Chapter 9 Homework-Mcgraw hill
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
108 Terms
Which muscle is an involuntary type of muscle?
cardiac
What root word means between?
inter-
What prefix means work?
erg-
A bundle of skeletal muscle fibers enclosed by a perimysium forms a(n) _____ within a muscle.
fascicle
a muscle fiber is a muscle ____.
cell
What term is used for the plasma membrane of a muscle fiber?
Sarcolemma
they are elongated, they are multinucleated, they have a cylindrical shape. this describes what type of muscle fiber?
skeletal muscle fiber
Muscle cells are also known as muscle fibers. In a skeletal muscle, muscle fibers are found as bundles called ______, each enclosed in a connective tissue sheath, called the ____.
fascicle; perimysium
The cytoplasm of a muscle fiber is called the _____.
sarcoplasm
Which muscle type has multinucleated cells that are cylindrical in shape?
skeletal.
What are myofibrils?
bundles of proteins in a muscle cell
The sarcoplasm of a muscle fiber contains many parallel structures made of proteins. These structures are called ______.
myofibrils
The cytoplasm of a muscle fiber is called the ______
sarcoplasm
Which muscle type has multinucleated cells that are cylindrical in shape?
Skeletal muscle
which protein is found in the thick filaments
myosin
which proteins are found in the thin filaments?
Actin, Troponin, Tropomyosin
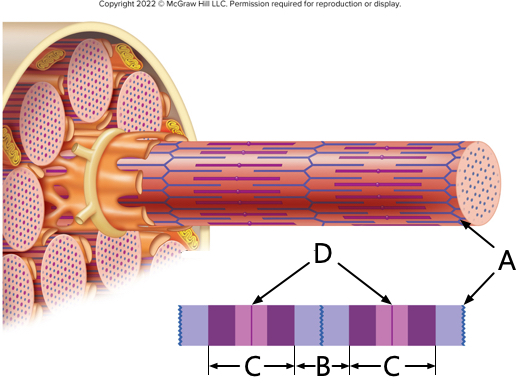
what is letter A?
Z-line
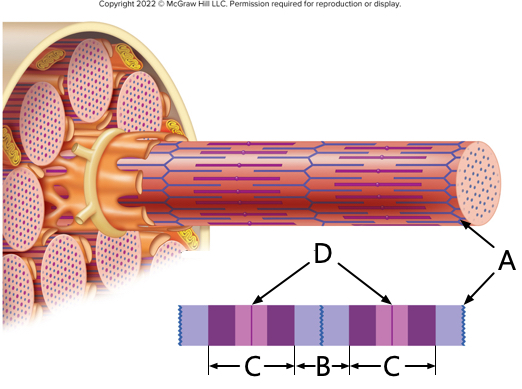
what is letter B?
I - band
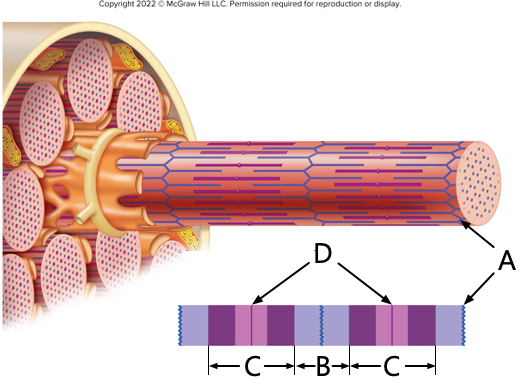
what is letter C?
A - band
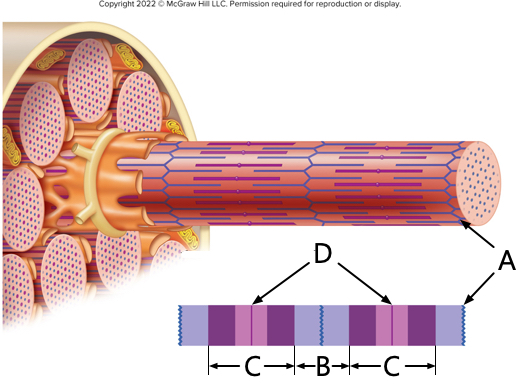
what is letter D?
M-line
What forms the striations seen in skeletal muscle?
The arrangement of thin and thick filaments
Actin (thin) filaments are attached to a Z line, which is located in the middle of what region of the striations in a skeletal muscle?
I band
What are the two major protein types found in myofibrils?
Actin, Myosin
What are the repeating units within muscle fibers that act as the functional units of muscle contraction?
sarcomeres
Within myofibrils, thick filaments are composed of which protein?
myosin
thin filaments primarily contain which protein?
actin
Within myofibrils, the area between two successive Z lines is called a(n) ______.
sarcomere
Actin (thin) filaments are attached to a Z line, which is located in the middle of what region of the striations in a skeletal muscle?
I band
What are thin filaments composed of?
