Plate Tectonics
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
lithosphere
crust and uppermost mantle = tectonic plate (continental crust OR oceanic)
asthenosphere
lower mantle and below
hot & weak, it is able to move
in relation of density
continental crust(granitic) _ oceanic (basalt)
continental < oceanic
is less dense
both crust still float ontop of the mantle
Describe the process of Tectonic Plate motion
“slab pull”
denser plate subducts (pulled under) into athenosphere
heats up in convection stage and circulates back to mid ocean ridge
hot spot melts the litospheric crust, the crust spreads (ridge push)
tectonic plaltes begin to move side to side and the new oceanic crust takes its place
Linear Sea
a result of divergence two land masses separated by water and can still fit perfectly together
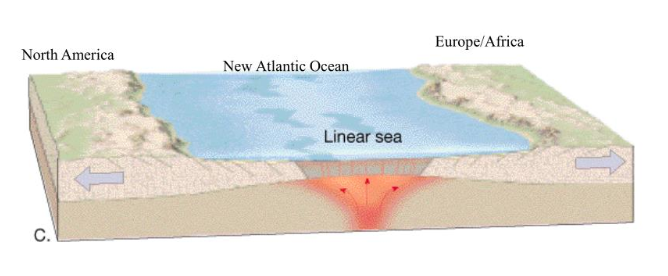
Ocean
result of divergence: bigger body of water, can fit together but not perfectly
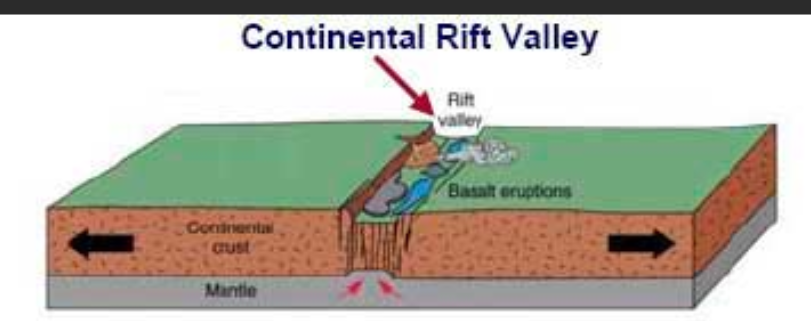
Rift Valley
result of divergence: seperation of crust where water begins to seep in
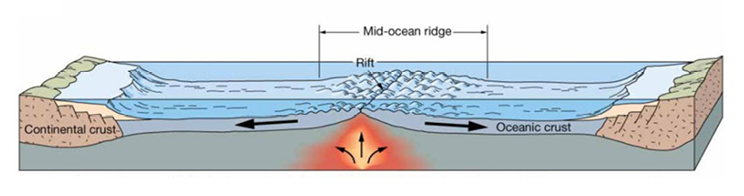
Mid Ocean Ridge (generic term)
spreading centers
most extensive chain of mountains on Earth (mostly underwater)
magma will fill cracks in sea floor and solidify & magma erupts onto seafloor as lava unless spreading is very rapid
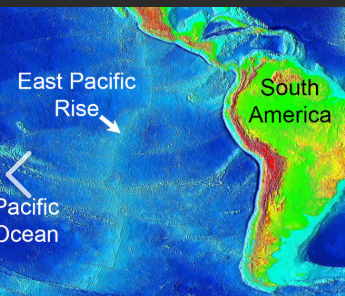
East Pacific Rise
divergent plate boundary
MOR: not centered
very FAST SPREADING(10s cm/year), gentle slopes
Mid Atlantic Ridge
divergent plate boundary
MOR: slow spreading, STEEP SLOPES
in iceland, the divergent plate boundary is about sea level

Ocean - Continental Convergent Plate Boundary
