The Reproductive System
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Gonads
ovaries and testes
-produce sex steroid hormones
-females: estradiol, progesterone
-males: testosterone
Gametes
ova and sperm
gonads
Where are gametes produced?
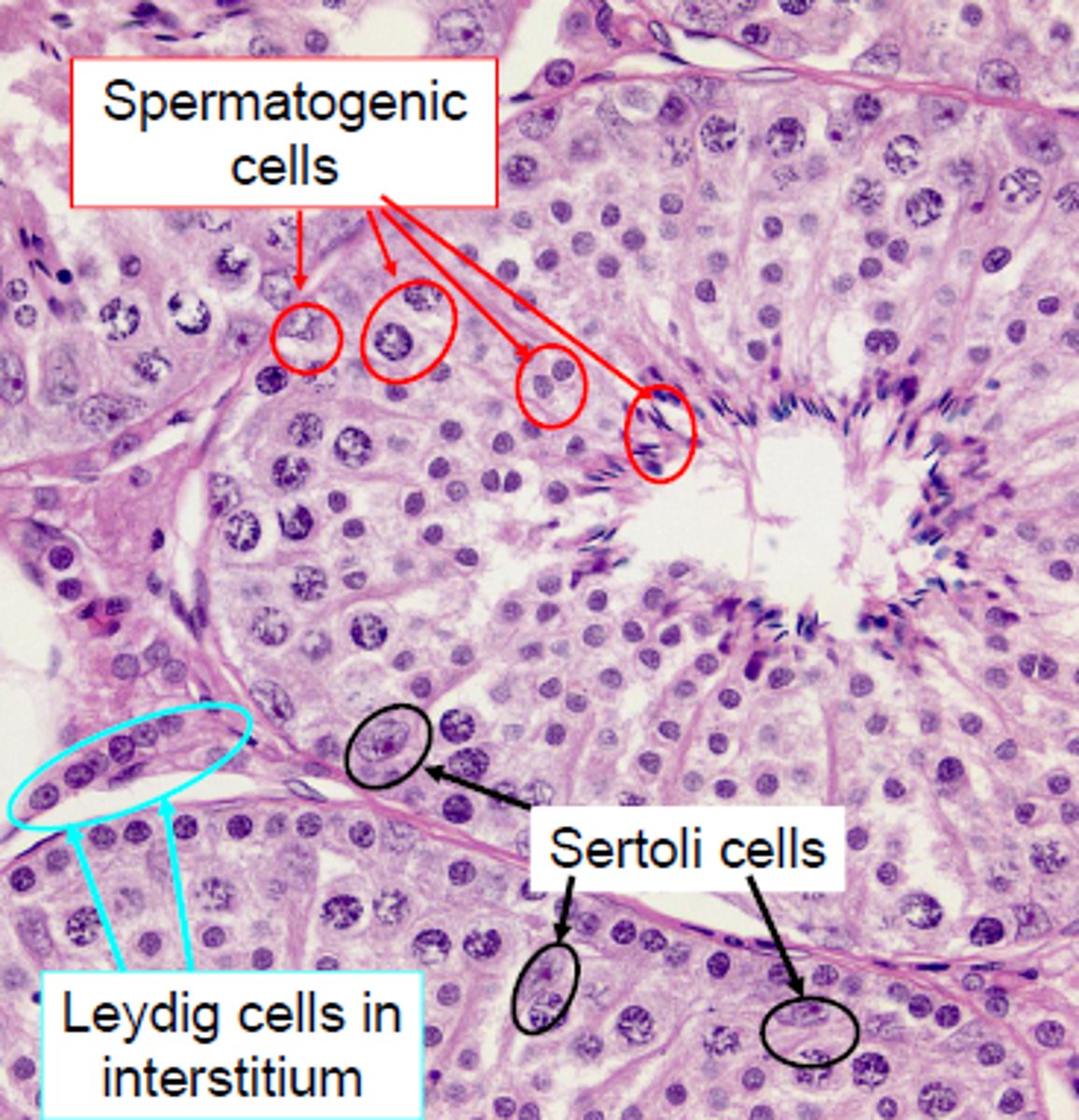
Seminiferous tubules
Where spermatogensis occurs
-lined by Sertoli cells
Spermatogenesis
production of sperm
Sertoli cells
protect and nuture developing sperm
-control the release of testosterone (needed for spermatogenesis
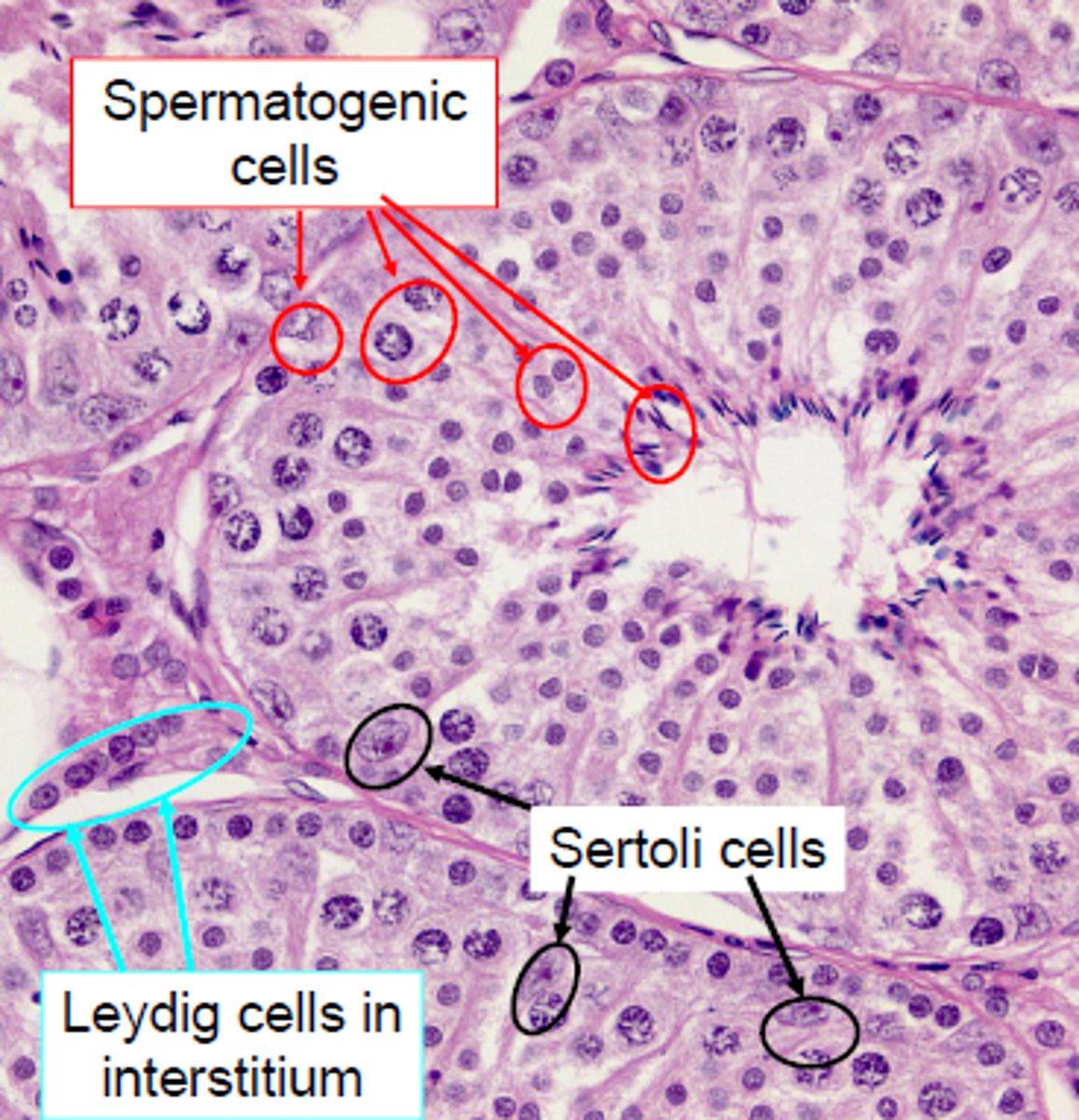
Leydig cells
produce testosterone
-located between the seminiferous tubules
-under influence of lutenizing hormone (LH)
