Week 2: Understanding Normal
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
1
New cards
3 general domains/dimensions
physical, cognative, social and emotional
2
New cards
Physical Domain
changes in height/ weight, gross/ fine motor skills, sensory capabilities, the nervous system
3
New cards
Cognitive Domain
changes in intelligence, wisdom, perception, problem solving and language
4
New cards
social and emotional domain
changes in emotion, self perception, interpersonal relationships with family, friends, peers
5
New cards
The periods of development
Prenatal Development (conception through birth)
- Infancy and Toddlerhood (birth through 2
years)
- Early Childhood (3 to 5 years)
- Middle Childhood (6 to 11 years)
- Adolescence (12 years to adulthood)
- Infancy and Toddlerhood (birth through 2
years)
- Early Childhood (3 to 5 years)
- Middle Childhood (6 to 11 years)
- Adolescence (12 years to adulthood)
6
New cards
Prenatal development
- conception to birth
- major structures of the body are forming
- health of mother and labour and delivery is primary concern
- major structures of the body are forming
- health of mother and labour and delivery is primary concern
7
New cards
Infancy and toddlerhood
- birth through 2 years
- dramatic growth and change
- walking, talking toddler
- dramatic growth and change
- walking, talking toddler
8
New cards
Early Childhood
- 3-5 years
- preschool years
- learning language
- gaining self and independence
- preschool years
- learning language
- gaining self and independence
9
New cards
Middle childhood
- 6-11
- school age
- growth rates slow down
- fine motor skills are refined
- social relationships beyond family members
- school age
- growth rates slow down
- fine motor skills are refined
- social relationships beyond family members
10
New cards
Adolescence
- 12 to adulthood
- overall physical growth-spurt
- sexual maturation
- sense of invincibility
- overall physical growth-spurt
- sexual maturation
- sense of invincibility
11
New cards
nature vs nurture
Nature:
- hereditary role in the upbringing of a child (genetic)
Nurture:
- Environments role: social interactions
- hereditary role in the upbringing of a child (genetic)
Nurture:
- Environments role: social interactions
12
New cards
Continuity vs Discontinuity
- The stage theories or discontinuous development assume change often occurs in distinct stages. At each stage, children have different qualities and characteristics
- Continuous theorists belive development is gradual and skills become more advanced with time.
- Continuous theorists belive development is gradual and skills become more advanced with time.
13
New cards
longitudinal research
pros:
starts with a group of people of the same age
- these groups can be followed over time and be compared with them when they were younger
- provides developmental analysis
cons
- expensive
- takes a long time
- participant attrition
starts with a group of people of the same age
- these groups can be followed over time and be compared with them when they were younger
- provides developmental analysis
cons
- expensive
- takes a long time
- participant attrition
14
New cards
cross-sectional research
pros:
- sample that represents are cross section of the population
- provides info on age related change
cons:
- cannot examine change over time
- cannot examine cohort efforts
- sample that represents are cross section of the population
- provides info on age related change
cons:
- cannot examine change over time
- cannot examine cohort efforts
15
New cards
sequential research
pros:
- combines aspects of the previous two techniques, beginning with a cross-sectional sample and measuring them through time
- good or studying: age, gender, social class
cons:
- expensive
- practice efforts
- combines aspects of the previous two techniques, beginning with a cross-sectional sample and measuring them through time
- good or studying: age, gender, social class
cons:
- expensive
- practice efforts
16
New cards
Biology and evolutionary theories
genetics and epigenetic interact with the environment to shape health/ wellbeing
- genes control specific characteristics
- polygenic (height) and recessive genes (red hair)
genotype and phenotype, patterns of inheritance
- genes control specific characteristics
- polygenic (height) and recessive genes (red hair)
genotype and phenotype, patterns of inheritance
17
New cards
Developmental Plasticity:
- developing fetuses form characteristics well adapted to the environments they are likely to live in
eg. temperatures, stress environments
eg. temperatures, stress environments
18
New cards
4 evolutionary theories:
Ethology:
- genetically determined survival behaviours that are assumed to have evolved through natural selection
Behaviour genetics:
- traits are influenced by genes - when related people are more similar than those who are unrelated
Evolutionary Psychology:
- the view that genetically inherited cognitive social traits have evolved through natural selection
Evolutionary developmental psychology:
- genetically inherited cognitive and social characteristics promote survival and adaptations at different times across
the lifespan (programmed with predispositions)
- genetically determined survival behaviours that are assumed to have evolved through natural selection
