Immunology Chapter 1 - Elements of the Immune System and Their Roles in Defense
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Immunology is a branch of biology and medicine that covers the study of immune systems in ___________.
all organisms
Father of Immunology is ________. Found in 1796 that inoculation with _________ could protect against smallpox. Called the procedure ______________. Took two centuries for samllpox vaccine to become universal.
Edward Jenner; cowpox (vaccinia); vaccination
_________ devised a vaccine again cholera in chickens and developed a rabies vaccine. Was about to demonstrate the process called _________. Contributed to the ___________ of disease.
Louis Pasteur; pasteurization; germ theory
___________ discovered that bacteria (bacillus) is responsible for causing tuberculosis. Proved that infectious diseases are caused by microorganism, each one responsible for a particular disease called _____________.
Robert Koch; Koch’s postulates
We now recognized four broad categories of disease-causing microorganism or ________: viruses, bacteria, fungi and parasites.
pathogens
_______________ discovered that many microorganisms could be engulfed by phagocytotic cells, whish he called _______________, which are a front-line defense of the innate immune system.
Elie Metchnikoff; macrophages
Any microorganism that casues disease
Pathogen
Normally, inhabit the human body and do not cause a disease in healthy people, but become pathogenic when the body’s defense system is impaired. Some that people with HIV may get include candidiasis, salmonella infection, toxoplasmosis, and tuberculosis (TB).
Opportunistic pathogen
Skin and mucosal surfaces that form barriers against infection
Hair
Sinuses
Trachea
Lungs
Respiratory Tract
Mammary Glands
Ryes
Oral Cavity
Kidneys
Bladder
Vagina
Esophagus
Stomach
Intestines
Gastrointestinal Tract
Urogenital Tract
Skin
Nails
Recognition Mechanism of Innate Immunity
Rapid Response (hours)
Fixed
Limited Number of Specificities
Constant During Responses
Recognition Mechanism of Adaptive Immunity
Slow Response (days to weeks)
Variable
Numerous Highly Selective Specificities
Improve During Responses
Phase 1 of the Innate Immune Response
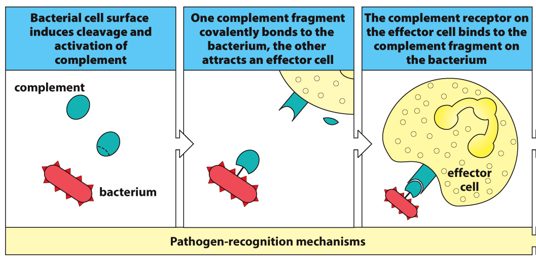
Phase 2 of Innate Immune Response
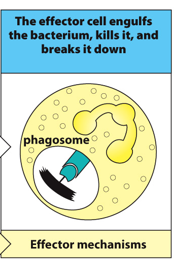
Human health requires both _______ and _______ immunity.
innate; adaptive
Historically, ___________ (adaptative immunity) and __________ (innate immunity) were separate medical disciplines that began to merge in study in the 1980s.
immunology; inflammation
____________ is the formation of ______ cellular components.
Hematopoiesis; blood
All cellular blood components are derived from ____________
hematopoietic stem cells
Three main types of lymphocytes _______, _______ and _________ cells.
B cells; T cells; natural killer (NK)
Leukocytes are the white blood cells while the ___________ are a type of leukocyte. Thus, all lymphocytes are leukocytes but all leukocytes are not lymphocytes.
lymphocytes
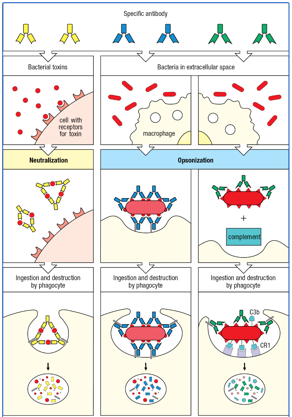
Antibody-mediated mechanisms that combat infection.
Primary Lymphoid Tissue
Red
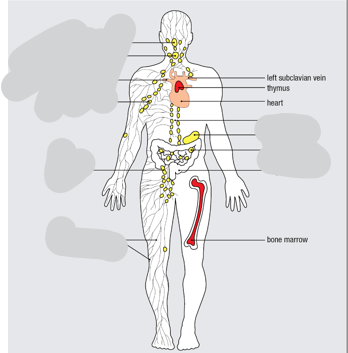
Secondary Lymphoid Tissue
Yellow
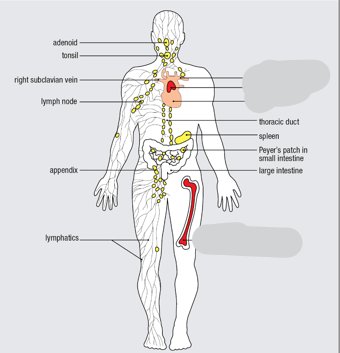
Activated pathogen-specific B cells proliferate in each follicle, forming a dense structure, the ______________.
germinal center