psychology year 10
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
what is the nervous system
The nervous system includes the brain, spinal cord, and a complex network of nerves. This system sends messages back and forth between the brain and the body.
what is the central nervous system
is the part of the body made up of the brain and spinal cord. It controls most functions of the body and mind, including thought, movement, and sensation.
peripheral nervous system
is the part of the nervous system outside the brain and spinal cord. It connects the central nervous system to the rest of the body and includes nerves that control muscles, organs, and sensory
autonomic nervous system
•Carries messages between the central nervous system and visceral muscles in organs and glands to allow involuntary movement
Somatic nervous system
•Carries sensory information from the body to the central nervous system
Enteric nervous system
is a network of nerves in the gastrointestinal tract that controls digestion independently of the brain and spinal cord
Sympathetic nervous system
•Arouses body to deal with a
stressor,
threat or
extreme
emotion
Parasympathetic nervous system
•Restores body to normal state of functioning after stressor, threat,
or extreme
emotion has
passed
what are neurons
Neurons are cells that send and receive nerve signals.
Neurotransmission
is the process of one neuron communicating with another neuron
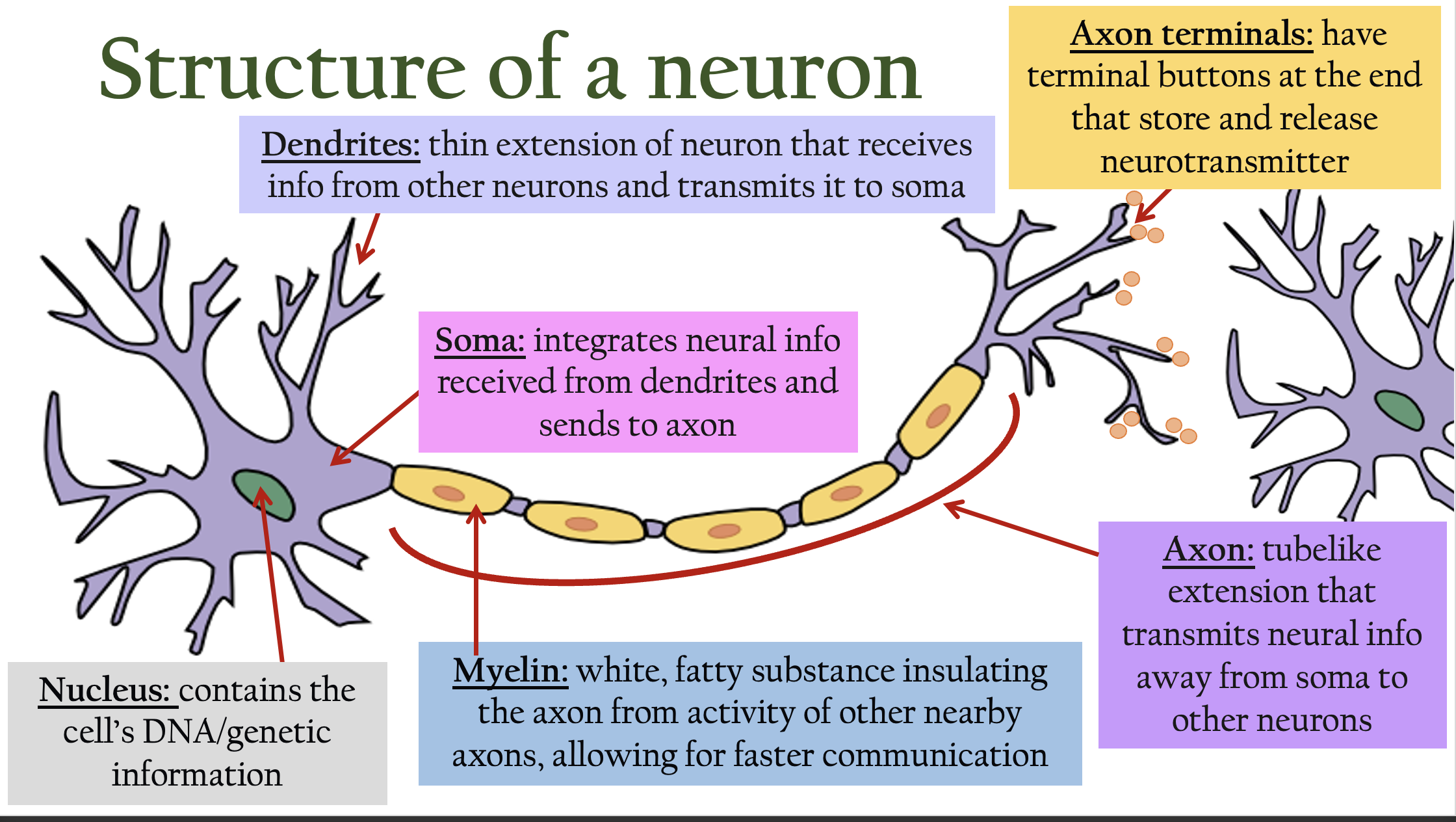
Dendrites
Dendrites are neuron branches that receive signals from other cells.
