PHYS1103_Unit 3_Energy and Momentum 낱말 카드 | Quizlet
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Front: What is the definition of work in physics?
Back: Work is the energy transfer that occurs when an object is moved over a distance by an external force parallel to the displacement.
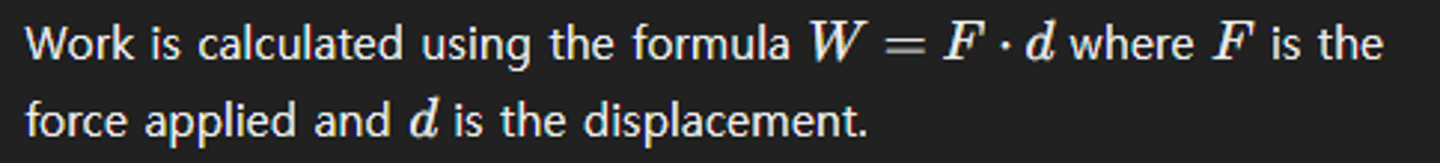
Front: How is work calculated when force and displacement are in the same direction?
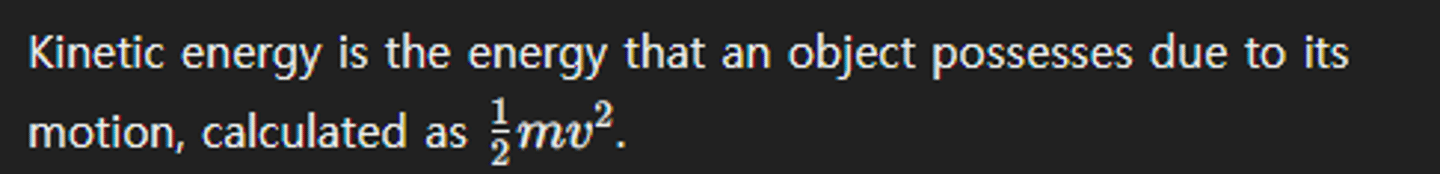
Define kinetic energy.
What does the Work-Energy Theorem state?
The theorem states that the work done on an object is equal to the change in its kinetic energy.
What is gravitational potential energy?

How is gravitational potential energy affected by height?
Gravitational potential energy increases with height because the energy is proportional to the distance from the ground.
What is a nonconservative force?
Nonconservative forces, such as friction, cause energy to be lost from the system, usually as heat.
How do nonconservative forces affect mechanical energy?
They decrease the total mechanical energy of a system because the work done by nonconservative forces is not recoverable.
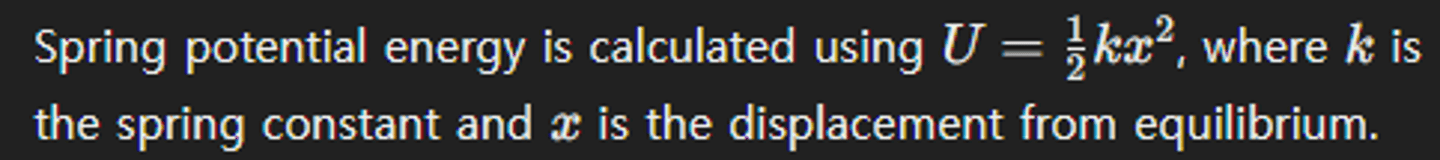
How is spring potential energy calculated?
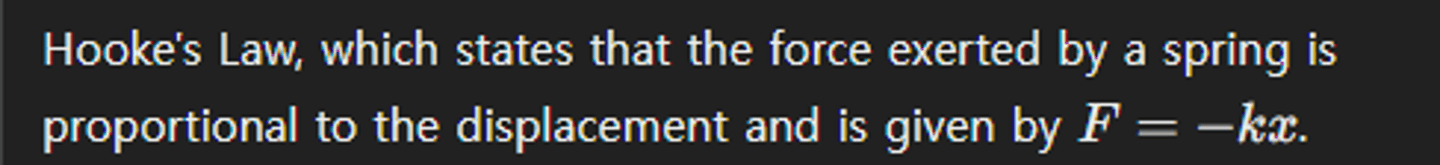
What law describes the force exerted by a spring?
What is the principle of conservation of mechanical energy?
This principle states that if only conservative forces are doing work, the total mechanical energy (kinetic plus potential) of a system remains constant.
