AP Biology: Cell Signaling
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Local Signaling
Messenger molecules are involved in signaling that travel only short distances
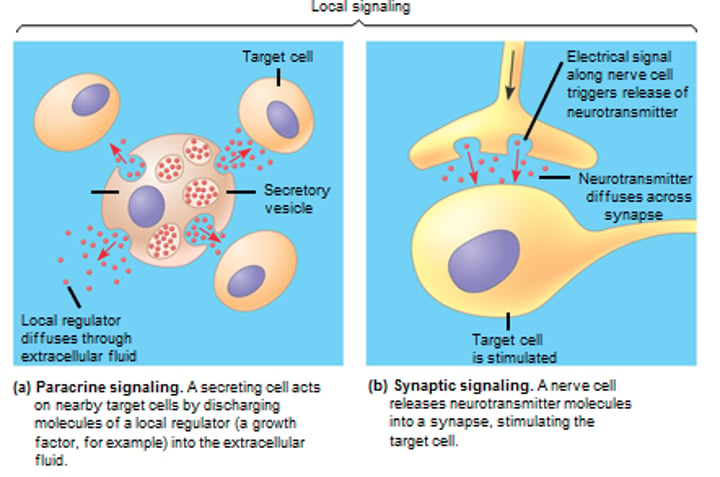
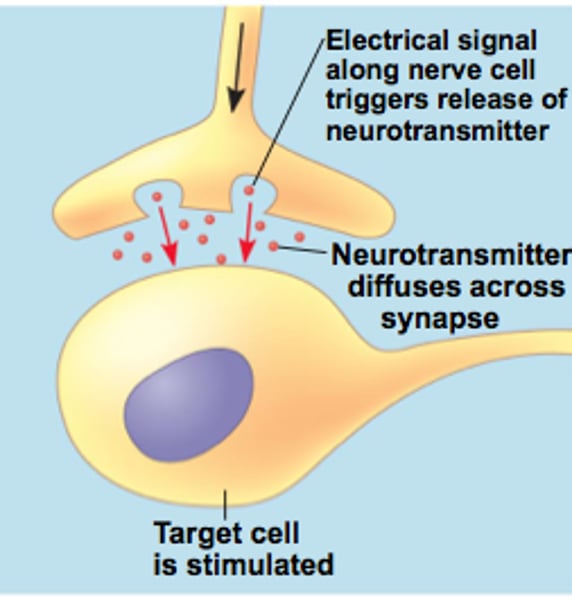
Synaptic Signaling
A nerve cell releases neurotransmitter molecules into a synapse, stimulating the target cell
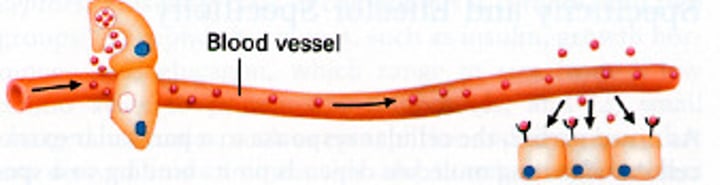
Endocrine Signaling
endocrine cells secrete hormones, which travel via the circulatory system to other parts of the body, where they reach target cells
Reception
The target cell's detection of a signaling molecule coming from outside the cell; involves the binding of the signaling molecule to a receptor protein
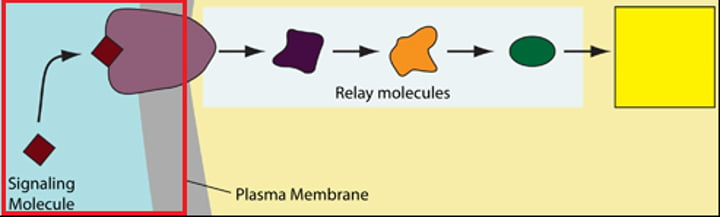
Transduction
A step or series of steps that converts the signal to a form that can bring about a specific cellular response
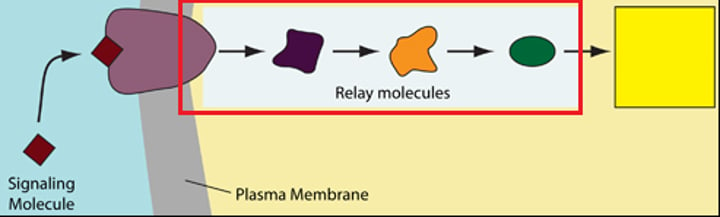
Signal Transduction Pathway
A sequence of changes in a series of different molecules during transduction
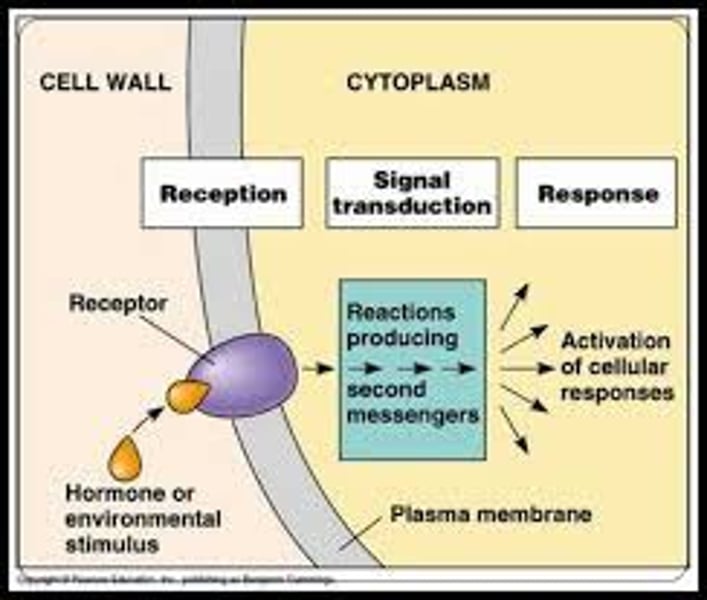
Response
The transduced signal triggers a specific change in cellular activity
Ligand
A molecule that specifically binds to a receptor based on complementary shape and causes a change in shape of the receptor
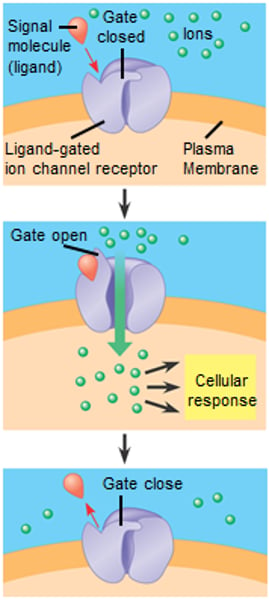
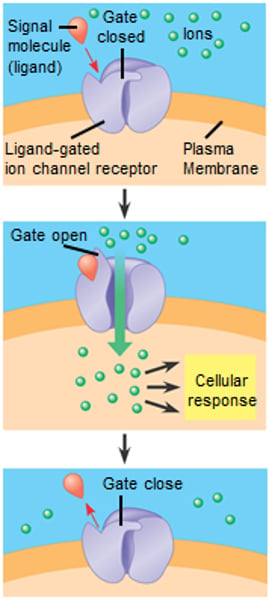
Examples of Transmembrane Receptors
G protein-coupled receptors, tyrosine-kinase receptor and ligand-gated ion channels
Ligand-gated Ion Channel
