Leadership Midterm
1/158
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
159 Terms
Person factors
characteristics that give individuals their unique identities
Situation factors
elements outside us that influence what we do, the way we do it, and the ultimate results of our actions
IPO model
inputs, processes, outputs
What to consider to choose processes?
1. Selection criteria- what are you looking for? Ex. Job pay, locations
2. Consequences - trade-offs ex. Opportunity cost, cons
3. Choice process0 who needs to help make this decision ex. Ask significant other, family
4. Necessary resources- what do you need to implement the solution ex. Transportation, new apt.
Organizational behavior
Investigated impact of individuals, groups and structure on behavior to apply strategies to improve organization's effectiveness
Attitudes impact
behaviors
Cognitive/Evaluative Attitude component
an evaluation/opinion/thought ex. "My supervisor promoted a coworker who deserved it less than I did. My supervisor is unfair."
Affective Attitude component
A feeling. Ex. "I'm angry at my supervisor"
Behavioral Attitude component
An action. Ex. Looking for a new job
4 main attitudes
Organizational commitment
Employee engagement
Perceived organizational support
Job Satisfaction
Organizational commitment
Extent to which an employee identifies with organizational values and commitment (employee retention, motivation towards company goals)
Employee engagement
Amount of motivation and effort an employee has
Perceived organizational support
Degree to which employees believe that the organization values their contributions or genuinely cares about their well being
Organizational citizenship behavior
Anything you do extra that is not part of the job description to help. Can show you have higher perceived organizational support, engagement or org commitment.
Job satisfaction
Extent to which an employee enjoys their job (satisfied with pay, coworkers, actions, manager)
Responses to Job Dissatisfaction
Voice, Exit, Loyalty, Neglect
Voice response
Active, constructive response by suggesting improvements, discussions, unions. Ex. Making a list of feedback to talk about later
Exit response
Active, destructive response by leaving the job
Loyalty response
Passive, constructive dimension by optimistically waiting for conditions to improve
Neglect response
Passive, destructive dimension by allowing conditions to worsen and giving up.
Cognitive dissonance
Psychological discomfort a person a person experiences when they experience inconsistency between behavior and moral attitudes
Ajzen's Theory of Planned Behavior
Our attitudes, subjective norms, and perceived behavioral control contribute to our intentions and lead to behaviors
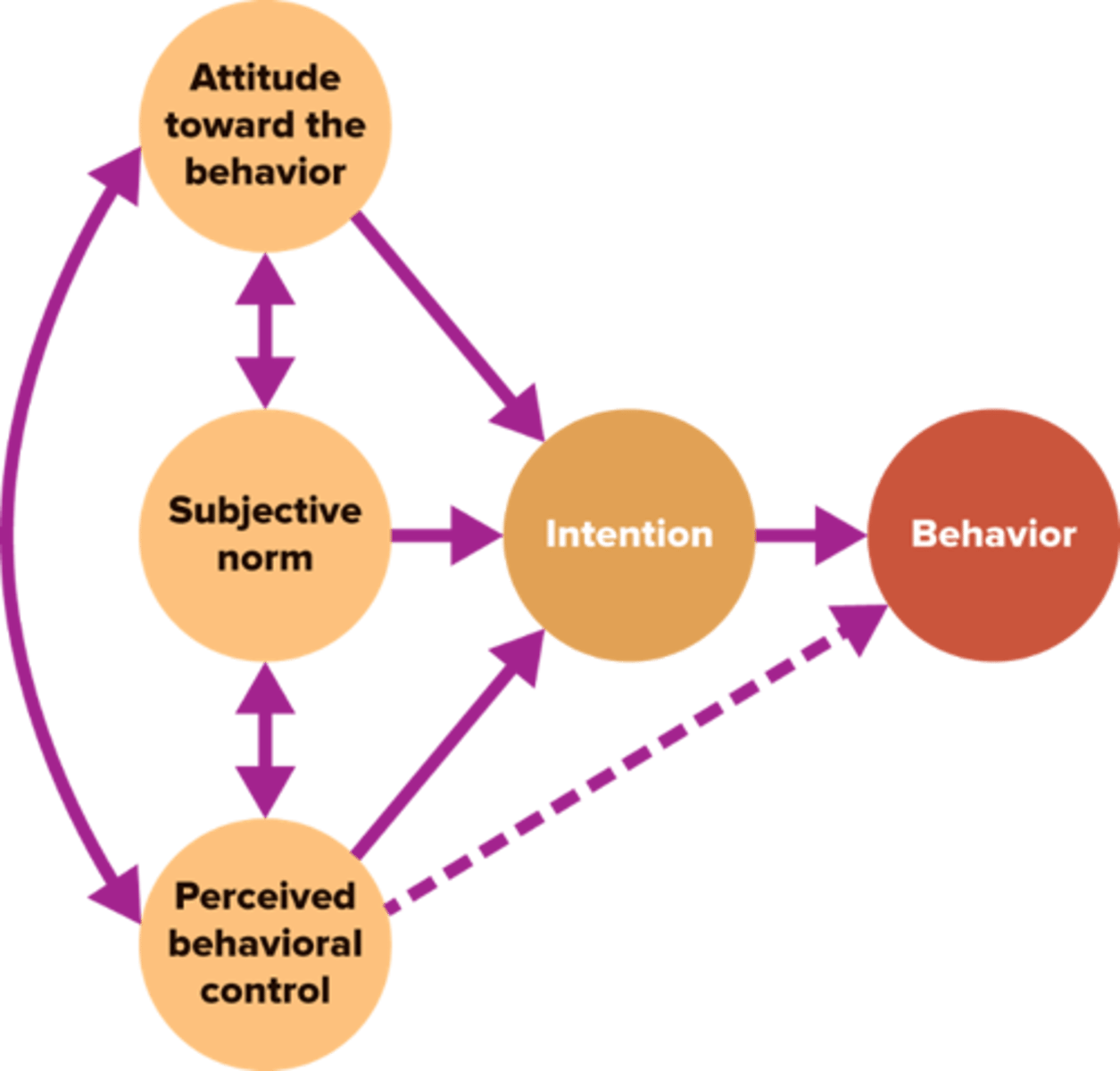
Subjective norm
Something that everyone else does
Counterproductive work behaviors
Actions that damage the org. Ex. Stealing, late, absent, happens often when employees are dissatisfied
Withdrawal cognition
Thinking about exiting company
Person-job fit
The extent to which the job description matches your personality, including strengths and weaknesses. The fit between personality type and occupational values affect performance and turnover. (personality types: realistic, artistic, conventional, enterprising, social)
Person-organization fit
People are attracted to and selected by organizations that match their values and they leave the incompatible ones.
Personality