How can you determine if energy is conserved in a system?
If nonconservative forces like friction are absent, or if their work is counterbalanced, energy is conserved.
Define power in physics.
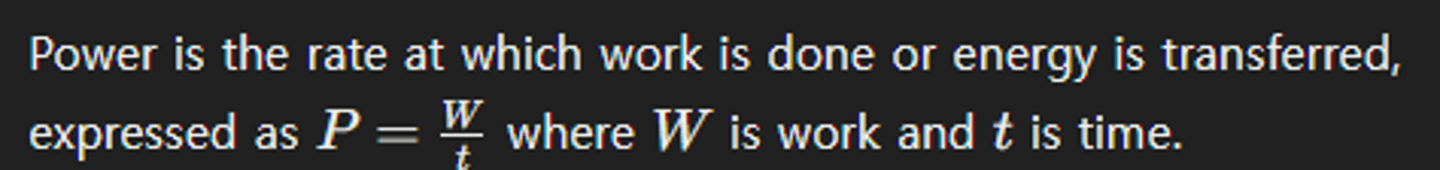
How is power related to energy?
Power is the time rate of energy use or transfer, indicating how fast energy is being converted from one form to another.
Explain how conservation of energy is used in analyzing roller coaster motion.
Conservation of energy allows us to relate the potential energy at the highest points to the kinetic energy at the lowest points, ignoring frictional losses.
What is the effect of a force perpendicular to the displacement on work?
A force perpendicular to the displacement does no work because the cosine of 90 degrees is zero.
Describe the energy transformations that occur when a spring drives a mass.
Potential energy stored in the spring is converted into kinetic energy of the mass as it moves away from equilibrium.
What happens to the total mechanical energy in a system when only conservative forces do work?
The total mechanical energy remains constant, although it may be redistributed between potential and kinetic forms.
How does increasing the angle of a ramp affect the power required to move an object up the ramp at constant velocity?
Increasing the angle increases the component of gravitational force opposing the motion, requiring more power to maintain the same velocity.
What is an instantaneous power and how is it calculated?

What role does the angle of force application play in calculating work done by a force?
The angle affects the component of force used to calculate work; only the component of force parallel to displacement contributes to work.
What is the significance of the spring constant in Hooke's Law?
The spring constant kkk measures the stiffness of the spring; higher kkk values mean a stiffer spring that requires more force to compress or stretch.
Explain the concept of energy transfer using power.
Power quantifies the rate at which energy is moved from one system to another, useful in understanding how quickly work is done or energy is used.
What factors influence the power needed to perform a task?
Factors include the amount of work to be done, the time available to do the work, and the presence of forces such as friction.
Describe a scenario where potential energy is converted back into kinetic energy.
A roller coaster reaches the top of a track (maximum potential energy) and then descends, converting potential back into kinetic energy.
What does it mean for a force to be conservative?
A conservative force, like gravity, does work that is fully recoverable from the system's potential energy, independent of the path taken.
How do you calculate the change in an object's mechanical energy due to work done by nonconservative forces?
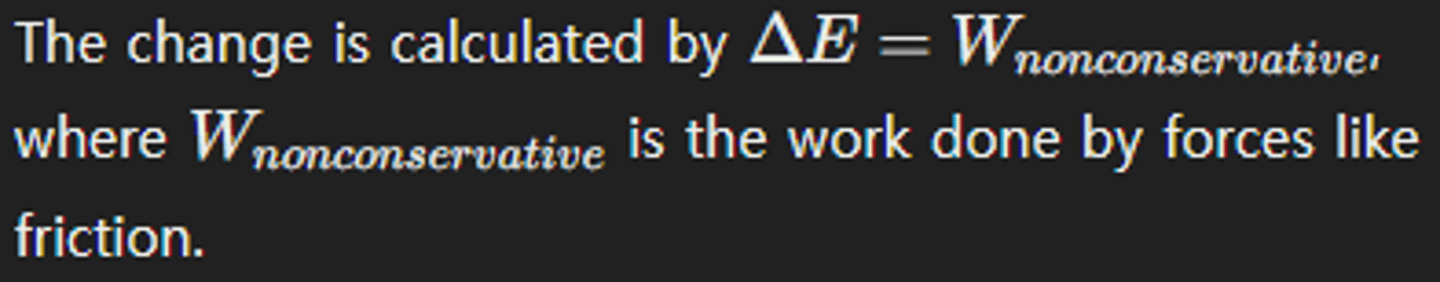
What unit is used to measure work and energy?
