cool
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
An electron enters the magnetic field above. What direction is the magnetic force acting on the charge when it enters?
Up

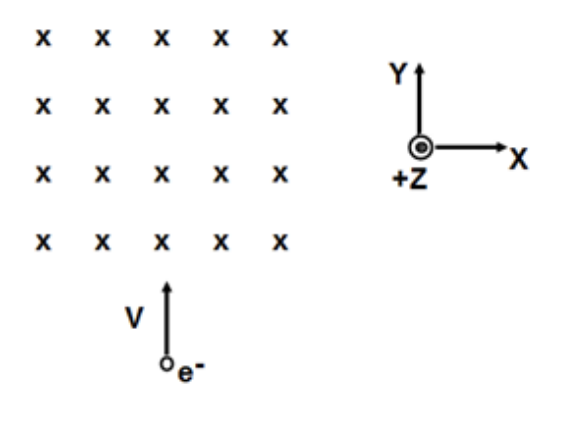
An electron enters a region of uniform magnetic field in the -Z direction. What is the direction of the magnetic force on the electron due to the magnetic field?
+X direction
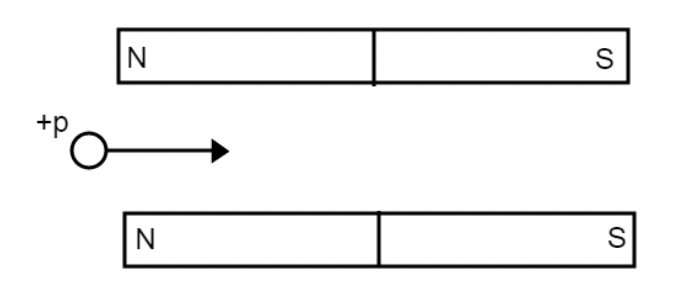
Shown above are two identical bar magnets that are fixed in place with a proton moving to the right about to enter the region between these two magnets. Which statement below best describes what happens to the proton while traveling in between the magnets?
The proton continues to move to the right in a straight line
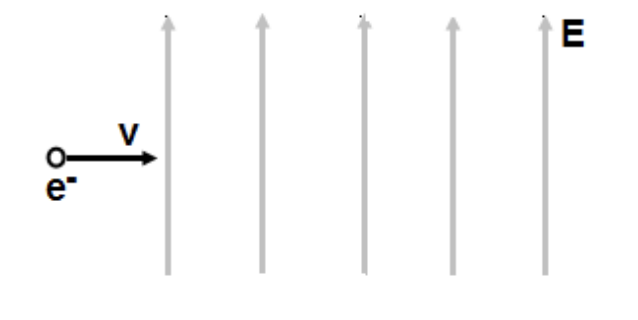
An electron enters a uniform electric field perpendicular to the field lines. What must be the direction of the magnetic field in order to cancel the electric force effect?
Out of the page
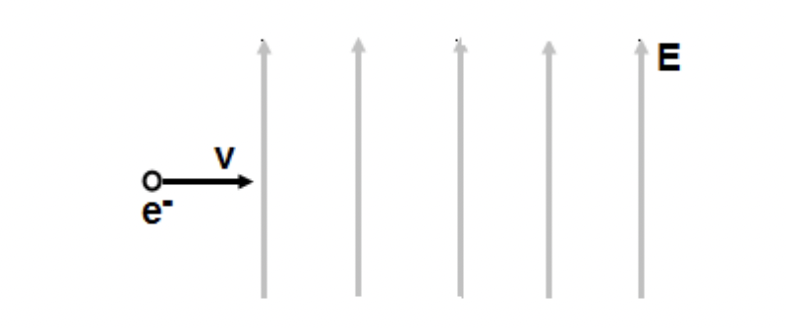
An electron enters a uniform electric field perpendicular to the field lines. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field if the electric effect completely canceled?
E/v
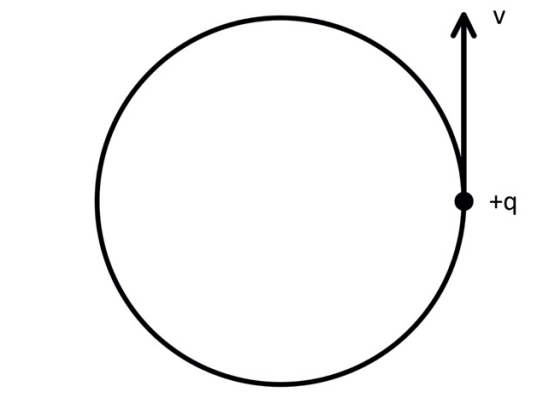
A charge of + q and velocity v is moved into a magnetic field of B. Which of the following orientations of magnetic field should the system have in order to make the charge move in a circle?
