DNA replication
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
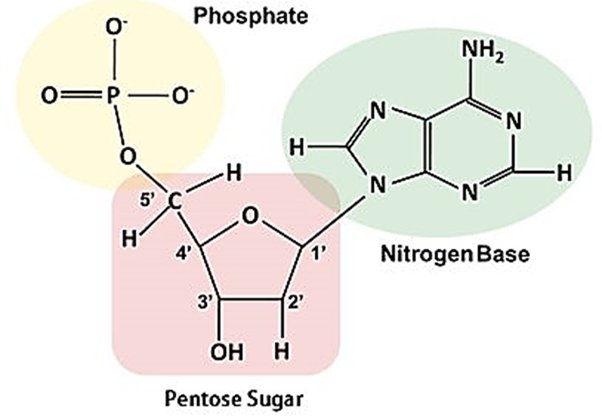
How are the carbon atoms in a sugar molecule numbered?
When orienting the sugar to have the single oxygen at the top, start counting clockwise
The 5th carbon is not apart of the ring structure but is attached as a chain
The fifth carbon is always attached to the phosphate group
The third carbon has an attached hydroxyl group (-OH)
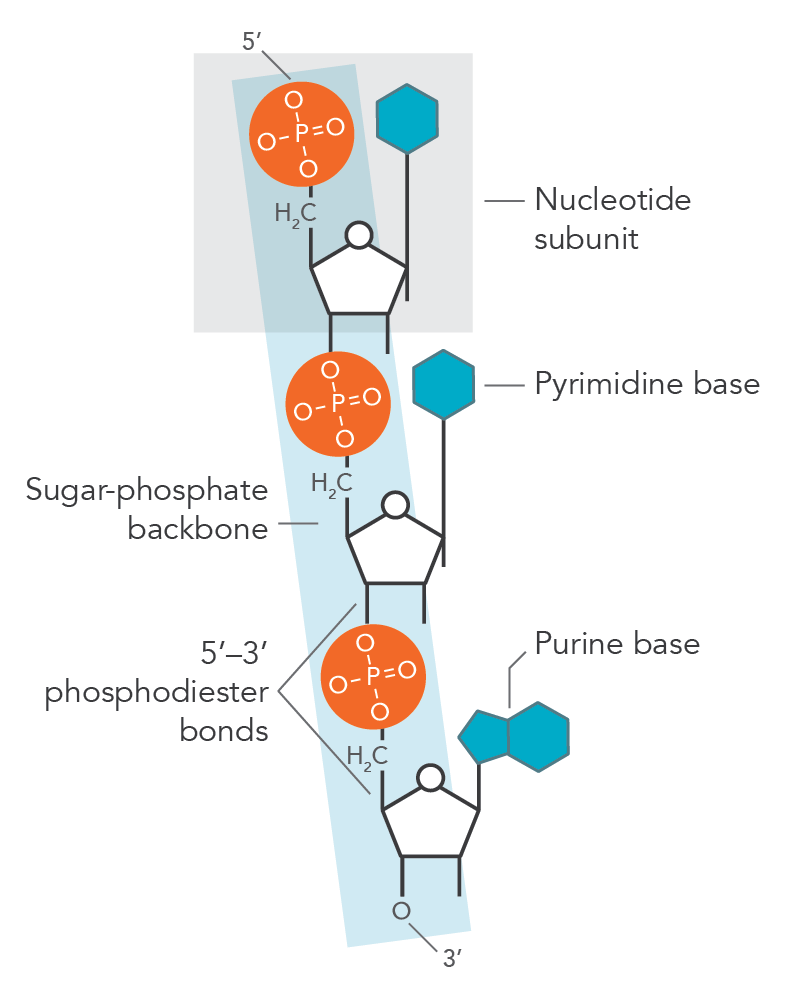
What is the bond called between the phosphate and the two pentose sugars
Phosphodiester bond (phosphate bonded with 3’ of one sugar molecule, and 5’ of another sugar molecule)
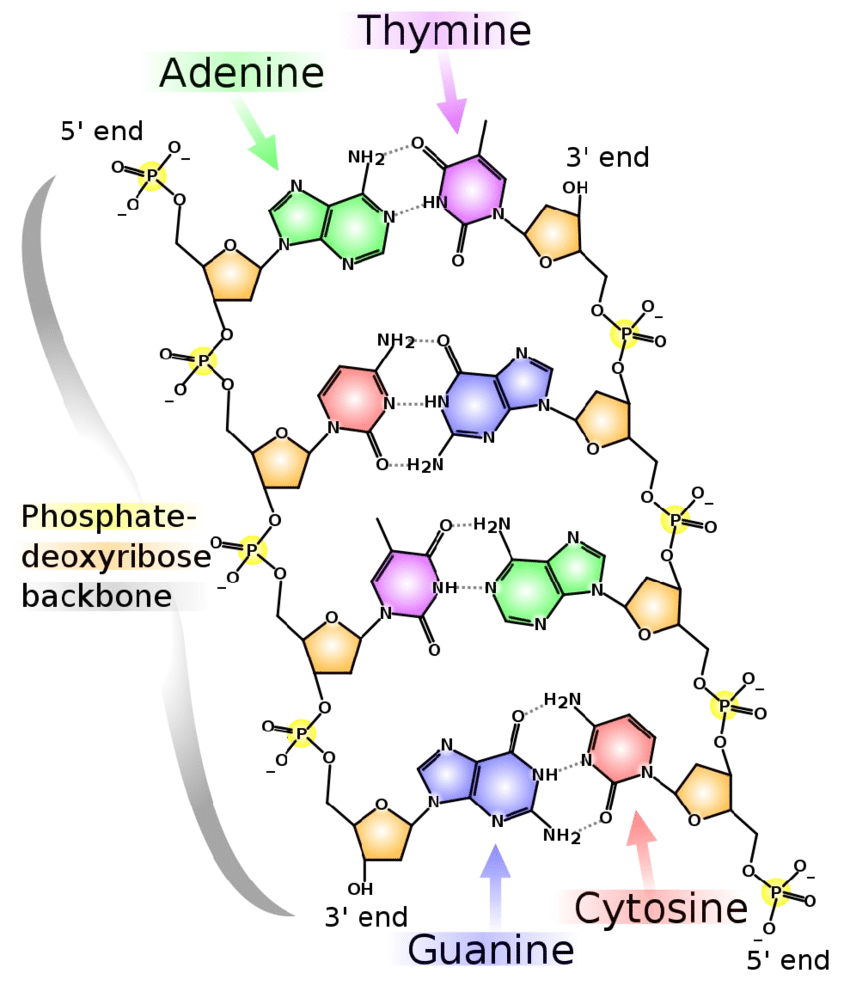
Is DNA parallel or antiparallel and why?
Antiparallel