The Joule (J), where 1 Joule is the amount of work done when a force of one newton displaces an object by one meter in the direction of the force.
What is the relationship between force, work, and energy?
Work is the process of energy transfer via force acting over a distance. Energy is the capacity to do work.
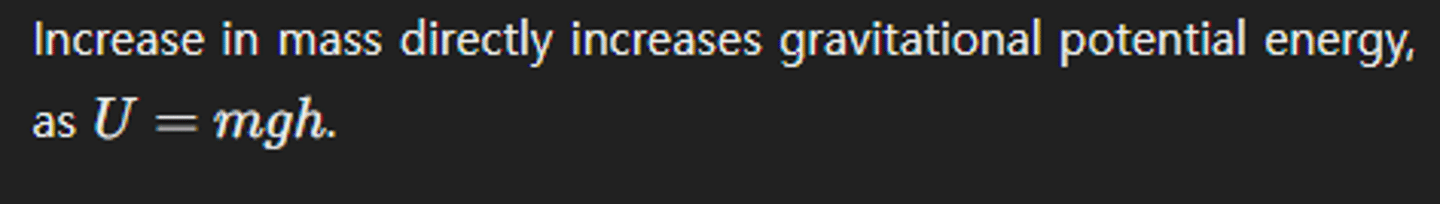
How does an increase in the mass of an object affect its gravitational potential energy?
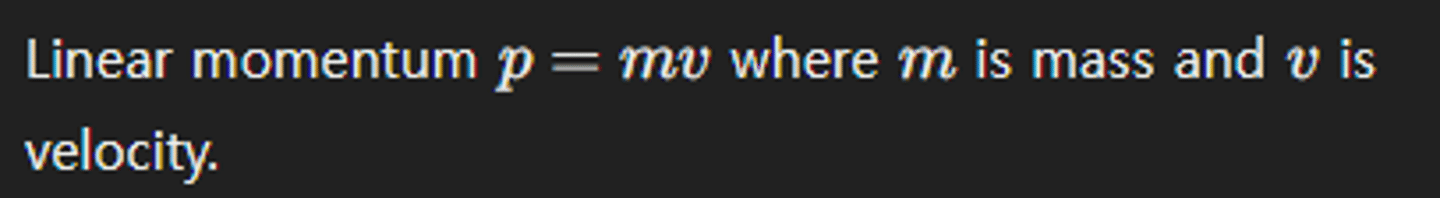
What is the formula for linear momentum?
What is the unit of momentum?
Kilogram meter per second (kg·m/s).
What is impulse?
Impulse is the change in momentum resulting from a force applied over a time interval.
How do you calculate impulse?
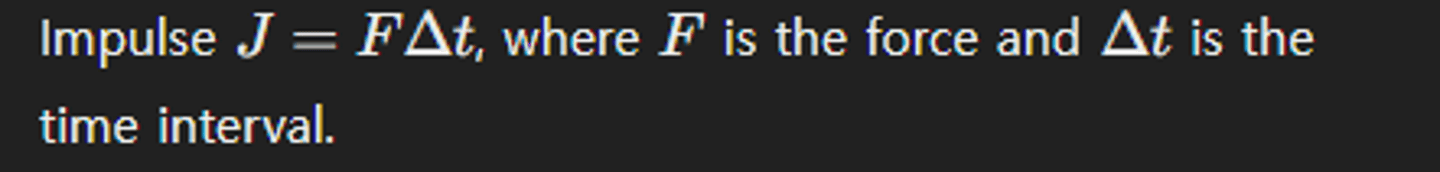
What does the impulse-momentum theorem state?