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
causes the secretion of testosterone in the testes
Spermatocytogensis
the first phase of spermatogenesis, -sperm cells multiply by miotivc division in order to produce pprimary permatocytes
-number of chromosomes is diploid
Spermiogenesis
spermatids transform into nonmotile spermatozoa
-formation of tail, condensation of nuclear chromatin, development of acrosomal cal
Spermiation
non-motile spermatozoa are released into the lumen of the seminiferous tubules
-under control of LH
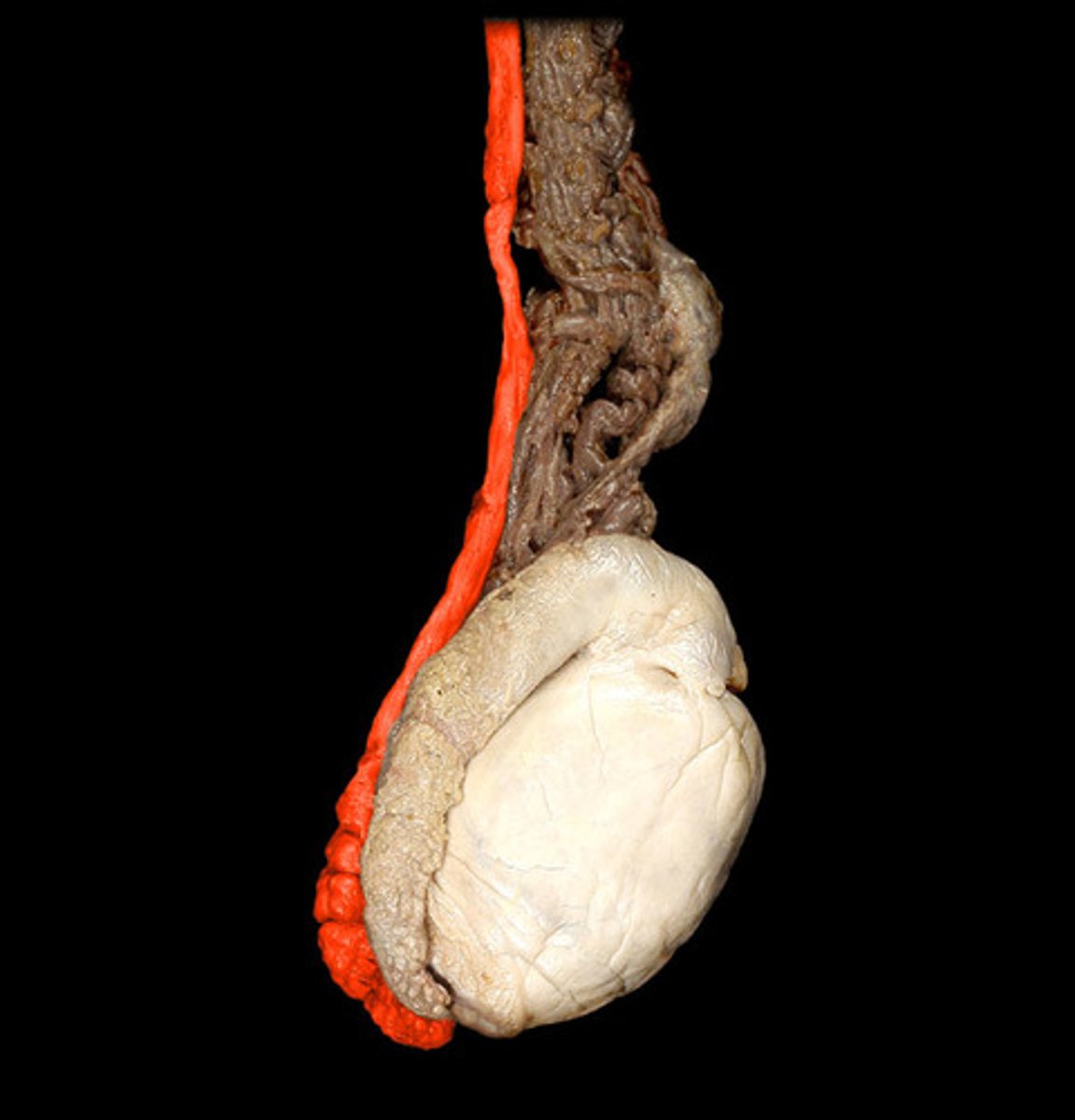
Epididymis
houses sperm during maturation
-mature, motile sperm are stored in the tail and vas deferens
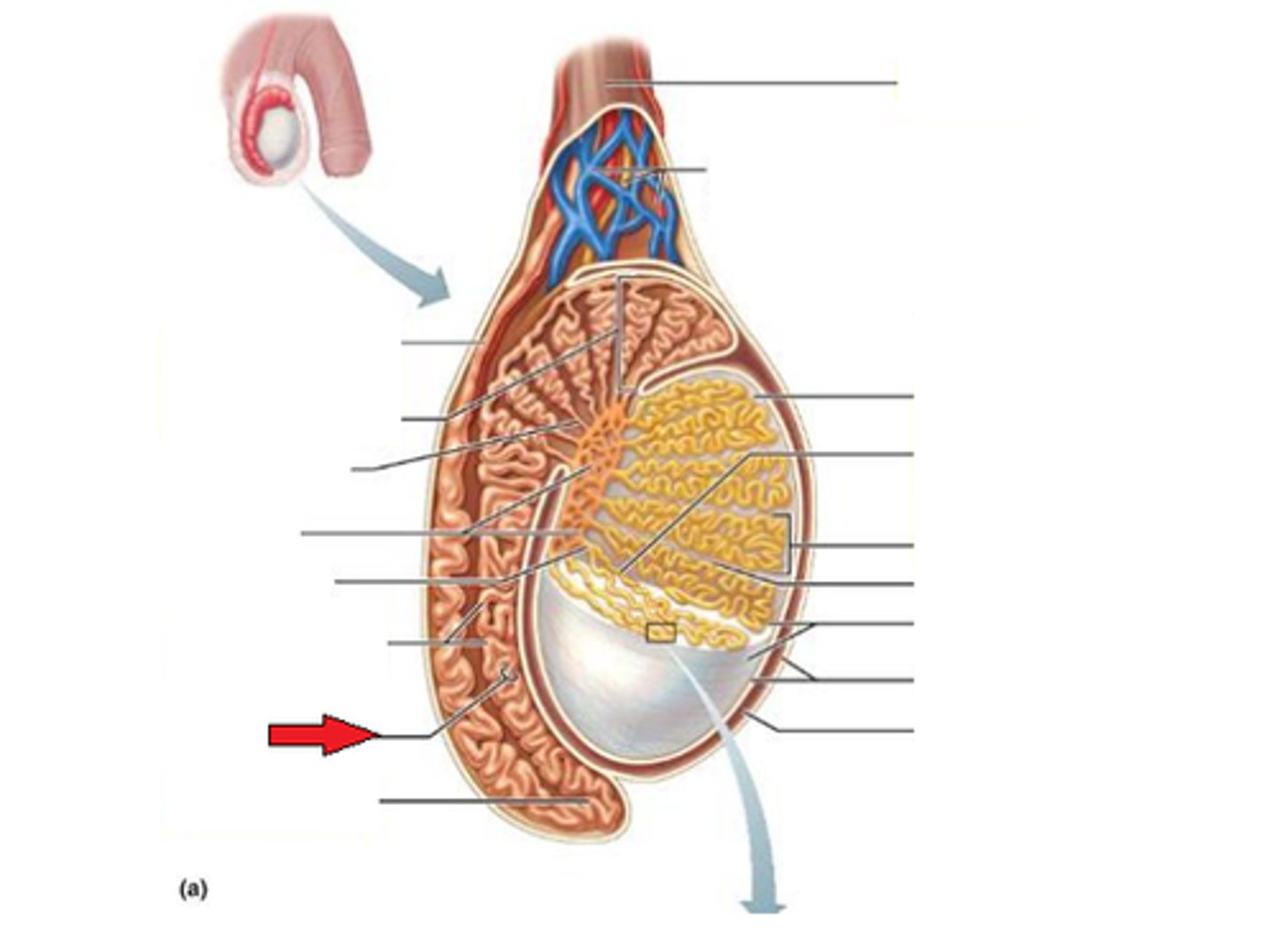
