BIO- DNA structure and Function
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Fredrich Meischer
Isolated phosphate rich acidic compounds from the nuclei of leucocytes in pus hospital bandages, and called it Nuclein.
Fredrick Griffiths
Transforming Principle— Used strands of streptococcus pneumonia in rats (S and R) and injected mice with a heat-killed mixture of both, later concluding that something had transformed after recovering the S-Strain bacteria.
Oswald Avery Colin Macleod, and Maclyn McCarty
In 1944, they concluded that the Transforming Principe was most likely nucleic acids. they recovered the cell extracts of the S-Strain mice and used enzymes to degrade macromolecules. They mixed these extracts with the R-Strain and injected the mice.
Breaks lipids Down
Lipase
Breaks down Nucleic acids.
DNAse and RNAse
Breaks proteins down
Trypsin
Hershey and Chase
The Blender experiment— Injected bacteriophages with radiolabeled 25S for protein and 32P for DNA and blended the bacteria so that the phage was knocked off the host.
Erwin Chargaff
In 1950, he showed that A and T where the same amount, and C and G were also the same amount. He then concluded that DNA was comprised of four nucleotides: Adenine, Guanine, Thymine, and Cytosine.
Chargaff’s Rules
Equal % of A and T, Equal % of G and C
Structure of a nucleotide
Deoxyribose or Ribose, a nitrogenous base, and a phosphate group.
Roseland Franklin
In 1953 she concluded that DNA was a double-helix structure using a DNA diffraction patters of DNA. This discovery was later stolen from her by James Whatson and Francis Crick.
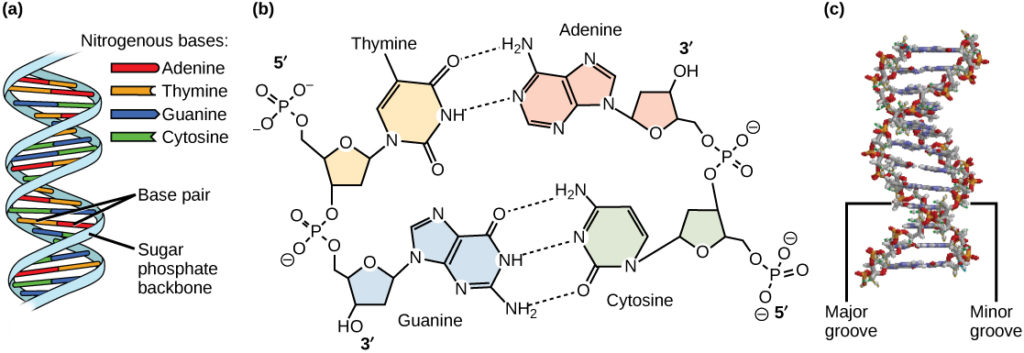
Structure of DNA
An antiparallel, double helix structure with alternating nucleotides linked by phosphodiester bonds and Hydrogen bonds. The double helix is formed by major and minor grooves used by binding proteins during transcription and replication.
Matthew Meselson & Franklin Stahl
Proved that DNA replication is semiconservative, meaning each new DNA molecule consists of one original (parental) strand and one newly synthesized strand. They achieved this by using a heavy isotope of nitrogen 15𝑁 to label the DNA of E. coli bacteria, then transferring the bacteria to a medium with normal nitrogen 14N. After one replication cycle, the DNA was an intermediate density, supporting the semiconservative model
Conservative Strand
Original parent strand stays in tact, and a completely new strand is synthesized.
Semiconservative Strand
Parent strand breaks apart, acting as a template for the synthesizing strand.
Dispersive strand
The parent strand is broken into small pieces and incorporated into the new strand.
Topoisomerase
Relieves additional coiling in DNA replication.
helicase
Unzips DNA in replication
single-stranded binding proteins
stabilizes the opened DNA and keeps it from re-binding during replication.
primase
Makes the DNA primer, and makes the starting point for DNA polymerase using RNA primer in DNA replication.
DNA polymerase
Synthesizes the new strand, from 3’ to 5’. Proofreads any possible errors.
Okazaki Fragment
The lagging strand of DNA replication when the DNA polymerase is on the 5’ to 3’ strand. Having to keep going backwards, resulting in fragments in the synthesized strand.
ligase
Glues the Okazaki fragments together.
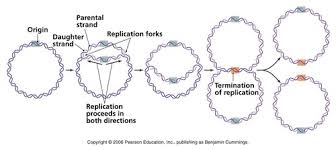
DNA Replication in Prokaryotes
Replicates their DNA in a circle, starting with the Origin point, with replication proceeding in both directions. The part where the DNA is being replicated is called 'Replication Forks' The two strands bud off each other from the 'Termination of Replication'
DNA Polymerase I
Replaces RNA primer with DNA
Mismatch Repair
The incorrect base that was added is detected after replication The mismatch repair proteins detect this and remove it from the strand using nuclease action The gap is then filled with a correct pair
Nucleotide Excision
Repairs Thymine dimers. When exposed to UV, thymie dimers lying adjacent to each other can form covalently linked thymine dimers In normal cells, these mutations are replaced
telomerase enzyme
Maintains the end of the chromosome
Elizabeth Blackborn
Discovered how telomerase works
Point Mutations
Silent, Missense, and Nonsense
Silent Mutation
no effect on protein sequence, codon swapped for another of the same amino acids.
Missense Mutation
Results in an amino acid substitutions
Nonsense
Substitutes a 'stop' codon for an amino acid.
Frameshift Mutation
Insertions or deletions may result in a shift in the reading frame or the insertion of the 'stop' codon
Chromosome Mutation
Insertions, deletions, translocations, inversions, fusions, and duplications