Because of the way bases pair through hydrogen bonds, the two DNA strands are antiparallel (they run in opposite directions)
Notice in the picture, the top of one strand is 5’ and the top of the other strand is 3’ (this is because they are antiparallel and the pentose sugars are oriented differently)
What is cell theory?
All cells come from pre-existing cells, and cells reproduce by mitosis (dividing in half)
What do the two daughter cells get from the parent cell?
Each of the two daughter cells gets an exact copy of parent cell’s genetic information
What must happen in a cell before mitosis must occur?
DNA must duplicate
What is duplication of the parent cell’s DNA called?
DNA replication
What is the first step in DNA replication?
The DNA double helix must be opened up
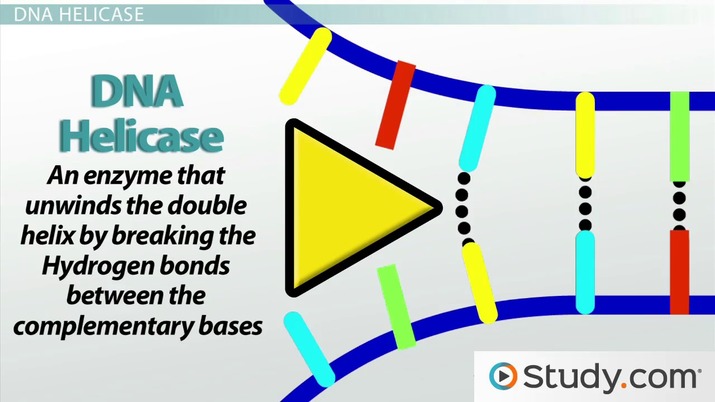
What is DNA helicase?