Into the page
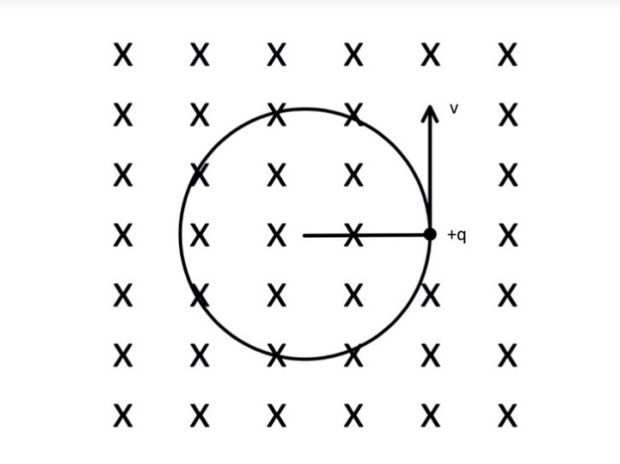
A charged particle, with a charge q, mass m and velocity v, moves in a circular path due to a magnetic field B. Which of the following is the acceleration that the charge feels?
qvB/m
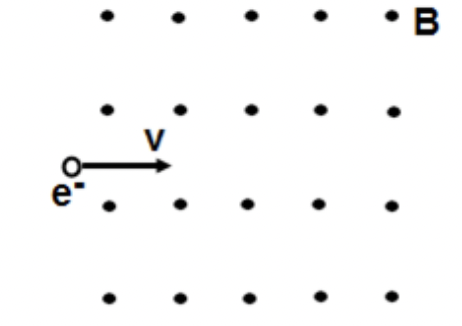
An electron with a mass m and a charge e enters a uniform magnetic field B at a velocity v. What is the radius of the curvature of the electron in the field?
mv/eB
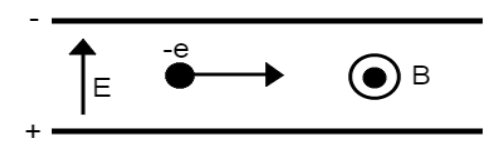
Shown below there is an electron moving to the right undeflected by both the electric field in between the plates and the magnetic field coming out of the page in between the plates. The magnetic field has a magnitude of 2.0 T and the electric field has a magnitude of 8 N/C. What is the speed of the electron?
4 m/s
A particle with a negative charge has an initial velocity that is parallel to a magnetic field moving to the right. What path would this negatively charged particle follow?
Straight line parallel to the field
Four charges are launched into different magnetic fields. All the charges are the same mass, charge, and have the same speed. Which of the four magnetic fields is the strongest?
A
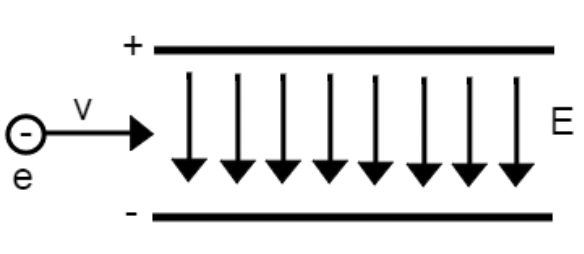
An electron is travelling with a velocity v and charge e into a region between two charged plates. There is a magnetic force that opposes the electric force due to the electric field of magnitude E on the electron. a) What direction would the magnetic field have to be in?
Directed into the page
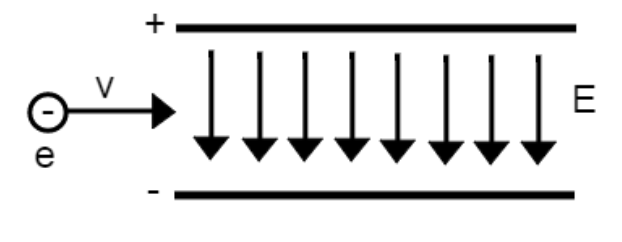
What would the magnitude of the magnetic field be for the electron to pass through
b) the region between the plates undeflected?
E/v
A long straight wire carries a current I toward the right. What is the direction of the magnetic field resulting from the wire at point x?
