Clinical Skills Handbook 3
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Week 6
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
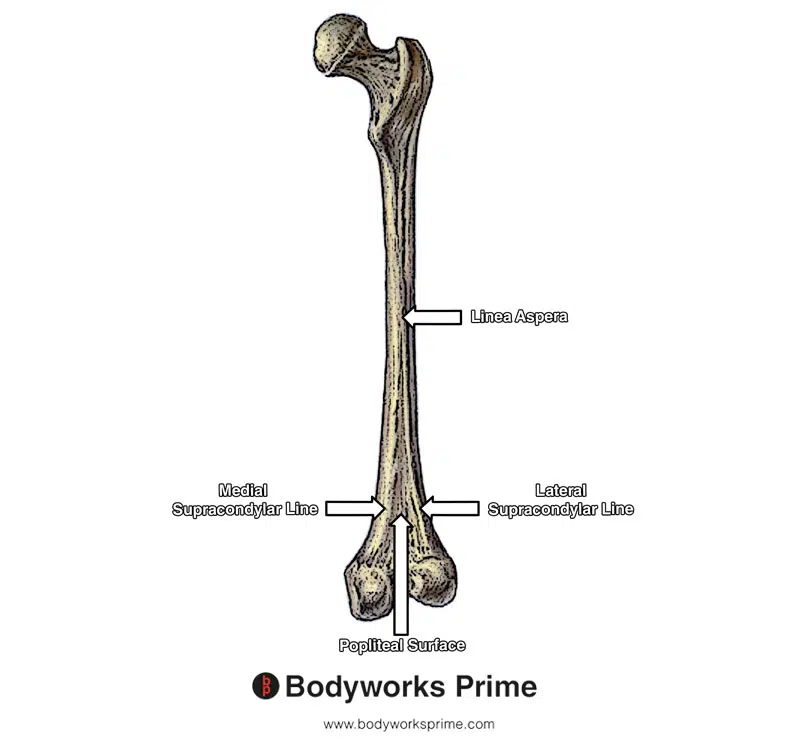
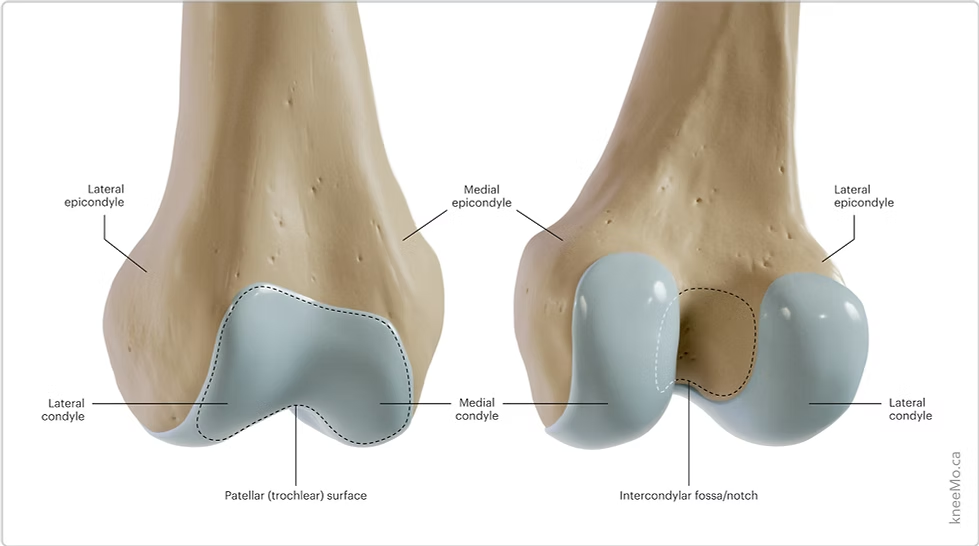
Femur:
Supracondylar lines (Medial and lateral)
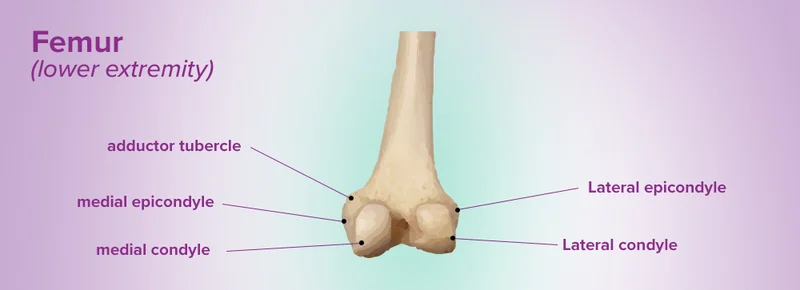
Femoral Condyles (medial and lateral)
Femoral epicondyles (medial and lateral)
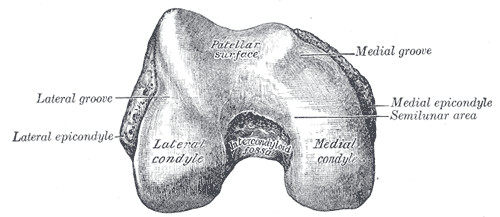
