Phylogenies
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
A. Allopatry
On the Bahamian island of Andros, mosquitofish
populations live in various, now-isolated, freshwater
ponds that were once united. Currently, some predator-
rich ponds have mosquitofish that can swim in short,
fast bursts; other predator-poor ponds have
mosquitofish that can swim continuously for a long
time. When placed together in the same body of water,
the two kinds of female mosquitofish exhibit exclusive
breeding preferences. What force in the wild is leading
to this?
A. Allopatry
B. sympatry
A. behavioral isolation
On the Bahamian island of Andros, mosquitofish
populations live in various, now-isolated, freshwater
ponds that were once united. Currently, some predator-
rich ponds have mosquitofish that can swim in short,
fast bursts; other predator-poor ponds have
mosquitofish that can swim continuously for a long
time. When placed together in the same body of water,
the two kinds of female mosquitofish exhibit exclusive
breeding preferences. Which type of reproductive
isolation operates to keep the mosquitofish isolated,
even when fish from different ponds are reunited in the
same body of water?
A. behavioral isolation
B. habitat isolation
C. temporal isolation
D. mechanical isolation
D. II, III
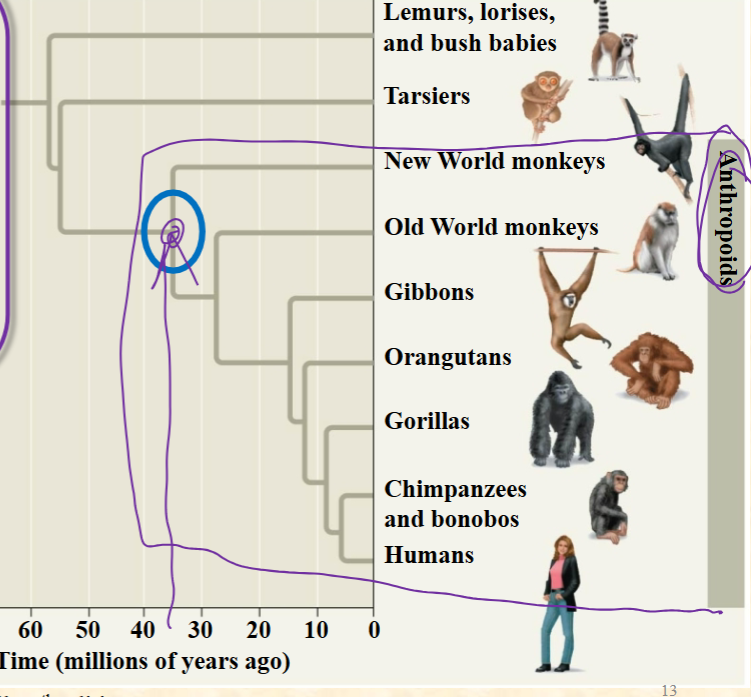
The circled point is a node. What can
we say about this?
I. The organism in the blue circle is
definitely represented in the fossil
record
II. The organism in the blue circle is a
common ancestor of all antrhopoids
III.The organism existed ~35 MYA
A. I-III
B. II
C. I, III
D. II, III
E. None are true
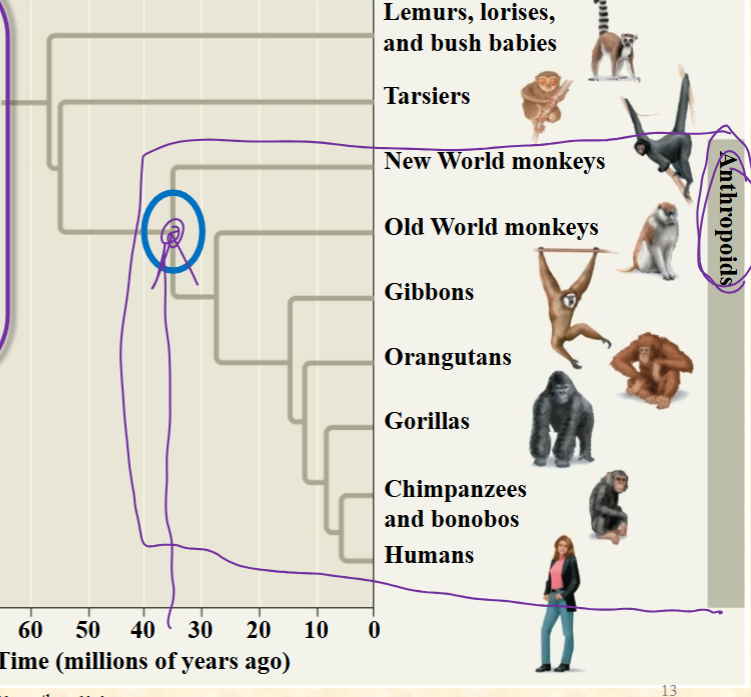
A. Humans and chimps
Which has the closest relationship:
sibling taxa
A. Humans and chimps
B. Gorillas and chimps
C. New world monkeys
and old world
monkeys
D. Tarsiers and lemurs
E. These are all
equivalent
B. II
Which tree correctly suggests that old world monkeys are more closely related to apes
than they are to new world monkeys
II III
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. II, III
E. None of them

B. Pan (chimps and bonobos)
What is the outgroup here?