Out of the page
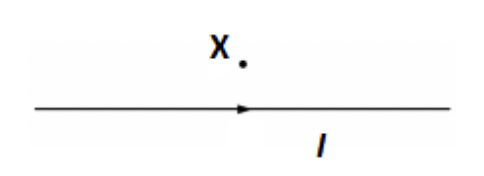
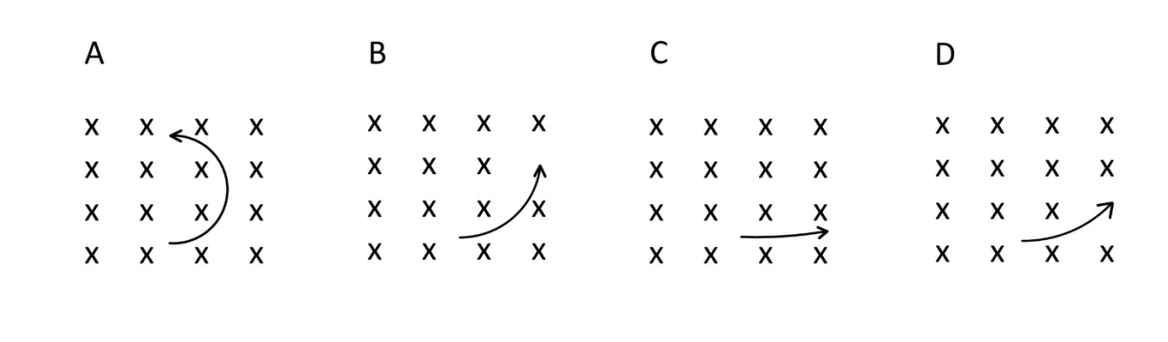
Which of the following diagrams accurately portrays the magnetic field resulting from
a wire carrying current directed out of the page?
D
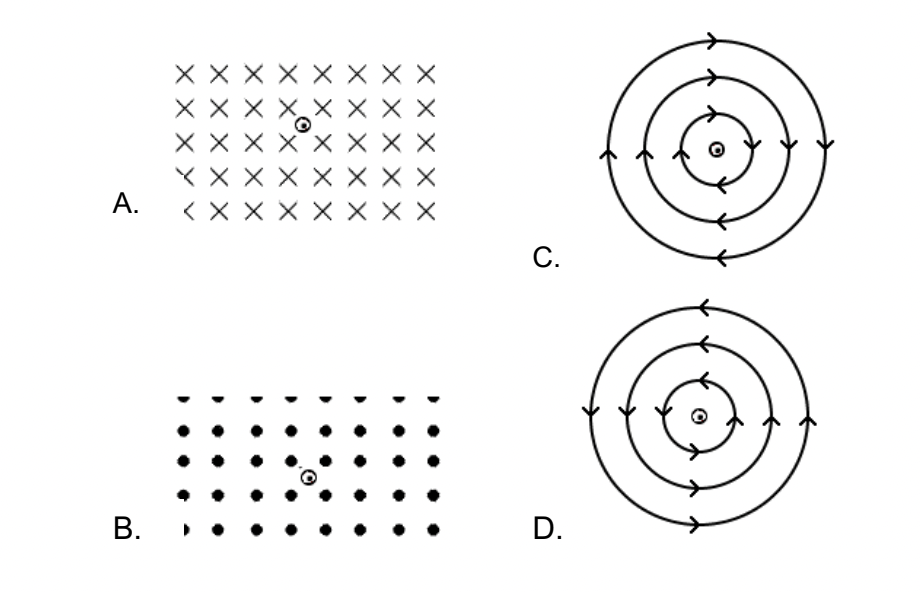
A straight wire carries a current into the page. What is the direction of the magnetic field at a point east of the wire?
South
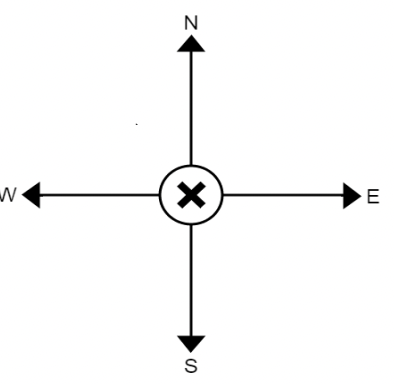
Above there is a circular loop of wire that has a counterclockwise current running through it. What is the direction of the magnetic field inside of the loop?