Patellar surface of femur
Intercondylar fossa
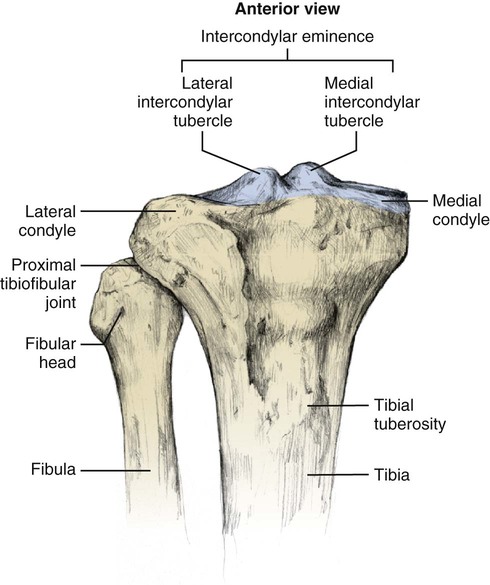
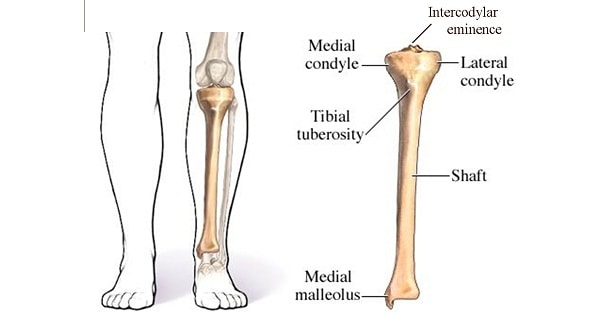
Tibia:
Intercondylar eminence
Medial Intercondylar Tubercle
Lateral Intercondylar Tubercle
Medial and lateral tibial condyles
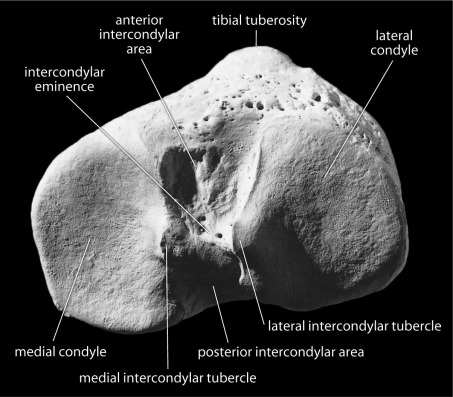
Anterior + posterior Intercondylar area
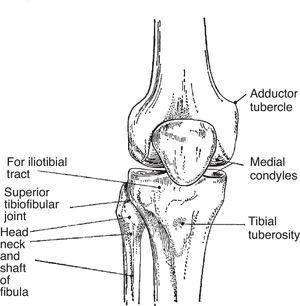
Gerdys Tubercle
Tibial Tuberosity
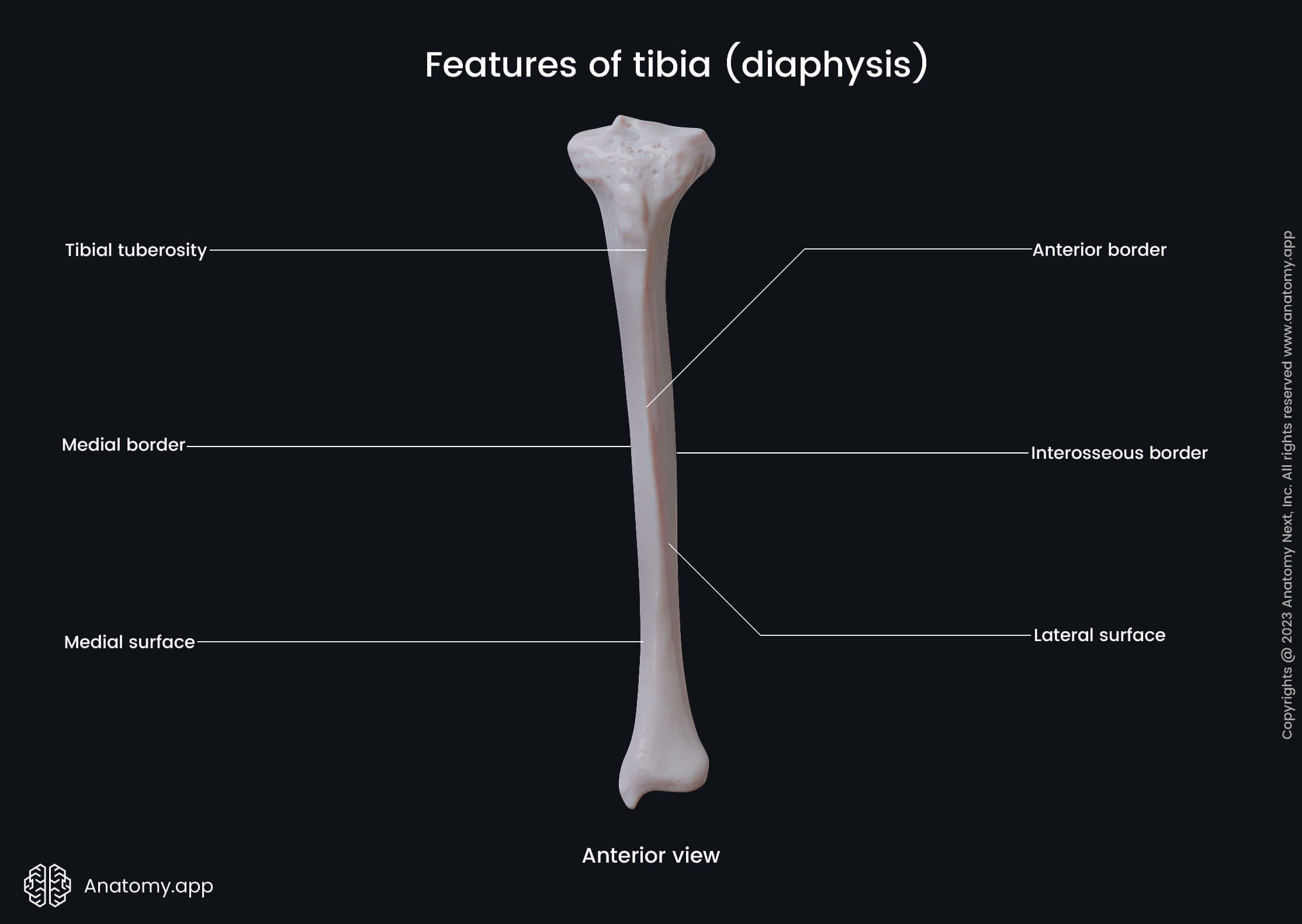