Vas Deferens
"ductus deferens"
-transports mature sperm to the urethra during ejaculation
-connects to tail of the epididymus
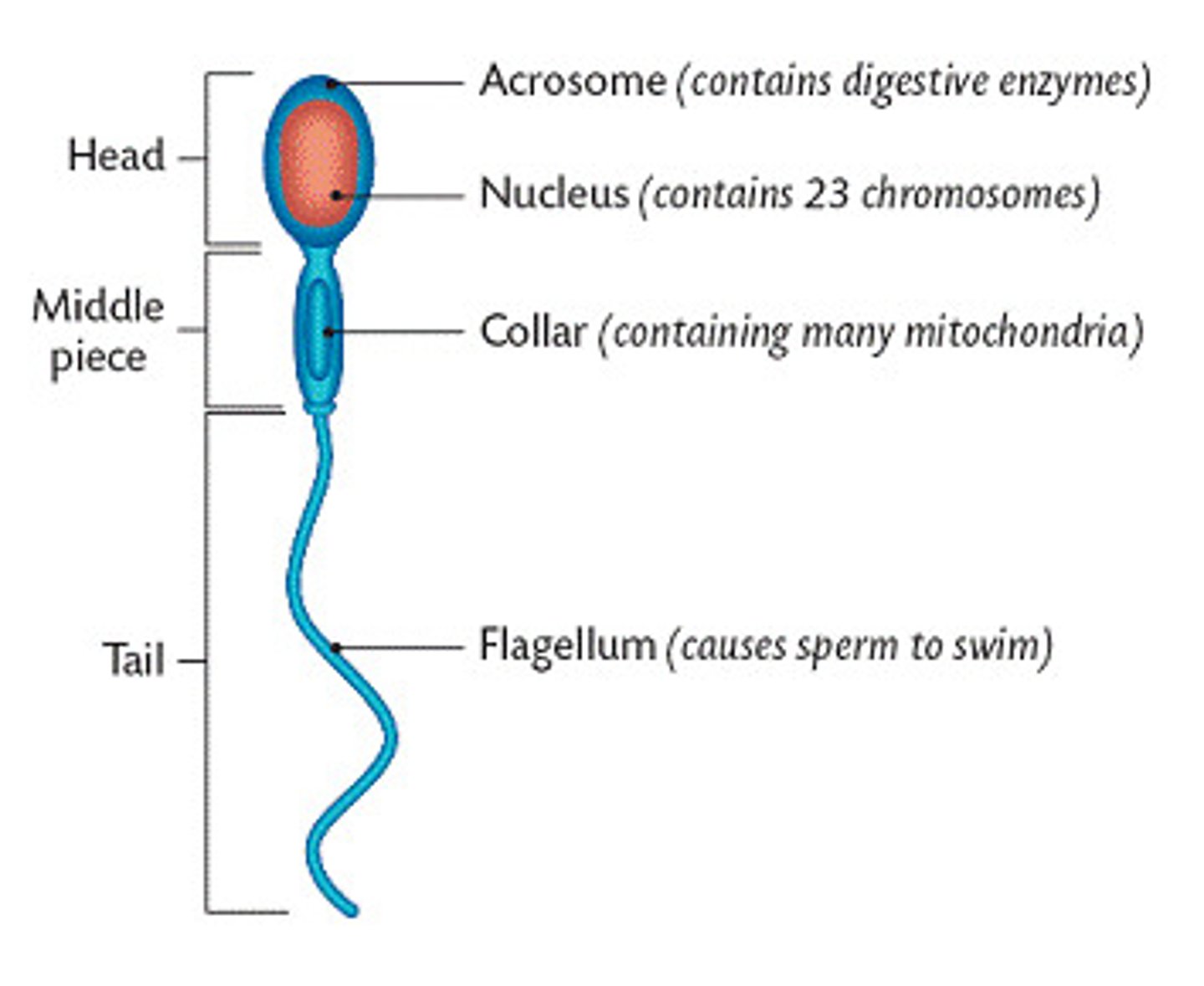
head of sperm
contains genetic material (haploid number of chromosomes)
-acrosome of head has enzymes that help sperm penetrate the egg
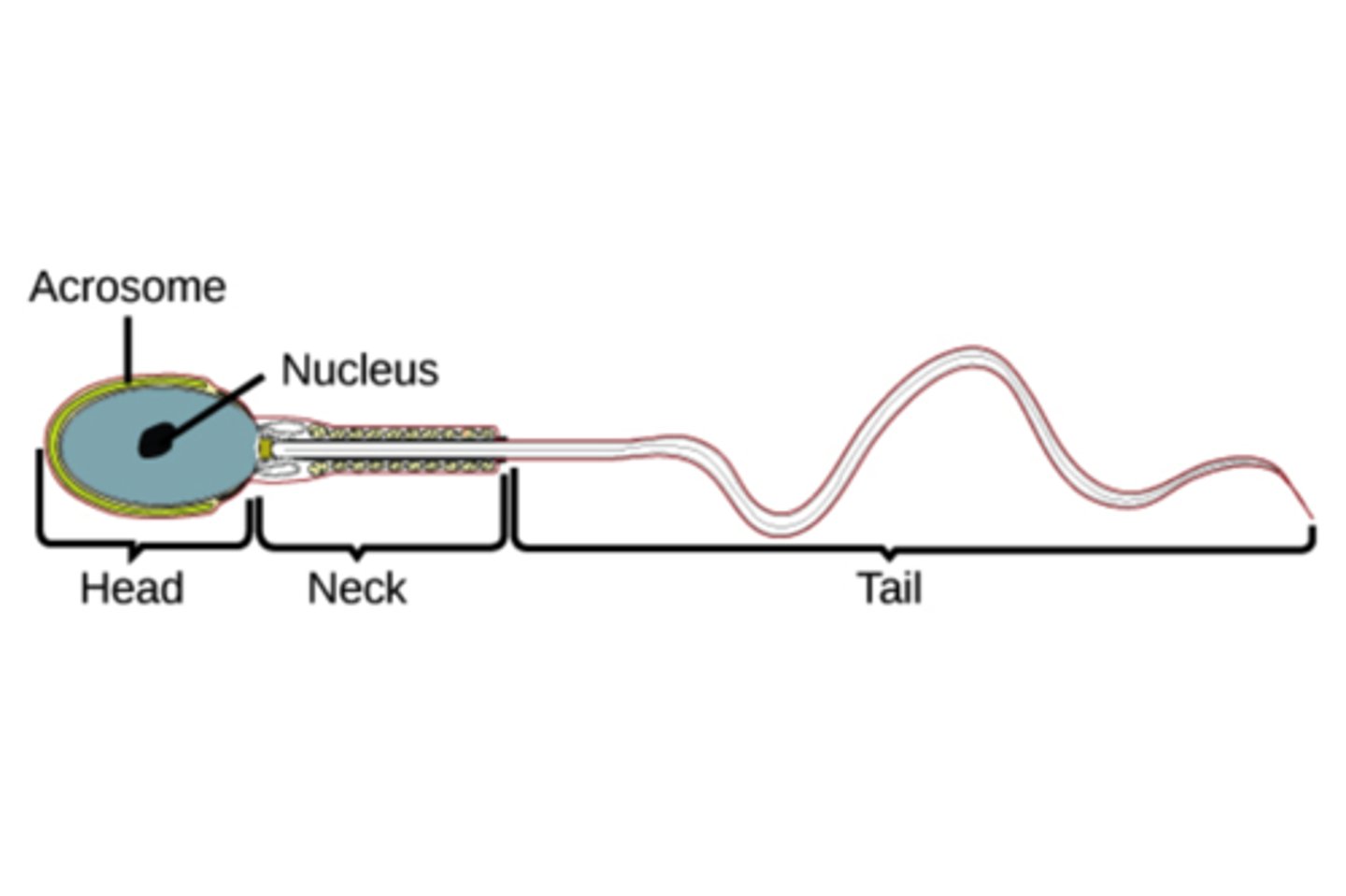
midpiece of sperm
contain mitochondria for generation of energy
tail of sperm
propels sperm froward
Accessory sex glands
seminal vesicles, prostate gland, bulbourethral glands
Seminal vesicles
secrete prostaglandins, which stimulate contraction of uterine muscles to move semen
-fluid, mucus, amino acids, fructose secreted provide energy for sperm