The unzipping enzyme
What does DNA helicase do?
Separates and unzips the two strands by breaking the hydrogen bonds between complimentary base pairings, beginning at one point and moving in opposite directions
What does DNA helicase create when it starts unzipping the DNA?
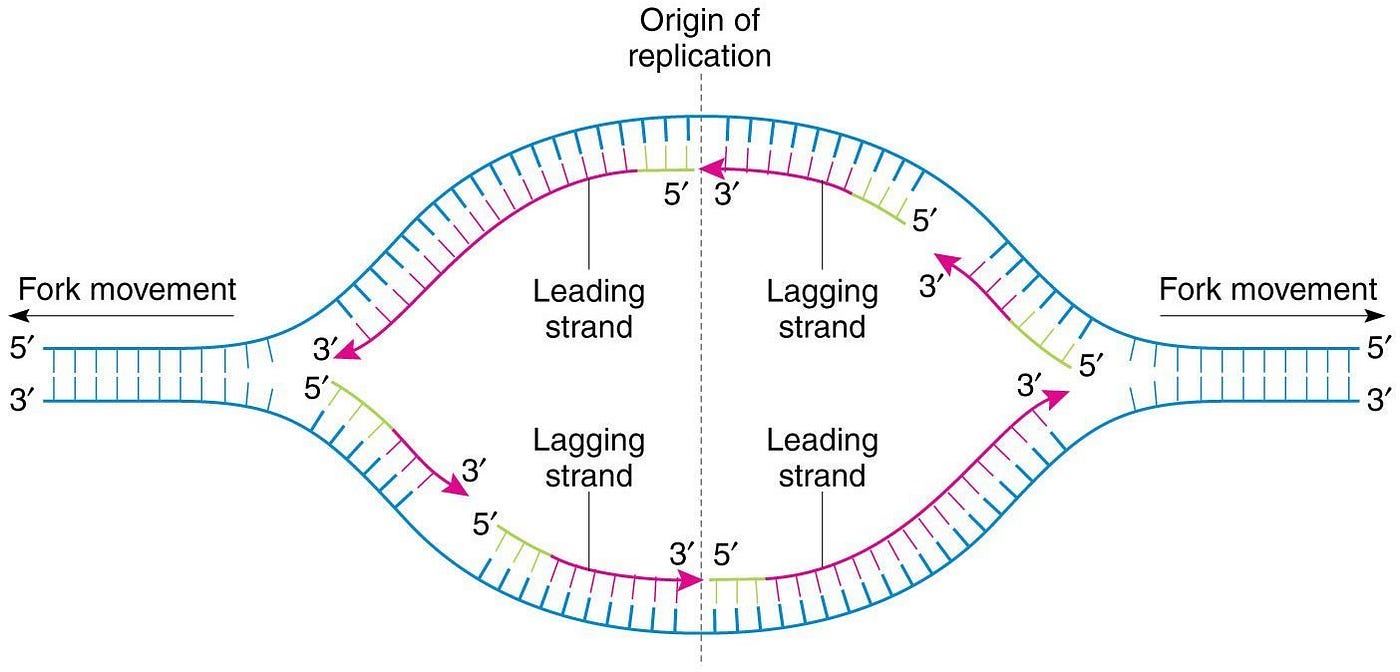
A replication bubble and two forks
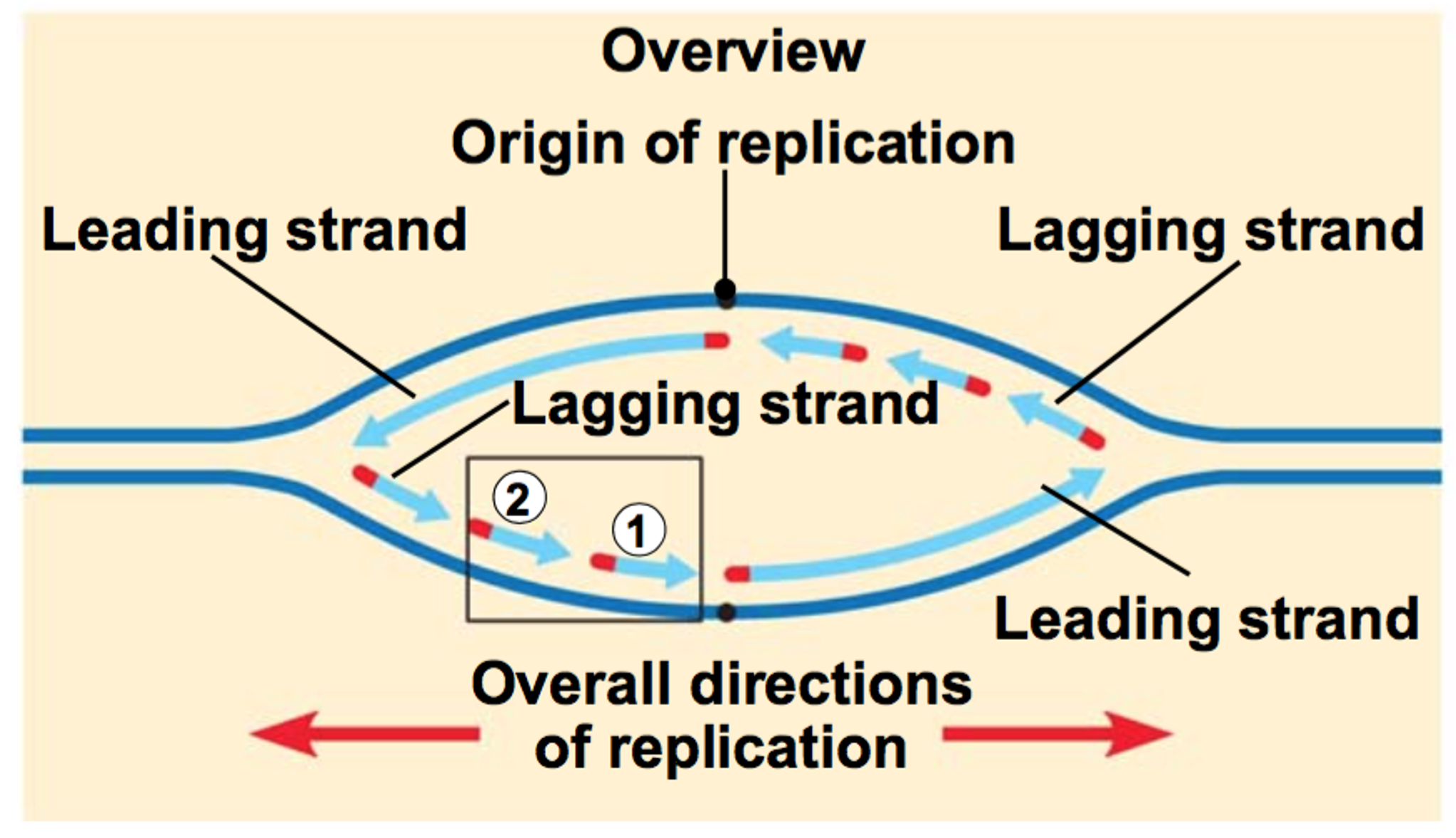
How many DNA helicases are at every bubble?
Two, moving in opposite directions
What is the starting point of DNA helicase called?
The origin of replication
How many origin points are there?
They can be one or multiple along the strand of DNA depending on the organism.
What is step 2 in DNA replication?
New DNA strands with base sequences complementary to the original strands must be synthesized
What is primase?
The initializer enzyme
What does primase do?
Creates primers that act as signals for where new DNA synthesis will begin
What are primers?
Short sequences of RNA generally about 5-10 nucleotides long
What is DNA polymerase?
The builder enzyme
What does DNA polymerase do?
