Urinalysis
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Urine sample Acquisitions
-Midstream "Clean Catch": Sterile container; sterile wipes
-Catheter Acquisition: Indwelling-Foley; One time sampling
Colony forming units
-Usually only indicative for a concern when it reaches past 10^5
-Seen in Pylonephritis
Dipstick Colors for UA
-The darker the color, the more saturated that variable is in the urine
Yellow Urine Colors
Pale: Volume replete, hydrated
Dark: volume depleted, hyperbilirubinemia
Gross Hematuria
-Red Color
-Red Sediment
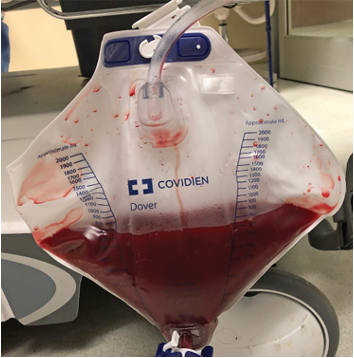
Hemoglobinuria & Myoglobinuria
-Red color
-Red Supernatant

Diet Related Red Urine
Beets, Rhubarb, blackberries
Orange colored Urine causes
Medication-induced:
Rifampin, Azo (UTI; bladder numbing)
Blue-Green Urine
-P. Aeruginosa UTI
Cloudy/turbid urine
pyuria - infection
Foamy/Frothy Urine
proteinuria
Specific Gravity (Dipstick UA)
how concentrated are solutes in the urine compared to water
-Density of urine relative to water
-Normal: 1.009-1.030
Presence of urinary glucose, protein, or RBC's invalidate test and urine osmolality must be used
Urine Osmolality (Lab)
-Concentration of particles per kilogram of solution
-Normal: 50-1200
Dilute Urine (specific Gravity & Osmolality)
-Low for both
Concentrated Urine (Gravity & OSmolality)
-High SG or osmolality
Arginine Vasopressin (AVP) and SG/Osmalality
AKA antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
Act on renal tubules to increase water retention → increases concentration of urine
(less water to particle ratio)
Diabetes Insipidus: SG/OSmolality
-Central: Inadequate AVP production
-Nephrogenic: Impaired AVP action on kidney
Cx: Polyuria, Polydipsia, large urine volumes; hypernatremia; Low Urine gravity
(you have no ADH. body can not reabsorb the water it is losing to urine. low urine gravity. lots of water, not a lot of stuff)
Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone (SIADH)
-Excessive production of AVP: Neoplasms; CNS disorders, medications, or infections
-CX manifestations: H/A, confusion, N/V, Coma; Hyponatremia; Elevated Urine gravity
(body make too much ADH. very high SG. not much water in urine)
Acidotic Urine
pH <5
-Common causes: Metabolic acidosis
Alkalotic Urine
pH >7
Common causes: metabolic alkalosis. Infection with urea causing pathogen (Proteus spp); Standing urine samples
Urine Bilirubin
Total: direct and indirect
-Either Direct (Conjugated) or indirect (unconjugated)
Indirect/Unconjugated: bound to albumin and is NOT filtered by the kidney (bilirubin in urine can only be conjugated)
Direct/Conjugated: filtered but most is reabsorbed within proximal tubules
bilirubin presence is indicative of Hepatocellular disease
-May occur with jaundice
Urobilinogen
-Conjugated bilirubin is broken down by Gut Bacteria and leads to formation and absorption of urobilinogen
-Most is excreted by the liver
-Small amounts are excreted by the kidneys (should be very small amount in urine)
-In Liver failure: liver will be unable to clear this → increased levels of Urinary excretion
Gross or Microscopic Findings: Hematuria
loss of RBC in urine
(+) Heme
(+) Microscopic RBC's
Gross/Micro Findings: Hemoglobinuria (Hemolysis) or Myoglobinuria (Rhabdo)
(+) Heme
(-) Microscopic RBC's
Obstructive Jaundice UA
cannot pass bile into GI tract
Color: dark yellow (pigment of conjugated bilirubin)
Bilirubin: positive
Urobilinogen: depends on how much it is obstructed. less ub, more obstructed.