Prostate gland
-largest accessory gland
-prostate fluid is thin, milky, alkaline
Bulbourethral glands
"Cowper's glands"
secrete a viscous fluid before emission of sperm/semen
Fertilization
fusion of ovam and sperm
-signals beginning of gestation
Parturition
act of giving birth
Zona pellucinda
an extracellular matrix that surrounds the plasma membrane of the egg cell. It helps protect the egg, and has an essential role in fertilization by sperm. It is surrounded by the corona radiata.
Granulosa cells
protect the developing oveum
-have FSH receptors
-produce aromatase
Aromatase
enzyme that converts testosterone to estrogen
Ovulation
release of an ovum and parts of its follicle from the ovary
luteinizing hormone (LH)
ovulation occurs under the influence of?
Corpus luteum
secretes progesterone and estrogen
Progesterone
produced by copus luteum
-helps prepare uterus for implantation of ovum
-helps maintaine pregnancy
Oviducts
"fallopian tubes"
site of fertilization
Endometrium
inner lining of the uterus
Myometrium
smooth msucle layer of the uterus
-stretches to accomidate fetus
Cervix
gatewat to the uterus and terminal portion of femal repro system
estrogen and other hormones
growth of duct structures of mammary glands is under the influence of?
progesterone
Development of secretory tissue is under the influence of?
Prolactin
Stimulates milk production in mammary glands
