1 (P)- etiology of malocclusion- genetic basis
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What may lead to an uncoordinated inheritance of teeth and jaws?
Inheriting dissimilar genetic material, race, ethnicity, regional intermixture
What 3 factors are genetically influenced and have an effect on each other and the overall dentition?
Muscles inserted in bone- alters it function and shape
Teeth in bone- normal or malocclusion
Muscles influence bone growth- condition it’s position
What 2 considerations maximise the chance of successful Ortho treatment?
Identify cause of problem before treating
Identify factors that will influence the treatment outcome
What can a pedigree be used to help understand and what is it especially useful in?
Approx likelihood sibling may develop same trait
Monogenic traits-
class 3 malocclusion
hypodontia
primary failure of eruption
developmental dysplasias- (dentinogenesis/amelogenesis imperfecta)
What 5 malocclusions have a strong genetic influence?
Mandibular prognathism/class 3 skeletal
Size and shape- BL MD dimensions
Number of teeth
Chronology
Root formation
What parts of the dentition have a low genetic association?
Tooth position and dental relationship-
Width and arch length
Overbite
Overjet
Molar relationship
What is mandibular prognathism also known as and how does it present?
Habsburg jaw due to inbreeding
Upper lip thicker
prominent nose
Everted lower eyelids
Maxilla hypoplasia

What is mandibular prognathism caused by?
Deficiency of maxillary growth, excessive mandibular growth- or combo
What is dental agenesia (most frequent dental anomaly), its link to genetics, correlation with other teeth and presentation?
One or more teeth fail to erupt/develop
High heritability
Rarely caused by mutation
Other teeth have smaller md dimension
Peg shaped or lateral conical- can skip generations
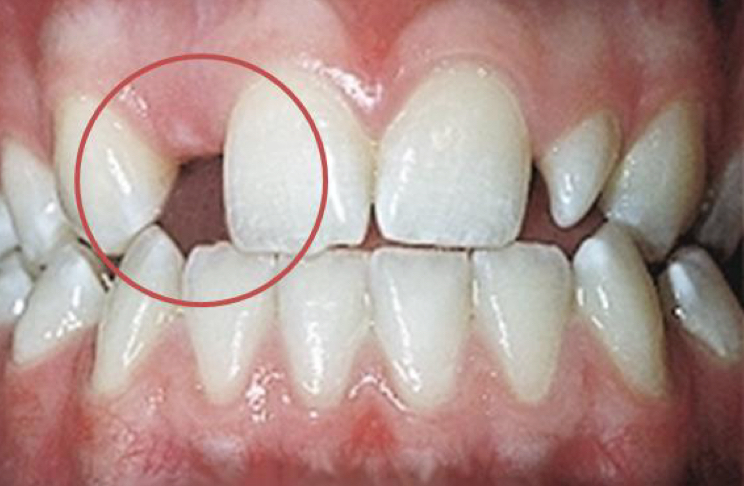
What is the difference between anodontia, oligodontia, hypodontia?
Total vs multiple vs some teeth absence
In which teeth is a congenital absence more likely?