ocean plate subducted
continental arc (volcano) is created
explosive andeistic (new minerals) in the volcanic eruption
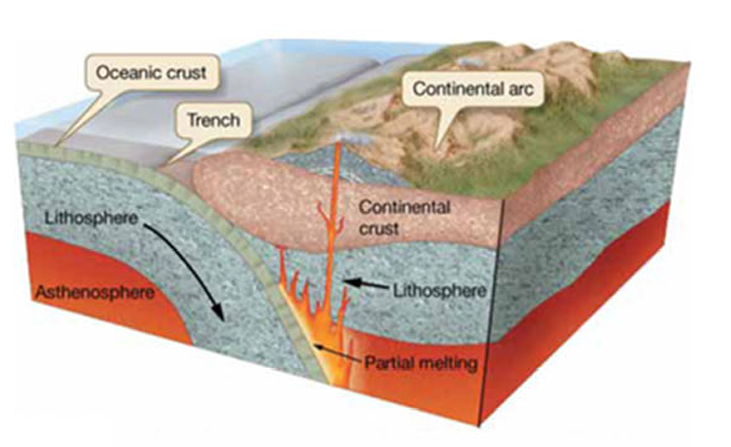
Ocean - Ocean Convergent Plate Boundary
denser plate subducts
deep trenches are generated
volcanic island arcs are built
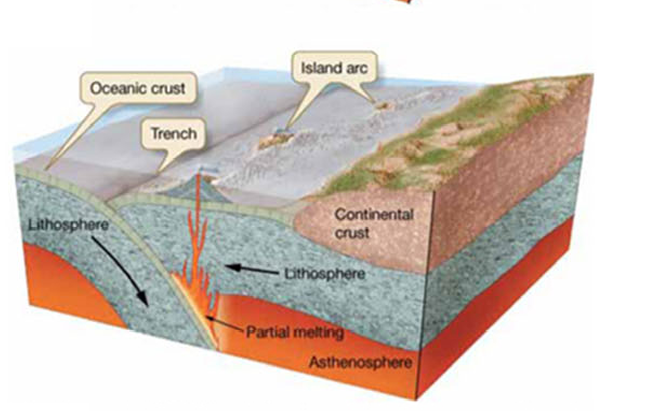
Continental - Continental Convergent Plate Boundary
subduction ceases
collision generates tall mountain chains
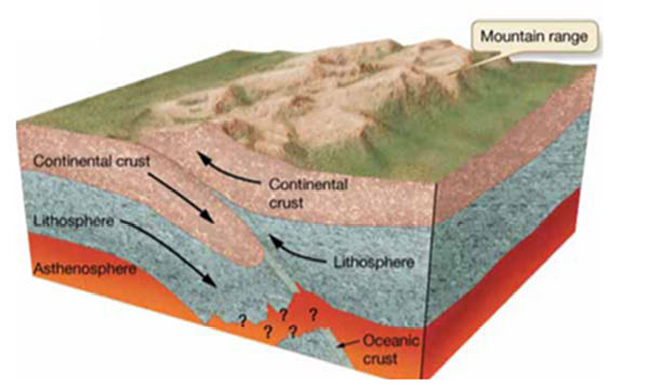
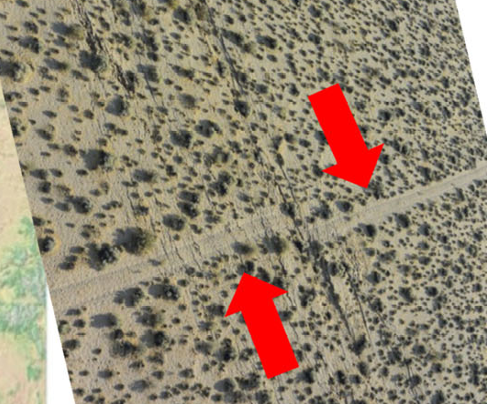
Describe Transform Plate Boundary
segments of plates slide past each other
permit the MOR to move apart at different rates
Results of Transform Plate Boundary
shallow & strong earth quakes (not deep within the mantle)
fault margin

What is a real world example of a convergent plate boundary?
O - C: peru - chile trench, andes mountains
O - O: mariana trench
C - C : himalaya mountains
what is a real world example of a divergent plate boundary?
O-O: mid atlantic ridge (MOR)
O-C: the red sea
what is a real world example of a transform plate boundary?
oceanic: mendocino fault
continental: san andreas fault
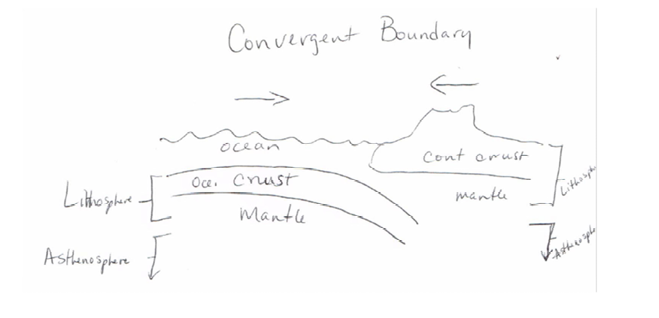
draw a converging plate boundary
oceanic to continental
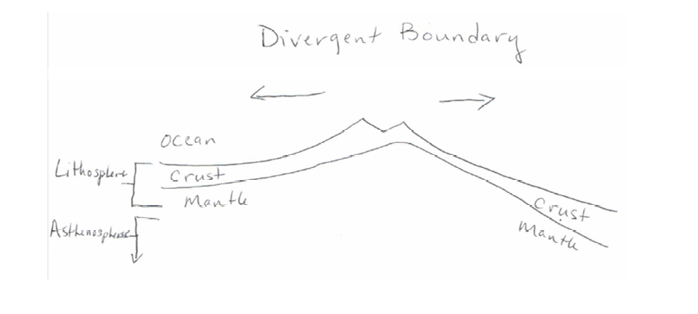
draw a diverging plate boundary
oceanic - oceanic
Oceanic crust is very dense and relatively thin. Continental crust is less dense and relatively thick. What happens when an oceanic plate and a continental plate converge?
a. Transform faulting rips open the mid-ocean ridge.
b.The continental plate is subducted.
c.The denser oceanic plate is subducted.
d.Subduction stops and mountain ranges are uplifted.
C