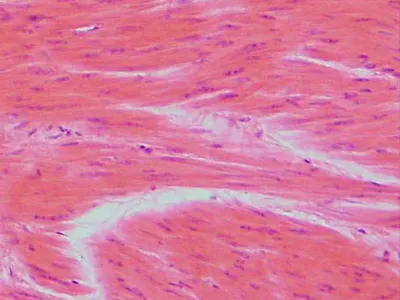
Smooth muscle
muscle that’s spindle-shaped cells with central nuclei; no striations; cells arranged
closely to form sheets.
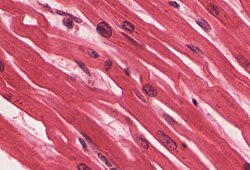
Cardiac muscle
muscle that’s branching, striated, generally uninucleate cells that interdigitate at
specialized junctions
Endothelium
simple squamous epithelium that lines the interior of the circulator vessels and the heart
Mesothelium
simple epithelium that lines the internal organs such as intestine, lungs, and heart