Permanent dentition
Maxillary lateral incisors
Usually if temp teeth absent- permanent teeth won’t form
Associated with ectodermic dysplasia
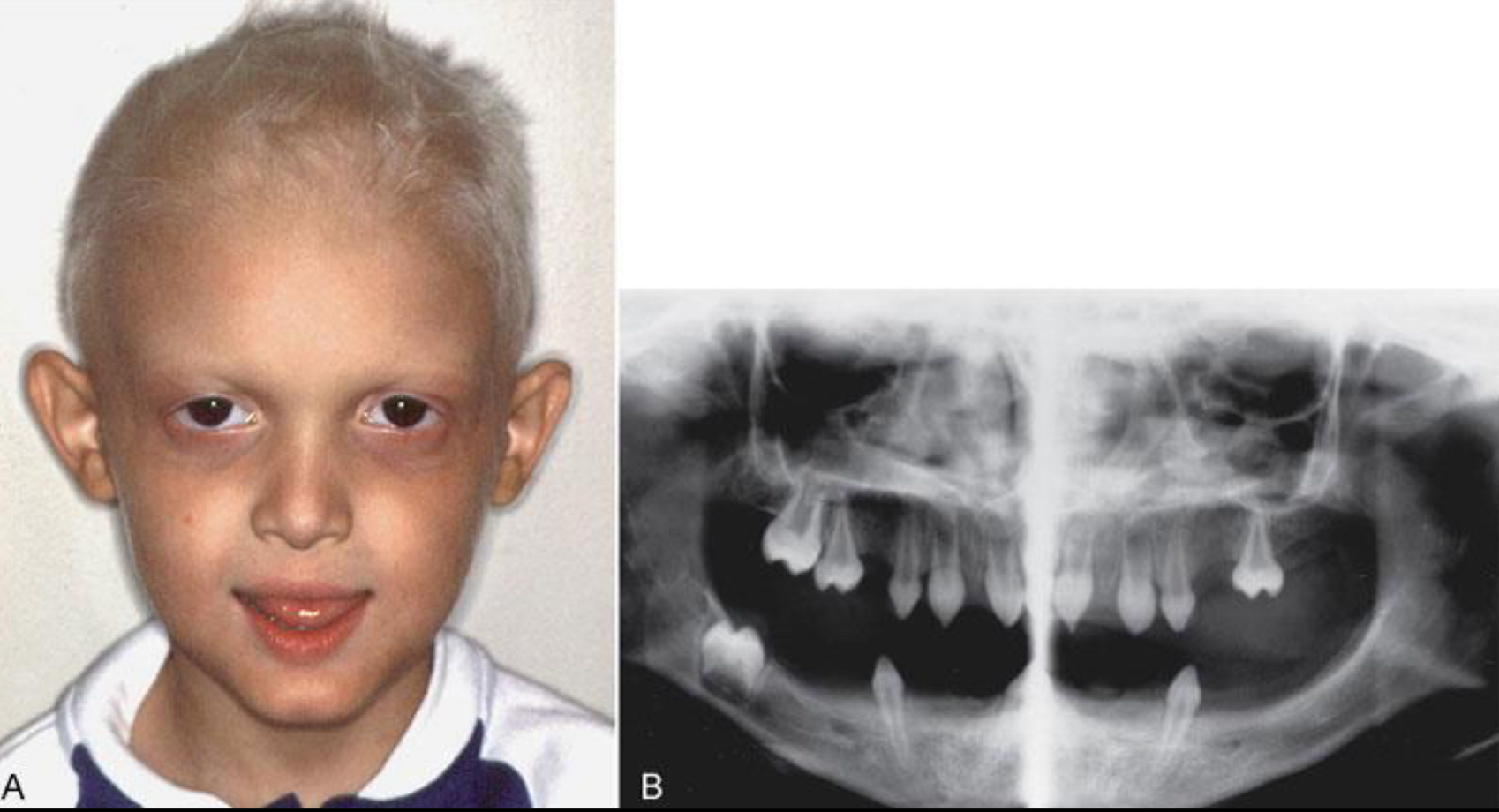
Which teeth are frequently supernumerary teeth?
Mesiodens- between max ci- concern if blocks eruption of permanent incisors
Lateral incisors, 2pm, 4m
If impacted- risk of cyst formation
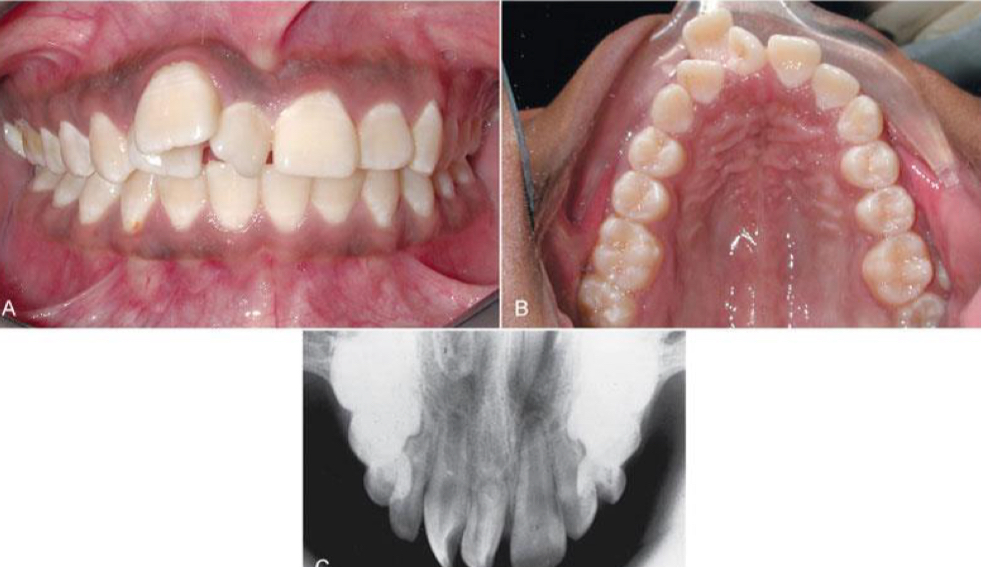
What can supernumerary teeth cause and how can we treat it?
