3.7 Classical Conditioning
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
Any relatively permanent change in a subjects behavior brought about by experience or practice
Learning
Examples of behaviours that are not learnt:
Inborn reflexes, maturation and biological processes, temporary states
Examples of inborn reflexes:
Blinking and swallowing
Example of biological processes:
Natural growth
Examples of temporary states:
Fatigue, emotional states, psychoactive drugs
What does behavioural perspective examine?
How observable behaviors are learned and reinforced through interactions with the environment
Learning occurs mostly through what?
Interactions with the environment
A process of learning in which an individual forms connections between events that occur together
Associative learning
A learning method where we associate two stimuli, enabling us to anticipate events
Classical conditioning
Example of classical conditioning:
A child develops a fear of dogs by association of a negative past experience
Any stimulus that produces no conditioned response prior to learning:
Neutral stimulus
What type of thing is a neutral stimulus?
Impartial
Does a neutral stimulus cause a change or reaction?
No
Example of neutral stimulus:
Bell
A stimulus that naturally elicits a reflexive response without prior learning:
Unconditioned stimulus
Examples of unconditioned stimuli:
Food, light, noise
The natural, reflexive response caused by an unconditioned stimulus without prior learning:
Salivation, dilation, startle reflex, fight/flight response
What did the conditioned stimulus use to be?
Neutral stimulus
What does a conditioned stimulus elicit?
A conditioned response
A conditioned stimulus elicits a conditioned response after what?
Intentional repeated pairings with the unconditioned stimulus
Example of conditioned stimulus:
Bell that used to be neutral
What happens to a reflex after it’s been paired and associated with the conditioned stimulus?
Becomes learnt
Similarities between conditioned and unconditioned response:
Same response
Differences between conditioned and unconditioned response:
Not naturally occurring vs naturally occurring, learnt vs not learnt
Examples of conditioned response:
Salivation, eye blink
The process of developing a learning response:
Acquisition
What happens when a neutral stimulus is repeatedly paired with the unconditioned stimulus?
Begins to trigger conditioned response
What is crucial in acquisition?
Timing
What happens when pairing stops?
There is a gradual weakening of conditioned behavior
Reappearance of extinguished CR after some time even though the association is weakened:
Spontaneous recovery
Graph of amount of salivation vs number of trials for acquisition, first extinction, spontaneous recovery, and second extinction:
/
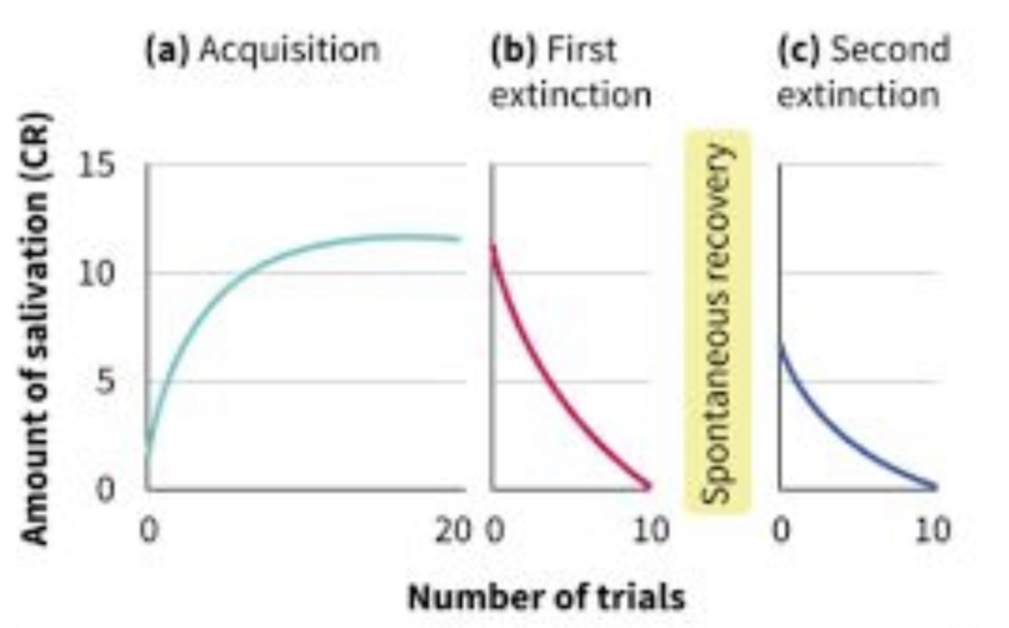
The tendency to respond to stimuli that are similar to the conditioned stimulus, as a result of the conditioning process:
Stimulus generalisation
The ability to differentiate between similar stimuli and respond differently to them, learned through the conditioning process:
Stimulus discrimination
Example of stimulus discrimination:
Math classroom is conditioned stimulus for anxiety due to pop quizzes, while science classroom does not trigger this response as it is not associated with the same stressor
What is habituation also called?
Non-associative learning
When does habituation occur?
When organisms grow accustomed to and exhibit a diminished response to a repeated or enduring stimulus
What is habituation in simple terms?
Getting used to something over time
Example of habituation:
Not reacting as strongly to a ringing phone over time
The reappearance of a previously extinguished conditioned response after a period of rest:
Spontaneous recovery
What does spontaneous recovery suggest?
