Psychology Nervous System
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/50
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
1
New cards
Nervous System
System of networks of specialised cells (neurons) that connect different parts of the body to each other and the brain to perform complex activities.
2
New cards
Main Functions Of Nervous System
● Receive information
● Process information
● Coordinate a response to information.
● Process information
● Coordinate a response to information.
3
New cards
Divisions Of The Central Nervous System
Brain and Spinal Cord
4
New cards
Divisions Of Peripheral Nervous System
Autonomic Nervous System, Somatic Nervous System
5
New cards
Autonomic Nervous Divisons
Sympathetic Nervous System, Parasympathetic Nervous System, Enteric Nervous System
6
New cards
Central Nervous System
Receives sensory information from the peripheral nervous system and also sends motor information to the peripheral nervous system
7
New cards
Central Nervous System: Brain
is the command system. Responsible for receiving and processing neural information from the Peripheral NS and generating responses to it.
8
New cards
Central Nervous System: Spinal Cord
Connects Peripheral NS to the brain. Carries Sensory messages along ascending tracks and carries motor messages along descending tracts. Controls the spinal reflex arc
9
New cards
Peripheral Nervous System
Includes all the nerves throughout the body, outside of the brain and spinal cord. Responsible for sending messages to the CNS and carrying out instructions sent from the CNS
10
New cards
Peripheral Nervous System: Somatic Nervous System
Responsible for movement of skeletal muscles and controls muscles attached to skeleton. Major functions are:
* Transmits sensory information from receptors in the skin to the brain via the spinal cord (central nervous system)
* Receives motor information from the central nervous system to skeletal muscles and carries out
voluntary movement \n
* Transmits sensory information from receptors in the skin to the brain via the spinal cord (central nervous system)
* Receives motor information from the central nervous system to skeletal muscles and carries out
voluntary movement \n
11
New cards
Sensory (Afferent) Neurons
They travel towards the CNS along ascending tracts, arriving at the CNS.
12
New cards
Motor (Efferent) Neurons
Tell out skeletal muscles to extend or contract. Travel away from the CNS along descending tract
13
New cards
Peripheral Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System
Relays messages between the CNS and the involuntary muscles. Operates without awareness as it is self-regulating. Is possible to control some of our vital functions.
14
New cards
Autonomic Nervous System: Enteric Nervous System
Embedded within the walls of the gastrointestinal tract between the oesophagus and rectum. Works together with CNS to control digestive system.
15
New cards
Autonomic Nervous System: Sympathetic nervous System
Also known as '“Emergency System”. Becomes active when the organism perceives itself to be in danger on in stress. Organs and glands alter to physically prepare our body for action. Adrenaline released. Activates the Flight-Fight-Freeze response.
16
New cards
Autonomic Nervous System: Parasympathetic Nervous System
○ Operates in circumstances where it is relatively calm.
○ Responsible for maintaining automatic day-to-day bodily functions (e.g. digestion, heart rate).
○ Brings the body back to a balanced/stable level after any arousal due to sympathetic nervous
system activity.
homeostasis
○ Responsible for maintaining automatic day-to-day bodily functions (e.g. digestion, heart rate).
○ Brings the body back to a balanced/stable level after any arousal due to sympathetic nervous
system activity.
homeostasis
17
New cards
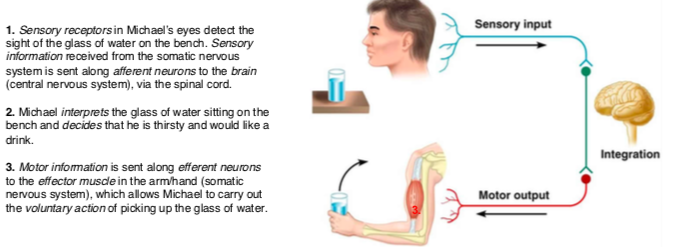
Conscious Responses
Occur when you deliberately tell your body to do something. Voluntary and require conscious effort or decision making.
18
New cards
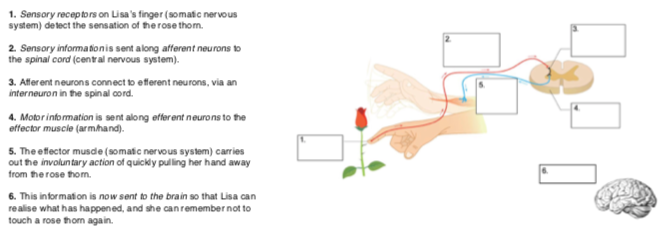
Unconscious Responses
Occur when you body automatically does something. Also known as the ‘Spinal Reflex’. Does not involve awareness and is voluntary.
