[ GEN BIO ] Lesson 5: Structures and Functions of Animal Cells
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Atoms
Molecules
Organelles
Cells
Tissues
Organs
Organ Systems
Organisms
Population
Community
Ecosystem
Biome
Biosphere
The hierarchy of biological organization
Chemical
atoms and molecules that make up the basic unit of life
Organelle
distinct and specialized subcellular structures that contribute to the cell’s maintenance and reproduction; membrane-bound structures in eukaryotic cells
● carbohydrates
● proteins
● lipids or fats
● nucleic acids
Four types of biomolecules or molecules associated with life:
Organelle
Examples: mitochondria, nucleus, Golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum
Cell
the smallest, basic, functional unit of life formed when different atoms and molecules combine and function together
Cell
Examples: skin cells, blood cells, muscle cells or fibers, neurons
Tissues
groups of cells that work together to perform a specialized function
● epithelial tissue
● connective tissue
● muscle tissue
● nervous tissue
Four types of animal tissue:
Organ
groups of tissues that work together to perform a specialized function
Organ
skin, lungs, heart muscle, brain
Organ System
groups of organs that work together to perform a certain process in the body
Organ System
Examples: integumentary system, respiratory system, circulatory system
Organism
formed by different organ systems that create complex interactions with one another to maintain balance or homeostasis, and sustain life
Organism
humans, grasses, dogs, cats, mushroom
Population
organisms that belong to the same species and live in the same area
Population
Examples: humans living in the same house, koalas living in an area of the forest
Community
different populations living in the same area
Ecosystem
includes all the communities interacting with one another and with their environment
Biosphere
includes all the different kinds of ecosystem
Biosphere
the entire surface of Earth where life thrives
Tissues
These refer to groups of cells that are similar in structure and function.
Epithelial tissue
or epithelium is a type of animal tissue that forms the inner and outer lining of organs, the covering in surfaces, and the primary glandular tissue of the body.
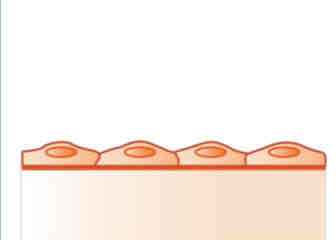
simple squamous
(Under Epithelial Tissue)
Function: site of diffusion or exchange of substances; secretion.
Examples: air sacs or alveoli, capillary walls
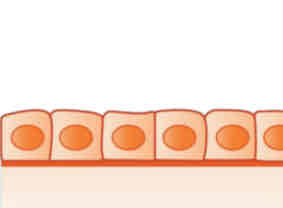
Simple Cuboidal
(Under Epithelial Tissue)
Function: absorption and secretion
Examples: glands and their ducts, ovaries, and lining of kidney tubules
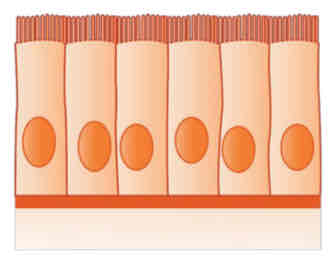
Simple Columnar
(Under Epithelial Tissue)
Functions: absorption and secretion; contains goblet cells that secrete
Examples: walls of the gastro-intestinal tract and body cavities
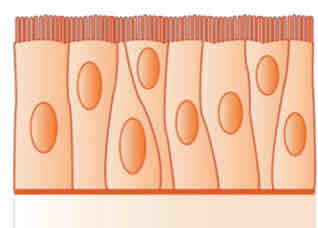
pseudostratified columnar
(Under Epithelial Tissue)
Functions: absorption and secretion; usually ciliated; cells have unequal length and position of nucleus forming a false layering of cells
Examples: the lining of the respiratory tract
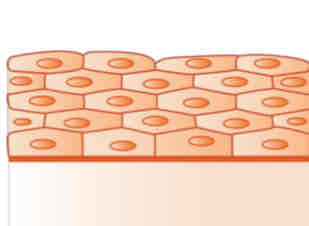
stratified squamous
(Under Epithelial Tissue)
Functions: protection against abrasion or constant exposure to friction.