Behaviour genetics:
- traits are influenced by genes - when related people are more similar than those who are unrelated
Evolutionary Psychology:
- the view that genetically inherited cognitive social traits have evolved through natural selection
Evolutionary developmental psychology:
- genetically inherited cognitive and social characteristics promote survival and adaptations at different times across
the lifespan (programmed with predispositions)
19
New cards
Evolutionary theories:
The good, the bad, the ugly
The good, the bad, the ugly
good:
- understanding biology improves precision medicene
bad:
- large emphasis on heredity
ugly:
- may underestimate impact on environment
- understanding biology improves precision medicene
bad:
- large emphasis on heredity
ugly:
- may underestimate impact on environment
20
New cards
Epigenetics
the study of changes stemming from the modification of gene expression rather than the alteration of the genetic code
- epigenetic markers regulate gene expression (turn genes off and on)
- by controlling gene expression
- epigenetic markers regulate gene expression (turn genes off and on)
- by controlling gene expression
21
New cards
Sigmund Freud's Psychosexual Theory
- personality forms during the 1st few years of life
- parents/ caregivers have a big impact on children's emotional state
- proven wrong since research has proven children can overcome harsh backgrounds with no emotional scars
- parents/ caregivers have a big impact on children's emotional state
- proven wrong since research has proven children can overcome harsh backgrounds with no emotional scars
22
New cards
Freuds 3 parts to self:
id:
- inborn
- biological urges
- the thing that feels good to do
- eg. newborn crying when hungry
- PLEASURE PRINCIPLE - guided by need and selfishness
ego:
- develops through interaction with others
- guided by logic or reality
- mediates between id and superego using logic and reality to calm the other parts of the self
- defence mechanisms
- REALITY PRINCIPLE
superego:
- concerned by what is socially acceptable
- guided by guilt, values, morals, conscience
- MORALITY PRINCIPLE
- inborn
- biological urges
- the thing that feels good to do
- eg. newborn crying when hungry
- PLEASURE PRINCIPLE - guided by need and selfishness
ego:
- develops through interaction with others
- guided by logic or reality
- mediates between id and superego using logic and reality to calm the other parts of the self
- defence mechanisms
- REALITY PRINCIPLE
superego:
- concerned by what is socially acceptable
- guided by guilt, values, morals, conscience
- MORALITY PRINCIPLE
23
New cards
Freuds stages
oral stage:
- infant is id
- simulation and comfort is focused on mouth and sucking
- too much or too little may lead to fixation
Anal stage:
- potty training
- learning to control biological urges
- ego develops
Phallic stage:
- marks the development of the superego and a sense of masculinity or femininity
Latency:
- child's urges quiet down and friendships become the focus. ego and superego become refined
Genital stage:
- begins with puberty and continues through adulthood. preoccupation is sex and reproduction
- preoccupation is of sex and reproduction
- infant is id
- simulation and comfort is focused on mouth and sucking
- too much or too little may lead to fixation
Anal stage:
- potty training
- learning to control biological urges
- ego develops
Phallic stage:
- marks the development of the superego and a sense of masculinity or femininity
Latency:
- child's urges quiet down and friendships become the focus. ego and superego become refined
Genital stage:
- begins with puberty and continues through adulthood. preoccupation is sex and reproduction
- preoccupation is of sex and reproduction
24
New cards
Psycho-analytic Feminism
- dominated by Freud
- Chodorow emphasized the difference in mother-daughter vs. mother-son relationship
- mother son relationships= independent sons
- mother daughter relationships = feminine daughters
- Chodorow emphasized the difference in mother-daughter vs. mother-son relationship
- mother son relationships= independent sons
- mother daughter relationships = feminine daughters
25
New cards
Erik Erikson's Psychosocial Theory
- student of freud but emphasized the importance of the ego, or conscious urges/ thought
- considered father of developmental psychology because his model gives us a guideline for the entire lifespan and suggests primary social and psychological concerns throughout life
- emphasizes continued development during adulthood
- considered father of developmental psychology because his model gives us a guideline for the entire lifespan and suggests primary social and psychological concerns throughout life
- emphasizes continued development during adulthood
26
New cards
Erikson's 8 stages (crises) of the lifespan
trust vs mistrust (0-1):
- infant has basic needs met in a consistent way in order to trust the world
.
Autonomy vs. shame and doubt (1-2):
- mobile toddlers exercise and learn independence
.
Initiative vs. guilt (3-5):
- preschoolers doing things "all by myself"
.
Industry vs. inferiority (6-11):
- school children focus on accomplishments and make comparisons between themselves and classmates
.
Identity vs role confusion (adolescence)
- teens gain a sense of identity as they experiment
.