Anterior, medial and interosseous borders of Tibia
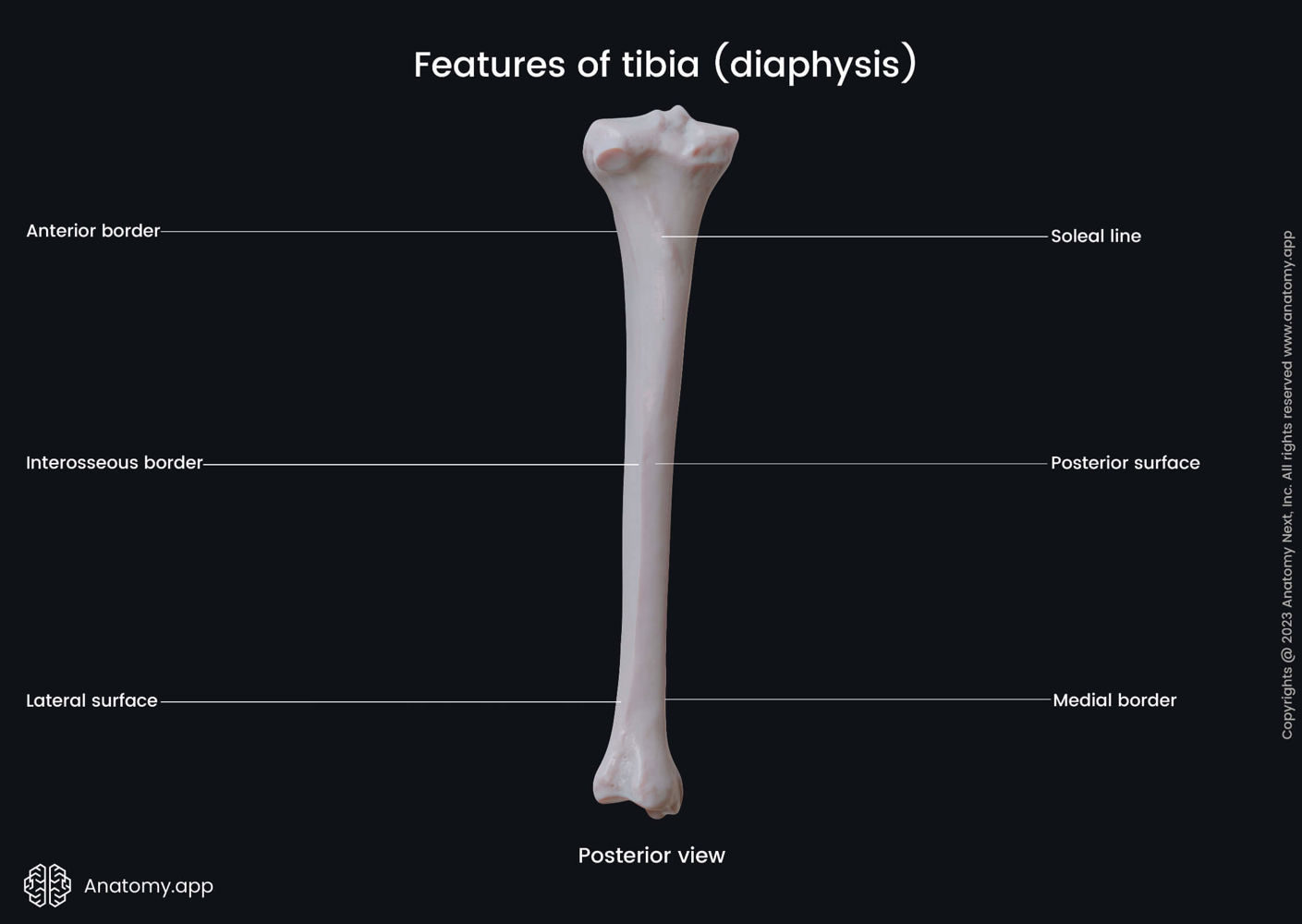
Medial, lateral and posterior surfaces of Tibia
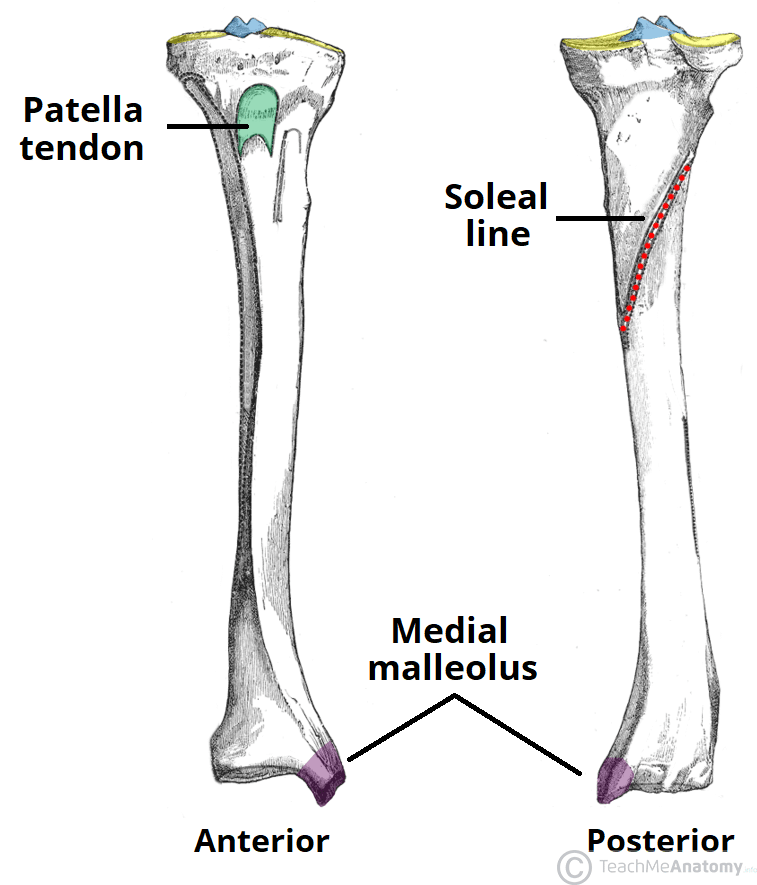
Soleal Line of Tibia
Medial Malleolus
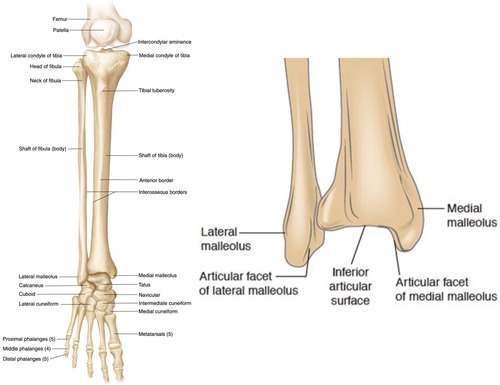
Inferior articular surface of tibia
Articular facet on medial malleolus
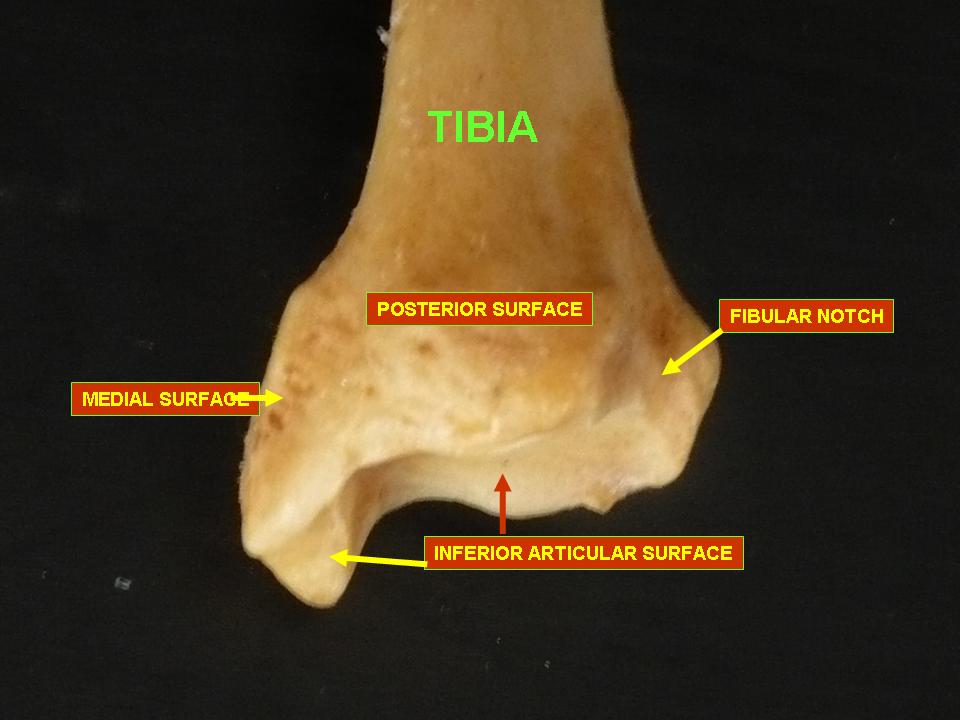
Fibular notch (of tibia)
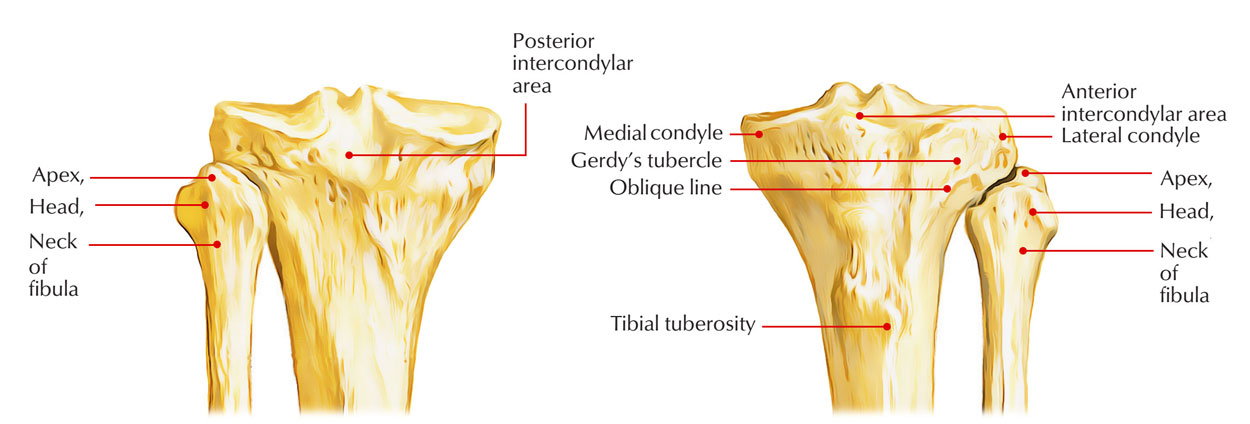