Oxytocin
Stimulates uterine contractions and milk ejection
Estrous cycle
period of time an animal shows sexual receptivity to the next (estrus to estrus)
Estrus
period of sexual receptivity
-increased levels of estrogen (causes LH) surge-->ovulation occurs
Metestrus
period during which the corpus luteum develops
-starts after ovulation
-under influence of LH
Diestrus
A period of sexual inactivity between recurrent periods of estrus
-corpus luteum is fully developed, secreting large amounts of progesterone and small amoutns of estrogen
prostaglandins secreted by the endometrium
The corpus luteum degenerates under the infulence of?
Proestrus
begins after regression of corpus luteum
-marked by rapid growth og follicles
Follicle stimulating hormone
FSH
-stimulates production of ova and sperm
-stimulates follicualr growth and secretion of estrogen by growing follicles
Anestrus
period of inactivity between breeding seasons in seasonally polyestrous animals
21 days
length of cow estrus cycle?
21 days every 6 to 7 months
length of dog estrus cycle?
Monestrous
one estrous cycle per year
Polyestrous
more than one estrous cycle per year (most domestic animals)
during estrus and immediately following
When are most animals onyl sexually receptive?
Induced ovulators
ovulate in response to copulation
follicular and luteal
What are the phases of the ovatian cycle?