Out of the page
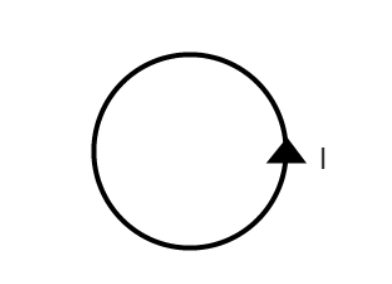
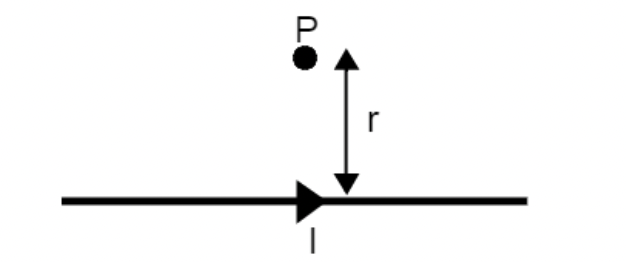
The wire above has a current being carried to the right and point P is a distance r away from the wire.
a) What is the direction of the magnetic field at P?
Out of the page
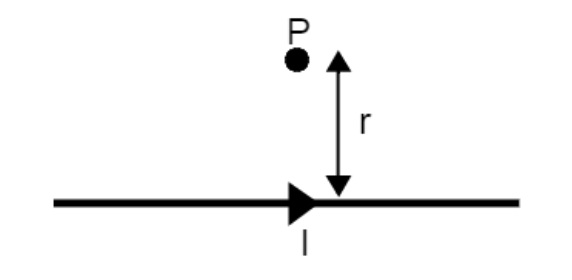
The wire above has a current being carried to the right and point P is a distance r away from the wire.
b) By how much would the magnetic field change if the current was doubled and the distance r was doubled?
No change
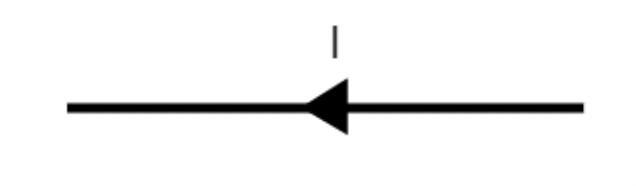
A wire carries current out of the page in a region of magnetic field directed north. What is the direction of the magnetic force on the current due to the magnetic field?
West
The wire above has a current I flowing to the left of the page, a mass m, and a length L.
a) In what direction would a magnetic field have to be placed so that the magnetic force could cancel out the gravitational force on the wire?
Out of the page
[NOT ON THE TEST]
The wire above has a current I flowing to the left of the page, a mass m, and a length L.
b) If the magnitude of the magnetic field is B what must the magnitude of this field be to cancel out the gravitational force on the wire?
mg/IL
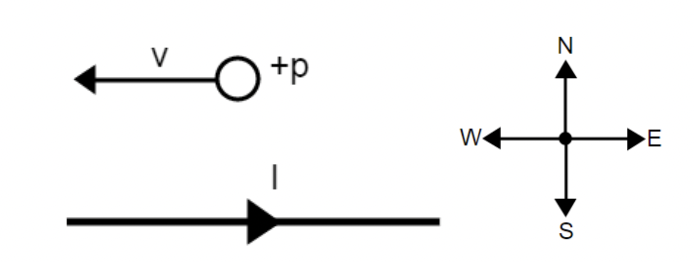
A horizontal wire is carrying current to the east and a proton is moving with a velocity v to the west. What is the direction of the magnetic force acting on the proton due to the current carrying wire?
North
What is the magnitude of the magnetic field at point B produced by a current I if the magnitude of the field at point A is B0?
B₀/2
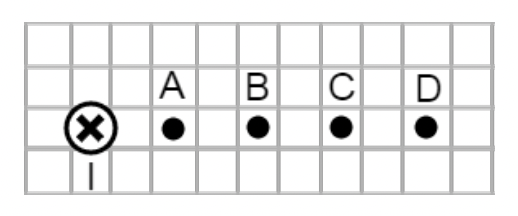
A wire is placed in between two magnets and feels the effects of gravity. Which of the following directions of current must the wire have to be suspended in place?
Out of the page
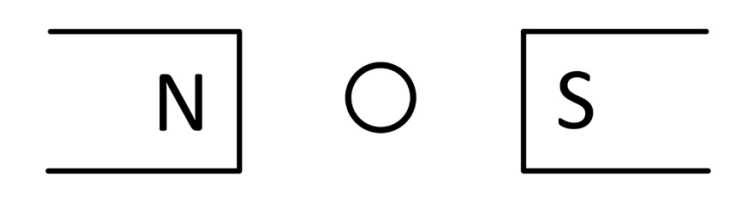
Two magnets and a wire with current coming out of the page are positioned in space as shown above. The wire is suspended in air by the magnetic force. What will happen to the wire when more current runs through it?
