Week 3 - Visual Agnosia
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Visual Agnosia
A neurological disorder which interferes with the ability to recognise visual stimuli.
Distortions of perception with visual agnosia can not be explained by:
can not be explained by:
memory
attention
language problems
lack of familiarity
what perceptual systems can agnosia affect
Visual, auditory and somatosensory
apperceptive agnosia
Inability to accurately perceive visually presented stimuli as a whole.
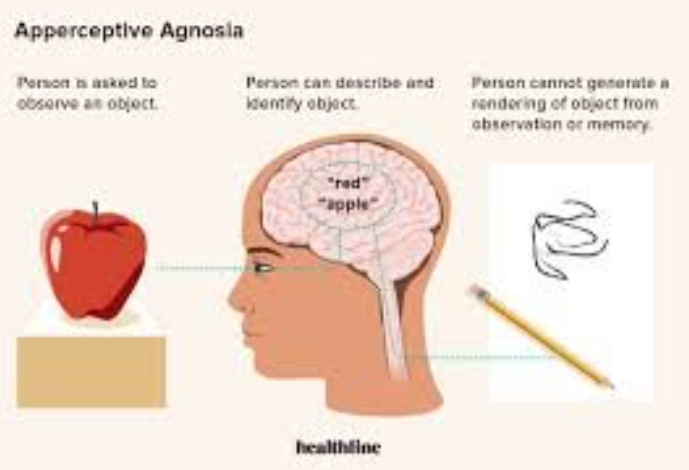
What can and can’t a person with apperceptive agnosia do?
Can:
see visual stimulus
can describe/verbally name objects
identify using non-visual cues
Can’t:
perceive or process visual stimulus as whole
draw an image of visual stimulus
recognise stimulus
what is apperceptive agnosia caused by?
dementia
physical injury
oxygen deprivation
carbon monoxide poisoning
brain tumor
damage to posterior of brain
associative visual agnosia
inability to recognise/retrieve knowledge from memory despite being able to perceive visual stimuli.
What can and can’t a person with associative agnosia do?
can:
perceive visual stimulus
draw visual stimulus
describe physical features of object
can’t:
recognise and name objects visually
recognise faces or words (severe)
what is associative agnosia caused by?
injury
lesion in temporal lobe
Differences between apperceptive and associative agnosia
Apperceptive:
lesions to parietal and occipital lobe
Unable to process or perceive visual stimuli
Unable to recognise stimulus
Unable to draw or copy a drawing of stimulus
Associative:
lesions to temporal lobe
Able to process or perceive visual stimuli
Unable to translate perception into recognition
Able to draw or copy a drawing of stimulus
Prosopagnosia
Inability to recognise familiar faces.
What cues must someone with prosopagnosia rely on to identify people?
hair
tattoos
age
gender
way a person walks
voice
What causes prosopagnosia?
autism
lesions in occipital and temporal lobe (linked with facial perception)
Alzheimers
Agnostic Alexia
Also referred to as pure agnosia or letter by letter reading, the inability to read words but are able to write and spell them.
What is the cause of Agnostic Alexia?
When language functions remain intact but have an impairment when recognising words. Has to do with visually identifying words rather than a language imparement.
What causes Agnostic Alexia?
Lesion in occipital lobe
What can and can’t someone with Agnostic Alexia do?
can:
recognise objects, people, symbols without difficulty
write normally
understand spoken language perfectly
can’t:
read fluently
colour agnosia
Inability to distinguish difference of colours despite having functional colour vision.
What can and can’t someone with colour agnosia do?
can:
name a colour individually
name an object individually
see colour
can’t:
correlate an object with it’s associated colour
verbally describe colours of an object
what causes colour agnosia?
damage to the temporal and occipital lobe on the left hemisphere.
akinetopsia
inability to perceive motion. Can be present in either two forms: permanent or transient
What can akinetopsia look like depending on severity?
complete → seeing motion as a series of images
inconspicuous → seeing motion as slowed/blurred
What can and can’t someone with akinetopsia do?
can:
perceive motionless objects
recognise static facial expressions
identify slow movement
can’t
perceive continuous motion (objects jump from one place to another)
pour liquids accurately
What causes akinetopsia? And where does it occur?
damage to MT/V5 in brain
bilateral damage
medication
seizure/migraine
simultanagnosia
inability to perceive multiple objects at once caused by damage in the posterior parietal lobe.
What can and can’t someone with simultanagnosia do
can:
perceive one object at a time
can’t:
perceive multiple objects at once
see a visual scene as a whole
topographical agnosia
inability to perceive location in relation to familiar environments.