It begins at the primers and moves along each separated parental DNA strand, matching bases on the strand with complimentary free nucleotides
Also helps hydrogen bond the free nucleotides together to form new DNA strands, each complimentary to one of the parental strands
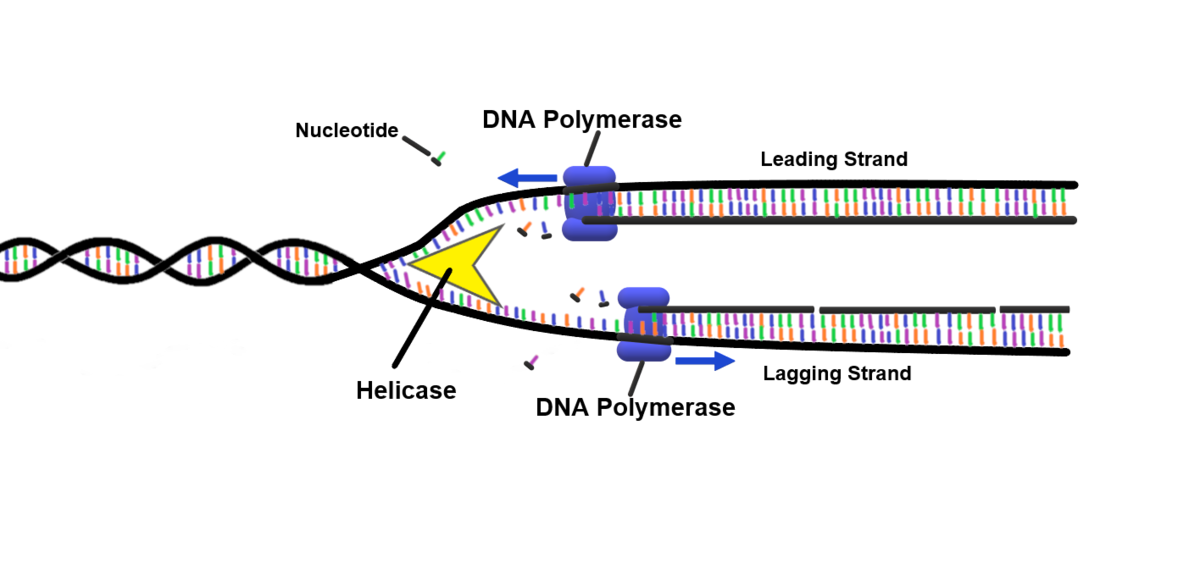
What causes the DNA polymerase to move in opposite directions?
DNA polymerase always moves in the 3’ to 5’ direction and DNA is antiparallel, so the DNA polymerases move in opposite directions when forming the two daughter strands
This means the daughter strand is synthesized from 5’ to 3’, as it will be antiparallel to its complimentary parent strand
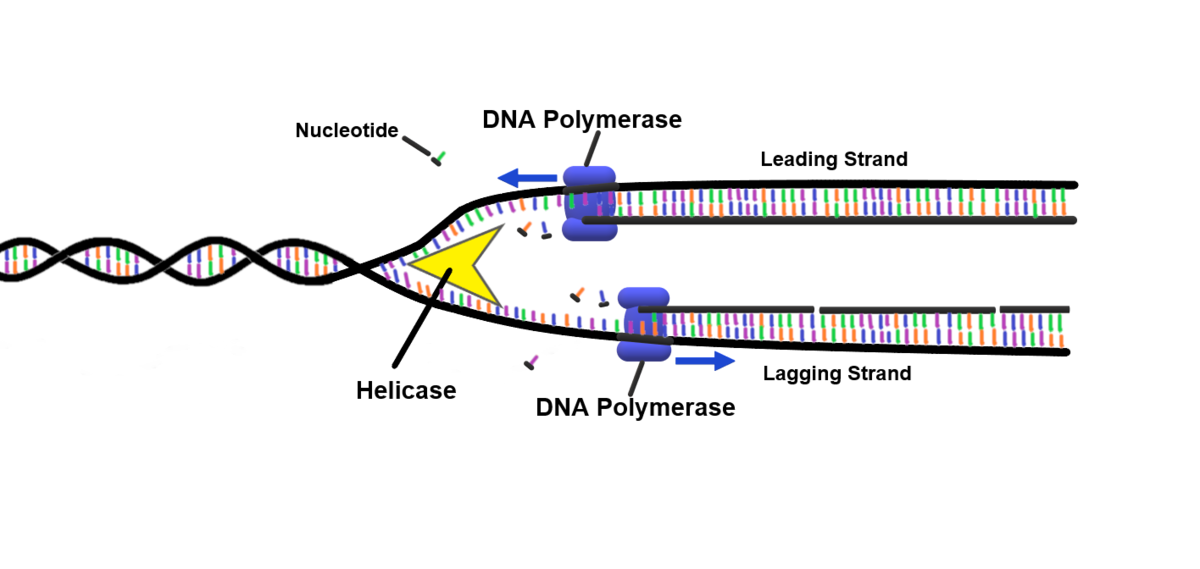
Which way does DNA polymerase move?