Fibula:
Head
Apex
Neck
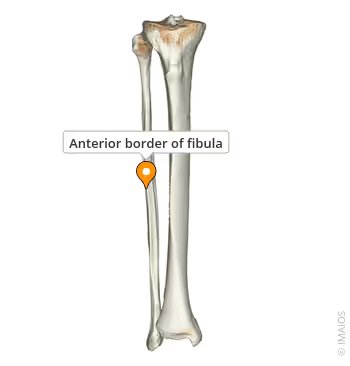
Fibular Anterior Border
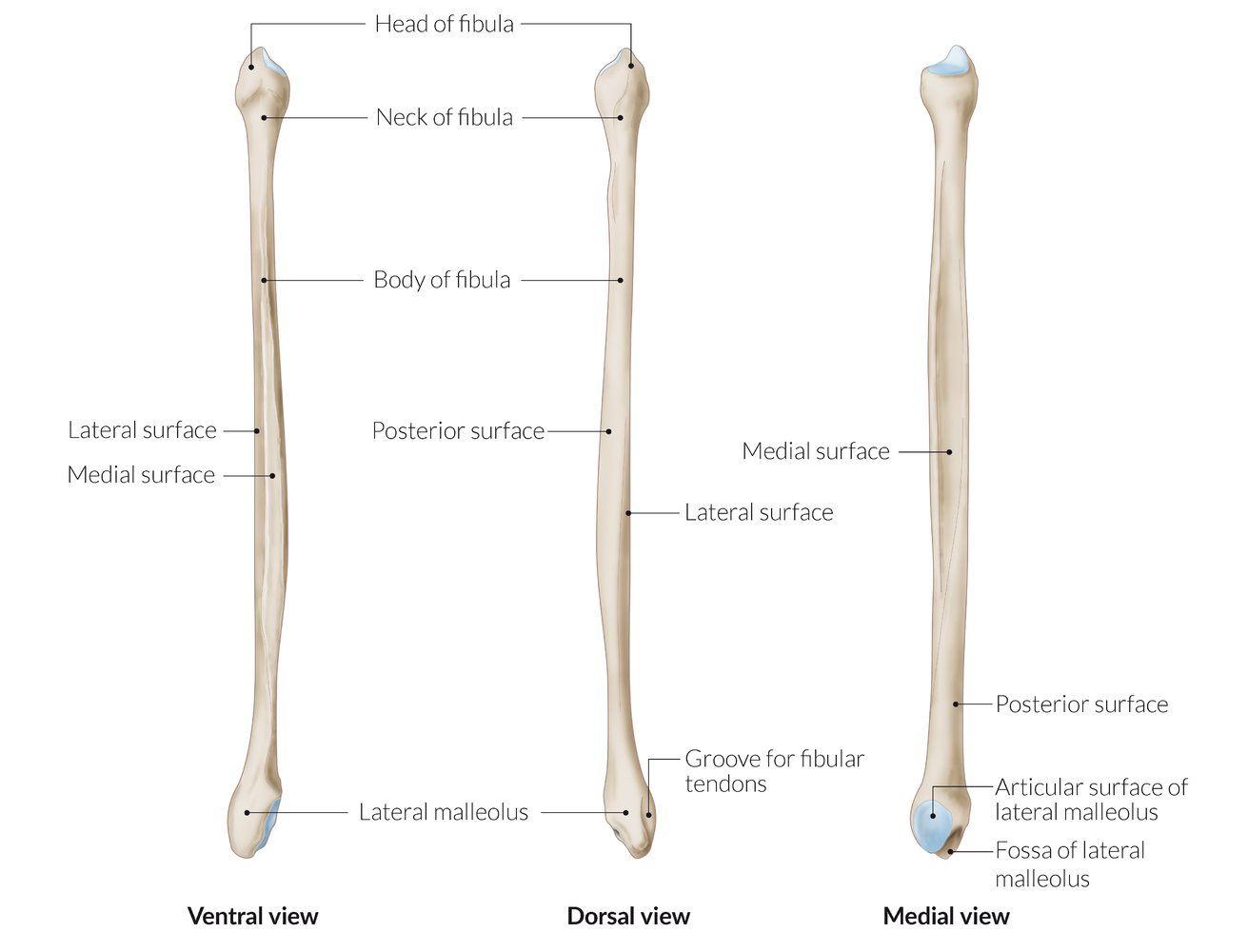
Medial, lateral and posterior surface of Fibula
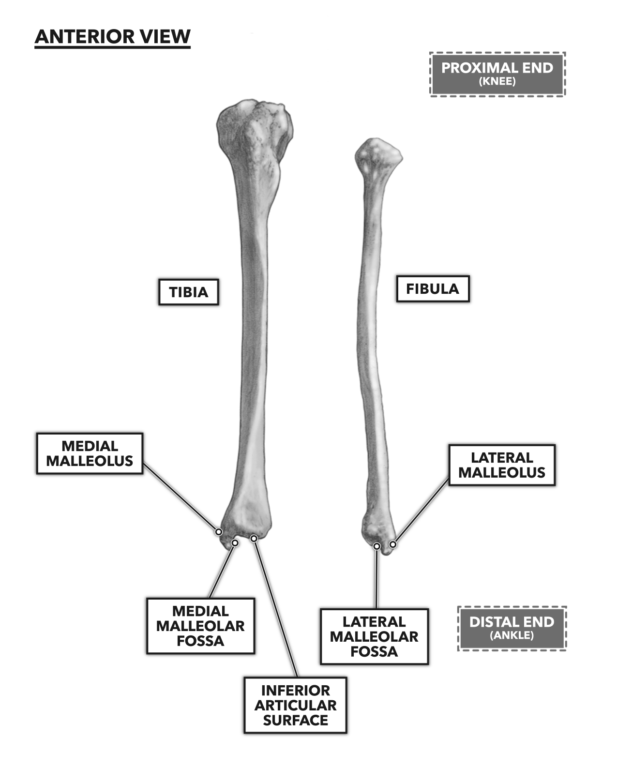
Lateral malleolus
Malleolar Fossa
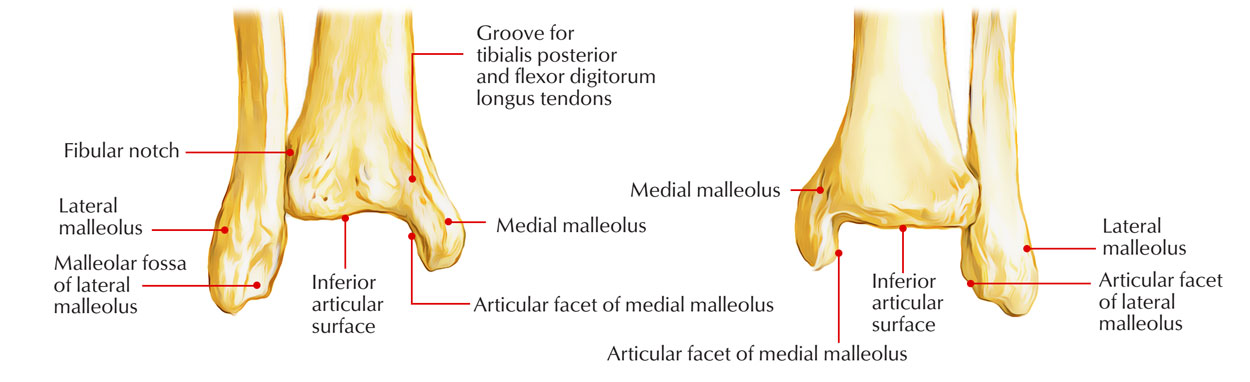
Articular facet on lateral malleolus
Palpate the distal thigh and as you approach the knee, find the prominent condyles medially and laterally.
