INTECH 3201 - Cryptography and Encryption
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Cryptography and Encryption
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Cryptography
The art of communication between two users via coded messages
Encryption
The process of scrambling data into a code that can only be decoded with a key.
Plaintext
The original representation of the information
Ciphertext
The encoded version of the information
Encryption key
A unique digital key that unlocks the code
Decryption
The process of turning ciphertext back into plaintext
earliest written evidence of encryption can be traced to ancient ___. Nearly ____ years ago
Egypt, 4’000
tomb of nobleman ____ contained a script recording his deeds in life (ENCRYPTED)
Khnumhotep II
Ancient encryption in Egypt was used mainly to ______, as education was a privilege limited to the highest circles of society and was also a way to show one’s skills in writing. It was also used for religious reasons, for example, to discuss taboos.
protect knowledge
The first recorded instance of encryption being used for military purposes dates to around ____ BC
500
scytale
Spartan encryption used an invention called the ______, which allowed secret messages to be sent and received.
common key
first time the concept of a ____, seen even today in modern cryptographic technologies, was used for both encryption and decryption.
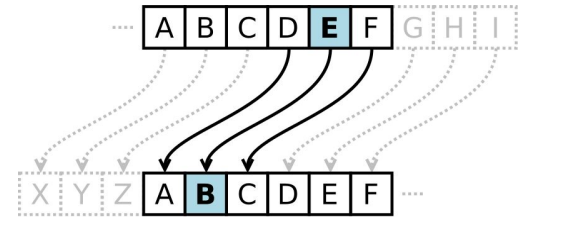
Caesar Shift Cipher
World War II (ENIGMA)

World War II (ENIGMA)
has an electromechanical rotor mechanism that scrambles the 26 letters of the alphabet.
When did data encryption become popular?
Through the early 1970s, cryptology was dominated by governments both because computers were very expensive and because of the need for information retention.
RSA algorithm (named after its inventors ______, ______, __________)
Ron Rivest, Adi Shamir, and Leonard Adleman
RSA introduced the concept of a __________ for encryption
public-private key pair
Confidentiality
Integrity
Authentication
Non-repudiation
Key management
Cryptography - Principles
Confidentiality
Cryptography - Principles - The main idea of Confidentiality is to keep data safe so that information stays private and secure
Cryptography - Principles -
Integrity means ensuring that our data in transit or after receiving is intact or not.
It is the ability to make sure that data or information has not been changed or modified with.
Integrity
Cryptography - Principles -
Authentication is the process of validating the identity of a user or device. Cryptographic methods, like digital signatures, can be used to securely verify the identification of a person or device.
Authentication
Cryptography - Principles -
___________ is a method of stopping a person from denying that he or she has committed a particular act or crime.
Non-repudiation
Cryptography - Principles -
Key management is the process of creating, distributing, and managing cryptographic keys
Key Management
2 main type of cryptographic systems
Symmetric
Asymmetric
Symmetric Encryption
________ uses a single key for both encryption and decryption. The sender and receiver must share this key securely.
How symmetric encryption works?
▪ The sender encrypts the plaintext using a secret key and an encryption algorithm (e.g., AES). ▪ The encrypted ciphertext is sent to the receiver. ▪ The receiver decrypts the ciphertext using the same secret key to retrieve the original plaintext.
Examples of Symmetric Encryption Algorithms
▪ Data Encryption Standard (DES) – A 56-bit key encryption method, now considered weak.
▪ Triple DES (3DES) – An improved version of DES that applies encryption three times. ▪ Advanced Encryption Standard
▪ (AES) – A widely used and highly secure algorithm with key sizes of 128, 192, or 256 bits.
Advantages of Symmetric Encryption
Fast and efficient (suitable for large amounts of data).
Requires less computational power compared to asymmetric encryption.
Disadvantages of Symmetric Encryption
Key distribution is a challenge—if the key is intercepted, security is compromised. Not ideal for secure communication between unknown parties.
Asymmetric Encryption
______, also known as public-key cryptography, uses two keys: Public Key (used for encryption) Private Key (used for decryption)
Asymmetric Encryption
type of encryption where The public key is shared openly, while the private key is kept secret.
How asymmetric encryption works?
The sender encrypts the plaintext using the recipient’s public key. ▪ The encrypted message (ciphertext) is sent to the receiver. ▪ The receiver decrypts the ciphertext using t
Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA) – A widely used encryption algorithm, often used for securing online transactions and emails.
Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) – A more efficient alternative to RSA, used in mobile and IoT security.
Examples of Asymmetric Encryption Algorithms
Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA) – A widely used encryption algorithm, often used for securing online transactions and emails.
Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) – A more efficient alternative to RSA, used in mobile and IoT security.
Advantages of Asymmetric Encryption
Disadvantages of Asymmetric Encryption
Slower than symmetric encryption due to complex computations.
Requires more computational power.
Real-World Use Case

Real-World Use Case