How someone reacts and interacts with the world around them
Personality traits
Enduring characteristics that describe an individual's behavior. Summarize regularity in behavior and explain behavior
Personality traits predict
Other, more specific behaviorsr
Big Five Model
Rates personality based on conscientiousness, emotional stability, extraversion, openness to experience, agreeableness, and nueroticism
Conscientiousness
level to which you are consistent, reliable, responsible, organized.
Emotional Stability
level to which you are able to withstand stress.
Extraversion
level to which you are gregarious, sociable, assertive, optimistic in your approach to the social world
Openness to experience
level of interests in novelty, creative, curious, abstract thinkers
Agreeableness
level of uncomfortability in deferring others. Warm, trusting, cooperative
Neuroticism
low emotional stability
Trait Activation Theory
some situations activate certain personality traits more than others. (Strong situations)
Situation strength theory
the way personality translates into behavior depends on the strength of a situation. A strong situation is the degree to which norms, cues, standards dictate appropriate behavior. (Class, funeral, fancy restaurant = strong)
Internal locus of control
"I make things happen, I accept responsibility for failures"
External locus of control
"Things happen to me, I do not control my actions and outcomes"
Dark Triad
Machiavellianism, Narcissism, Psychopathy
Machiavellianism
manipulative, pragmatic, emotionally distant, ends can justify means, will do anything for gain
Narcissism
arrogant, grandiose sense of self importance, difficulty taking negative feedback
Psychopathy
lack of concern for others, enjoy suffering of others, no remorse when actions cause harm, stress immunity
Core self evaluations
bottom-line conclusions individuals have about their capabilities, competence, and worth as a person
Self-monitoring
ability to adjust behavior to external, situational factors
Proactive personality
identify opportunities, show initiative, take action, and persevere until meaningful change occurs
Cognitive ability
ability to learn, or potential to learn and acquire new skills, knowledge (wonderlic test avgs peak at 30)
Emotion
Caused by an event, short and intense
Mood
No external stimuli, last a long time, and less intense
Attitudes =
Cognitive (thought) + Affect (feeling) + Behavioral (action)
Affective events theory
employees react emotionally to things that happen to them at work and this reaction influences their job performance and satisfaction
Emotional contagion is made up of
individual, interpersonal, and contextual factors
(individual factor) High self awareness =
low emotional contagion
(individual factor) High stress =
high emotional contagion
(individual factor) High self monitoring =
low emotional contagion
(interpersonal factor) High cohesiveness (how close of friends you are) =
high emotional contagion
(interpersonal factor) High congruence (how similar you are) =
high emotional contagion
(contextual factor) High power & status =
high emotional contagion (more likely to pick up on leader's emotions)
(contextual factor) High group composition (more alike the group is) =
high emotional contagion
Emotional Intelligence
a persons ability to perceive emotions in their self and others, discriminate those emotions, understand their meaning, and regulate their emotions to guide their thinking accordingly.