Intimacy vs. Isolation (young adulthood):
- long term relationships in our 20s and 30s
Generativity vs. stagnation (middle adulthood):
- 40s and 60s focus on productivity and focus on contribution to society
Integrity vs. despair (late adulthood):
- look back on lives and have sense of integrity
- infant has basic needs met in a consistent way in order to trust the world
.
Autonomy vs. shame and doubt (1-2):
- mobile toddlers exercise and learn independence
.
Initiative vs. guilt (3-5):
- preschoolers doing things "all by myself"
.
Industry vs. inferiority (6-11):
- school children focus on accomplishments and make comparisons between themselves and classmates
.
Identity vs role confusion (adolescence)
- teens gain a sense of identity as they experiment
.
Intimacy vs. Isolation (young adulthood):
- long term relationships in our 20s and 30s
Generativity vs. stagnation (middle adulthood):
- 40s and 60s focus on productivity and focus on contribution to society
Integrity vs. despair (late adulthood):
- look back on lives and have sense of integrity
27
New cards
Learning Theories
- focus on how experience in the environment shape the child
- human behaviour is seen as being shaped by processes such as classical and operant conditioning
- human behaviour is seen as being shaped by processes such as classical and operant conditioning
28
New cards
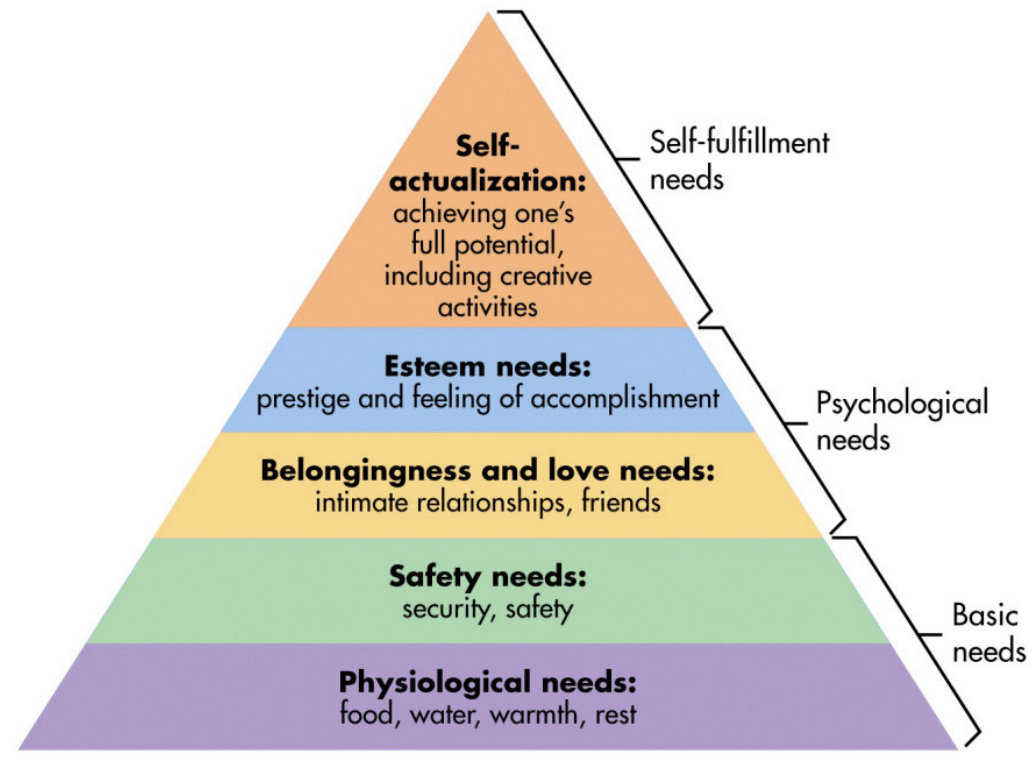
Humanistic alternative
image: Maslow's Hierarchy of needs
- most important internal drive is to achieve one's full potential- self actualization is the ultimate goal in human life
- most important internal drive is to achieve one's full potential- self actualization is the ultimate goal in human life
29
New cards
Carl Rogers, Inherent optimism
- focused on capacity of each person to become a 'fully functioning person' without guilt or seriously distorting defences
- not linear, more freedom than Freud and Eriksons theories
- however hard to test and measure
- not linear, more freedom than Freud and Eriksons theories
- however hard to test and measure
30
New cards
Behaviorism
- rejected any reference to mind and viewed overt and observable behaviour as the proper subject matter
- Pavlov, Watson, Skinner, Bandura
- Pavlov, Watson, Skinner, Bandura
31
New cards
Ivan Pavlov
- studied digestion and salivation in his lab dogs
- he figured out dogs learned to associate the sound of a bell with food and would salivate
- This learned response, he called= conditioned response
