Chapter 14 Touch and Pain
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Week 12
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
epidermis vs dermis
outer layer of the skin vs inner layer of the skin (houses touch receptors)
mechanoreceptors
transduce physical movement on the skin into neural signals
→ send to the brain
SAI mechanoreceptors
slow adapting receptors using Merkel cells
small receptive fields
densely packed near the surface of the skin
SAII mechanoreceptors
slow adapting receptors using Ruffini endings
large receptive fields
widely distributed
deeper in skin
FAI mechanoreceptors
fast adapting receptors with Meissner corpuscle endings
smaller receptive fields
densely packed near the surface of the skin
FAII mechanoreceptors
fast adapting receptors with Pacinian corpuscle endings
large receptive fields
widely distributed
deeper in skin
meissner corpuscles
specialised transduction cells in FAI mechanoreceptors
Pacinian corpuscles
specialised transduction cells in FAII mechanoreceptors
Merkel cells
specialised transduction cells in SAI mechanoreceptors
Ruffini endings
specialised transduction cells in SAII mechanoreceptors
proprioception
perception of the movements and positions of our limbs
muscle spindles
receptors in the muscles that sense info about muscle length
if you can figure out muscle length, you therefore know muscle action (stretched out, resting)
joint receptors
receptors found in each join that sense info about the angle of the joint
golgi tendon organs
receptors in the tendons that measure the force of a muscle contraction
afferent fibres
neural fibres that carry sensory information to the central nervous system
thermoreception
ability to sense changes in temperature on the skin
thermoreceptors
sensory receptors that signal info about the temp as measured on the skin
cold fibres
thermoreceptors that fire in response to colder (30c and below) temps on the skin
warm fibres
thermoreceptors fire to warmer temps (36c and above) on the skin
pain
perception and experience of actual or threatened tissue damage
nociceptive pain
pain from tissue damage that causes nociceptors in the skin to fire
nociceptors
sensory receptors that when activated cause us to feel pain
found in dermis and epidermis
A delta fibres
myelinated nociceptors that conduct signals rapidly
respond to heat and pressure
c fibres
NON-myelinated nociceptors that are slower
respond to pressure, extreme cold or heat, and toxic chemicals
dorsal root ganglion
node on the spine where nerve cells carry signals from sensory organs toward the somatosensory areas of the brain
dorsal root
end of the spinal nerve where sensory information enters the spinal cord
ventral root
the end of the spinal cord where motor info leaves the spinal cord
dorsal
toward the back of the body
top of the head
remember: shark’s dorsal fin is right on the top of their back
ventral
toward the front of the body
bottom of head
remember: in fishies, ventral fin is on the belly/in front of them
dorsal column medial lemniscal pathway
mechanoreceptors (touch) and proprioceptors (muscle position) travel up the spinal column on the ipsilateral side and cross to the contralateral side in the medulla
ipsilateral
same side of the nervous system as it entered
ex. feel on right, travel up right side
contralateral
sensory info is on opposite side of the nervous system that it entered
ex. feel on right side, info travels to left side
somatosensory cortex
in the parietal lobe of the cerebral cortex (outermost layer of the brain)
all about processing info coming from skin senses
ventral posterior nucleus of the thalamus
area in thalamus that gets input from dorsal column medial lemniscal pathway AAAAANDD spinothalamic pathway
spinothalamic pathway
path for the nociceptors (pain) and thermoreceptors (temp)
travels up contralateral side of the spinal column
doesn’t synapse in brain until ventral posterior nucleus of the thalamus
somatotopic map
skin of body maps onto the surface of the primary somatosensory cortex in a systematic way
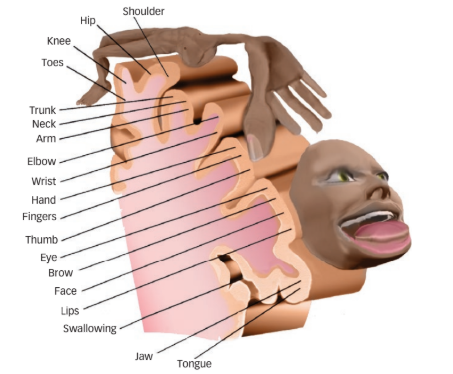
homunculus
horrifying drawing of a human but the proportions of the body parts match the relative sides of each body part with the somatotopic map
gate control theory
model that allows for top down control of the pain signal coming up the spinal cord
substantia gelatinosa
region of the dorsal horn where neurons meet
dorsal horn
area of spinal cord that receives input from nociceptors and feedback from the brain
anterior cingulate cortex
region in prefrontal lobe
emotional experience of pain
endogenous opioids
chemicals produced by the body that reduce pain
analgesia
processes that act to reduce pain perception
pruriceptors
receptors that respond to mild skin irritants by making the dreaded ITCH
haptic perception
how we use touch to actively identify objects
(hmm this is round and fuzzy, must be a kiwi)
must have to read braille
exploratory procedures
hand movements made in order to identify an object
tactile agnosia
inability to identify objects by touch
(man I know this is smooth and long but I have no idea what it could be!!)
vestibular system
sensory system in charge of perception of balance and acceleration
in the semicircular canals and otolith organs (beside the inner ear)
semicircular canals
3 tubes in the inner ear that signal head rotation
otolith organs
detect acceleration of the head and can tell you when the head is tilted at an angle
endolymph
fluid that fills the semicircular canals
ampulla
at the base of each semicircular canal
holds the crista
crista
in the ampulla of each semicircular canal
contains receptors
macula
in the otolith organs
contains the receptors
vestibular complex
area of brain stem
receives input from vestibular nerve and sends info to the forebrain
parietal insular vestibular cortex
in the parietal lobe (shocker)
gets input from vestibular nerve
all about perception of balance and orientation
electroception
ability to detect electric fields
fishies
passive electroreception
can only detect electric fields
active electroreception
generate electric fields (woah!) and then detect changes to those electric fields causes by external events
ex. someone is messing with my electricity rn
phantom limb syndrome
illusory sensory reception in a missing appendage
ex. my hand is gone but I feel it still..
phantom limb pain
pain in a limb that has been amputated
ex. god my ankle hurts but I actually have nothing below the knee
visual capture
visual input can dominate the input from other senses when they conflict
ex. ventriloquism and those freaky puppets