Chapter 4: Overview of Tissue Types and Histology
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Tissue
Group of cells found together within a body that share an embryonic origin
Histology
Microscopic study of tissue appearance, organization, and function
Light microscopy
Can view many different tissues and dyes
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM)
Views high magnification in grayscale
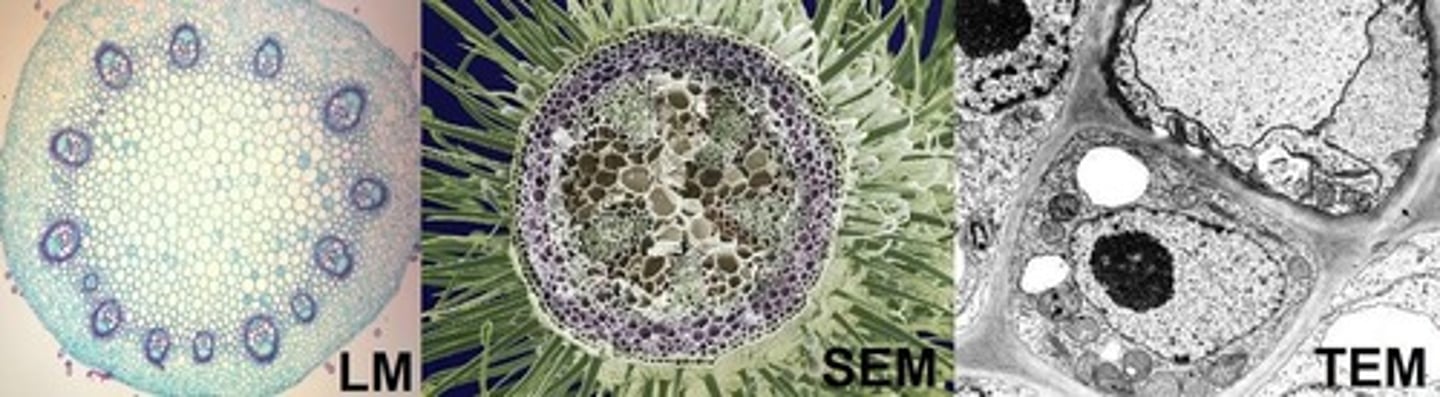
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM)
Allows 3D views of tissue
Epithelial Tissue
Sheets of cells exposed to the environments