A membrane receptor that has a region that can act as a "gate" for ions when the receptor assumes a certain shape
Testosterone
A steroid hormone that passes through the cell membrane and binds to a receptor within the cytoplasm and turns on specific genes that control male sex characteristics
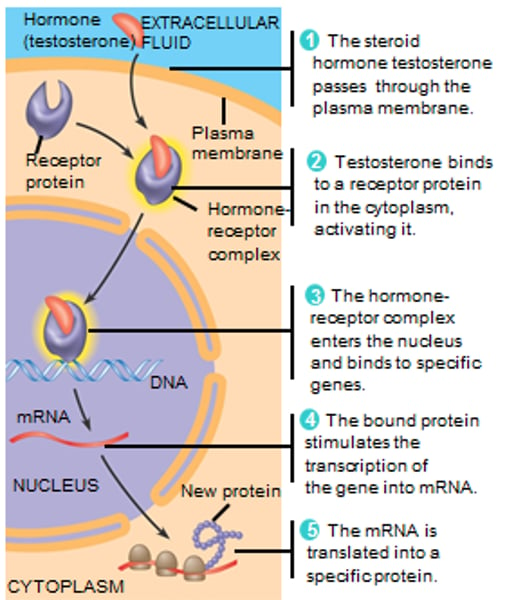
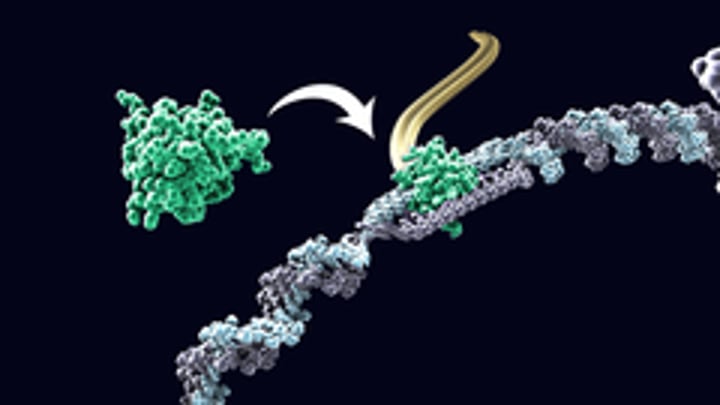
Transcription Factor
Special proteins that control which genes are turned on (transcribed into mRNA) in a particular cell at a particular time
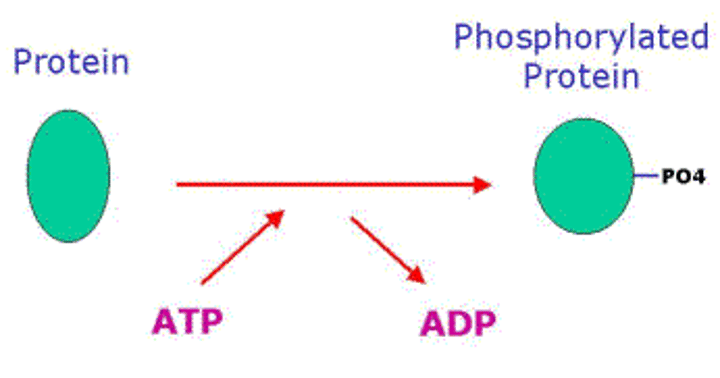
Protein Kinases
Enzymes involved in phosphorylation cascades that transfer phosphate groups from ATP to other proteins; addition of phosphates activates the protein
Second Messengers
Small, nonprotein water-soluble molecules or ions involved in a signaling pathway; examples include cAMP and calcium ions
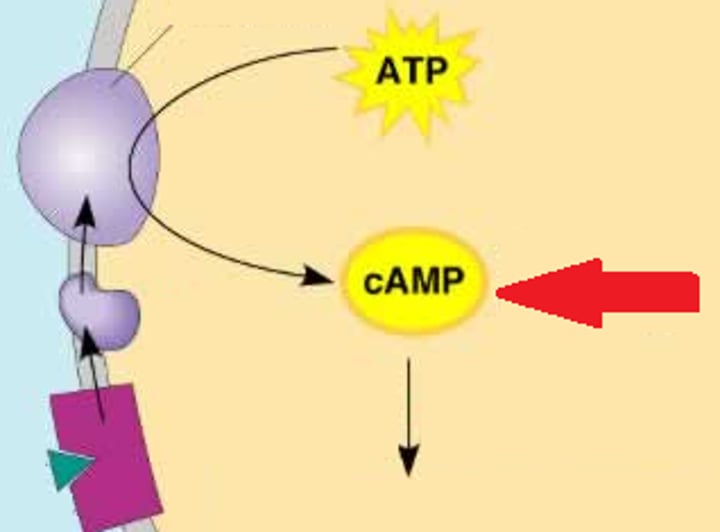
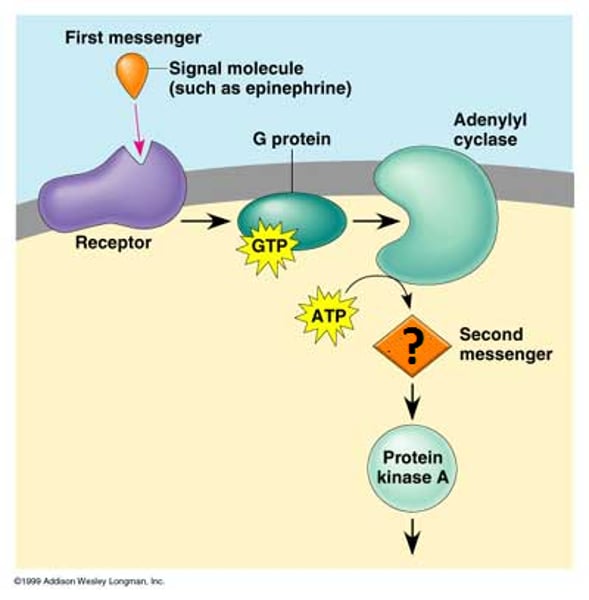
cAMP
Cyclic AMP; a second messenger that is activated by adenylyl cyclase
Cell Signaling Disruptors
Diabetes, neurotoxins, poisons, pesticides, cholera, anthrax, antihistimines
Diabetes
The ligand insulin is not produced (Type 1) or the insulin receptor does not bind to the ligand (Type 2)
Acetylcholine
Neurotransmitter that produces an impulse in a muscle cell
botulism toxin (botox)
A toxin that prevents the release of acetylcholine, preventing muscular contraction
anti depressants
drugs that increase the availability of neurotransmitters serotonin and norepinephrine , which elevate arousal and mood and appear scarce during depression
Epinephrine
An example of a chemical messenger (ligand) that binds to a transmembrane receptor (GPCR) and signals the breakdown of glycogen into glucose
direct contact signaling
Direct signaling can occur by transferring signaling molecules across gap junctions or plasmodesmata between neighboring cells
neurotransmitter
Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons.
glycogen
An extensively branched glucose storage polysaccharide found in the liver and muscle of animals; the animal equivalent of starch.
insulin
A protein hormone synthesized in the pancreas that regulates blood sugar levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose into tissues
amplification
The strengthening of stimulus energy during transduction.
myelin sheath
a fatty covering around the axon of neurons that speeds the neural impulse
resting potential
when the outside of the neuron has a net positive charge and the inside of the neuron has a next negative charge
action potential
A momentary reversal in electrical potential across a neural membrane that occurs when a cell has been activated by a stimulus.
sodium potassium pump
Process by which ATP is used to move sodium ions out of the cell and potassium ions back into the cell; completely restores the resting conditions of the neuron.
sodium channel protein
opens to allow Na+ to enter the neuron during depolarization
hypothalamus
A portion of the forebrain that controls homeostatic and endocrine functions by controlling the release of pituitary hormones.