A. Ardipithecus
B. Pan (chimps and bonobos)
C. Homo sapiens
D. Sharks
E. This phylogeny doesn’t have an
A. Ancestral
These are morphological traits.
Ancestral traits existed in an
ancestor (and often in the
descendant)
Derived traits are in the
descendent (and not in the
ancestor). Is a tough rump an
ancestral or derived trait for the
apes?
A. Ancestral
B. Derived
C. Neither
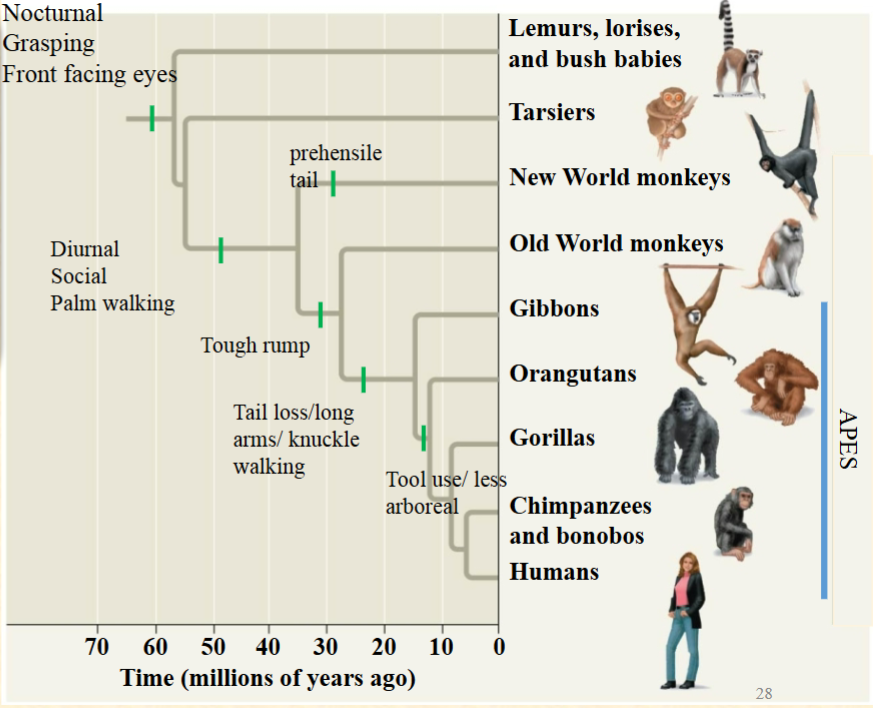
A. Derived
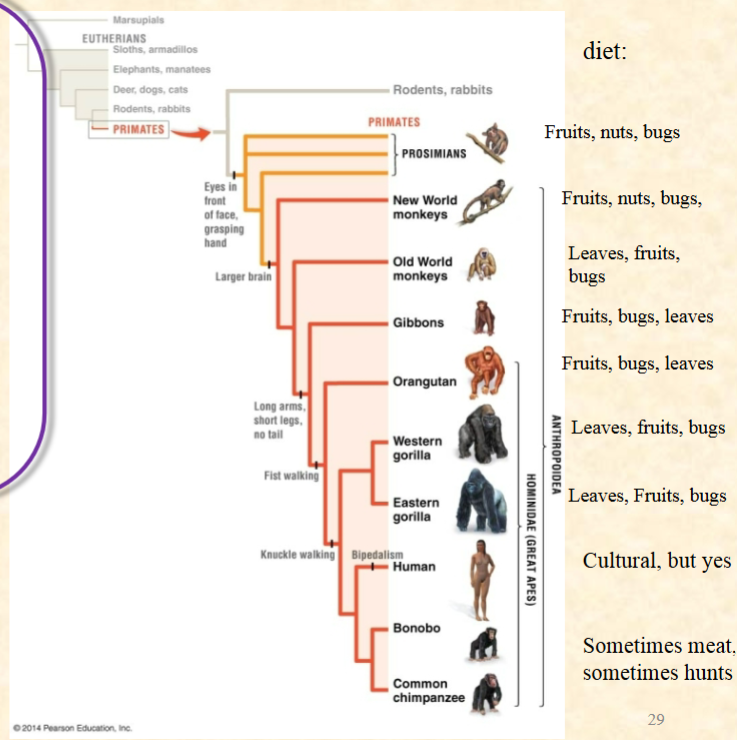
All of these animals are opportunistic
feeders and will eat vertebrate meat if
they find it. Is hunting for vertebrate
meat likely a derived or ancestral trait
in the primates (hint: outgroup)?