Adjacent teeth won’t erupt or delayed
Deflect erupting teeth into abnormal locations
Crowding
Extract early
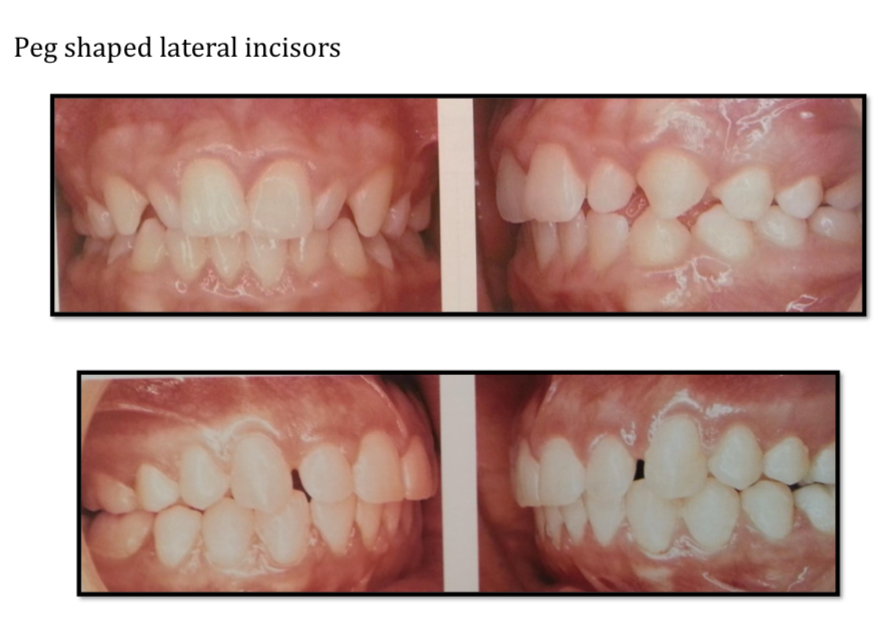
How do peg-shaped lateral incisors vs macrodontic teeth affect occlusion, and what are their treatment options?
Both alterations of Bolton index
Open space and reconstruct with filling, crown or veneer
Interproximal reduction
Need to achieve desirable intercuspation and class 1 canine
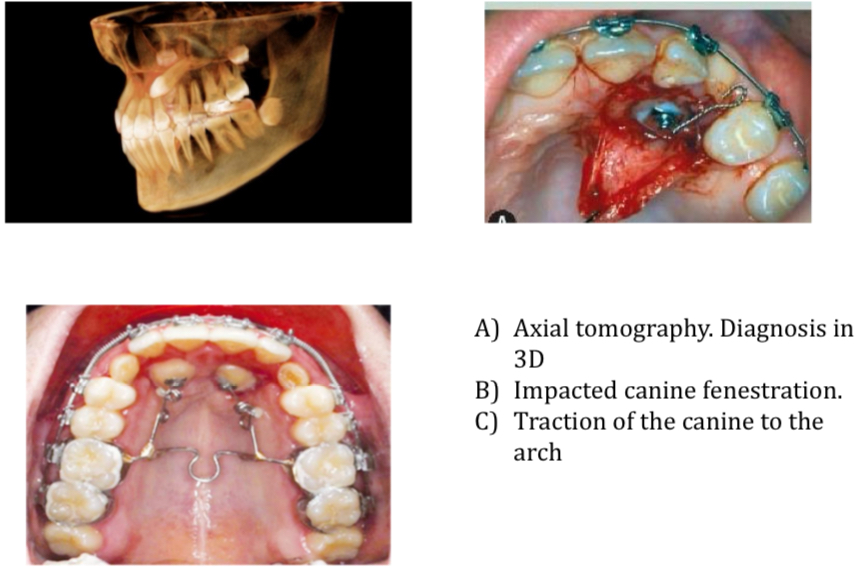
How does an impacted canine present and what anomalies may be presented alongside it?