- classical conditioning
- he figured out dogs learned to associate the sound of a bell with food and would salivate
- This learned response, he called= conditioned response
- classical conditioning
32
New cards
John B. Watson
- fears and emotional responses are classically conditioned
- expert on parenting advice
- Little Albert experiments
- Introduced him to 'scary' objects to see his response
- introduced little alberts favourite white rat with the sound of a loud noise
- little Albert began to fear the rat because he feared the loud noise
- expert on parenting advice
- Little Albert experiments
- Introduced him to 'scary' objects to see his response
- introduced little alberts favourite white rat with the sound of a loud noise
- little Albert began to fear the rat because he feared the loud noise
33
New cards
B.F. Skinner and Operant Conditioning
- reinforcement is more effective than punishment
positive reinforcement
- cookie for cleaning your room
negative reinforcement
- electric fence shocking animals when they go near it
positive reinforcement
- cookie for cleaning your room
negative reinforcement
- electric fence shocking animals when they go near it
34
New cards
MUST UNDERSTAND!! difference between Pavlov's classical conditioning and Skinners operant conditioning
Classical:
- stimulus - involuntary response
- dog salivation
- think Jim giving Dwight mints at the sound of his computer
Operant
- punishment behaviour
- positive reinforcement
- negative reinforcement
- rat in a box
- stimulus - involuntary response
- dog salivation
- think Jim giving Dwight mints at the sound of his computer
Operant
- punishment behaviour
- positive reinforcement
- negative reinforcement
- rat in a box
35
New cards
Albert Bandura,
Social learning theory
Social learning theory
- learning doesn't always require reinforcement
- emphasis on attention, memory and motivation
- learn through observation, imitation and modelling
- emphasis on attention, memory and motivation
- learn through observation, imitation and modelling
36
New cards
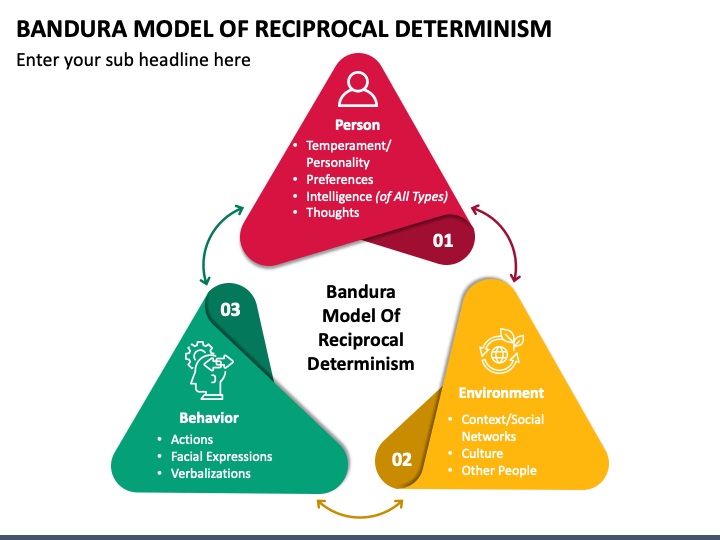
Reciprocal Determinism
Bandura's central social learning theory
- model composed of three factors that influence behaviour:
- the individual (including how they think and feel),
- their environment
- behaviour itself.
- model composed of three factors that influence behaviour:
- the individual (including how they think and feel),
- their environment
- behaviour itself.