A. Derived
B. Ancestral
C. You can’t tell from this information
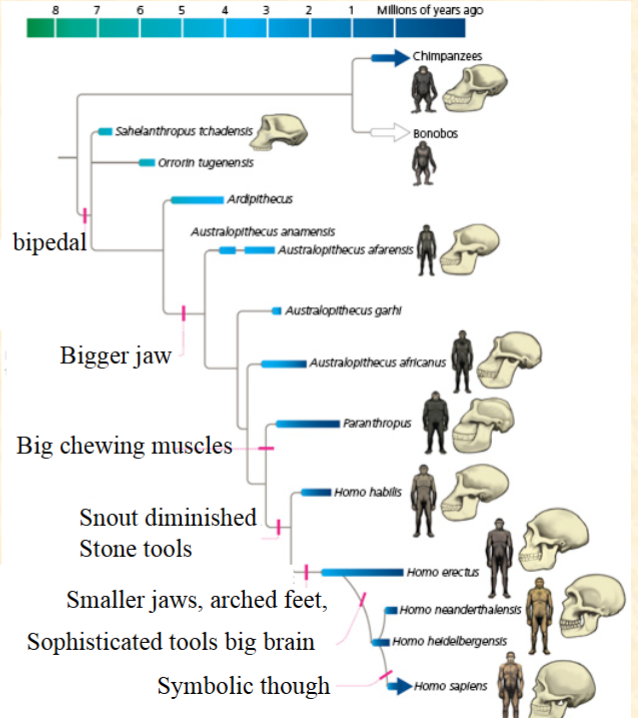
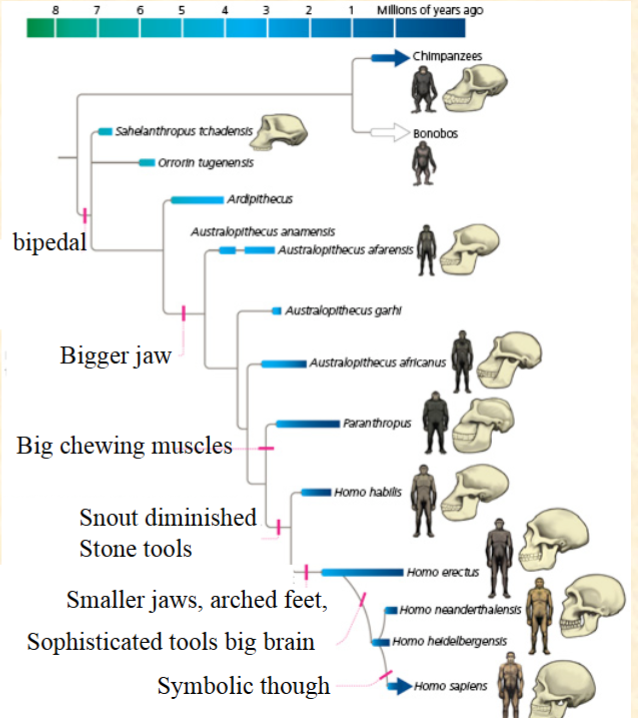
B. Bigger jaw
Which is a synapomorphy
for the Australopithecines?