Surface Anatomy: Talk through palpation
Femoral Condyles
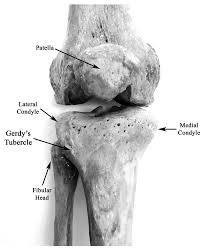
Resist hip abduction to create tension in the iliotibial band. Find where the band ends on the lateral tibial condyle.
Gerdy’s tubercle
Find the prominent bony tuberosity inferior to the patella, on the superior tibia. Move your fingers medially and laterally onto the condyles on either side.
Tibial tuberosity & condyles (Medial + lateral)
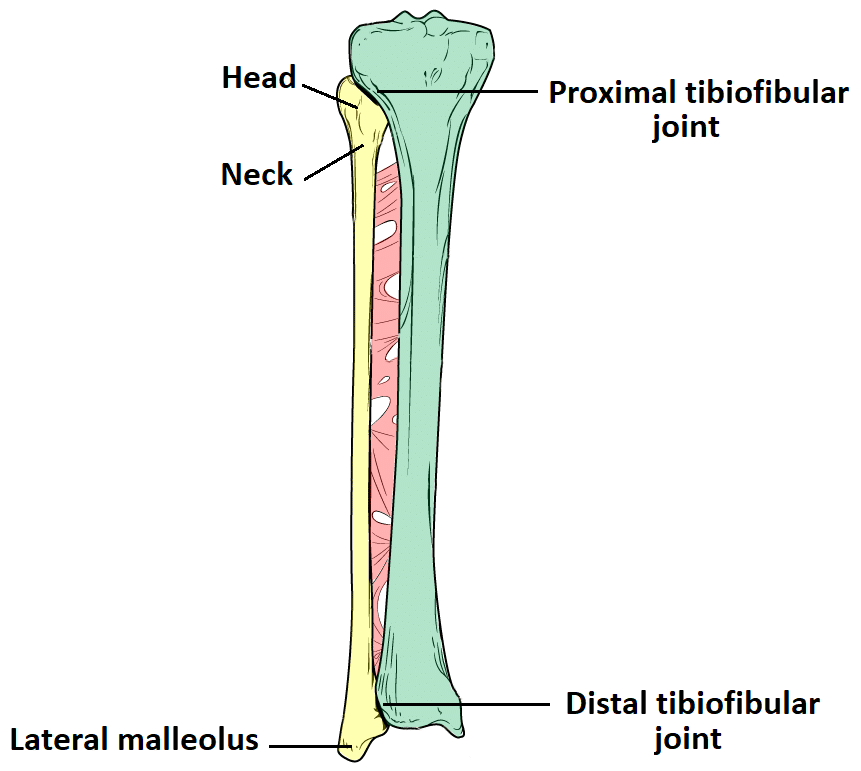
If you continue to move laterally from the lateral tibial condyle, you will move onto the head of the fibula.
Head of Fibula
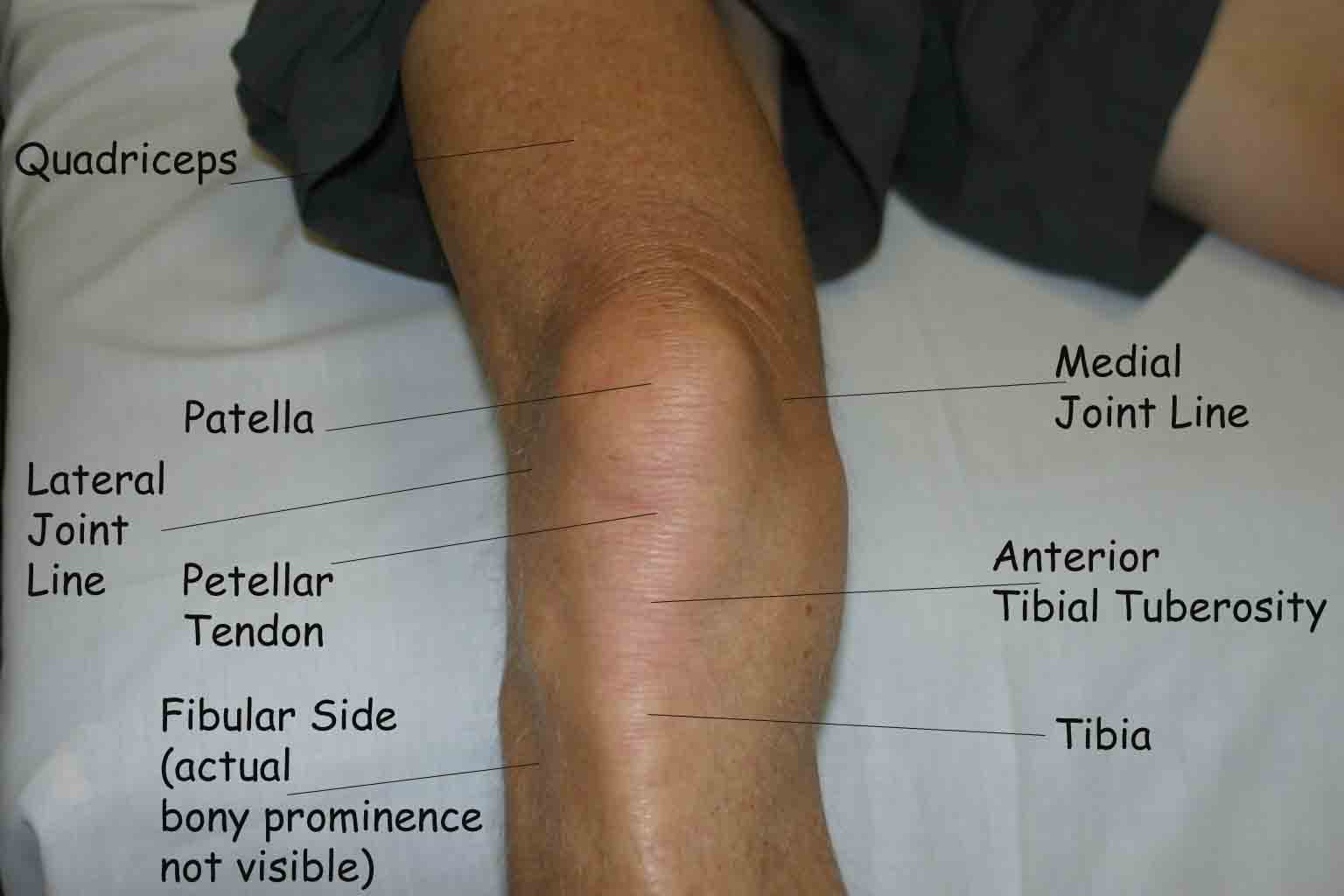
Go back to the femoral condyles, and with 90 degrees knee flexion (foot flat on plinth), palpate the space between the femoral condyles and tibial condyles on either side. You may start centrally either side of the patellar tendon and move in either direction. Tenderness on the joint line may indicate meniscal injury. Medially and laterally rotate the knee.