Two intertwined strands of actin
The globular actin proteins that make up thin filaments in a myofibril have binding sites for ______.
myosin
A sarcomere extends from one ______ to the next.
z line
Myofibrils are formed by many _____ positioned end-to-end.
sarcomeres
Intertwined strands of actin make up part of the ______ filaments. thick or thin?
thin
Actin molecules are globular and have binding sites to which the heads of a(n) _____ molecule can attach.
myosin
How many protein strands are found in each myosin molecule?
2
Each myofibril contains many _______, each extending from one Z line to the next.
sarcomeres
Troponin and tropomyosin are part of the _____ filaments within muscle myofibrils. thick or thin?
thin
A sarcomere extends from one ______ to the next.
z-line
Within a muscle fiber, troponin and tropomyosin are associated with ______. actin or myosin or the sarcoplasmic reticulum?
actin
In a skeletal muscle fiber, each myofibril is surrounded by a network of membranous channels that runs parallel to the myofibril and is called the_____________.
sarcoplasmic reticulum
actin (thin) filaments only associate with which band in the sarcomere?
I band
actin and myosin filaments associate with which band in the sarcomere?
A band
myosin (thick) filaments only associate with which structure in the sarcomere?
H zone
What is the name of the invaginations of the sarcolemma that extend through the muscle fiber?
Transverse (T) tubules
Intertwined strands of actin make up part of the ______ filaments. thick or thin?
thin
true or falseThe transverse tubules are located between structures called cisternae.
True
Within myofibrils, the area between two successive Z lines is called a(n) ______.
sarcomere
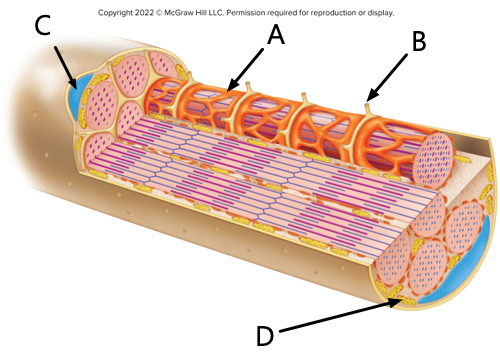
what is label A?
sarcoplasmic reticulum
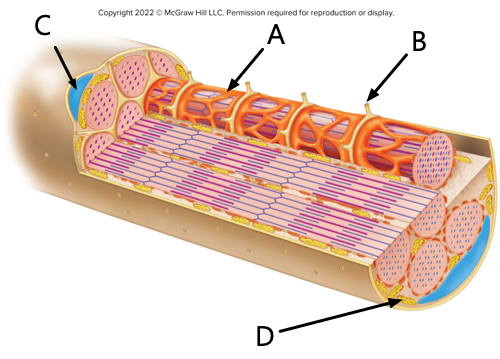
what is label B?
transverse tubule
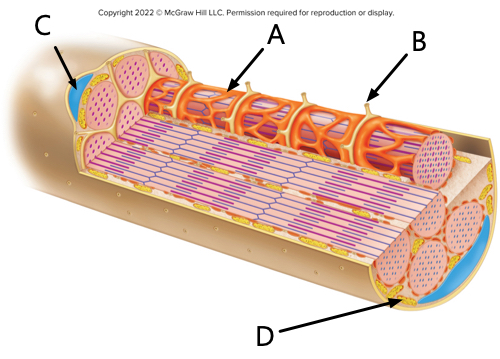
what is label C?
nucleus
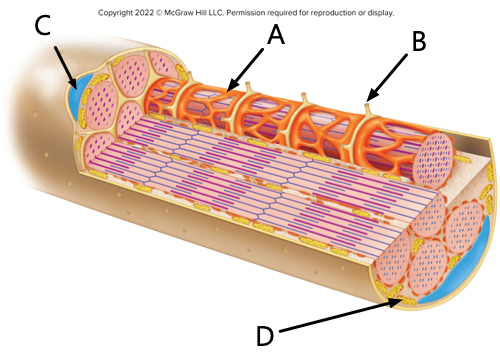
what is label D?
mitochondrion.
Numerous invaginations of the sarcolemma of a muscle fiber lead down into structures called the _______.
transverse tubules
what is the process called when an axon of a neuron conducts electrical impulses towards the end of the axon that innervates a target cell?
action potentail
What structures are positioned between adjacent cisternae of the sarcoplasmic reticulum?
Transverse tubules
The T tubules of a muscle fiber are extensions of the ______ and contain extracellular fluid.
sarcolemma
What is the name of the process on a neuron that carries electrical impulses toward the cell to be stimulated?
axon
During excitation-contraction coupling, calcium binds to ______.
troponin
T or F: The transverse tubules are located between structures called cisternae.
true
During excitation of a muscle fiber, which one of the following events comes immediately after the release of acetylcholine from the motor neuron?
Acetylcholine diffuses across the synaptic cleft
What is the name of the network of membranous channels that surrounds each myofibril within a muscle fiber?