Palatine 85%, 15% Buccal- effected by genetic and environmental factors
Peg shaped or lateral incisor agenesia
Hypodontia
Diastema
Retarded development
How can you diagnose and treat an impacted canine?
Diagnose with axial tomography (CT), ortho, x ray
Early treatment to prevent lateral incisor root resorption
What are local factors that contribute to malocclusion?
Tooth size arch length discrepancy
Ectopic eruption
Premature loss of temp teeth
Absence of permanent teeth
What causes are the consequences of a large tooth-size arch-length?
Dietary change, racial mix
Crowding- specially in last teeth to erupt
Protrusion- leads to lip hypotonicity- low muscle tone of lips

Which teeth suffer from ectopic eruption?
Lower incisors
1st permanent upper molar
Canine
How do lower incisors suffer in ectopic eruption and how do you treat it?
Changes normal tooth eruption pathway
Improve the positions and extract temp tooth
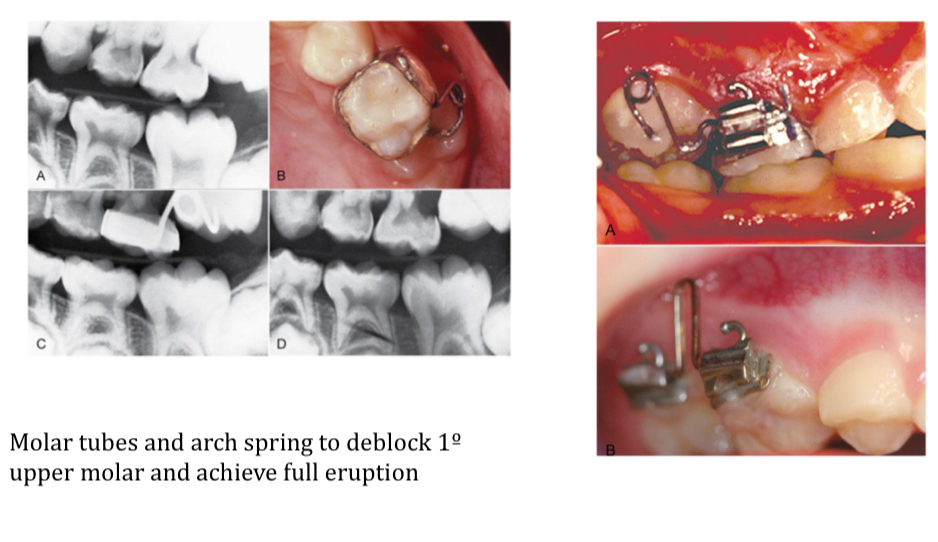
How does the ectopic eruption of the upper first molars effect the tooth size arch length?
When erupting mesially, reabsorbs 2nd temp molars prematurely
Negative discrepancy
If root resorption limited to 1-1.5mm- no treatment
Treat if blocks for over 6 months or root resorption continues- Arkansas spring, molar tubes, arch spring
Why do canines tend to erupt ectopically and how to treat it?
Last teeth to erupt- may lack space so erupt buccally and high in arch
Create space, Analyse discrepancy, extract premolars
What may happen if there’s a premature loss of temp teeth and how do you treat it?