Polarity
Characteristic of epithelial tissue indicating distinct structural differences between the apical and basal surfaces
Tight junctions
Specialized connections between epithelial cells that prevent leakage
Desmosomes
Anchoring junctions that provide mechanical stability to epithelial tissues
Highly regenerative
Ability of epithelial tissue to quickly replace lost or damaged cells
Avascular and innervated
Epithelial tissue lacks blood vessels but has nerve endings
Simple squamous epithelium
Found in endothelium of vessels and mesothelium of serous membranes
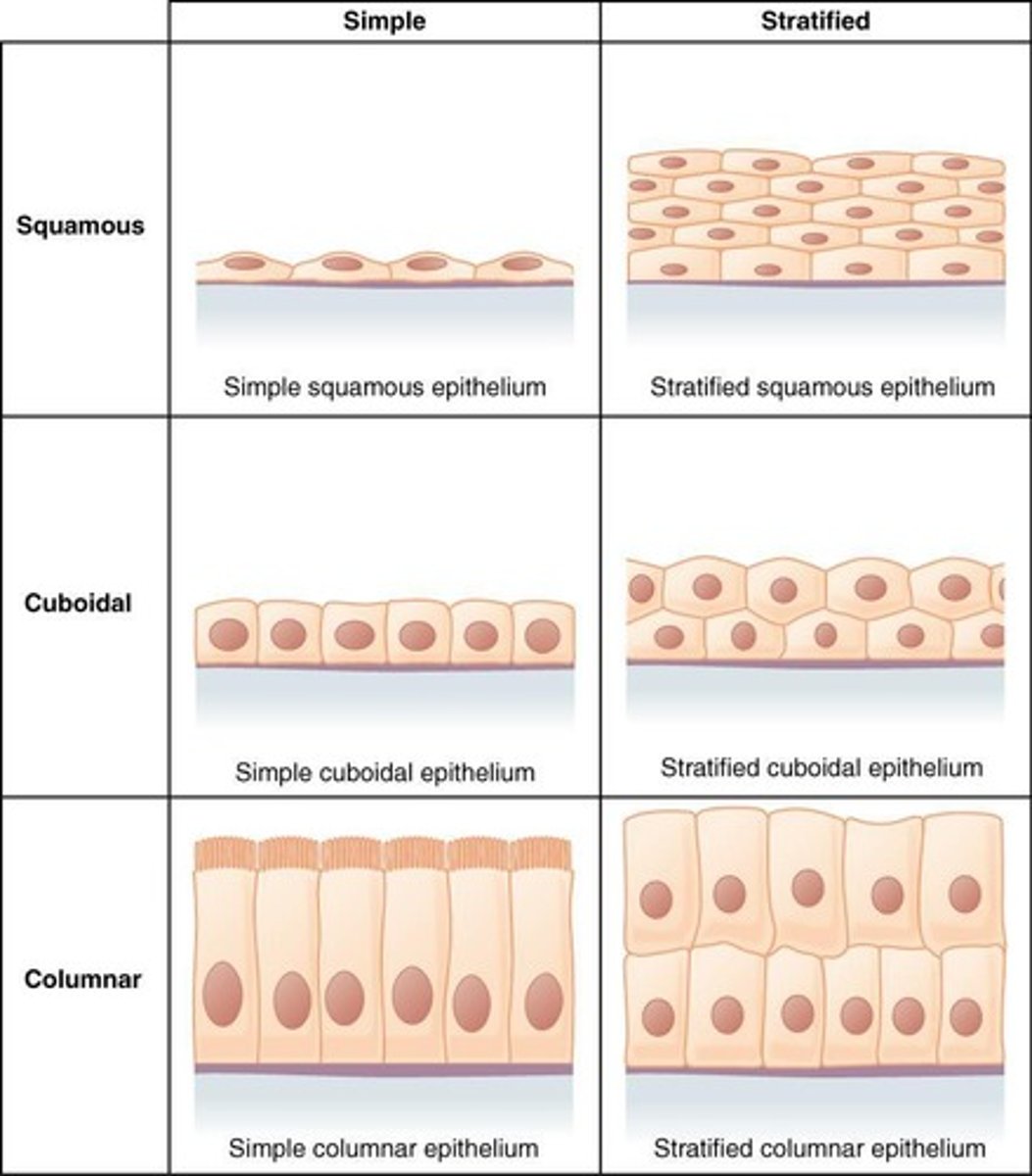
Simple cuboidal epithelium
Specialized for secretion and absorption
Simple columnar epithelium
Specialized for absorption and secretion
Stratified squamous epithelium
Most common type of stratified epithelium
Pseudostratified epithelium
Single layer of cells with varying heights, nuclei at different levels
Transitional epithelium
Stratified tissue that can change shape from cuboidal to squamous to enable stretch
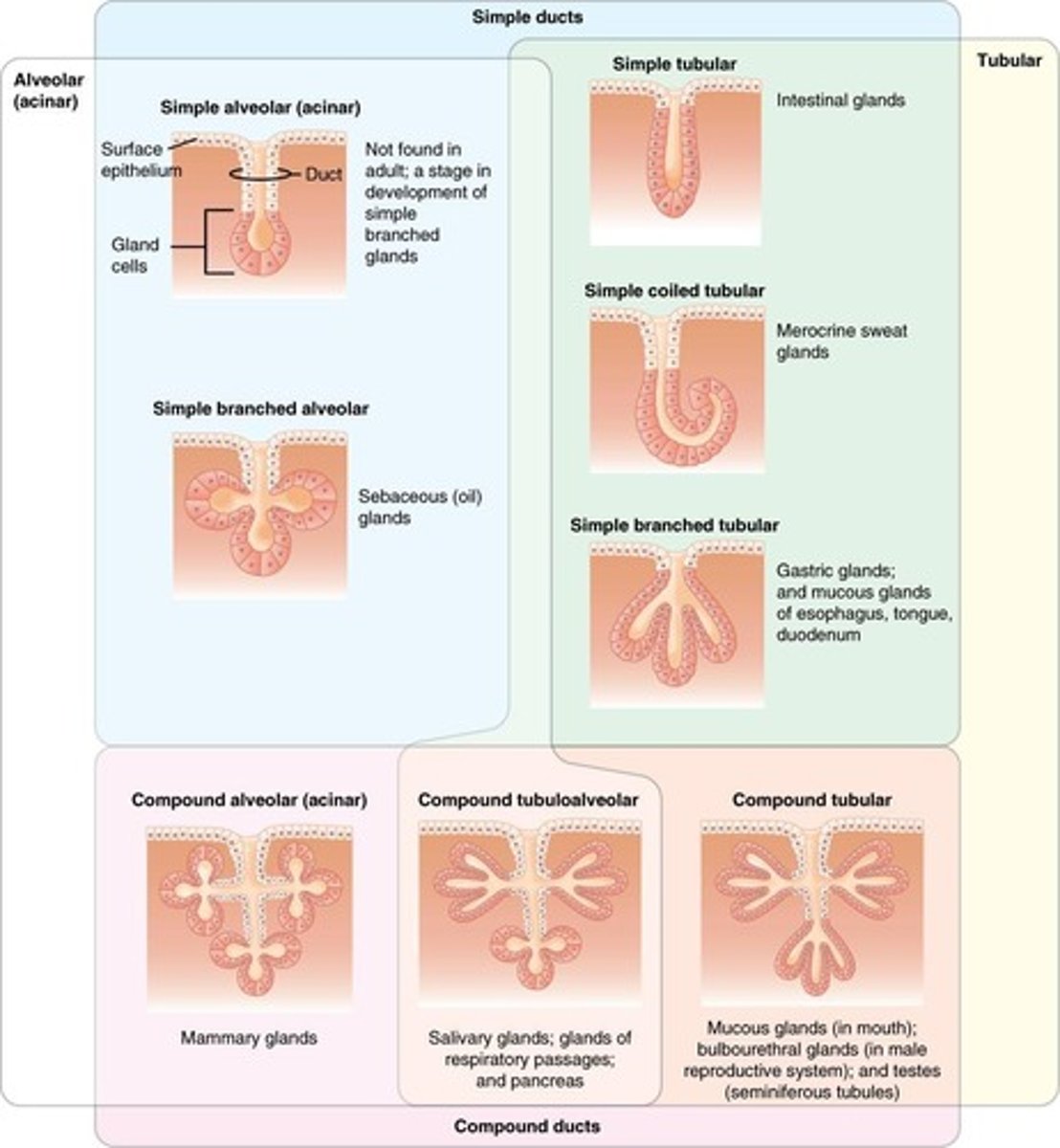
Gland
One or more cells that produce and secrete a specific product
Endocrine glands