37
New cards
Cognitive theories
- emphasize mental aspects of development
- logic and memory
- logic and memory
38
New cards
Piaget, theory of cognitive development
understanding is motivated by what we see and what we know. Knowledge is created in categories
- cognitive theory based on scheme, assimilation, accommodation and equilibrium
Scheme:
- internal cognitive procedure eg. brushing teeth
- the way children interpret the world
Assimilation:
- process of applying schemes to experiences
- interpret schemes through assimilation
Accommodation:
- changing the scheme as a result of new information
Equilibration:
- balance of assimilation and accommodation
- learning what works and what doesn't
example:
- scheme: child looks in the sky and sees a bird
- assimilation: child sees plane (sees it has wings, pointed front and flies = must be a bird)
- Accommodation: Adult tells child that its actually a plane (doesn't have eyes and has wheels) - child can now see the difference between bird and plane
- equilibration: refining and transforming schemes as a whole
- cognitive theory based on scheme, assimilation, accommodation and equilibrium
Scheme:
- internal cognitive procedure eg. brushing teeth
- the way children interpret the world
Assimilation:
- process of applying schemes to experiences
- interpret schemes through assimilation
Accommodation:
- changing the scheme as a result of new information
Equilibration:
- balance of assimilation and accommodation
- learning what works and what doesn't
example:
- scheme: child looks in the sky and sees a bird
- assimilation: child sees plane (sees it has wings, pointed front and flies = must be a bird)
- Accommodation: Adult tells child that its actually a plane (doesn't have eyes and has wheels) - child can now see the difference between bird and plane
- equilibration: refining and transforming schemes as a whole
39
New cards
Piagets 4 stages of cognitive development
Sensorimotor (0-2):
- Sensory curiosity about the world
- language for demands
Pre Operational (2-7):
- symbolic thinking
- proper grammar