Extinction does not erase an association but suppresses it temporarily
Example of spontaneous recovery:
A student is anxious whenever she enters a classroom as she always gets pop quizzes during class in that classroom. The teacher decided to stop giving pop quizzes, causing the association between classroom and anxiety to go extinct. However, after a long holiday, the student is anxious again upon entering the class room (spontaneous recovery)
Example of stimulus generalization:
Feeling anxious when entering a new classroom that have the attributes of the classroom that always makes you anxious due to the pop quizzes
A process where a previously conditioned stimulus is used to create further associations with new neutral stimuli, resulting in those stimuli also eliciting a conditioned response:
Higher-order conditioning
Another phrase to describe higher-order conditioning:
Layering of associations
Example of higher-order conditioning:
Linking a classroom in which you get pop quizzes to anxiety, and then linking the bell in the classroom with anxiety
Changing a learned response to something more preferred by pairing it with a different experience:
Counterconditioning
Techniques to apply counterconditioning:
Relaxation techniques like deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, or visualization
What serves as the new stimulus during counterconditioning?
Relaxation techniques like deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, or visualization
Example of counterconditioning:
Associating a class in which you get pop quizzes to calmness by pairing relaxation techniques with the classroom
How to associate previously anxiety-inducing stimuli with calming responses?
By practicing relaxation techniques while exposed to or thinking about the previously anxiety-inducing stimuli
The avoidance of a certain food following a period of illness after consuming that food
Taste aversion
What is taste aversion also known as?
Garcia effect
What are taste aversions examples of?
How classical conditioning can result in changes in behavior after only one incidence
What does biological preparedness state?
Some associations form more readily because they aid in survival
Are all associations learnt the same way?
No
Example of biological preparedness:
Sickened rats develop aversions to taste but not sights or sounds
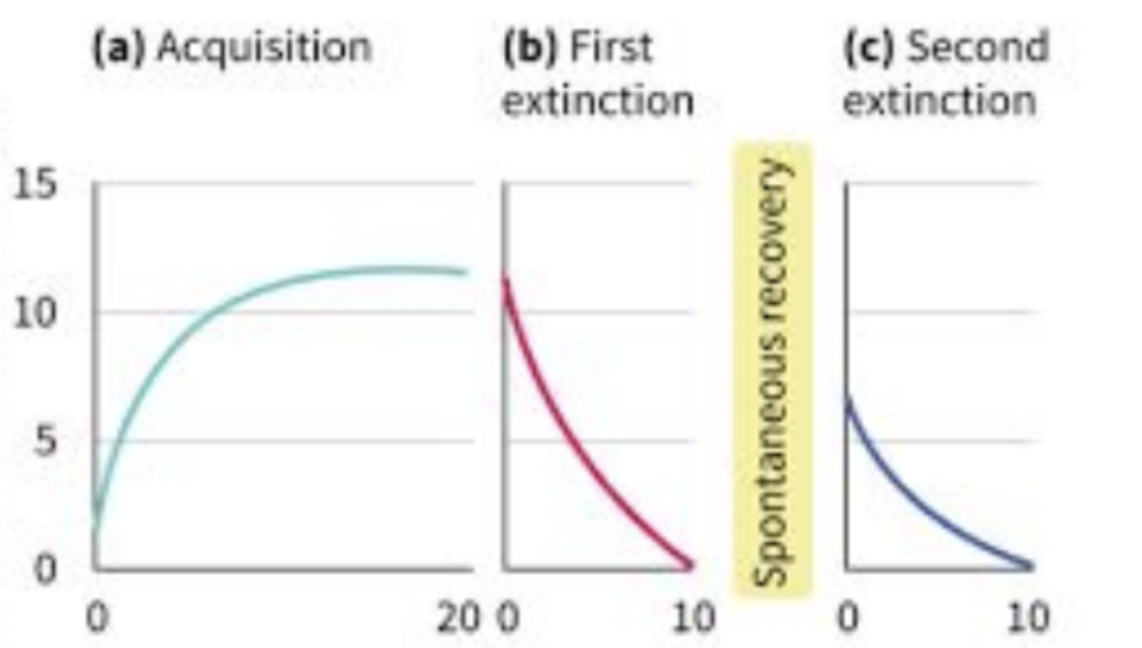
Diagram of CR for acquisition, first extinction, spontaneous recovery, second extinction:
Responses vs time for fixed interval reinforcement:

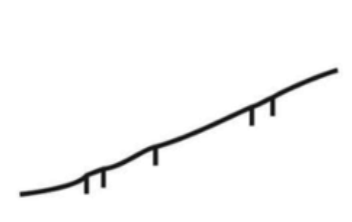
Responses vs time for variable interval reinforcement:
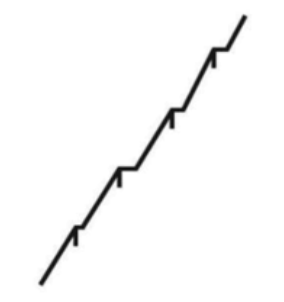
Responses vs time for fixed ratio reinforcement:
Responses vs time for variable ratio reinforcement:

Nature of classical vs operant conditioning:
Involuntary, reflexive responses vs voluntary, chosen behaviors
Basis of classical vs operant conditioning:
Association linking two stimulus events vs associating behavior with a consequence
Role of stimulus in classical vs operant conditioning:
Neutral stimulus becomes meaningful vs Behavior is strengthened or weakened by consequences
Key elements in classical vs operant conditioning:
NS, US, UR, CS, CR vs Reinforcer and punisher
Purpose of classical vs operant conditioning:
Predicts the occurrence of a significant event vs Increases or decreases the likelihood of behavior
Arrange in terms of aggression scores for children after watching model from lowest to highest: aggressive model rewarded, aggressive model punished, no model, non-aggressive model
No model, non-aggressive model, aggressive model punished, aggressive model rewarded
Does latent learning improve with reinforcement?
Yes