Soma
is the neuron's cell body that processes incoming signals.
Axon terminals
are the endpoints of an axon where signals are passed to other cells
Axon
An axon carries signals away from the neuron's cell body.
Myelin
Myelin is a fatty layer that speeds up nerve signal transmission.
different areas of psychology
•Sport
•Clinical
•Neuro-clinical
•Forensic
sport psychologist
A sport psychologist deals with the influences of the mind on physical activity and athletic performance. Sports psychologists can help sports people to improve performance through mental training, goal setting, motivation and managing self-confidence. They may assist teams to bond and build their leadership before an important match,
clinical psychologist
Clinical psychologists specialize in the assessment, diagnosis and treatment of mental health disorders such as depression.
Places of work vary widely and include hospitals, universities, community health centers and private clinics.
Clinical psychologists work with people of all ages who are suffering from mental health problems, including eating disorders, depression, anxiety, addiction, phobias and more
neuro clinical psychologist
Neuro-clinical psychologists are concerned with how problematic behaviour and thinking patterns are affected by brain dysfunction.
They work with people who have been affected by brain-related illness or have brain damage. For example, dementia (memory loss) or head injury from a car accident.
forensic psychologist
Forensic Psychologists specialise in applying psychology to the legal and criminal justice system.
Forensic Psychologists can work with convicted offenders, people who are ‘unfit for court’ because of a mental disorder, victims of crime and ex-criminals who may re-offend
ADAPTIVE BEHAVIOUR
Behaviour that enable an indvidual is “adjust” to the demands of daily life in age appropriate ways and be able to do so independently
MALADAPTIVE BEHAVIOUR
●Impairs a person’s ability to function properly and adjust to the challenges and stresses of everyday life.
Mentally wellbeing
•Good social and emotional wellbeing.
Mental health problem
•Affects thoughts, feelings and behaviours in daily life.
Mental health disorder
•Affects thoughts, feelings and behaviour in a severe way that causes distress to a person in daily life.
Normal + abnormal behaviour
refers to the behaviour of everyone in a society.
Typical + atypical
can refer to behaviour of everyone or only the way an individual behaves (depending on the context).
The Biopsychosocial model
•The biopsychosocial model is a way of describing and explaining how biological, psychological and social factors combine and interact to influence the state of a person’s mental health.
what does the biopsychological model state
•The model states that multiple factors contribute to a person’s mental state. There is usually no single factor that causes a mental health disorder on its own.
internal factors that influence an individual mental wellbeing
•are influences that originate inside or within a person. These can be organised as biological and psychological factors.
external factors that influence an individual's mental wellbeing
•are influences that originate outside a person. Social factors are external factors.
biological factors example
beliefs and attitudes , personality traits , coping skills
biological factors example
genes, female/male, brain function
social factors example
lifestyle, level of education , poverty
Social stigma
refers to the negative attitudes and beliefs of the wider community that lead people to avoid, dislike, discriminate and fear people with mental disorders.
Self-stigma
occurs when an individual accepts the negative views and reactions of others and apply them to themselves (leads to low self-esteem).
structure of a neuron
Dependent variable
whats measured
independent variable
what will be changed
control group
•The group not exposed to the added independent variable in the experiment
experimental group
•The group exposed to the added independent variable in the experiment.
research hypothesis
should include:
• the independent variable
• the dependent variable
• a prediction about the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable (increase/decrease/etc)
research hypothesis example
Students in Middle School (IV) will have higher (prediction) attendance (DV) than Junior School or Senior School (IV) students.
population
•is the entire group of people of interest for a study
the sample
is a smaller subset of the population who participate in an experiment – E.g. 100 members at Crunch Springvale
A representative sample
a sample that accurately
reflects the characteristics of the population
Convenience sampling
involves selecting participants who are readily available without any attempt to make the sample representative of a population
Stratified sampling
Involves dividing the population into subgroups/strata based on specific categories and then selecting a sample from each strata in the same proportion that they occur in the population.
ethical guidelines - informed consent
The researcher must first fully explain to participants the true purpose and risks of the study, and get written permission on a consent form in order to take part.
If under 18 or incapable, parental/guardian consent should be given.
ethical guidelines - Voluntary participation
Each participant must willingly choose to take part in the research and must not be coerced, forced or tricked into taking part.
ethical guidelines - Withdrawal rights
Each participant may leave study at any time without negative consequences or pressure to stay, and may remove their results from the data at any time.
Y Roles of a Forensic Psychologist
conducting mental health assessments for courts, evaluating a defendant's competency to stand trial, providing expert testimony in court, and assisting in criminal profiling
SPECIALISATIONS IN FORENSIC PSYCHOLOGY
Police psychology- seeks to ensure law enforcement are able to perform their jobs safely, effectively, ethically, and lawfully
Criminal psychology-studies the behaviours and thoughts of criminals
Behavioural Evidence Analysis
5 Steps
1. Analyse the Forensic Evidence, 2. Analyse the Victims characteristics, 3. Analyse the Crime Scene Characteristics, 4. Develop a Criminal Profile, 5 , the apprehension