A. Bipedal
B. Bigger jaw
C. Big chewing muscles
D. Snout diminished
E. These are all synapomorphies
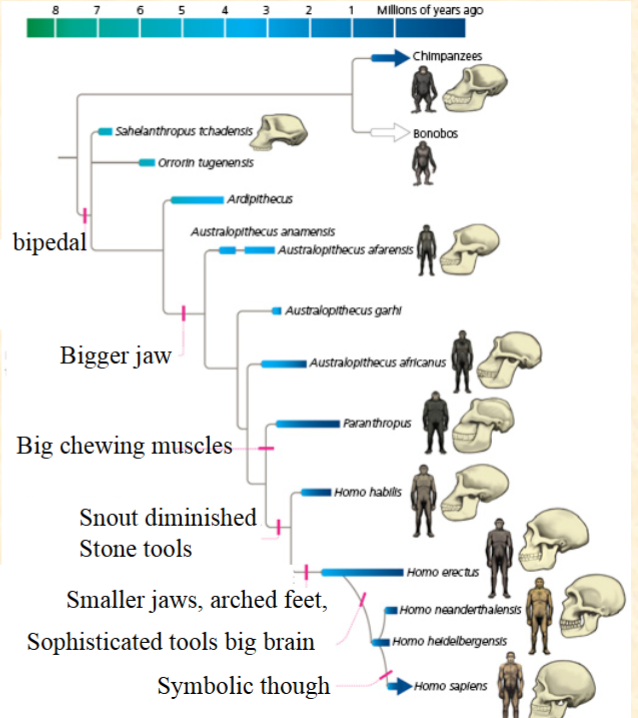
B. False
Bipedalism is a
synapomorphy for the genus
Homo.
A. True
B. False
A. Plants
B. Fungi
D. Mammals
E. Arthropods
onophyletic group (pick those that
apply)
A. Plants
B. Fungi
C. Reptiles
D. Mammals
E. Arthropods
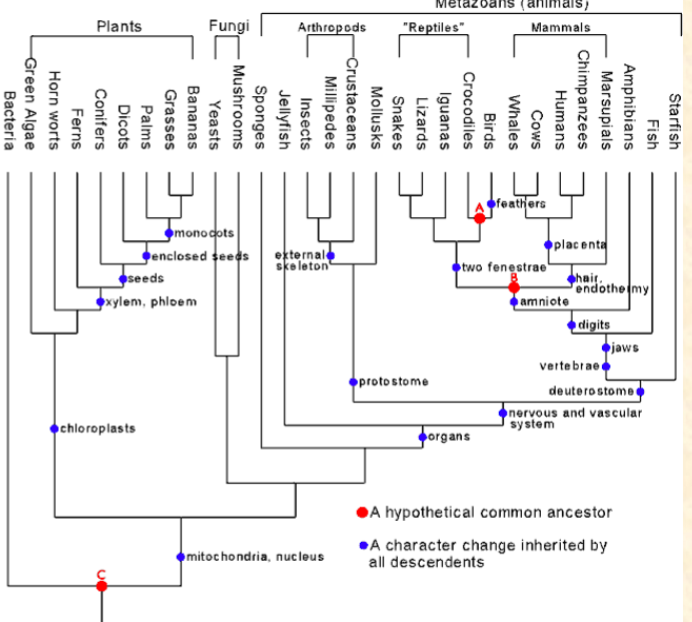
C. Mammals with fins
Example of polyphyly (a
polyphyletic trait)
A. Mammals with teeth
B. Mammals with fur
C. Mammals with fins
D. Mammals with tails
D. Convergent evolution.
Very detailed squamate phylogeny.
Limblessness has evolved ~dozen times in the
squamates (other times in amphibians and
mammals. What is this evidence of?
A. Stabilizing selection
B. Genetic drift
C. Gene flow
D. Convergent evolution.
E. Why aren’t there any vegetarian snakes?
F. Life is short, snakes are long.
phylogeny
potential reconstruction of an evolutionary relationship for specific species
sibling taxa
more closely related to each other than another taxa
node
represents common ancestor
taxa
end point that represents different species
outgroup
shares common ancestor with all organisms but less closely related to any of them
monophyletic
evolutionary unit that includes all descendants of an ancestral species and includes the ancestor
synapomorphy
shared derived trait that defines monophyletic groups
homologous trait
shared trait in monophyletic groups
analogous trait
shared trait that doesn’t come from a common ancestor
polyphyletic
evolutionary unit that includes only some of the descendants
paraphyletic
evolutionary unit that includes only some of the descendants and one common ancestor