Adjacent teeth drift so less space for permanent teeth to erupt
Treat by space maintainers or regain lost space with appliances
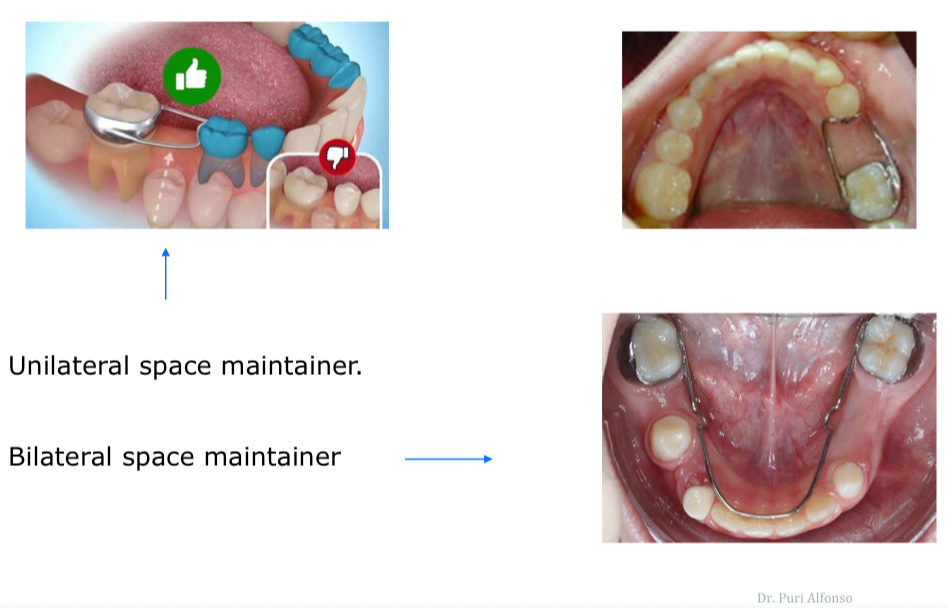
What does treatment of absent permanent teeth depend on and which teeth are most commonly missing?
Facial profile
Incisor profile
Space available or lack of
Usually 2pm
or upper lateral incisor- often replaced spontaneously by permanent canines
If 2nd permanent premolar missing…
If acceptable occlusion- maintain 2nd temp molar and reduce MD width
But extract (ages 7-9) if convex profile or protrusive incisors- will allow upper 1st molar to erupt mesially and occupy the space
What are the effects in breath, pressure and the tongue in normal breathers vs mouth breathers
Air enters nasally