Knee Joint Line
What might tenderness here indicate?
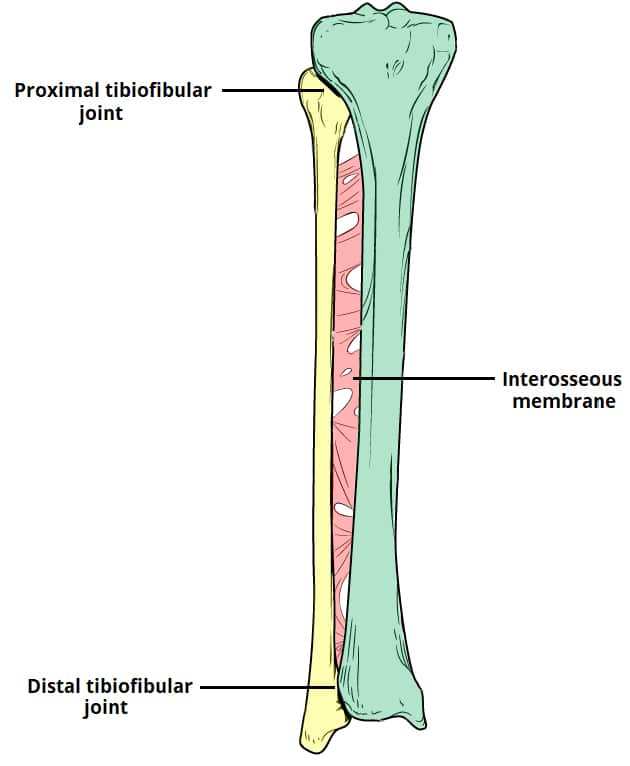
Proximal: Palpate the medial condyle of the tibia and the head of fibula and palpate the space between each.
Distal: Palpate the space between the distal tibia and fibula.
Tibiofibular Joint Lines - Proximal and Distal
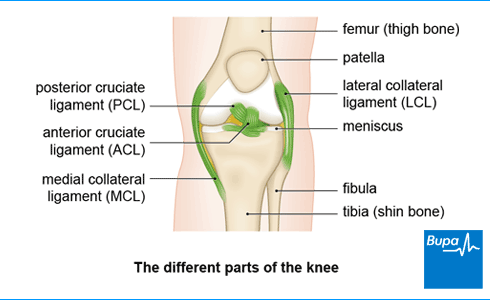
Medial: Palpate the medial femoral condyle and move your fingers inferiorly towards the medial tibial condyle (8-9cm), crossing the joint line in between.
Lateral: Palpate the lateral femoral condyle and move your fingers inferiorly toward the head of fibula (5cm), crossing the joint line.
Medial & lateral collateral ligaments
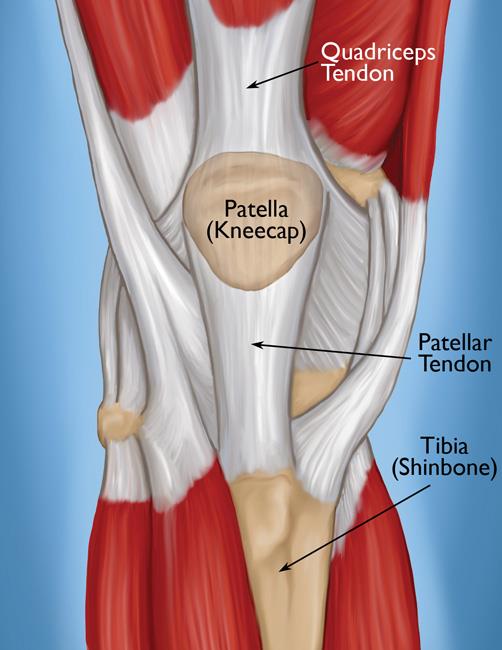
Palpate the patella medially laterally and the apex. Move the patella side of side across the femur (medial and lateral glides). Palpate the patellar tendon between the apex and the tibial tuberosity.
Patella, patellar tendon
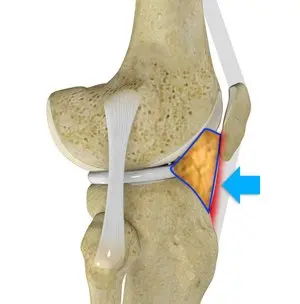
Palpate hoffas fat pad either side of the patellar tendon.
Hoffas Fat Pad
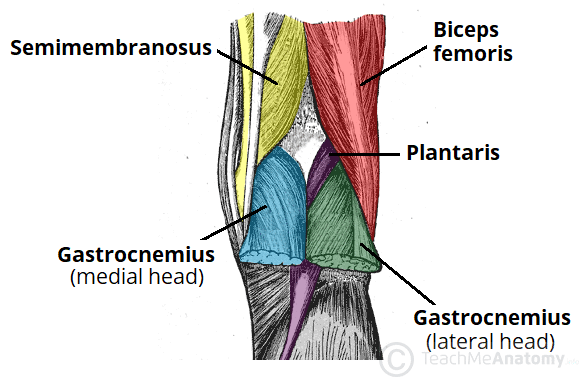
In prone, observe the posterior knee (lower leg on pillow to provide some knee flexion). Activate the hamstrings and then the gastrocnemius (knee flexion and plantarflexion) to identify the margins for the fossa.
Popliteal Fossa
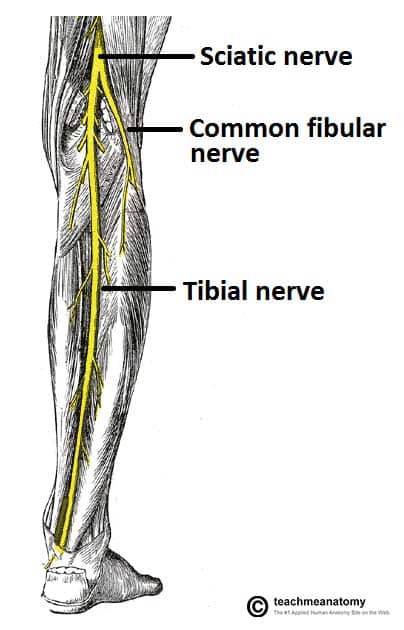
Palpate the tibial nerve on the lateral side of the popliteal fossa. This is easily palpated with the knee flexed, Run your fingernail across the nerve to feel the tension, then dorsiflex the ankle and tension should increase.