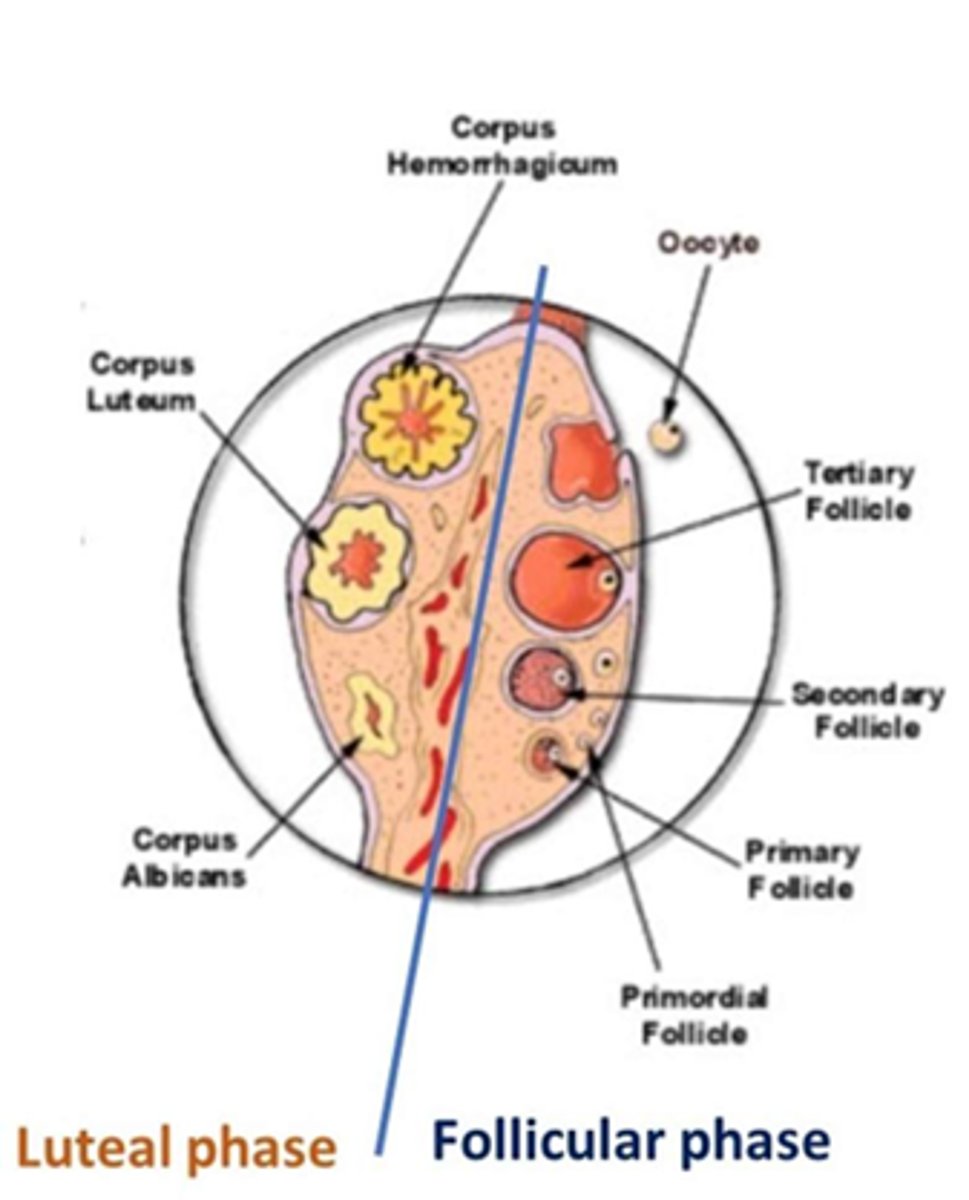
Follicular phase
several follicles begin to grow/secrete estrogen
ends when one or more follicles mature and ovulate
Luteal phase
phase of the ovarian cycle during which the corpus luteum is developed and active
proestrus and estrus
What parts of the estrus cycle make up the follicular phase?
metestrus and diestrus
What parts of the estrus cycle maye up the luteal phase?
prolonged estrus, pseudopregnancy
What occurs if the corpus luteum does not regress?