Creates negative pressure between tongue and palate
Tongue rests against palate- is positive stimulus for maxillary development
Vs
Air enters through mouth
Tongue drops to floor of mouth
No stimulated growth of the palate
What are 4 causes mouth breathing?
Chronic allergic
Deviated nasal septum
Abnormal development of nasal cavities
Enlarged adenoid tonsils
What are the facial features of a mouth breather/adenoid face?
Long narrow face and nose
Short upper lip
Expressionless
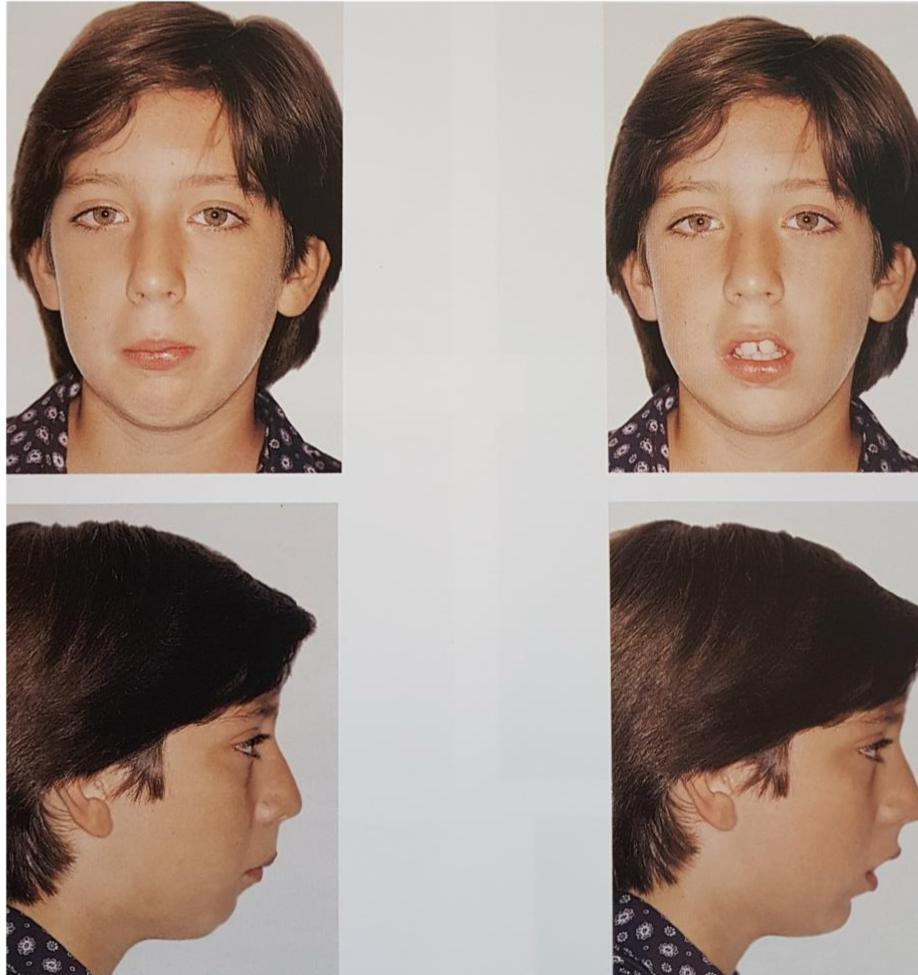
How does mouth breathing affect dentition?(5)
Protrusion of maxillary incisors
Decreased transversal development
Posterior crossbite
Anterior openbite
Chronic marginal gingivits
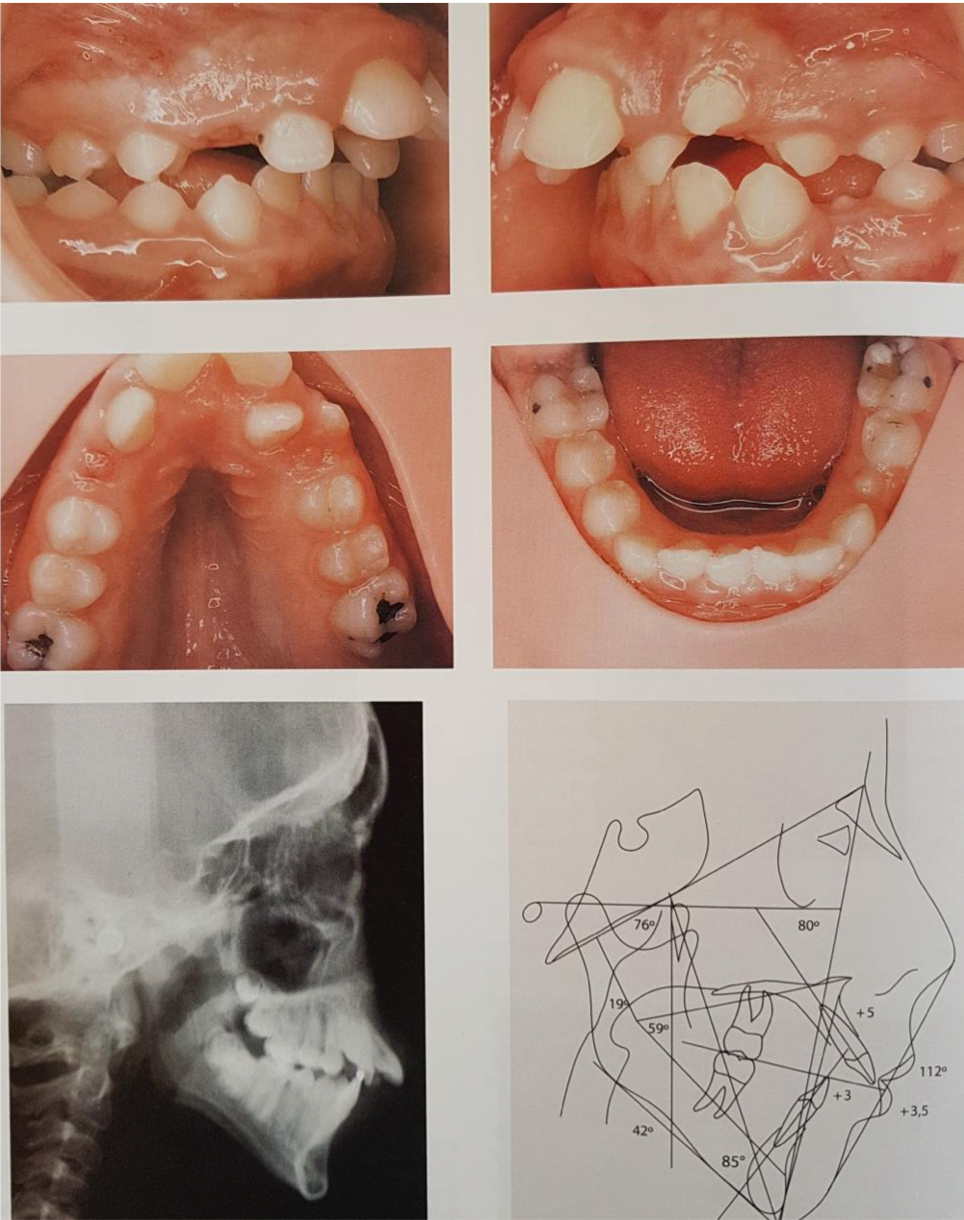
How to treat mouth breathing?