19
New cards
Spinal Reflex/Reflex Arc
Simple and automatic response that is hardwired into our nervous system. Adaptive response to protect body from severe injury. Unconscious and fast and doesn’t involve brain
20
New cards
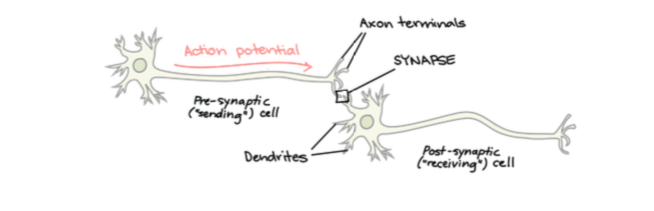
Neural Transmission
Occurs between two nuerons; a presynaptic neuron and a post-synaptic neuron. Occurs when a neuron fires by sending an action ptoential along the pre-synaptic neuron.
21
New cards
Synaptic Gap
The small space between the pre and post synaptic neuron. This is where neurotransmitters are released
22
New cards
Synapse
The site where communication occurs. Includes the terminal buttons of the presynaptic neuron, dendrites of the postsynaptic neuron and the synaptic gap
23
New cards
Energy Within Neuron
Electrical
24
New cards
Energy Between Synaptic Gap
Chemical
25
New cards
Dendrites In Neural Transmission
Thin extensions of a neuron that receive incoming information. Receptor sites are located on this structure, which receive neural information from neruotrabsmitters
26
New cards
Axon Terminals Within Neural Transmission
Responsible for storing neruotransmitters. At the end of each axon terminal are terminal buttons, which secrete the neurotransmitters into the synaptic gap.
27
New cards
Process Of Neural Transmission: Step One
When an action potential reaches the **axon terminals** of the pre- synaptic neuron, **vesicles** (containing neurotransmitters) inside of the terminal buttons move towards the membrane.
28
New cards
Process Of Neural Transmission: Step Two
**Neurotransmitters** from inside the vesicles release into the **synaptic gap**.
29
New cards
Process Of Neural Transmission: Step Three
The neurotransmitter then finds a matching **receptor site** on the dendrites of the post-synaptic neuron to bind to.
30
New cards
Process of Neural Transmission: Step Four
If the **neurotransmitter binds** to the receptor site, the neurotransmitter will either:
* Make the post-synaptic neuron more likely to fire (excitatory)
* Make the post-synaptic neuron less likely to fire (inhibitory).
* Make the post-synaptic neuron more likely to fire (excitatory)
* Make the post-synaptic neuron less likely to fire (inhibitory).
31
New cards
Neurotransmitter
Brain chemicals or chemical substances produced by a neuron. Released from the terminal buttons of the pre-synaptic neuron into the synaptic gap, and bind to receptor sites on the dendrites of the post-synaptic neuron
32
New cards
Excitatory Effects Of Neurotransmitters
Stimulate the post synaptic neuron, causing them to fire an action potential and pass the impulse on to neighbouring neurons. Glutamate
33
New cards
Inhibitory Effect Of Neurotransmitters
They prevent or block the neighbouring neuron from firing an action potential. GABA
34
New cards
Glutamate
MainExcitatory neurotransmitter. Stimulates and activates post-synaptic neurons. Associated with learning and memory. Responsible for fast transmission of neural messages. Too much results in anxiety disorders while too little results with impaired learning and memory.
35
New cards
Gamma-amino Butyric Acid (GABA)
Main inhibitory neurotransmitter. Prevents firing and activity within the post synaptic neuron. Responsible for calming the body by slowing down neural transmission and regulating nervous system arousal. Low levels associated with anxiety and anxiety disorders while too much results in impaired learning and memory.
36
New cards
Glutamate Vs. GABA: A Balancing Act
Both GABA and Glutamate balance each other out. GABA’s inhibitory influence counteracts the excitatory effect of glutamate. Neural transmission requires balance.
37
New cards
Neuromodulators
A subclass of neurotransmitters that alter the strength of neural transmission by increasing or decreasing the responsiveness of neurons to neurotransmitter signals. Affect large amount of neurotransmitters at a time. Released by neuron. Slow acting but long lasting changes to neurons and synapses.
