Electricity and magnetism
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
William Gilbert
English physician and scientist, published De Magnete in 1600. Summarized everything known about magnetism and electricity at the time.
Electricity
Has positive and negative electric charges.
Like charges repel, and unlike charges attract each other.
Charged objects set up electric field of forces
Certain materials can be electrified through rubbing.
i.e. ebonite rod with cat’s fur
Magnetism
Has north seeking poles and south seeking poles.
Like poles repel, and unlike poles attract.
Magnetic objects set up magnetic fields of forces.
Certain materials can be magnetized through rubbing
i.e. steel rod with lodestone
Magnetic fields
Vector fields that are used to determine the distribution of magnetic force in areas within and around a magnet. They allow magnets to attract objects without touching them.
Domain theory of Magnetism
Every atom ha a magnetic property, each electron in an atom has a magnetic field which is caused by its spin and movements round the nucleus, which causes electrons to act like tiny magnets.
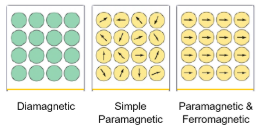
Ferromagnetic Materials
Materials STRONGLY attracted to magnets. Iron, nickel, cobalt, chromium dioxide.
Paramagnetic Materials
SLIGHTLY attracted by magnets. Iron bearing materials such as aluminum, platinum, manganese, and chromium.
Diamagnetic Materials
SLIGHTLY REPELLED by magnets. Bismuth, antimony, copper, zinc, mercury, gold, and silver.
Hans Christian Oersted
Discovered that a magnetic field exists around current-carrying wire. This has established a connection between electricity and magnetism.
BASIC PRINCIPLE OF ELECTROMAGNETISM
When electrons move through a conductor, a magnetic field is created in the region around the conductor
Generators
An electrical machine that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Uses Electromagnetic Induction, where electrical current is induced through the movement of the magnet or the coil of wire relative to each other.
Motors
An electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
Uses Electromagnetic Induction, where electrical current is induced through the movement of the magnet or the coil of wire relative to each other.
GEOTHERMAL ENERGY
Magma or hot rocks underneath the Earth’s surface naturally heat ground water, a production well is drilled into the earth in order to bring hot water or steam up, this steam then spins a turbine that powers a generator. Then the steam is cooled and condensed back into water and is injected back into the earth through a second well.
Renewable and sustainable, clean energy, reliable (not dependent on sun or wind)
Specific to locations with strong underground heat, high costs for the wells, environmental concerns if not managed properly, earthquake risks
Earth’s heat → Hot water/steam → Turbine spins → Generator → Electricity