From 3’ to 5’
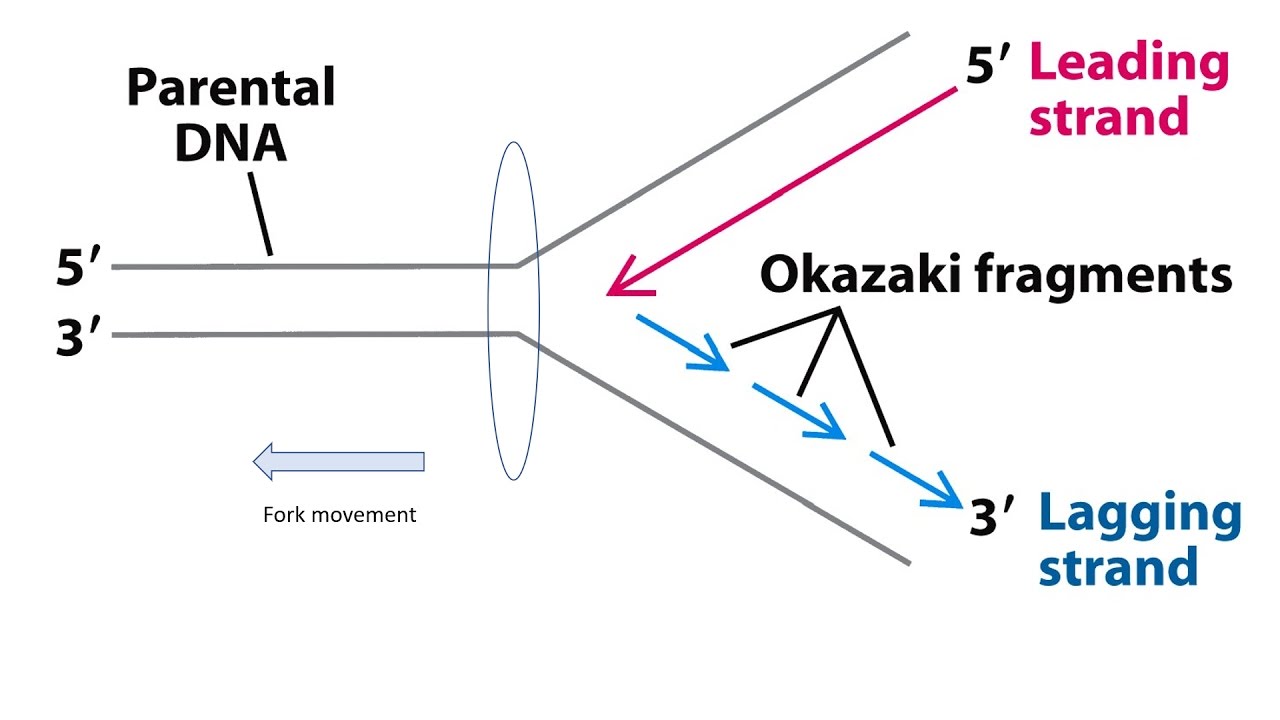
What is the leading strand?
On one template strand, DNA polymerase moves towards the replication fork, following DNA helicase
New nucleotides are added continuously as the new complimentary daughter strand is synthesized
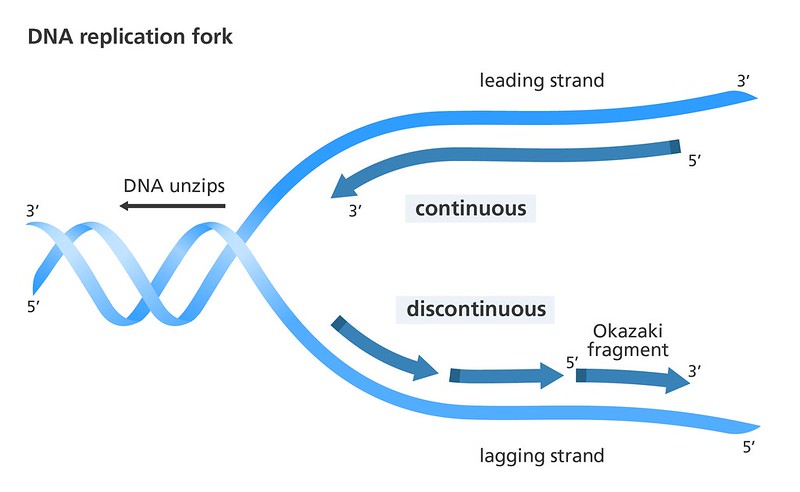
What is the lagging strand?