It will accelerate up
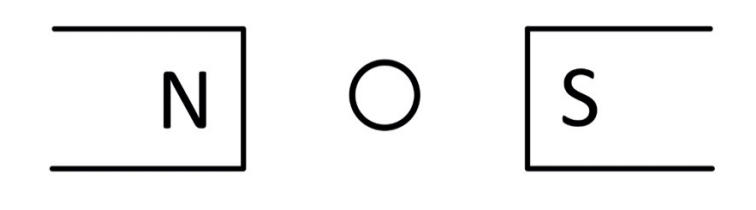
Shown above is a magnet on the left placed onto an electronic balance that gives a reading of 100g. To the right the same magnet is placed on the electronic balance but a wire carrying current out of the page is placed directly in between the north and south ends of the magnet. To the right the balance now reads 115 g.
a) What is the direction of the magnetic force acting on the wire?
Top of the page
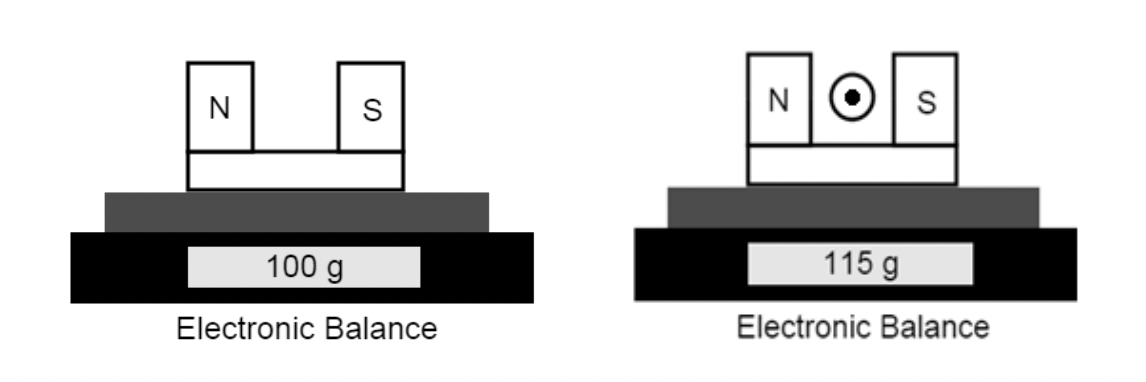
Shown above is a magnet on the left placed onto an electronic balance that gives a reading of 100g. To the right the same magnet is placed on the electronic balance but a wire carrying current out of the page is placed directly in between the north and south ends of the magnet. To the right the balance now reads 115 g.
b) What would happen if the current was increased in the wire?
The balance reading would increase
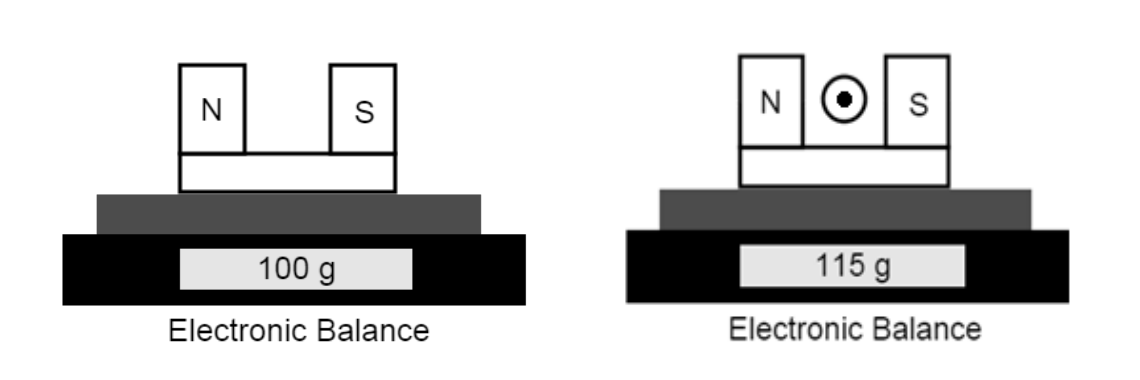
What is the magnitude of the magnetic force acting on the wire?