38
New cards
Dopamine
A neurotransmitter and a neuromodulator. Has both excitatory and inhibitory effects. Involved in:
* Voluntary movement
* Reward and pleasure (the reward system)
* Mood and motivation
* Thirst and hunger.
* Voluntary movement
* Reward and pleasure (the reward system)
* Mood and motivation
* Thirst and hunger.
39
New cards
Dopamine: The Reward System
Refers to a group of structures in the brain that are activated by rewarding or reinforcing stimuli, such as seeing a cold glass of water when you are thirsty.
40
New cards
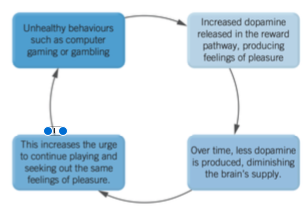
Dopamine Role In Addiction
Dopamine acts as a motivating agent for completing desirable activites, there is a link between dopamine and addictive behaviours. Common addiction behaviours include:
* Smoking
* ○ Over-eating
* ○ Alcohol or drug use
* ○ Gambling
* ○ Computer gaming
* ○ Excessive mobile phone use.
* Smoking
* ○ Over-eating
* ○ Alcohol or drug use
* ○ Gambling
* ○ Computer gaming
* ○ Excessive mobile phone use.
41
New cards
Serotonin
Both a neurotransmitter and a neuromodulator. Has inhibitory effects. Involved in:
* ○ Mood and emotional processing
* ○ Anger and aggression
* ○ Appetite
* ○ Sleep
* ○ Pain perception.
* ○ Mood and emotional processing
* ○ Anger and aggression
* ○ Appetite
* ○ Sleep
* ○ Pain perception.
42
New cards
Serotonin Role in Mood
\`\`When serotonin levels are high, mood improves. When serotonin levels are balanced, we feel calm, focuseed, happy and are in a stable mood. When setotonin levels are low, the brain ability to regulate mood becomes impacted.
43
New cards
Serotonin In Sleep
Lower levels of serotonin in the brain can disrupt the sleep-wake cycle. not the only factor in sleep, but is a factor none the less. Imbalance in serotonin can cause:
* Restless sleep
* Frequent awakenings
* Not meeting the number of recommended hours of sleep
* Daytime sleepiness.
* Restless sleep
* Frequent awakenings
* Not meeting the number of recommended hours of sleep
* Daytime sleepiness.
44
New cards
Serotonin In Agression And Impulsivity
Lower than normal levels of serotonin have been linked to impulsivity, while higher levels result in more patience. Lower than normal levels of serotonin have been found to affect communication between brain structures responsible for regulating emotions
45
New cards
Synaptic Plasticity
The ability of the synapse to change in response to experience. Enables change involving the strengthening or weakening of synaptic connections.
46
New cards
Processes Involved In Synaptic Plasticity
Long-Term Potentiation
Long-Term Depression
Long-Term Depression
47
New cards
Long-Term Potentiation
Refers to the long-lasting strengthening of synaptic connections, as a result of repeated stimulation
48
New cards
Long-Term Potentiation: Sprouting
Structural changes: growth of the axon terminals on the pre-synaptic neuron, as well as growth of the dendrites/dendrites spines on the post-synaptic neuron
\
Synaptic changes: Vesicles inside of terminal buttons contain more neurotransmitters, increase in the number of neurotransmitters are released into the synaptic gap, more receptor sites on post-synaptic dendrites.
\
Synaptic changes: Vesicles inside of terminal buttons contain more neurotransmitters, increase in the number of neurotransmitters are released into the synaptic gap, more receptor sites on post-synaptic dendrites.
49
New cards
Long-Term Potentiation: Rerouting
Occurs when new connections are made between neurons to create alternate neural pathways. may be entirely new neural pathways or connections to other pathways in the brain. May occur due to brain injury
50
New cards
Long-Term Depression
Long lasting decrease in the strength of synaptic connections as a result of lack of stimulation. Results from lack of stimulation between pre an post-synaptic neurons. Not always a bad thing
51
New cards
Long-Term Depression: Pruning
Occurs in structural changes:
* ○ Reduction of **axon terminals** on the pre-synaptic neuron
* ○ Reduction of **dendrites/dendritic spines** on the post-synaptic neuron
Results in less responsive post-synaptic neuron
* ○ Reduction of **axon terminals** on the pre-synaptic neuron
* ○ Reduction of **dendrites/dendritic spines** on the post-synaptic neuron
Results in less responsive post-synaptic neuron