Composites
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
how many phases are in a composite microstructure?
2, the matrix and the dispersed phase
are composite microstructures continuous or discontinuous?
discontinuous
what are the two phases in the composite microstructure?
dispersed and the matrix
what is the role of the matrix?
binding together
what is the dispersed phase?
surrounded my the matrix, usually particles
name three composite properties that effects the material properties
amount of phases
phase properties
geometry
orientation
distribution
what are particle reinforced composites?
defined by their strengthening mechanism
what is the particulate phase?
harder and stiffer than the matrix which creates a barrier to stop matrix deformation
how does the particulate phase transfer loads?
particles restrain matrix movement resulting in a transfer of load
what is the degree of reinforcement dependant on? (in terms of the composite microstructure)
a high degree of reinforcement is dependant on strong bonding at the matrix particle phase
how should particles be distributed and orientated for effective reinforcement?
for effective reinforcement particles should be in the same direction and evenly distributed throughout the matrix
what is the effect of the material volume fraction?
volume fraction influences behaviour, mechanical properties increase with particulate content
what is the rule of mixtures equation?
shows the upper and lower bounds for the dependence of the elastic modulus on the volume fraction of the phases
what is the equation for the upper bound?
Ec(U) = EmVm+EpVP
where:
E = elastic modulus
V = volume fraction
C = composite
M = matrix
U just refers to upper
what is the equation of the lower bound?
Ec(L) = EmVm / VmEp + VpEm
where:
E = elastic modulus
V = volume fraction
C = composite
M = matrix
L just refers to upper
what does this equation stand for?
Ec(L) = EmVm / VmEp + VpEm
elastic modulus of the lower bound
where:
E = elastic modulus
V = volume fraction
C = composite
M = matrix
L just refers to upper
what are 2 properties of tungsten particles in a copper matrix?
high heat resistance
low thermal expansion
what is cermet and 1 one of its properties?
hard ceramics in a metal matrix
prevents crack propagation
what is carbon black and what are two properties?
carbon black is small particles added to rubber
enhances toughness and abrasion
what is concrete and what is a disadvantage of it?
concrete is a mix of coarse aggregates, water and cement
weak and brittle
what is an advantage of reinforced concrete?
better maintains stresses as well as reduced corrosion
what is a dispersed strength composite?
small particles, strengthened at atomic levels
what is are two advantages of a dispersed strength composite?
particles hinder dislocations as well as restricting plastic deformation improving yield and tensile strength
what is a fibre reinforced composite?
within a fibre reinforced composite, the dispersed phase is a fibre that is either continuous or discontinues
what is the difference between continuous and discontinuous fibres?
continuous fibres - aligned
discontinuous fibres - short, aligned and randomly orientated
what do mechanical properties depend on within fibre-reinforced composites?
mechanical properties depend on fibre properties, and the degree in which load is transmitted to the fibres
what happens to the matrix bond when under applied stress?
the fibre matrix bond creases at the fibre ends when under applied stress, yielding a a matrix deformation pattern
what is needed for effective strengthening
critical fibre length
what is the equation for critical length?
where:
lc = critical length
σ*f = fibre ultimate strength
d = fibre diameter
τc = fibre matrix bond strength
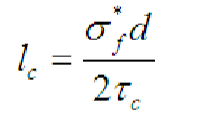
what does it mean if fibres are l > lc?
the fibre is continuous
what does it mean if fibres are l < lc?
the fibre is discontinuous
name 2 factors that have a strong influence on fibre strength
fibre arrangement
fibre concentration
distrubution

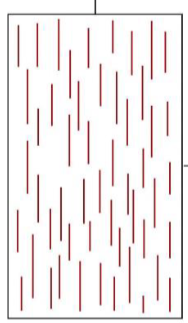
what is this arrangement?
discontinuous but aligned, short
what is this arrangement?
continuous
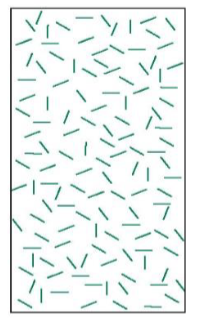
what is this arrangement?
discontinuous, randomly aligned
what does tensile stress strain behaviour in longitudinal loading depend on? (give 2)
stress strain behaviour of the fibre and matrix phases
phase volume fractions
direction of stress
are composites generally anisotropic or isotropic?
anisotropic
what happens in stage 1 of a stress strain diagram of a composite material?