Remove etiological causes
Ortho treatment- expand maxilla, align and level teeth
Promote nasal breathing
What is tongue thrusting and what malocclusions does it form in the maxilla vs mandible?
Forward movement of tongue tip between teeth to meet the lower lip during deglutition
Maxillary anterior proinclination
Increased overjet
Maxillary constriction
General spacing between teeth
Anterior open bite
Vs Retroinclination of incisors
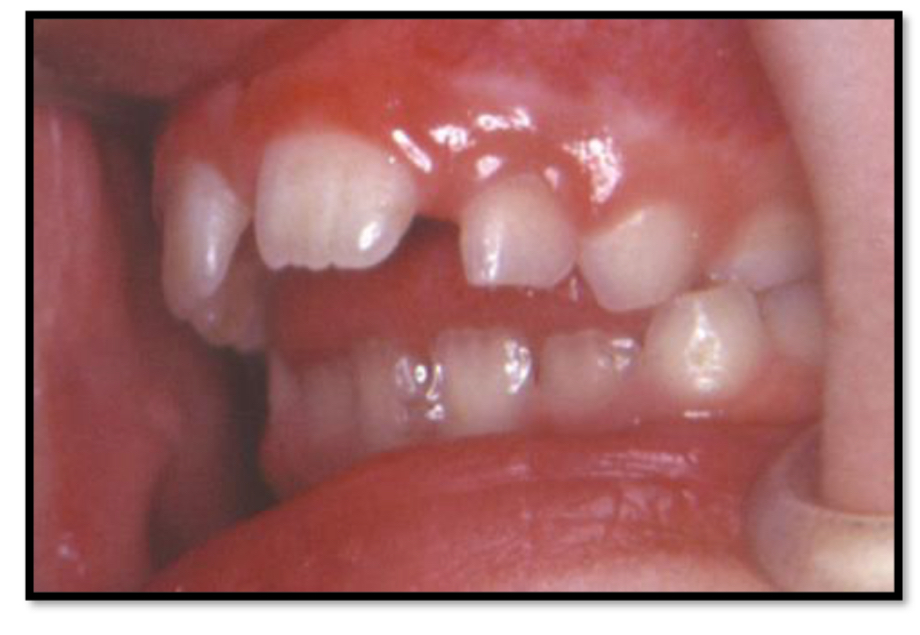
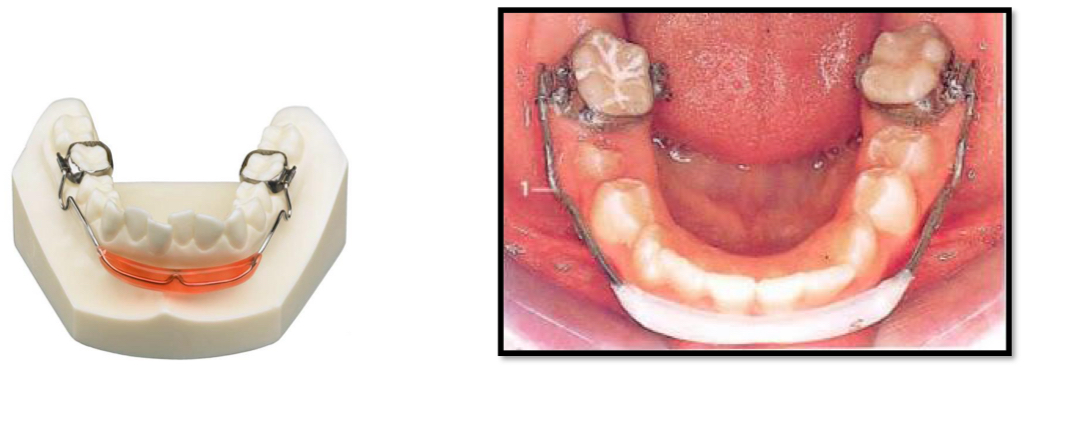
How to treat tongue thrusting?