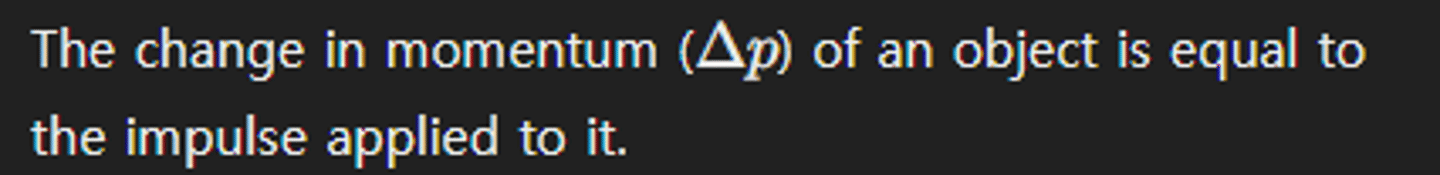
Define the law of conservation of momentum.
In a closed system, the total momentum before and after an event (like a collision) remains constant.
What is an elastic collision?
A collision where total kinetic energy and total momentum are conserved.
What is an inelastic collision?
A collision where the total kinetic energy is not conserved but momentum is.
How does the kinetic energy relate to momentum in a collision?
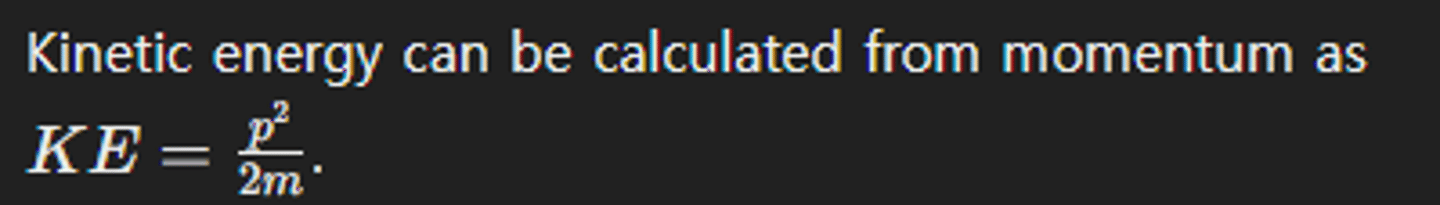
What is perfectly inelastic collision?
A type of collision where the colliding objects stick together after impact, maximizing kinetic energy loss.
What is the formula for final velocity in a perfectly inelastic collision?
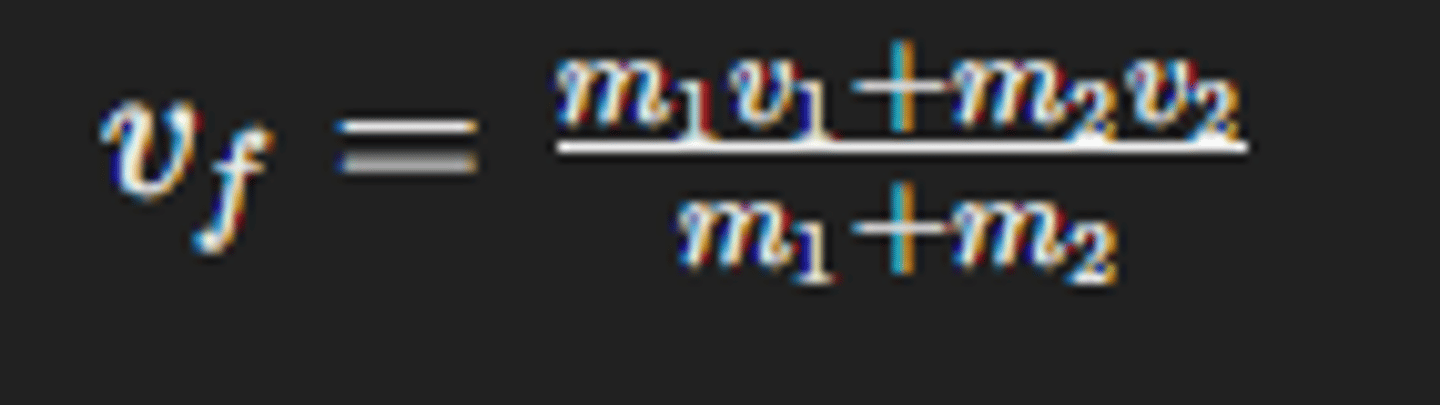
Describe momentum conservation in a two-object system.