fibres and matrix deform elastically (curve is usually linear)
what happens in stage 2 of a stress strain diagram of a composite material?
matrix yields and deforms plastically
fibres continue to stretch
failure begins once fibres start to fracture
generally, does the matrix or fibres have higher tensile strength?
the fibres have higher tensile strength
why is composite failure not catastrophic?
no all fibres fail at the same time. Once they have failed they are still embedded in the matrix which means they can still support a diminishing load
how does the fibre matrix bond react to longitudinal loading
the fibre matrix bond is good, meaning that deformation in the matrix and fibre is the same
what does this represent: εc = εm = εf
deformation is the matrix and fibres are the same (iso-strain)
what is the equation for the elastic modulus of a continuous and eloigned fibrous composited in the direction of the alignment.
Ecl = EmVm + EfVf
what is the ratio of the load carried by the fibres to that of the matrix?
Ff / Fm = EfVf / EmVm
what is iso- stress?
the composite and both phases are exposed to same amount of stress
what is the equation for iso-stress?
σc= σm = σf = σ
what is the equation for the modulus of elasticity in a continuous and aligned fibre-reinforced composite in the longitudinal direction?
1 / Ect = Vm / Em + Vf / Ef
what is transverse stress influenced by in fibre reinforced composites? (name 2)
properties of the matrix of the fibres
bond strength
presence of voids
do discontinuous or continuous composites have a higher reinforcement efficiency?
continuous
what is the modulus of elasticity of short composites?
short fibre composites have an elastic modulus of about 90% of continuous fibre composition
why are smaller diameter fibres stronger than the bulk material?
lower probability of a critical surface flaw
name 2 example of fibres
whiskers
fibres
wires
what are whiskers?
thin crystal strands with a high length to diameter ratio
what is an advantage of whiskers?
high degree of crystalline perfection creating high strength due to less flaws
why are whiskers not used
impractical and expensive
what type of structure can fibres have?
polycrystalline or amorphous
are fibres or wires larger in diameter?
wires
what are wires used for?
reinforcement
what can the matrix phase be made from
either polymer, metal or ceramic
give two functions of the matrix
binds fibres together
acts as a medium of stress
protects fibres from surface damage
separates fibres stopping propagation
is the matrix brittle of ductile?
ductile
the elastic modulus higher in fibres or the matrix?
fibres
what does the UTS of the composite depend on?
the bond between the matrix and fibres
name 2 advantages of glass fibre
easily fabricated
economical
strong
what is an advantage of carbon fibre reinforced polymers? (give 2)
high modulus to density ratio
high specific strength
retains strength at high temps
name a limitation of glass fibre reinforced polymer composites
not very stiff
limited applications
describe the carbon fibre structure
composed of graphitic and non-crystalline regions
coated carbon fibres
what are three advantages of aramid fibre reinforced polymer composites
high strength
high modulus
high strength to weight ratio
what is pultrusion used for?
used for continuous lengths and constant cross sectional shapes
describe the process of pultrusion
fibres are drawn together as strands
strands are impregnated with a thermosetting resin
fibres are pulled through a steel die to preform to a desired shape
die is heated to initiate the curing of the resin matrix
pulling device draws the stock through the dies
tubes are created by inserting hollow cores
what is filament winding
process of fibres are positioned in a predetermined pattern to form a hollow shape
what is the process of filament winding
fibres are fed through a resin bath
fibres are wound onto a mandrel using automated winding equipment
curing occurs and mandrel is removed
what is prepreg production
fibre is pre-impregnated with a polymer resin that is only partially cured
what is the pre-preg production process
delivered in a tape form
directly moulds and fully cures the product without needing to add resin
what is the process of creating a prepreg tape
spool wound fibres tows are sandwiched and pressed between sheets of papers using heated rollers
a doctor blade spreads resin into a film
final product is a thin tape of fibres in partially cured resin
what does final curing require during the pre preg process
heat and pressure
what are structural composites usually composed of?
homogenous and composite materials
what are properties dependant on in structural composites
material used
geometrical design
what are sandwich panels
lightweight beams of panels with high stiffness and strength
what are laminar composites?
composed of 2D shapes that have a preferred strength orientation
how do laminar composites create balance?
each board has a different direction of high strength, therefore they are swapped on each layer in order to balance out
what are sandwich boards made up of?
two beams that are separated by a adhesively bonded thicker core
what are the main properties of the core within sandwich boards? (give 2)
continuous support
must have shear strength to withstand transverse stresses
variety of applications