Kidney Anatomy, Physiology, and Measuring GFR: Pathology Final
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Anatomy of the genitourinary system
2 kidneys in the retroperitoneal space around the 11th-12th ribs
Connected to ureters which is connected to the bladder
How much cardiac output do the kidneys recieve
Around 25%
Size of the kidneys
120-150g, 10-12cm
Nephron
Functional unit of the kidney
Approximately 1 million nephrons per kidney (more than we need)
Contains the afferent and efferent arterioles, glomerulus in the Bowman's capsule, proximal tubule, loop of Henle, distal tubule, and collecting duct
From the collecting duct urine goes into the urinary bladder
Highly vascularized and folded in on itself
The glomerulus
Has the afferent and efferent arterioles and a ball of capillaries surrounded by podocytes
Capillaries and podocytes make up the glomerular basement membrane
Surrounding the epithelial cells there is an endothelial layer (Bowman's capsule). Inside of the Bowman's capsule there are mesangial cells
Glomerular basement membrane
Made of epithelial cells and podocytes
Mesangial cells
Cells that exist inside of the Bowman's capsule
Glomerular filtration by percents
Only filters about 20% of what comes to it, out of that 20%, 19% is resorbed and 1% goes into the urine
Where does filtration happen
At the glomerulus
Where does majority of resorption occur
Proximal tubule, fine tuned by loop of Henle and distal tubule
Kidney functions
- Metabolic
- Hemodynamic
- Endocrine
Metabolic kidney functions
- Electrolytes
- Acid/base status
- Excretions of toxins, drugs, metabolic biproducts
Hemodynamic function of the kidney
- Maintenance of blood pressure (through RAAS)
- Maintenance of body volume
Endocrine function of the kidney
- Release erythropoietin needed to make RBC
- Maintain bone homeostasis (involved in production of active vitamin D3)
Why is the kidney involved in bone homeostasis
Involved in the production of active vitamin D3
Glomerular filtration rate is determined by
- Filtration pressure
- Filtration coefficient (how much can get through the membrane)
Can we measure GFR directly?
No, need a surrogate measure
Autoregulation
Actions done by the kidney to maintain a constant GFR
Perfect molecule for measuring GFR
- Endogenous
- Only filtered, no secretion or resorption
- Easy to measure in blood/urine
- Inexpensive
The perfect marker does not exist!
Endogenous markers for GFR
- Creatinine
- Cystatin C
- Urea
Creatinine as a marker for GFR
Endogenous marker
- Most commonly used
- Related to muscle mass
- Freely filtered, secreted, no resorption
- Extra-renal secretion
Cystatin C as a marker for GFR
Endogenous marker
-More readily available as a test but more expensive
- Not related to muscle mass (good to use in those who have high or low protein diet or for extremes of body size)
- Non glycosylated protein
- Filtered but not absorbed
When is using cystatin C as a marker for GFR inaccurate
Hypothyroid or steroid use
Urea as a marker for GFR