On one template strand, DNA polymerase moves away from the replication fork and helicase
The strand is formed discontinuously, as only a segment of new daughter strand can be synthesized at once
What are the DNA segments of the lagging strand called?
Okasaki fragments
What is step three of DNA replication?
The new pieces of DNA must be stitched back together to form a continuous new strand of DNA
What is DNA ligase?
The glue enzyme
What does DNA ligase do?
Joins the sugar and phosphates between okazaki fragments to create the continuous sugar-phosphate backbone that makes up the new strand
Primers also get removed and replaced with free nucleotides, which are also glued together
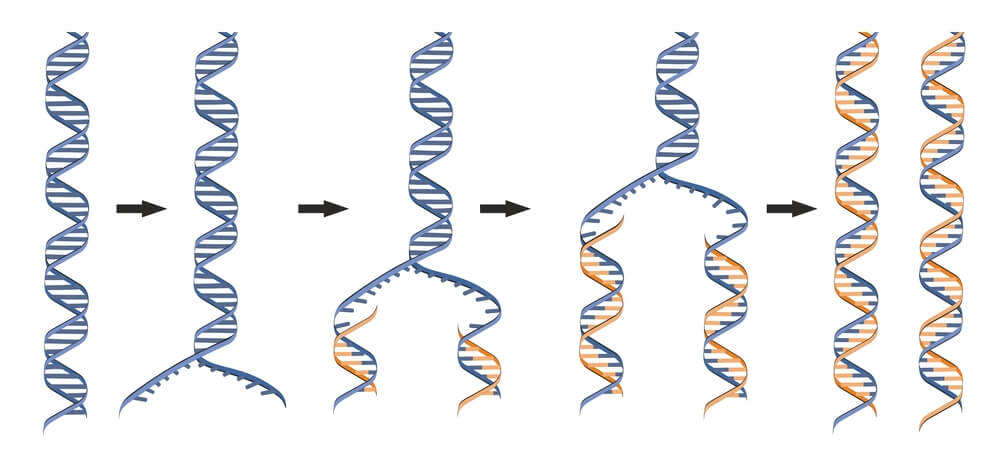
What happens when replication is complete?
Each original parental strand and its newly synthesized, complimentary daughter DNA strand wind up together, forming a new DNA double helix
What is semi conservative replication?
The two resulting DNA molecules are identical to each other and have one old parental strand and one new daughter strand
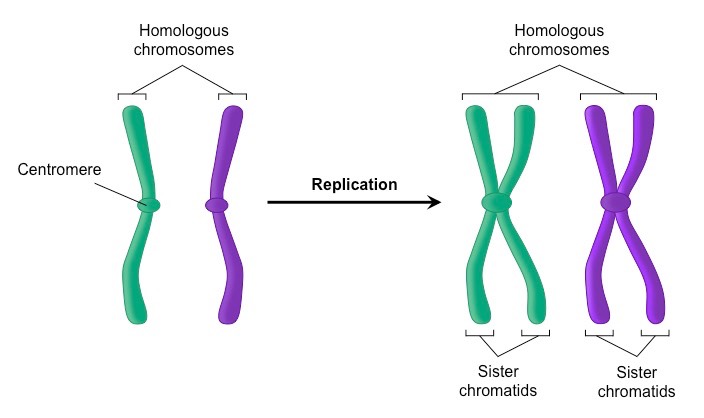
What are the recently replicated DNA strands a part of?
A single chromosome is replicated into two sister chromatids held together by the centromere