0.15 N
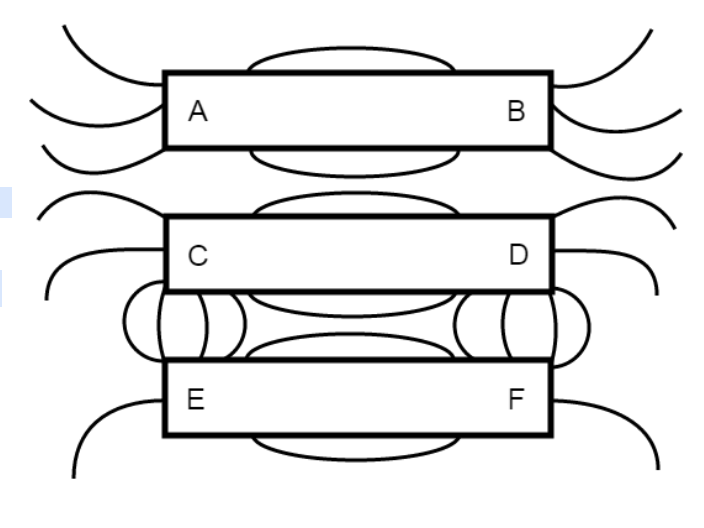
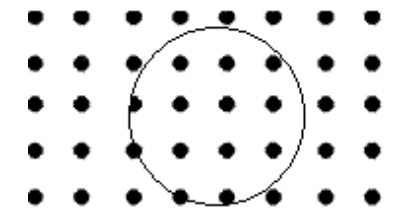
A physics student decided to fix three magnets in place and place iron filings around the magnets to view the magnetic field lines created. An image of what the student saw is shown above. According to this image what poles would have to be the same kind as pole E to produce the result shown above?
Select two answers.
B and D
Magnetic field lines _____.
leave the north pole and enter the south pole of a magnet
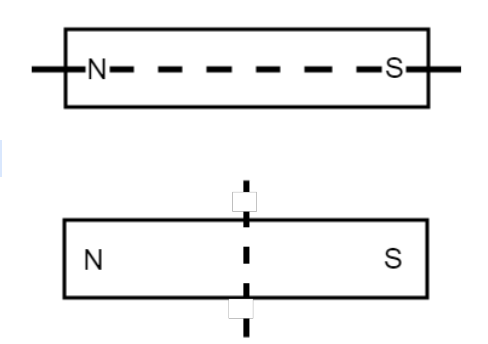
Assume that both magnets shown at right are far enough away that their forces do not affect each other. If each magnet shown was cut along the dotted line, then which statements below are true?
Select two answers.
1) The top pair of magnet would experience repulsion
2) The bottom pair of magnets would experience attraction
How can the magnetic flux through a coil of wire be increased? Select two answers.
1) Increase the magnitude of the magnetic field that passes through the loop.
2) Increase the cross-sectional area of the loop.
A loop of wire sits in an unchanging magnetic field. Which of the following is a not a way to induce a current through the loop?
spin the loop about its center
What is the SI unit for emf?
volt
A square loop of wire with 2 turns and a side length of 1.0 m is placed in a changing magnetic field. When the magnetic field changes from 2.0 T to 4.0 T within 8.0 s,
what is the average induced emf?
0.5 V
A square loop of wire with 10 turns and a side length of 1.0 m is placed in a changing magnetic field. If the magnetic field changes from 2.0 T to 4.0 T within 8.0 s, what is the average induced emf?
2.5 V
Which of the following will generate a current in a conducting loop?
Select two answers.
1) A magnet moving towards the loop.
2)The loop rotating on an axis perpendicular to the bar magnet.
A square coil of wire with a side length of 10 cm is looped around 10 times. The coil sits in an increasing magnetic field. The magnetic field increases linearly from 1.0 T to 2.0 within 5.0 s.
a. What is the induced emf of the coil?
0.02 V
A square coil of wire with a side length of 10 cm is looped around 10 times. The coil sits in an increasing magnetic field. The magnetic field increases linearly from 1.0 T to 2.0 within 5.0 s.
b. If the same loop of wire has a resistance of 2.0 Ω, what is the induced current in the loop?
0.01 A
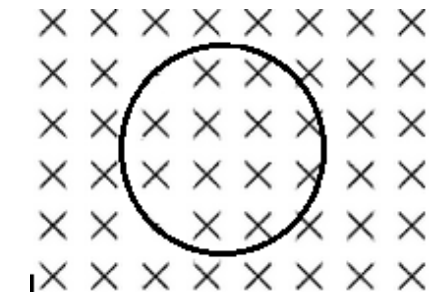
A conducting loop of wire is placed in an increasing magnetic field, B, directed into the page as shown. What is the direction of the induced current in the wire?
counterclockwise
Lenz’s law describes the direction of an induced current in a conductor by a changing magnetic flux. What other law can be used to find the direction?