- strong imagination
Concrete operational (7-11):
- time, space, quantity understood but not
applied
Formal Operational (11+):
- theoretical and hypothetical thinking
- abstract logic and reasoning
- concepts can be applied in context
- Sensory curiosity about the world
- language for demands
Pre Operational (2-7):
- symbolic thinking
- proper grammar
- strong imagination
Concrete operational (7-11):
- time, space, quantity understood but not
applied
Formal Operational (11+):
- theoretical and hypothetical thinking
- abstract logic and reasoning
- concepts can be applied in context
40
New cards
Vygotsky
Concentrated on child's interaction with peers and adults - child is apprentice
- socio-cultural theory asserts complex forms of thinking have their origins in social interactions
- scaffolding (guidance)
eg. helping a child learn to walk
- Zone of proximal development
- socio-cultural theory asserts complex forms of thinking have their origins in social interactions
- scaffolding (guidance)
eg. helping a child learn to walk
- Zone of proximal development
41
New cards
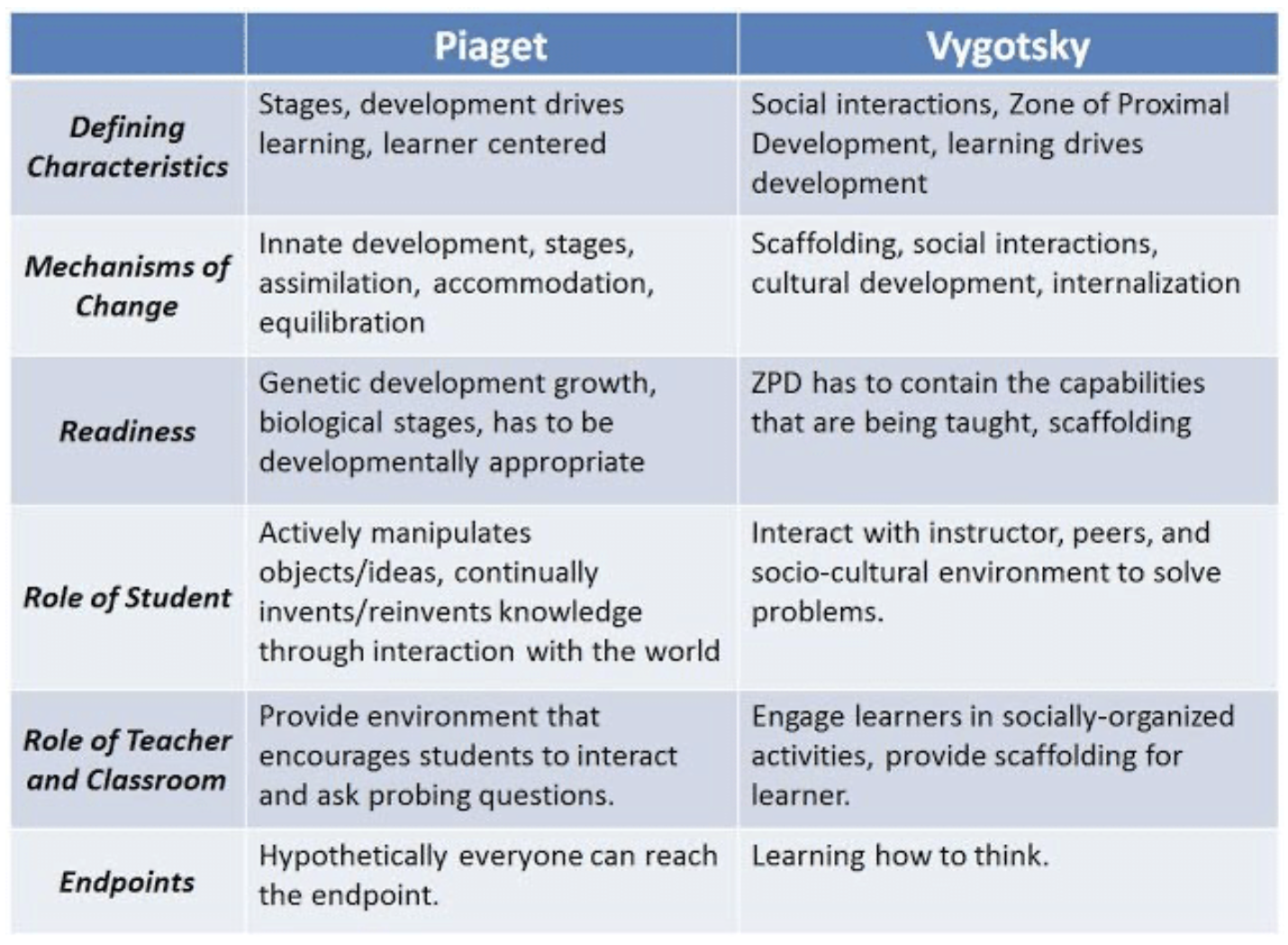
Piaget vs Vygotsky
Vygotsky:
- child's immediate social and cultural interactions with peers and adults
Piaget:
- child actively discovering the world through individual actions with it
- child's immediate social and cultural interactions with peers and adults
Piaget:
- child actively discovering the world through individual actions with it
42
New cards
Systems Theory
- personal and external factors form a dynamic integrate theory
HOLSIM - whole is primary and often greater than the sum of its parts
WELLNESS
- a result of adaptive adjustment
HOLSIM - whole is primary and often greater than the sum of its parts
WELLNESS
- a result of adaptive adjustment
43
New cards
Brofenbrenner
- Studied Freud, Erikson and Piaget
- foundation of scientific approaches to early childhood initiatives
- focused on relationships between environment and people
-eg. if a child is struggling to learn math, we have to look at all possible aspects of their learning, teacher, child's friends, classroom