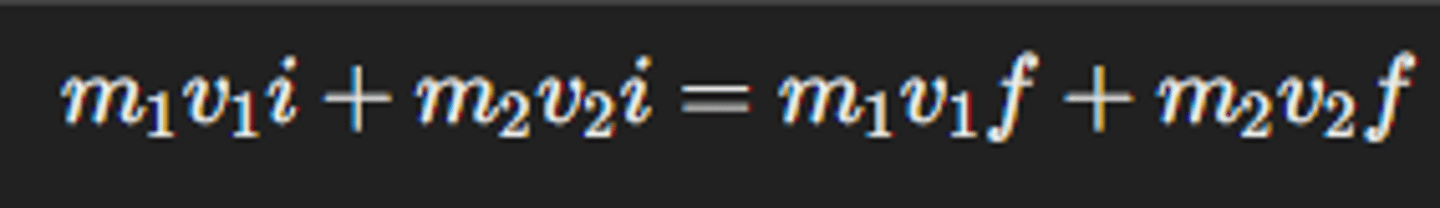
How do you calculate the speed of a projectile from recoil?

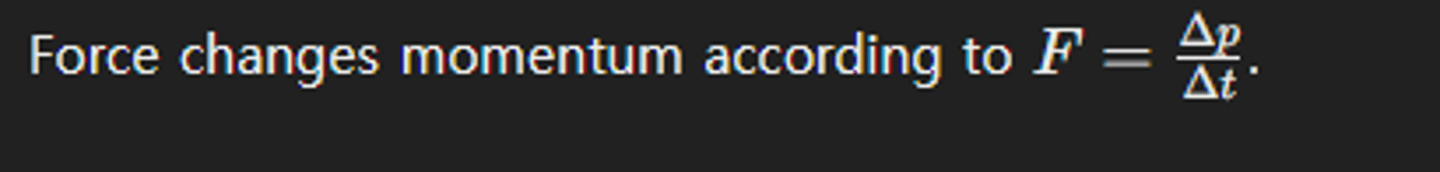
Explain the role of force in changing momentum.
How do you find the change in kinetic energy in a collision?
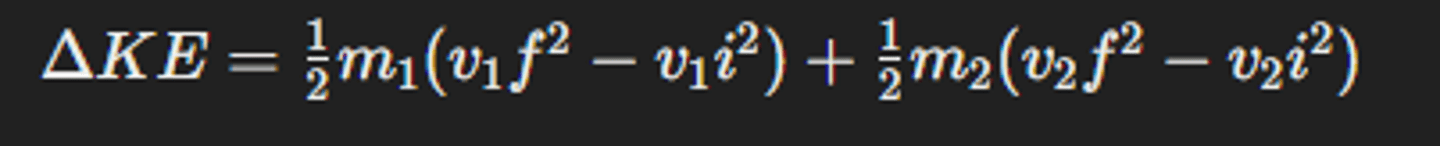
What is the significance of impulse having the same units as momentum?
It underscores the direct relationship between force exerted over time and the resultant change in momentum.
How is momentum conserved in explosions?
The total system momentum remains zero, as initial momentum (at rest) is zero.
What's the effect of an object's mass on its momentum?
Greater mass results in greater momentum for a given velocity.
How do velocities compare after a head-on elastic collision?
Velocities are exchanged between two objects of equal mass.
Describe Newton's cradle in terms of momentum and energy conservation.
Demonstrates conservation of momentum and kinetic energy through a series of elastic collisions.
How does angle affect momentum in a collision?
Momentum is conserved in each component direction independently.
How do you find the angle of deflection in a two-dimensional collision?
Using trigonometric relationships derived from conservation laws.
Explain how kinetic energy is not generally conserved but momentum is.
Kinetic energy can be converted to other forms like thermal energy, while momentum is conserved in isolated systems.
What is the significance of the coefficient of restitution in collisions?
It measures the elasticity of a collision, with 1 being perfectly elastic and 0 perfectly inelastic.
Why is momentum a vector quantity?
It depends on both the magnitude and the direction of velocity.
What happens to kinetic energy in an inelastic collision?
It decreases as some energy is transformed into heat or sound.
How does a cannon recoil relate to momentum conservation?
The cannon's backward momentum equals the forward momentum of the cannonball.
Why might two colliding objects have different final speeds?
Differences in mass and the direction of forces involved.
How does friction affect momentum on a horizontal surface?
Friction can reduce the system's kinetic energy but not its momentum.
What role does symmetry play in collisions?
In symmetrical systems, analysis simplifies as components can be mirrored, respecting conservation laws.