The Law of Conservation of Energy
A circular loop of wire is placed in a magnetic field as shown. If the magnetic field is
increasing, what direction is the induced current in?
clockwise
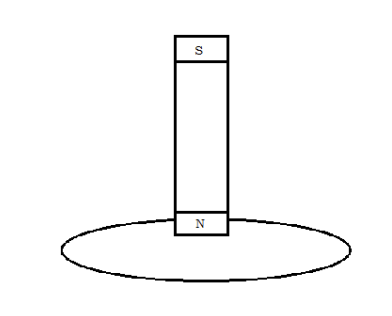
Why do you need to swipe your credit card in a credit card reader for it to accept
your charge?
The magnetic field in the credit card strip needs to move to induce a current in
the reader.
A magnet is slowly descending into a loop of wire. What
is the direction of the induced current?
counterclockwise
Which of the following laws is used to find the direction of the induced current in a
loop of wire placed in a changing magnetic field?
Lenz’s Law
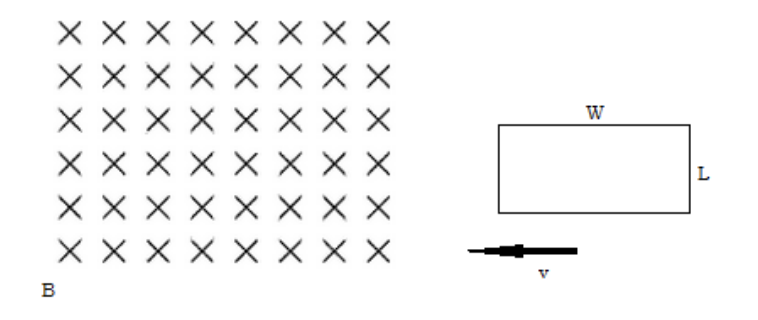
A loop of conducting wire with length, L, and width, W, enters a magnetic field, B, at velocity, v.
a) What direction is the induced current in the loop?
counterclockwise
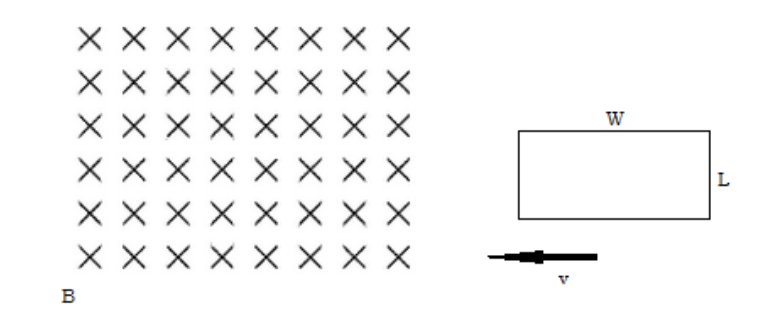
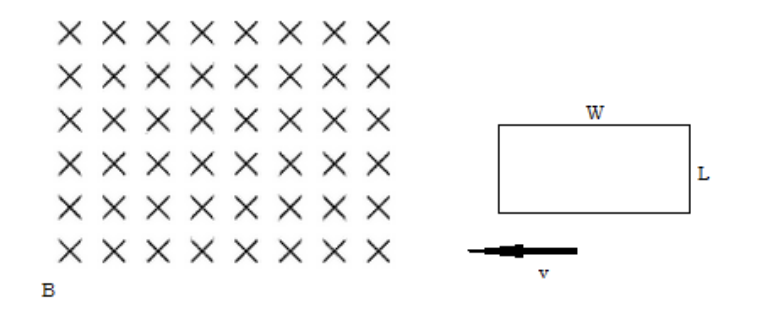
A loop of conducting wire with length, L, and width, W, enters a magnetic field, B, at velocity, v.
b) What is the induced emf?
BLv
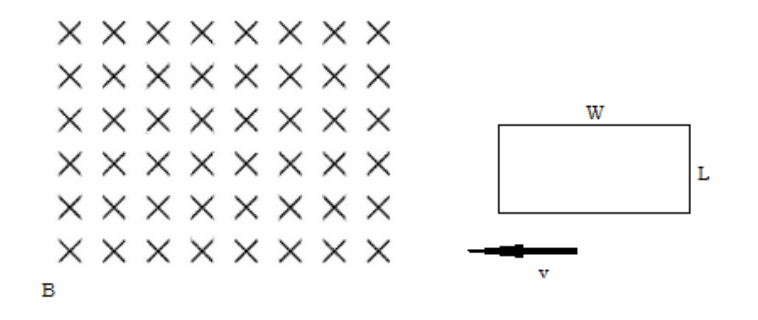
A loop of conducting wire with length, L, and width, W, enters a magnetic field, B, at velocity, v.
c) The loop of wire has a resistance R. What is the value of the induced current?