- foundation of scientific approaches to early childhood initiatives
- focused on relationships between environment and people
-eg. if a child is struggling to learn math, we have to look at all possible aspects of their learning, teacher, child's friends, classroom
44
New cards
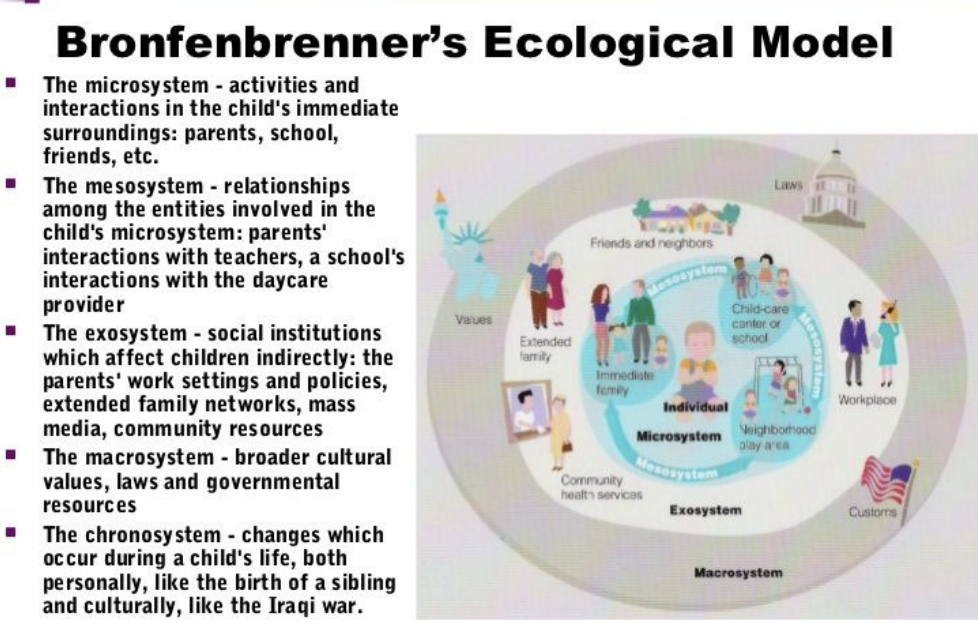
Brofenbrenners ecological model
The microsystem:
- immediate surroundings
- parents, school friends, family
The Mesosystem:
- relationships among the microsystem
- teachers + parents, friends and teachers
Exosystem:
- social institutions indirectly affecting child
- parents work, family network, community
resources
Macrosystem:
- broader cultural values, laws, governmental resources
Chronosystem:
- changes in a child's life
- birth of sibling, death of family member, war
- immediate surroundings
- parents, school friends, family
The Mesosystem:
- relationships among the microsystem
- teachers + parents, friends and teachers
Exosystem:
- social institutions indirectly affecting child
- parents work, family network, community
resources
Macrosystem:
- broader cultural values, laws, governmental resources
Chronosystem:
- changes in a child's life
- birth of sibling, death of family member, war
45
New cards
Complexity Theory
- grew from systems theory
- emphasized interactions and accompanying feedback loops
- systems are unpredictable and constrained by order-generating rules
- moves away for any oversimplification of childhood development
- emphasized interactions and accompanying feedback loops
- systems are unpredictable and constrained by order-generating rules
- moves away for any oversimplification of childhood development
46
New cards
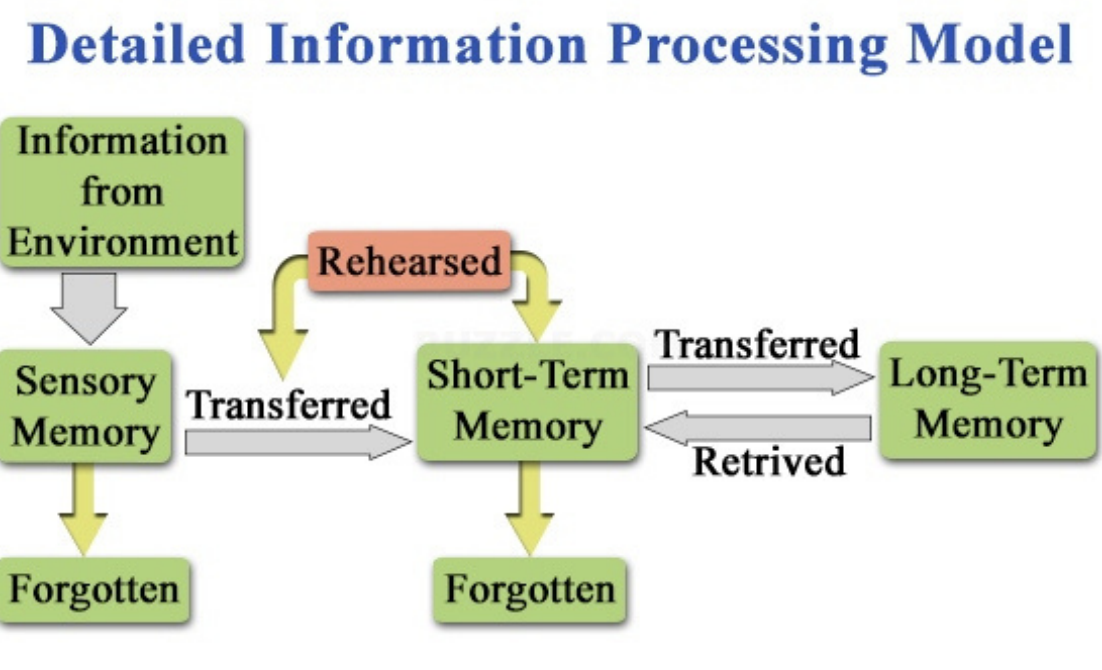
Detailed Information Processing model
47
New cards
Summary of each theory:
Bio/Evolutionary:
- genetics are selected for in terms of survival and adaptation
Psychoanalytical:
- internal drives and emotions impact behaviour
Learning:
- Experiences in the environment shape the child
cognitive:
- emphasize mental aspects of development (logic and memory)