Ductless glands that secrete hormones directly into tissues
Exocrine glands
Glands with ducts that lead to the epithelial surface
Merocrine secretion
Vesicles emptied into extracellular space

Apocrine secretion
Release of a portion of the cell
Holocrine secretion
Cell ruptures and is destroyed
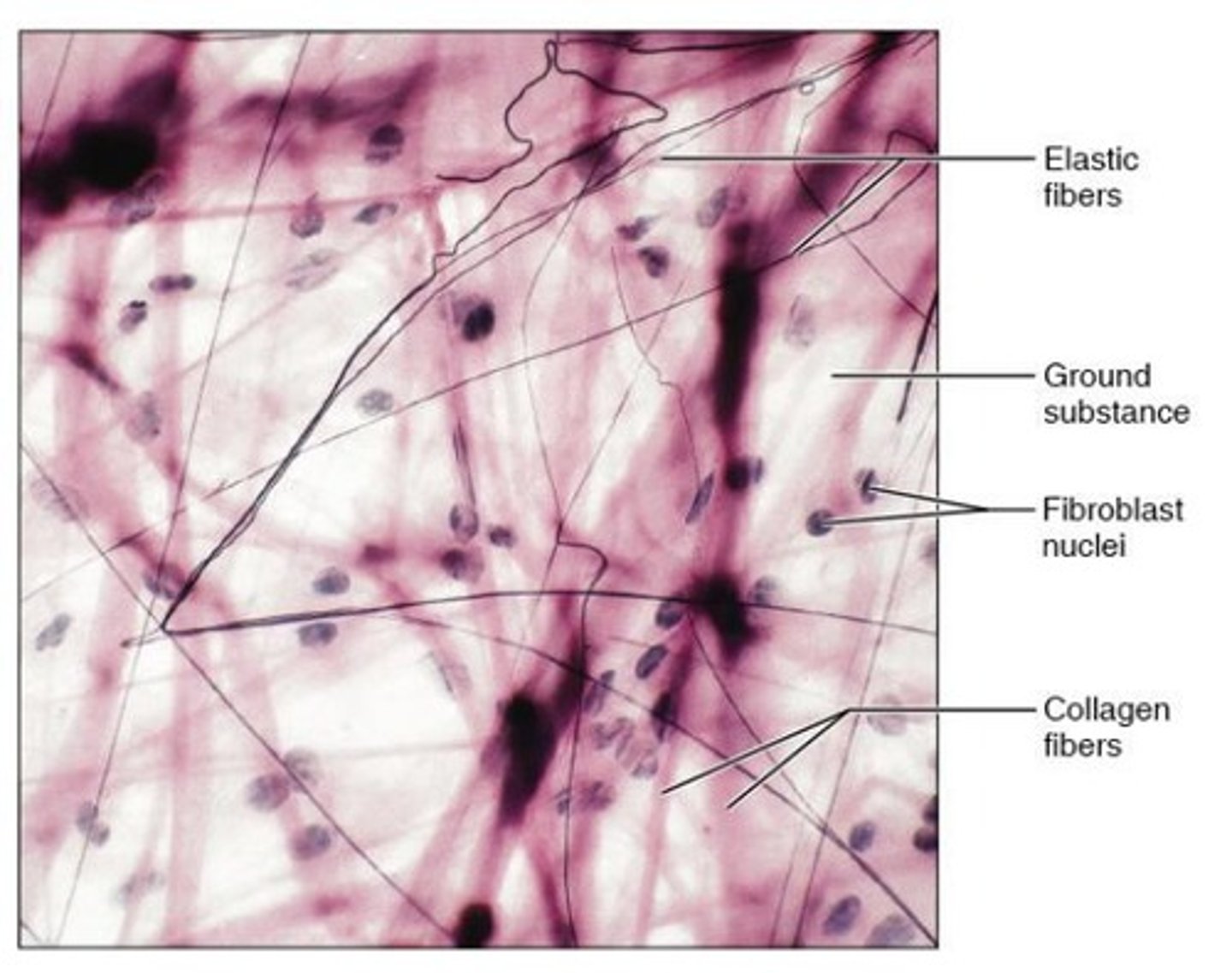
Connective Tissues
Loosely dispersed cells in a matrix with extensive extracellular material
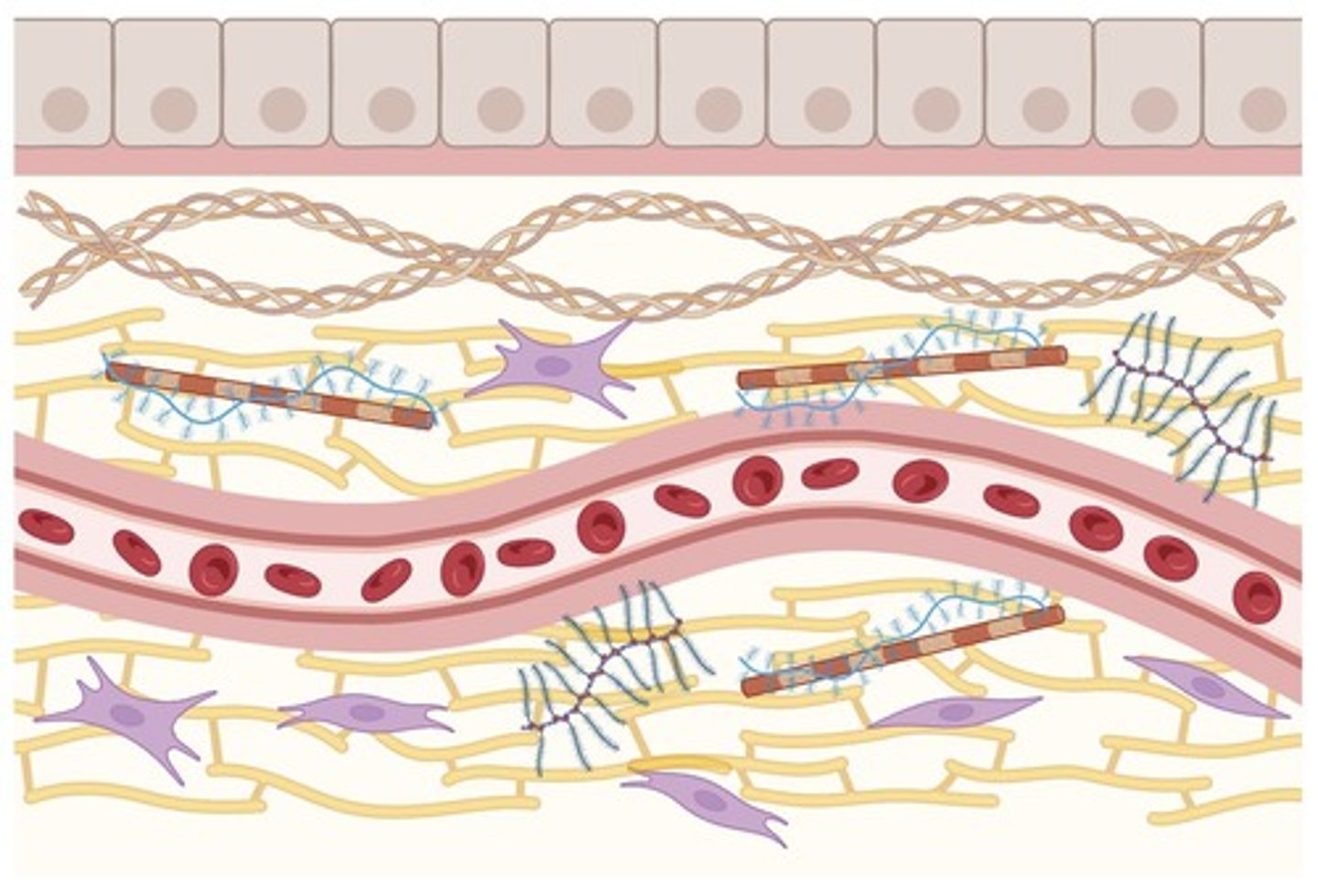
Ground substance
Material filling space between cells in connective tissue
Fluid Connective Tissue
Includes blood and lymph

Neuron
Cell that propagates information via electrochemical signals (action potential)
Synapse
Gap between neurons
Neuroglia
Support cells for neurons
Cutaneous membrane
Skin, keratinized epidermis attached to connective tissue (dermis)
Mucous membranes
Line all body cavities that open to outside, bathed in secretions
Serous membranes
Line closed ventral body cavities, consist of visceral and parietal layers
Regeneration
Replacement of destroyed tissue with correct tissue type
Fibrosis
Replacement of destroyed tissue with scar tissue
How do we study tissues?
Samples are fixed, preserved in formalin or frozen