BLv/R
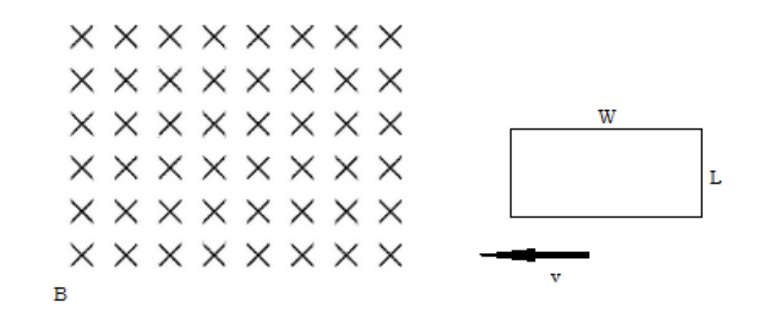
A loop of conducting wire with length, L, and width, W, enters a magnetic field, B, at velocity, v.
d) What is the direction of the magnetic force on the loop as it enters magnetic field B?
right
A loop of conducting wire with length, L, and width, W, enters a magnetic field, B, at velocity, v.
e) What is the direction of the magnetic force on the loop as it leaves magnetic field B?
right
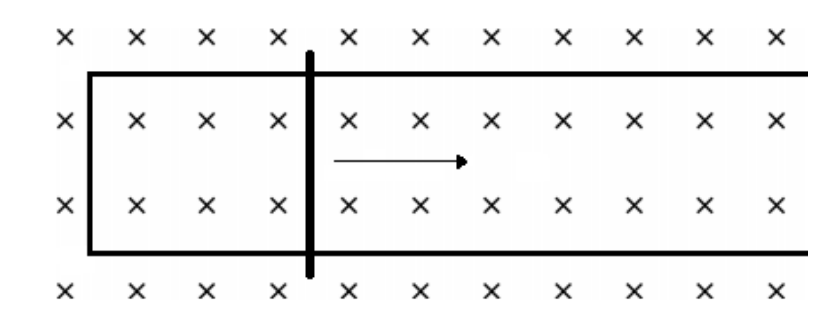
A conducting rod with length L moves horizontally on a set of conducting rails at a constant velocity v through a magnetic field, B.
a) What is the direction of the induced current in the circuit?
counterclockwise
A conducting rod with length L moves horizontally on a set of conducting rails at a constant velocity v through a magnetic field, B.
b) What is the induced emf in the circuit?
BLv
A conducting rod with length L moves horizontally on a set of conducting rails at a constant velocity v through a magnetic field, B.
c) If the resistance of the rod is R, what is the magnitude of the induced current in the circuit?
BLv/R
A conducting rod with length L moves horizontally on a set of conducting rails at a constant velocity v through a magnetic field, B.
d) What is the direction of the magnetic force?
left
A rod of length, L, lies on a set of conducting rails connected to a resistor, R. The rod is pulled to the right at a constant velocity v through a magnetic field, B. How much power is dissipated in the resistor as the rod is being pulled?
B²L²v²/R
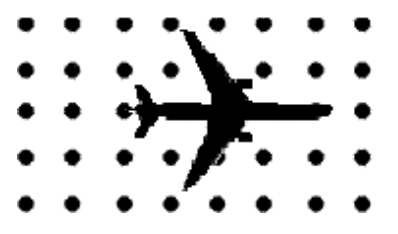
At the South Pole, the Earth’s magnetic field is directed upwards. If a plane is flying over the South Pole, which wing will have the higher potential?
the right wing
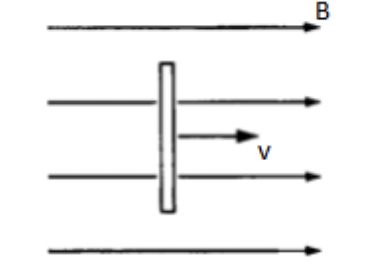
A conducting bar travels through magnetic field, B, at constant velocity, v. Which part of the bar has a higher electric potential?
neither
A metal bar is pushed along two conducting rails that are connected by a stationary wire parallel to the moving bar. What TWO factors are required to generate a constant current in the bar/rail/wire configuration? Select two answers.
1) An external constant perpendicular magnetic field within the bar/rail/wire
configuration.
2) The bar needs to be pushed so that it moves with a constant velocity.