Examples: the epidermis, lining of mouth, esophagus, and vagina
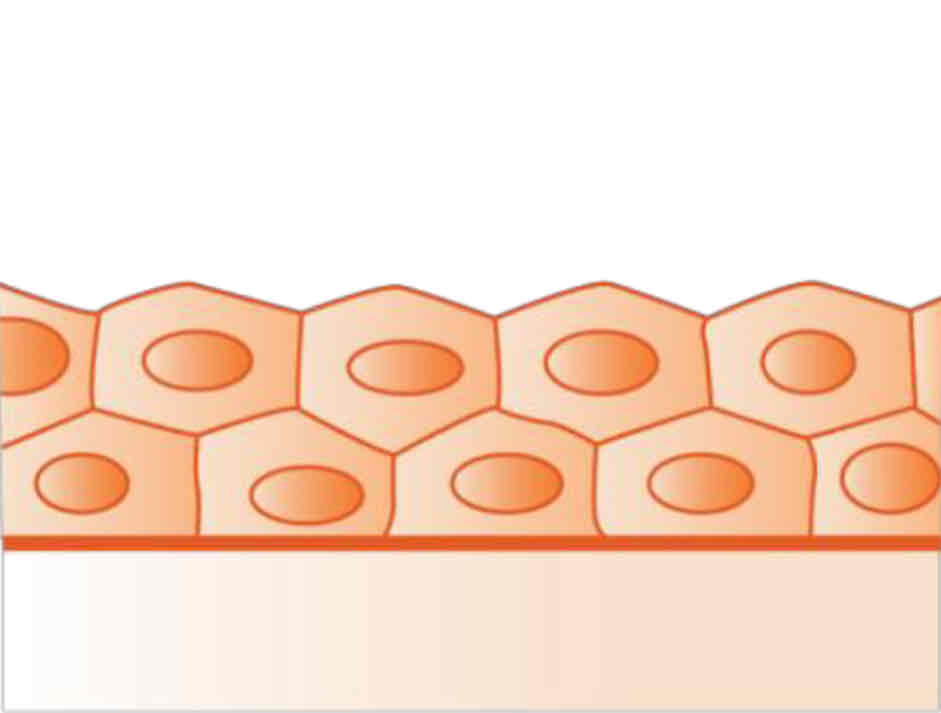
stratified cuboidal
(Under Epithelial Tissue)
Function: protection and secretion
Examples: sweat glands, salivary glands, and mammary glands
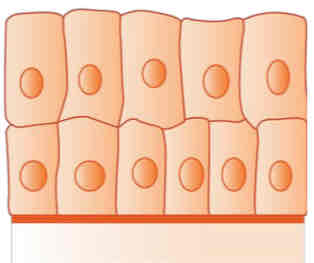
stratified columnar
(Under Epithelial Tissue)
Function: protection and secretion
Examples: male urethra and ducts of some glands
simple squamous
simple cuboidal
simple columnar
pseudostratified columnar
stratified squamous
stratified cuboidal
stratified columnar
Structures of Epithelial Tissues (7)
Bone or osseous tissue
(Under Connective Tissue)
layers of a very hard matrix with calcium salts and collagen fibers. It consists of bone cells called Lacunae
Cartilage
(Under Connective Tissue)
more flexible matrix than bone; called chondrocytes
Dense connective or dense fibrous tissue
(Under Connective Tissue)
Matrix is predominantly made up of collagen fibers and has lesser cells. This is a fibroblast or a fiber-forming cell.
Loose connective tissue
(Under Connective Tissue)
Matrix contains more cells and lesser fibers than dense connective tissue so it is softer.
Blood
(Under Connective Tissue)
plasma; Cellular components consist of blood cells with fibers that are only visible during clotting because they are made up of soluble proteins
Bone or osseous tissue
Cartilage
Dense connective or dense fibrous tissue
Loose connective tissue
Blood
Structures of Connective Tissues: (5)
Skeletal Muscle
Smooth Muscle
Cardiac Muscle
Structures of Muscular Tissues (3)
Skeletal Muscle
(Under Muscular Tissues)
long, cylindrical, striated (with visible stripes), and multinucleated (with more than one nucleus) attached to the skeleton or bones
Smooth Muscle
(Under Muscular Tissues)
made up of nonstriated, uninucleated, and spindle-shaped (have pointed ends) cells. Found in the walls of hollow organs such as intestines, stomach, bladder, blood vessels, and uterus
Cardiac Muscle
(Under Muscular Tissues)
uninucleated (one nucleus) and has striations and has intercalated disks. Found in the heart
Astrocytes
(Under Nervous Tissue)
These are star-shaped cells that support and control the chemical environment around the neurons. These are the most abundant glial cell in the CNS.
Microglial cells
(Under Nervous Tissue)
These are ovoid cells in the CNS that can transform into a phagocytic macrophage to clean neuronal debris and wastes.
Ependymal cells
(Under Nervous Tissue)
These are ciliated cells that line the central cavities of the brain and the spinal cord and form a fairly permeable membrane between the cavities with cerebrospinal fluid and the tissues of CNS.
Oligodendrocytes
(Under Nervous Tissue)
These are responsible for the production of the myelin sheath. In CNS
Satellite cells
(Under Nervous Tissue)
They surround the cell body of a neuron. In PNS
Schwann cells
(Under Nervous Tissue)
They surround all the nerve fibers and produce myelin sheath similar to the oligodendrocytes. In PNS
Connective tissue
is made up of cells and an extracellular matrix that connects, protects, and supports body parts. Bone, cartilage, dense connective tissue, loose connective tissue, and blood are the types of connective tissue.
Muscular Tissue
is composed of highly specialized muscle cells that contract to produce movement. It has three types: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscles.
Nervous Tissue
is made up of neurons that receive and conduct electrochemical signals and supporting cells (glial cells) that support, protect, and insulate neurons.