The common peroneal nerve is more difficult to palpate directly. Instead, visualize it winding around the neck of the fibula.
Tibial and common peroneal nerves
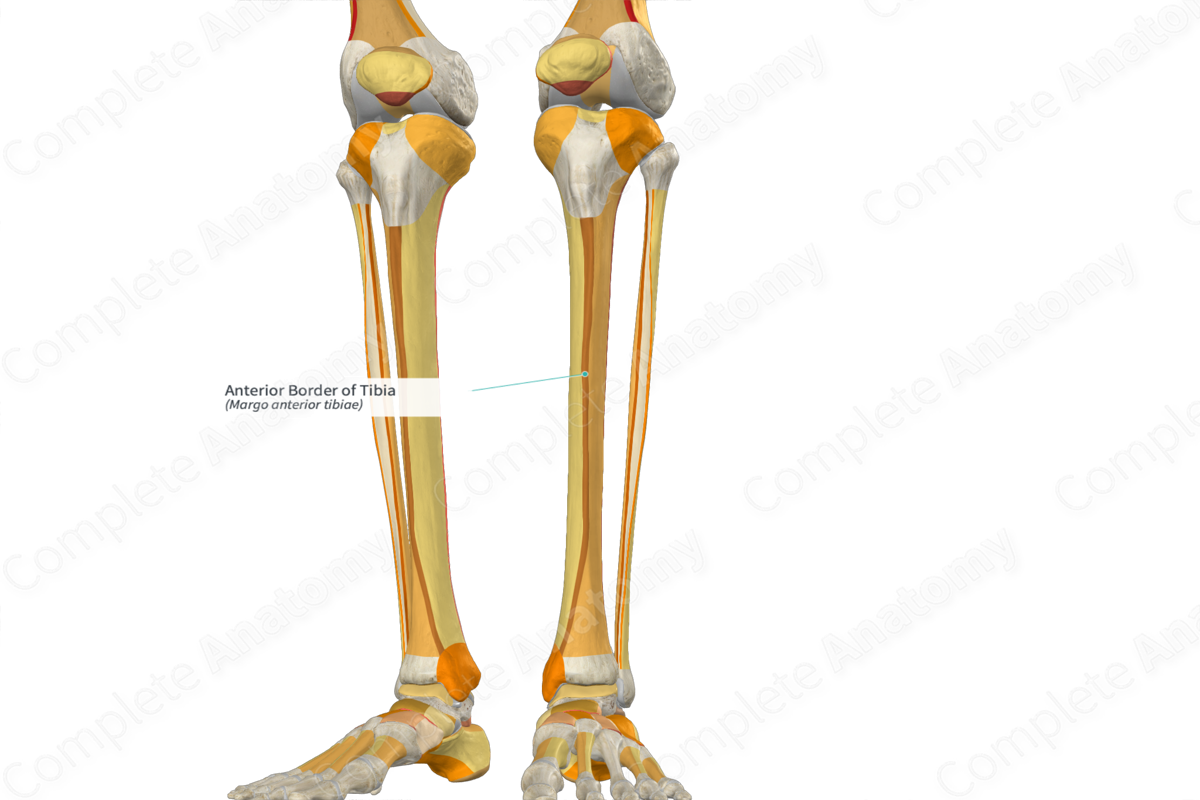
Palpate the shin bone
Anterior border of tibia
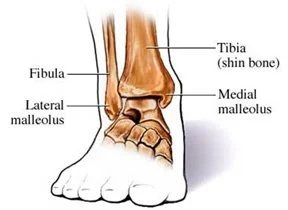
Palpate the prominent bony landmarks at the level of the ankle
Medial and lateral malleolus
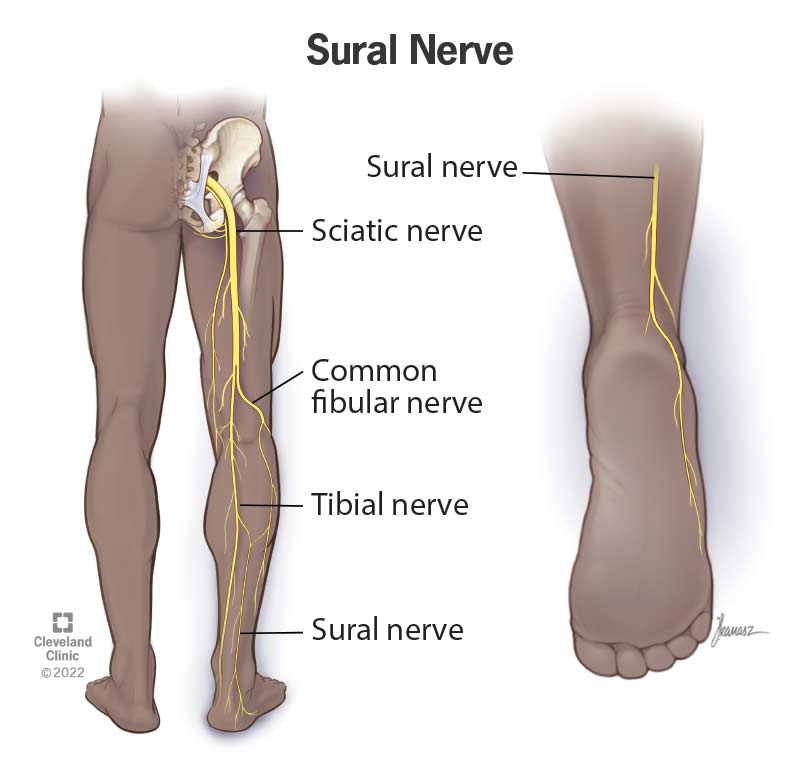
Occasionally, you may palpate this nerve running lateral to the Achilles tendon (between achilles and lat. malleolus - space)
Sural Nerve
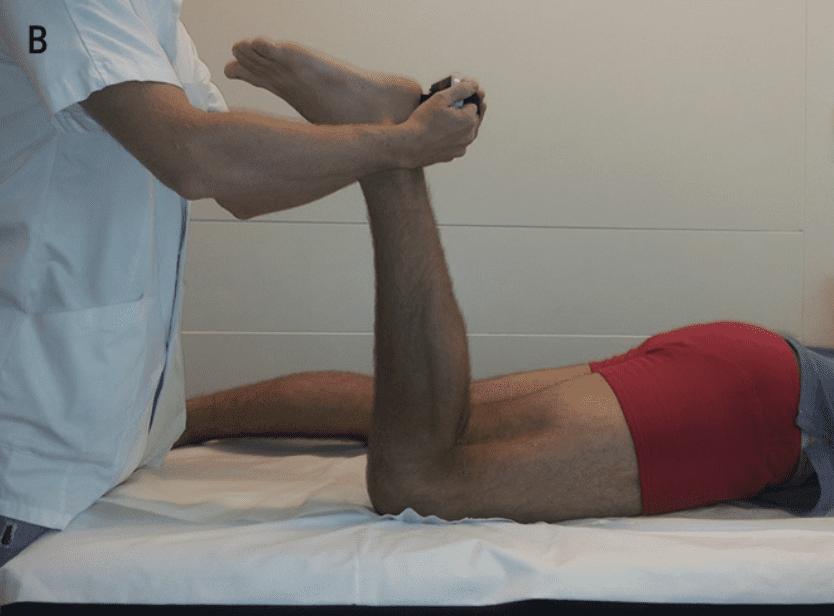
In prone, flex the knee joint. Apply resistance in inner, mid and outer range. Add medial and lateral rotation to bias the medial and lateral hamstrings.
