Biochemistry 8.3; Chemical Reactions Rates and the Effects of Catalysts
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
What does a single arrow mean between reactants and products?
Irreversible reaction; Reaction lies far to the right
What does a double arrow mean between reactants and products?
Reversible reaction
“Reaction rate” or “velocity”
The rate of formation of the product
What are the units of v?
Concentration per unit time (M x s-1)
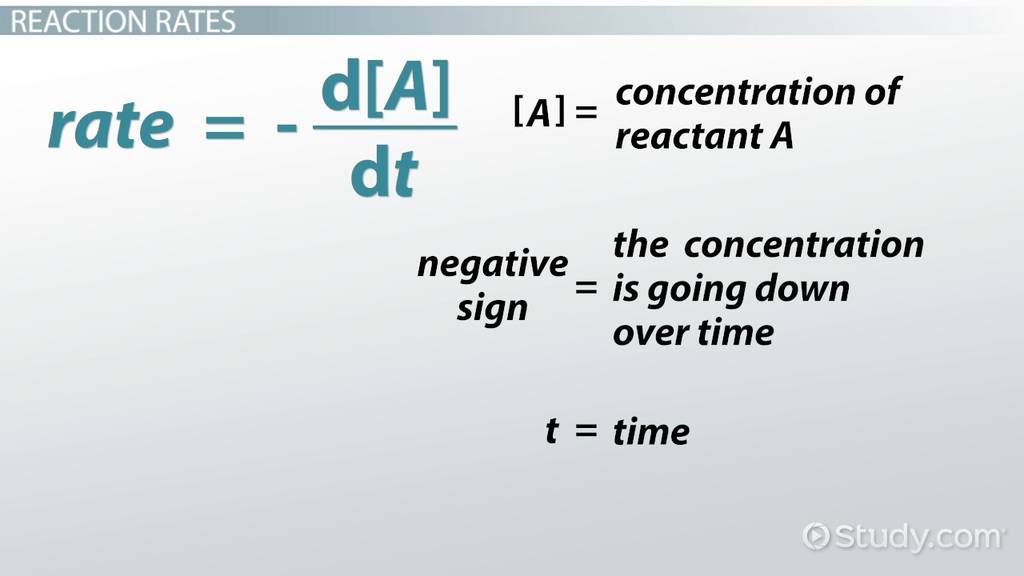
What reaction rate is this?
First
What does n=1 mean?
First order reaction
What type of graph does a first order reaction have?
Negative and linear
What is the purpose of the rate constant?
Direct measure of how fast a reaction is
What does it mean as k increases?
The faster the reaction is
How is the half-life of a reaction affected by first order?
Half-life is inversely proportional to k1
What different types of reactions usually distinguish first order from second order?
First order is using WITHIN a molecule, and second order is using BETWEEN 2 molecules
What is a simple equation that is usually first order?
A →B
What is a simple example of a second order reaction?
A + B → C
What order is it when:
[A] X2 and rate x2?
1st order
What order is it when:
[A] x2 and rate x4
2nd order
What order is it when:
[A] x2 and rate x1
Zero order
How do you find the overall reaction order?
Add the order of the reactants
“Rate-limiting step”
The slowest step in a multi-step process
What are the different units between first and second order rates?
1st= (time)-1
2nd= (concentration)-1 x (time)-1
What does the rate of a chemical reaction depend on? (4)
1) Order of the reaction
2) Concentrations of the reactants and products
3) Temperature
4) Value of the the rate constant for the reaction
“Reaction coordinate”
A generalized measure of the progress of the reaction through intermediate states.
What is important in determining the reaction rate?
What happens during the transition state between reactants and products
What is the relationship between the free energy of the products and reactants in a favorable reaction?
Energy of the products is lower than that of the reactants
Why may not all encounters between reactants be productive?
They may not be positioned correctly to each other.
What is an important concept regarding barriers to a chemical reaction
A reactant molecule must pass through a high-energy transition state to form products.
“Activation energy”
The energy barrier reactants must overcome to form products
What is the tensest state of a pyranose ring?
Half-chair
What are two strategies for increasing the reaction rate?
1) Raising the temperature
2) Lowering the free energy of activation
What happens to a molecule as temperature increases?
The energy also increases
What has been nature’s response for increasing reaction rates?
Use enzymes to lower the activation energy
What did Michael Polanyi propose in 1921?
A reaction catalyst preferentially binds the transition state structure and thereby stabilizes it relative to the ground state. (Leads to decrease in activation energy)
Basically, what does transition state theory assume?
A reactant molecule that attains the transition state rapidly decomposes to a lower-energy state
“Rate enhancement ratio”
The ratio of the rate constants for the catalyzed and noncatalyzed reactions for a given set of conditions