- genetics are selected for in terms of survival and adaptation
Psychoanalytical:
- internal drives and emotions impact behaviour
Learning:
- Experiences in the environment shape the child
cognitive:
- emphasize mental aspects of development (logic and memory)
48
New cards
Kent Thornburg TEDx video Key points
- Americas health has been declining over the past 35 years
- obesity, diabetes, high blood pressure increasing (basis of heart disease)
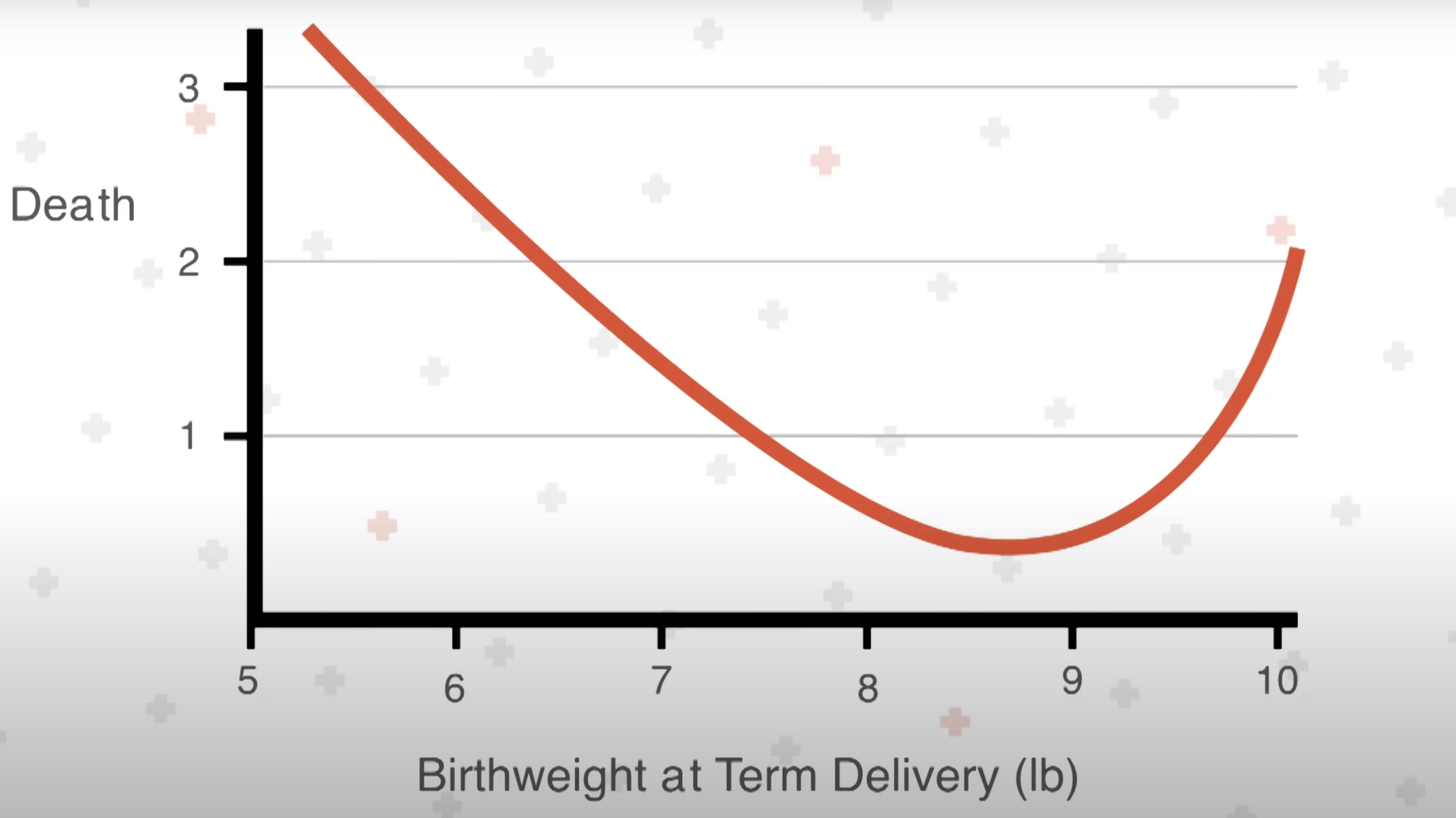
- David Barker showed chronic disease curve:
--born at 5 pound end of the birth weight scale, you
have a 5x higher risk of dying of heart disease
-- same with babies born at the 9 pound area
- how you grow before you are born MATTERS
- babies born small have more issues: less heart cells, fewer kidney filtering units, fewer insulin cells in pancreas
- babies born big have too much nutrition - too much glucose deposited into fat
- the egg that made in me was made in tanya's ovary in grannies womb
- the egg that made me was nourished by granny
- the nutrition a woman gives her baby comes from her diet AND the body she made when she was a child
- Epigenetics
- in 2015, 1 in 8 people are diabetic
- in 2050, 1 in 3 people will be diabetic
- obesity, diabetes, high blood pressure increasing (basis of heart disease)
- David Barker showed chronic disease curve:
--born at 5 pound end of the birth weight scale, you
have a 5x higher risk of dying of heart disease
-- same with babies born at the 9 pound area
- how you grow before you are born MATTERS
- babies born small have more issues: less heart cells, fewer kidney filtering units, fewer insulin cells in pancreas
- babies born big have too much nutrition - too much glucose deposited into fat
- the egg that made in me was made in tanya's ovary in grannies womb
- the egg that made me was nourished by granny
- the nutrition a woman gives her baby comes from her diet AND the body she made when she was a child
- Epigenetics
- in 2015, 1 in 8 people are diabetic
- in 2050, 1 in 3 people will be diabetic