You may also extend the hip with knee extended to bias hamstrings.
Musculature identification:
Hamstrings:
For all four quadriceps you can demonstrate knee extension in inner-outer range in a seated position.
Demonstrate hip flexion with knee extension (straight leg raise) to bias rectus femoris.
Quadriceps:
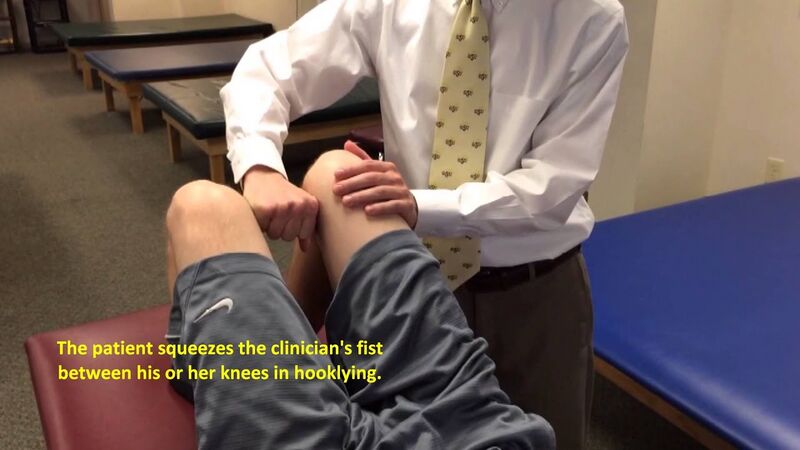
Position the model in supine with the hip abducted to 50 degrees. Use your own body to resist hip adduction.
Alternatively, perform a squeeze test with the knees flexed and extended to demonstrate inner range adduction.
Adductors:
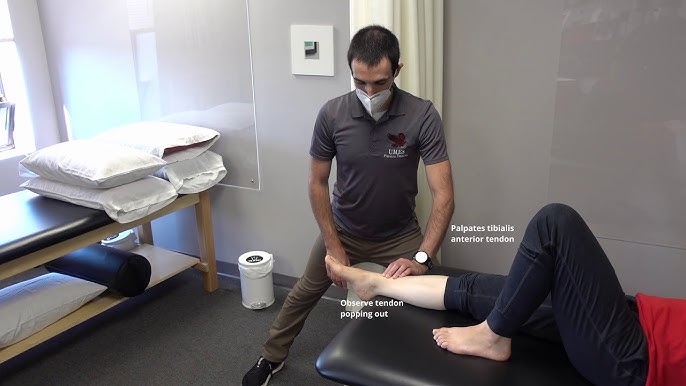
Demonstrate ankle dorsiflexion (+/- inversion), great toe extension and 2nd-5th to extension.
Support the lower leg and resist the forefoot for ankle/subtalar movement.
Support the foot and resist the distal phalanges for toe movements.
Observe the tibialis anterior tendon over the anterior ankle.
Observe the extensor hallucis longus and digitorum longus tendons in the forefoot.
Peroneus tertius is too deep to observe.
Anterior Compartment of leg:
· Tibialis anterior
· Extensor hallucis longus
· Extensor digitorum longus
· Peroneus Tertius
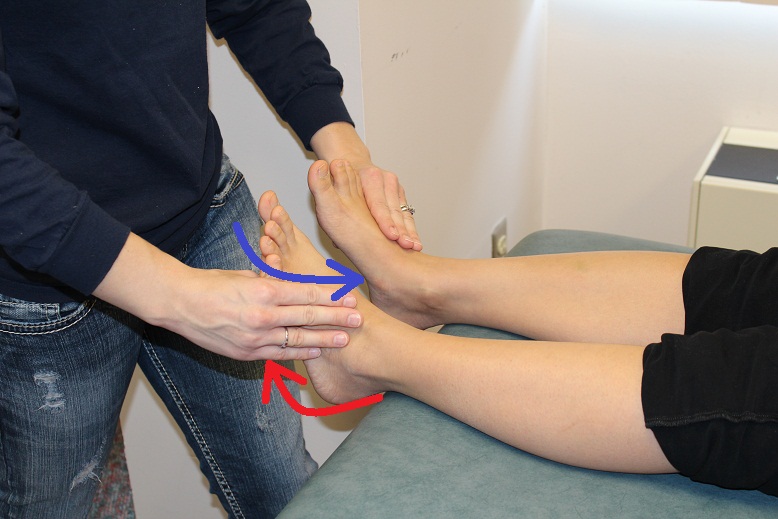
Demonstrate eversion and plantarflexion.
Observe and palpate the contraction of both muscles in the lateral leg.
Lateral Compartment of Leg:
· Peroneus longus and brevis
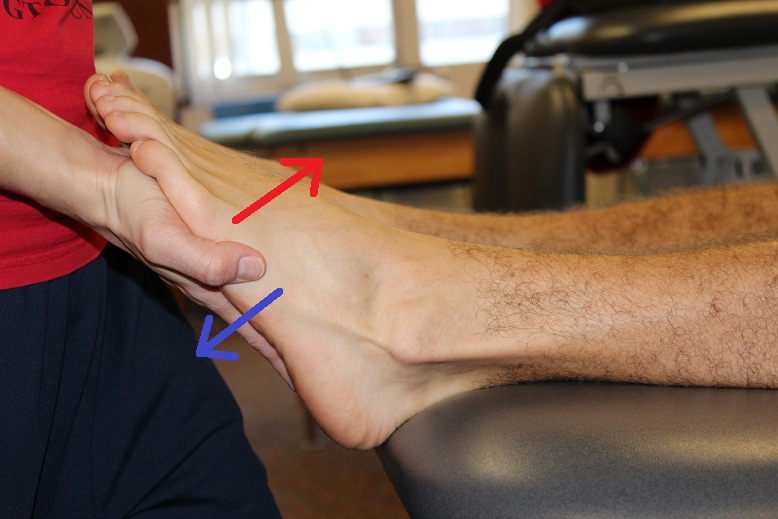
Plantarflex with knee extended (gastrocnemius) and flexed (soleus) in a prone or standing position.
Observe and palpate the muscles in the calf.Demonstrate plantarflexion +/- inversion (tibialis posterior) or toe flexion (flexor hallucis longus and flexor digitorum longus).
Support the lower leg and resist the forefoot for ankle/subtalar movement.
Support the foot and resist the distal phalanges for toe movements.
You may palpate tension in the tendons behind the flexor retinaculum or in the sole of the foot.
Choose a supine position for best control and communication with your model.
Posterior Compartment of Leg:
· Gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris
Tibialis posterior, Flexor hallucis longus, flexor digitorum longus.