Traits of emotional intelligence
Self awareness
Self management
Social awareness
Relationship management
Self awareness
your ability to identify which emotion you are experiencing
Self management
ability to control your emotions and actions
social awareness
can you identify what someone else is feeling
relationship management
ability to communicate clearly, disarm conflicts, and build bonds
Deep-level diversity
differences in values, personality, and work preferences (once you get to know someone)
Surface-level diversity
easily perceived differences (gender, race, age) that do not reflect the way people think/feel
Perception
how we organize/interpret sensory impressions to give meaning to our surroundings
Person perception
Our perception of others is influenced by:
1. our characteristics, experiences, and expectations
2. The target's characteristics, experiences, and expectations
3. The context of the situation (time, location, weather)
(Ex. seeing a resume from a school you love)
Contrast effect
evaluation of a person is affected by comparisons with other people recently encountered
Halo & Horns effects
Halo- tendency to draw positive general impression about an individual based on a single characteristic
Horns- negative impressions based on a single characteristic
Attribution theory
explain the ways we judge people differently, based on the meaning attributed to the behavior. Internal or External
Distinctiveness
do they regularly display this behavior in other situations? Yes = Low = Internal
Consensus
would everyone else act like that in this situation too? Yes = High = External
Consistency
do they regularly display this behavior? Yes = High = External
Internal
within the person. Perceiver believes to be under that person's control
External
perceiver believes the situation forced that person to act ex. "came to work late bc the train was late"
Stable
situation due to permanent factors
Unstable
situation due to temporary factors. Ex. "I aced that test because I worked so hard"
Self-serving bias
tendency for ppl to attribute their own success to internal factor and blame external factors for failures
fundamental attribution error
underestimated external factors and overestimate internal factors when perceiving others. Attribute success to external factors and failure to internal
"He aced that test because it was easy"
External, Unstable
"I aced that test because I'm smart"
Internal, Stable
Social Identity theory
a person's sense of who they are based on their group membership. Group achievements increase our self esteem, we tend to have group favoritism and outgroup rejection
Implicit bias
prejudice hidden, not aware
Stereotyping
judging someone based on perception of the group that person belongs to
Selective perception
tendency to choose to interpret what is taken in from the environment based on interests, background, attitudes
Affinity bias
tendency to trust / like people who are lot like us
Correlation
the strength of a relationship between x-test scores y-job performance
If negative correlation, hire the employees that have higher or lower scores?
Lower scores (picture the graph x-test scores y-job performance)
Validity
accuracy of a measure (whether the results really do represent what they are supposed to measure)
Content-related validity
does it measure job-related behaviors?
Construct-related validity
does the test actually measure what it claims to measure?
Criterion-related validity
does the test's scores actually actually predict job success?
Predictive method
measure criterion-related validity by tracking applicant scores and wait to compare scores to job performance
Concurrent method
measure criterion-related validity by having current employees take the test and look for correlation between scores and job performance
Reliability
consistency of a measure (whether the results can be reproduced under the same condition makes selection unreliable)
Random error
unpredictable factors that affect a score in no systematic way