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Numerous invaginations of the sarcolemma of a muscle fiber lead down into structures called the ______.
transverse tubules
In excitation-contraction coupling, the protein called _____ moves to expose binding sites on the actin filaments that can form cross-bridges.
tropomyosin
What structures are positioned between adjacent cisternae of the sarcoplasmic reticulum?
Transverse tubules
list the events leading to excitation of a muscle fiber in order.
1) nerve impulses arrives at a distal end of the axon
2) acetylcholine diffuses across the synaptic cleft
3) acetylcholine binds to its receptors on the muscle fiber sarcolemma
4) the permeability of sarcolemma to sodium ions increases.
What generates the force that shortens the sarcomeres to bring about muscle contraction?
Myosin cross-bridges pulling on the actin filaments
The T tubules of a muscle fiber are extensions of the _____ and contain extracellular fluid.
sarcolemma
During muscle contraction, the sarcomeres shorten because ______.
thick and thin filament slide past one another, increasing their overlap
What is the first source of energy that is used to convert ADP to ATP after a contraction in a skeletal muscle cell begins?
Creatine phosphate
During which phase are calcium ions actively transported into the sarcoplasmic reticulum?
Relaxation
T or F: Myofilaments shorten during contraction.
False
During excitation of a muscle fiber, which one of the following events comes immediately after the release of acetylcholine from the motor neuron?
Acetylcholine diffuses across the synaptic cleft
The process of glycolysis is (aerobic or anaerobic)______.
anaerobic
What generates the force that shortens the sarcomeres to bring about muscle contraction?
Myosin cross-bridges pulling on the actin filaments
During anaerobic metabolism, what is produced?
lactic acid
Prolonged or intense exercise can lead to a condition called muscle _____, defined as the loss of a muscle's ability to contract.
fatigue
T or F: Muscles generate heat when they contract.
True
During which phase are calcium ions actively transported into the sarcoplasmic reticulum?
Relaxation
During high-intensity exercise, anaerobic metabolism results in the production of pyruvic acid, which is then converted to ____ acid
lactic
If a muscle fiber is subjected to stronger and stronger electrical impulses, it will initially be unresponsive until a strong enough impulse is applied which causes it to contract. The level of electrical stimulation needed to stimulate contraction is called the ______.
threshold stimulus
A single contraction of a muscle fiber in response to a single stimulation is known as _____.
muscle twitch
During muscle relaxation, calcium levels in the sarcoplasm fall because _____.
calcium is actively transported into the sarcoplasmic reticulum
Why does summation result in an increased force of contraction?
Individual twitches combine due to the high frequency of stimulation.
When a single muscle fiber contracts when stimulated by a single impulse, the contractile response is called a(n) ____.
twitch
During a(n) _______ muscle contraction, the muscle either lengthens or shortens, while the tension stays constant.
isotonic
Muscle fibers with abundant mitochondria and myoglobin that are typically red in color are called ______ fibers.
type I
When a muscle fiber is stimulated at a high enough frequency that it doesn't have time to relax, the forces of the individual twitches combine. What is this process called?
Summation
A motor unit is comprised of a ______ and the _____ that it controls.
motor neuron; muscle fibers
Compared to skeletal muscle, smooth muscle is ______ to contract and _____ to relax.
slower; slower
What type of contraction is observed when a muscle shortens?
Isotonic
These characteristics define which type of twitch fiber, slow or fast?
They are well supplied with capillaries and mitochondria.
They contain large amounts of myoglobin.
They are also called red fibers.
slow-twitch fibers.
During a(n) _____ muscle contraction, the muscle either lengthens or shortens, while the tension stays constant.
isotonic
Muscle tissue that has a well-developed sarcoplasmic reticulum, many mitochondria, and branching cells with one nucleus is classified as ______ muscle.
option:
cardiac
smooth
skeletal
cardiac
Which of the following is a characteristic of slow-twitch (type I) fibers?
Multiple choice question.
a) They have poor blood supply.
b) They are red in color.
c) They are adapted for glycolysis.
d) They are susceptible to fatigue.
b) They are red in color.
The cells of _____ muscle are tapered, lack striations, and have a sarcoplasmic reticulum that is not very extensive.
smooth
A fulcrum, a force, and an object moved against resistance make up a ______.
lever
What is a motor unit composed of? (Select all that apply)
Multiple select question.
a) Several muscle fibers
b) A single motor neuron
c) Several motor neurons
d) A single muscle fiber
a) Several muscle fibers
b) A single motor neuron
Which end of a skeletal muscle is called its origin?
Multiple choice question.
a) The end that is attached to a movable part of a joint
b) The end that is attached to a relatively unmovable or fixed part of a joint
c) The end that contains the neuromuscular junction
d) The end that contains the longer tendon
b) The end that is attached to a relatively unmovable or fixed part of a joint
Smooth muscle can maintain a forceful contraction longer than skeletal muscle.
True false question.
true
Which type of muscle cells are striated, uninucleated (have one nucleus), and branching?
Cardiac muscle cells
When a part of the body moves, the muscles and bones responsible for the movement act as a mechanical device known as a(n) _____.
levers