Endogenous marker
- Not used in clinical practice
- Easy to measure
- Altered by protein intake/catabolism
- 50% reabsorbed
Inulin as a marker for GFR
Exogenous marker
- Gold standard
- 100% excreted
- Inert sugar
- Difficult and expensive
Iothalamate as marker for GFR
Exogenous marker, not used anymore
- Actively secreted leading to overestimation of GFR
- Expensive and difficult
DTPA/EDTA as marker for GFR
Exogenous marker
Attached to radioisotope that can dissociate from the molecule leading to underestimation of GFR
Expensive and difficult
How do we estimate GFR
Using equations! Most accepted one is CKD-EPI 2021
Others exist: Cockroft Gault, MDRD but not applicable to modern patient populations
Measuring blood and urine levels of endogenous marker
Requires 24 hour urine collection, cannot use cystatin C as it is not excreted (can only use creatinine)
3 assumptions made about creatinine when we are using it to calculate GFR
- Meets criteria for ideal marker for GFR
- Production = excretion, when GFR falls creatinine increases proportionally
- Accurate and reproducible
Between what values is GFR the most accurate
Between 30-60mL/minute
This is when there is a linear relationship between GFR and serum creatinine, after that it falls off
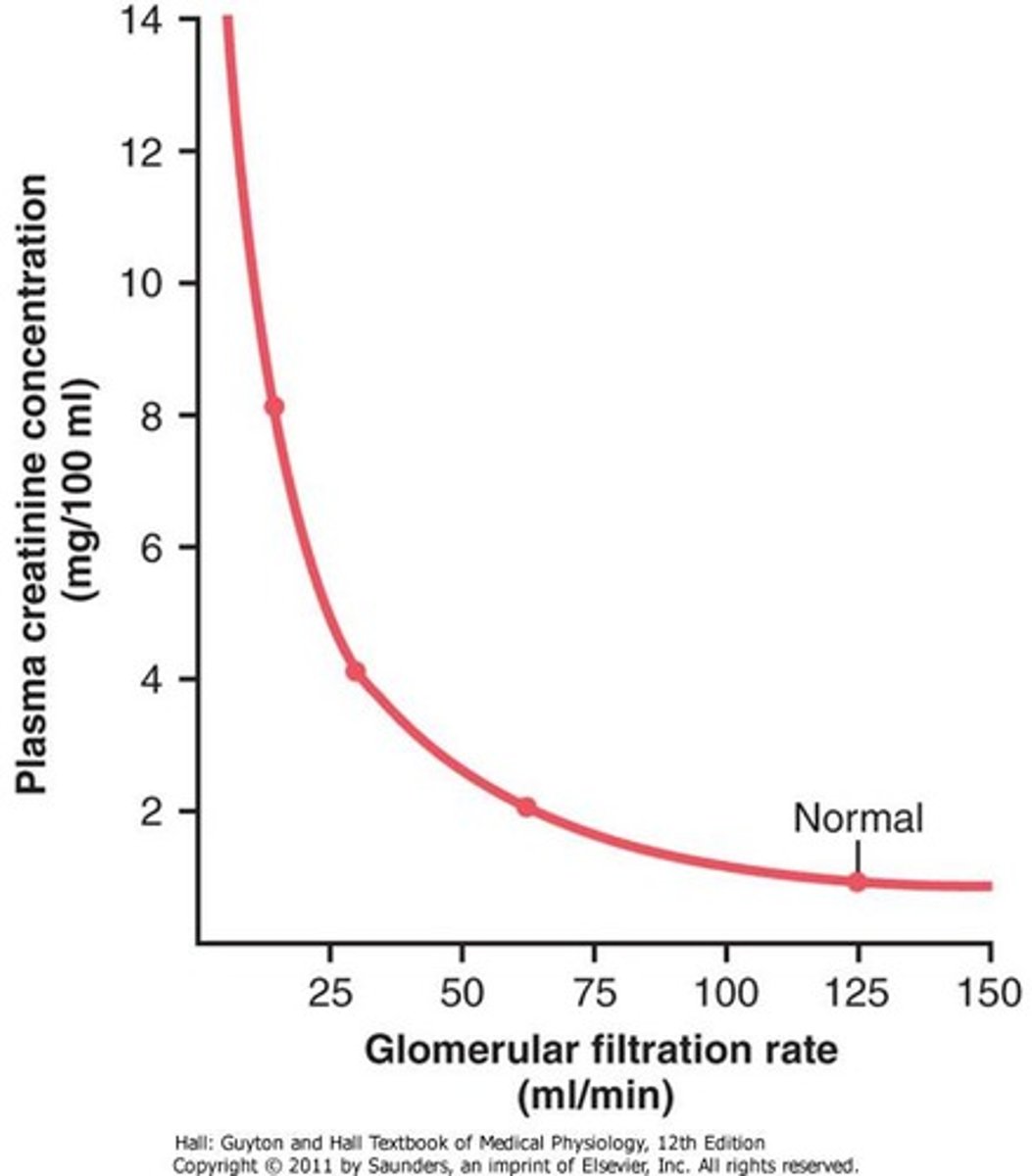
Does a change in creatinine equal a change in GFR
No, other things can be changing the creatinine such as:
- Aging
- Female sex
- Race
- Body habitus
- Chronic illness
- Diet
Creatinine in rapidly changing GFR
There is a lag between creatinine and GFR. If you were to remove someones kidneys the GFR would be 0, but the serum creatinine would not increase until later on. Then, it would increase at the rate of creatinine production.
When do we use cystatin c
- Medication that impairs creatinine kinase pathway
- Extremes of body mass
- Extremes of protein intake
CKD-EPI 2021
Currently used formula to estimate GFR, uses serum creatinine, age, and sex
Most accurate when eGFR is below 60mL/min
MDRD
Estimation of GFR, not used because it was created in a population with non-diabetic CKD and underestimates GFR
Cockcroft Gault
Estimation of GFR, measures creatinine clearance
Females adjusted by 0.85 but there is no evidence to prove that this should be done
Historically used in drug dosing
When does the Cockcroft Gault overestimate GFR
Edematous or obese patients
Developed before obesity was common
Race and GFR estimation
Used to be included in the CKD-EPI but has been taken out
Self reported black patients were seen to have higher eGFR (mechanism unknown)
Ultimately removed because race is a social construct and there is great diversity among black patients
24 hour urine collection
Patient collects urine for 24 hours, assumes production = excretion
Difficult for patients and prone to errors
Nuclear scan
Isotope is injected into kidneys to determine if there is a differential split in the kidneys
Often done before kidney donation to make sure there is not a split before donation