Speech therapy to train correct swallowing and posture of tongue
Appliance therapy- lingual interposition grid
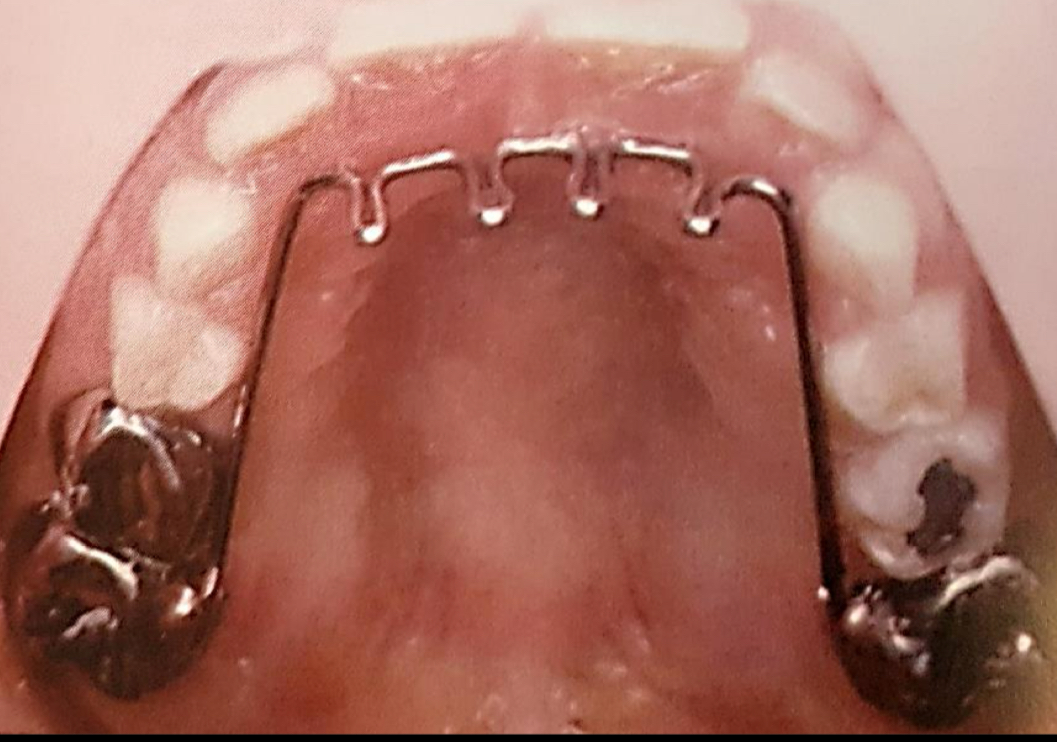
What are 5 features of finger sucking?
Maxillary protrusion
Mandibular retrusion
Increased overjet
Tongue placed inferiorly leading to posterior crossbite due to maxillary arch contraction
Anterior open bite
How do you treat thumb sucking?
Bitter taste on thumb
Ace bandage approach
Insert palatal crib
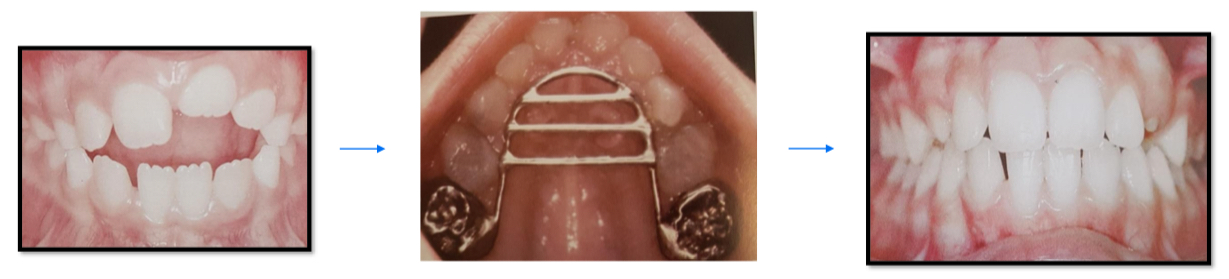
What are the features and treatment of lip sucking?
Protrusion of upper anteriors and retrusion of lower anteriors
Traps lips causing muscular imbalance
Lower incisor collapse with lingual crowding
Accentuated mentolabial sulcus
Treat- Lip bumper