Blood: negative
Hemolysis
Color: red
Bilirubin: negative
Urobilinogen: positive
Microscopy: no RBC
Urine Protein
Protein: too large to fit through glomeruli and should not be present in urine
Dip-sticks are usually insensitive to non-albumin substances
Dipsticks measure as +1, 2+, 3+, 4+
-Used as a screening tool for Renal Disease
Urine Glucose + associated diseases
Continuously filtered by glomeruli and reabsorbed within the renal tubules
Glucosuria occurs when Renal threshold for this reabsorption is exceeded (>180 mg/dL)
Associated: Diabetes Mellitus; Medications (SGLT2 Inhibitors increase urinary output of this)
Urine Ketones + associated with
Ketones: byproduct of fatty acid break down (Lipolysis)
-Should NOT be present in Urine
Associated with: uncontrolled DM; Diet; Starvation
-Associated with metabolic acidosis
Urine Nitrite
Nitrites: byproduct of Gram (-) species metabolism
Agents: E. Coli and other enterobacteriaecae (Klebsiella & Proteus)
-usually NOT produced by Gram (+) organisms
Leukocyte Esterase
-Enzyme within WBC's
-Will be + with infection or inflammation
Acute Tubular Necrosis causes/signs
-Renal Tubular Damage results in AKI
-Causes: Ischemia, Nephrotoxins, Sepsis
-Signs: AKI + Reduced Urine Output
Glomerulonephritis causes/signs
-Inflammation of the Renal Glomeruli
-Causes: Autoimmune Process, Infection Related (Group A Strep)
-Signs: Hematuria, AKI, Edema, Proteinuria, HTN
Nephrotic Disease causes/signs
-Glomerular disease which result in alterations of basement membrane permeability
-Causes: Diabetes Mellitus, Amyloidosis
-Signs: Proteinuria (>3 g/24 Hours); Hypoalbumemia, Edema, HLD
Hyaline Casts
-Faint, colorless
-Concentration of mucoproteins secreted from renal tubules
-Non-specific; can be normal
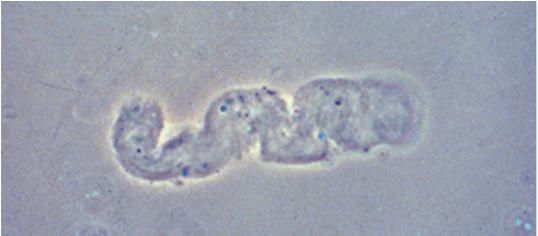
Granular Casts
-Broad, fine or coarse
-Degraded cell products and serum proteins
indicative of Renal Parenchymal Disease; ATN (acute tubular necrosis)
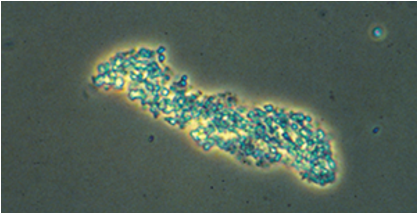
Renal Tubular Epithelial Cell Casts
-Collection of Renal tubular epithelial cells
-Associated with ATN
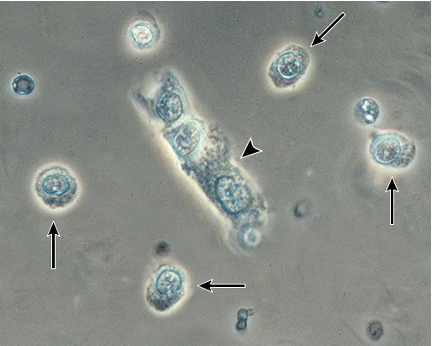
Fatty Casts
-Hyaline casts which contain lipid droplets and can be overserved in pts with lipuria
-Associated with Nephrotic syndromes
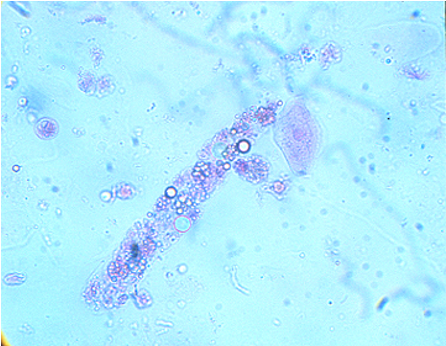
Red Blood Cell Casts
-Collection of RBCs which have leaked into renal tubules through damage of glomerular basement membrane
-Occurs in Glomerularnephritis
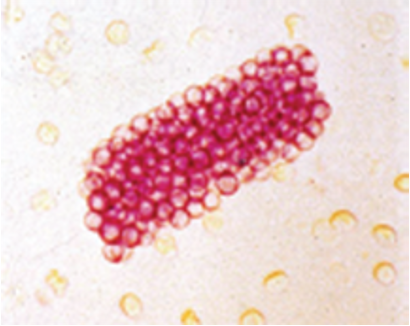
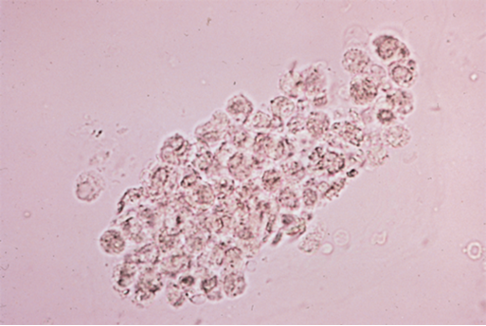
White Blood Cell Casts
-Collection of WBCs which leaked into renal tubules
-Typically occur in upper urinary tract infections (Pyelonephritis)
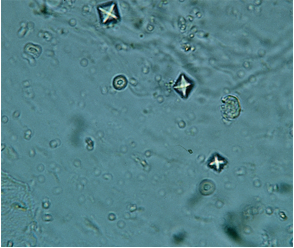
Calcium Oxalate Crystals
-Small square crystals with Central cross
MC stone type
Uric Acid Crystals
-Rhomboids, Hexagons, or Squares
-Acidic Urine (Gout)

Struvite Stone (Triple Phosphate)
-"Coffin-Lids"
-Alkaline urine (Proteus infections)
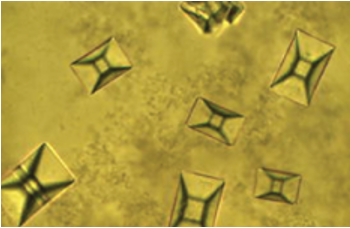
Cystine Crystals
-Colorless hexagons
-Seen in patients with Cystinuria
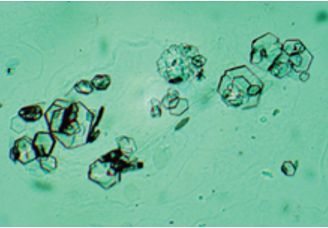
Pathologies for 24 hour urine collection
-Calcium
increased: hyperparathryroidism, sarcoidosis, hyperthryoidism
decreased: hypothyroidism, renal failure
-Catecholamines
oncreased: phoechromocytoma
-Free Cortisol
-increased: cushing syndrome
Creatinine
decreased: renal disease
Protein
nephrotic syndromes, peeclampsia
Urine Microalbumin
-Used as screening tool for diabetic pts for risk of nephropathy
tx: ACE inhibitor/ARB

Urine Electrolytes
-Urine can be used as a "Spot Test" for various electrolyte abnormalities and metabolic states
Urine Sodium:
-<10 mEg: Hyponatremia, volume depletion
->20 mEg: SIADH, ATN
->40 mEg: ATN
Urine Potassium:
-<10 mEg: Hypokalemia, potassium depletion, extrarenal loss