wk 9: Pediatric compounding
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
medication error per NCCMERP
-any preventable event that may cause or lead to inappropriate med use or pt harm, while the med is in control of the healthcare professional, pt, or consumer
NCC MERP Index for categorizing med errors
-Category A: no error but circumstances that have capacity to cause error
-Cat B: error occurred but did not reach the pt
-Cat C: error occurred that reached the pt but did not cause pt harm
-Cat D: error occurred that reached the pt and req monitoring to confirm if harm cause
-Cat E: error occurred that may have contributed to temporary harm, req intervention
-Cat F: error that resulted in temp harm to pt and req initial or prolonged hospitalization
-Cat G: error w/ permanent harm
-Cat H: error that req intervention to sustain life
-Cat I: error that caused death
multi-causal model of complex system failure
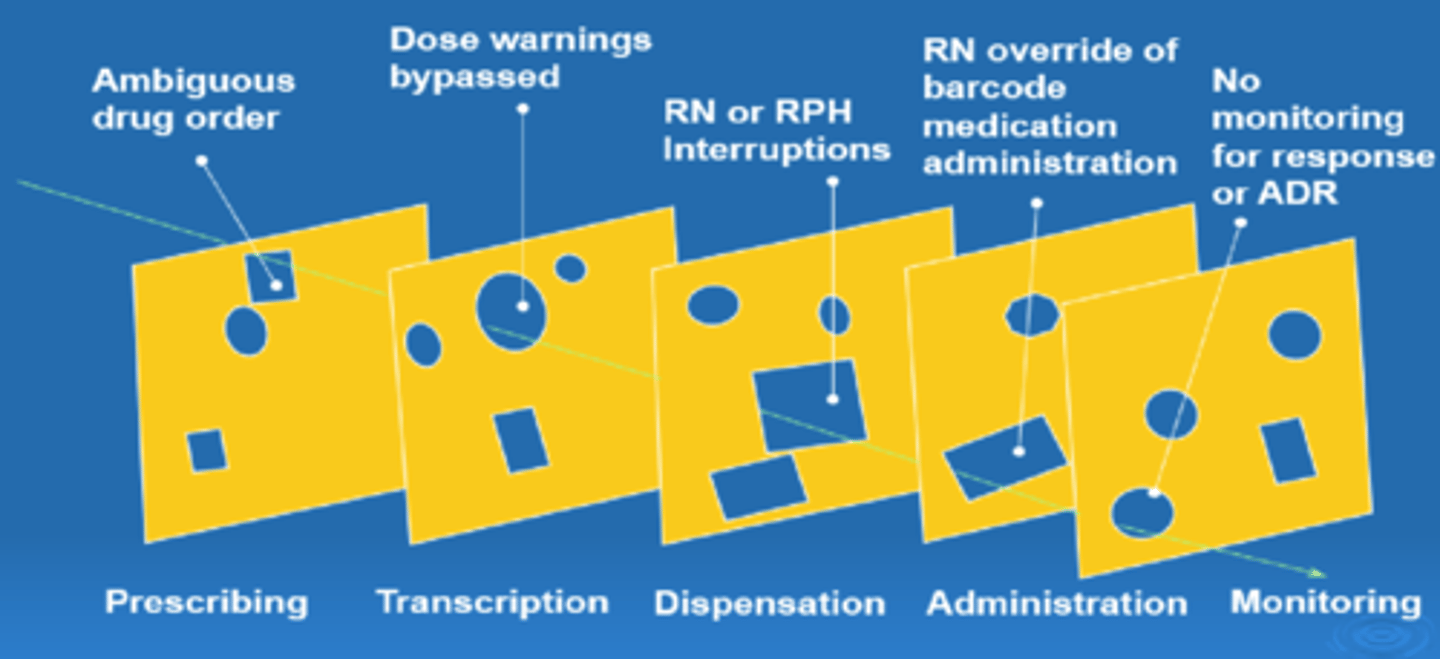
overview of medication management within hospitals
1. history: obtain and document med history
2. Prescribing
->decide on therapy
->prescribe med
3. transmission/transcription
->transmit order to pharmacy
->verify order and transcribe onto MAR
4. Pharmacy
->evaluate order and enter into system
->select and store med
->prepare med
->dispense and distribute
5. Administration
->select med
->identify pt
->educate pt
->admin med
6. documentation/monitoring
->document med admin
->asses pt response and notification
landmark pediatric med error cases
-18-month old Josie King at John's Hopkins
->died from dehydration and narcotic OD after admitted for treatment of sever burns (2001
-2 yr old Emily Jerry at Rainbow babies
->died when chemo was diluted in 23.4% NaCl instead of NS
->pharmacist sentenced to 6 months in jail, 6 months of house arrest and 3 yrs probation (2006)
-3 of 6 premature neonates at Methodist Hospital in Indianapolis
->died after receiving heparin 10,000 units/mL rather than 10 units/mL in NICU
->automated dispensing cabinet had been improperly stocked by pharm tech (2006)
-15 yr old and 8 month old at Seattle Chidlren's
->dentist prescribed fentanyl patch to autistic boy for routine tooth extraction and cleaning, resulting in death
->nurse fired and committed suicide after she admin 1400mg CaCl instead of 140 mg, child died 5 days after OD (2010)
-16 yr old at University of Cali San Fransisco med center
->developed numbeness, tingling and seizures after given 38.5 tablets of TMP-SMX
->multifactorial, 50 steps identified (prescribing to admin) (2013)
former nurse found guilty of accidental injection death of 75 yo pt
-75 yo women admitted for brain injury, improving status
-Midazolam ordered prior to MRI scan as sedative for anxiousness
-vecuronium pulled from med cabinet instead of midazolam
->paralyzing agent
Joint Commission: Sentinel Event Alert (SEA)
-any unanticipated event in healthcare setting resulting in death or serious physical or psychological injury to pt
->not related to natural course of pt's illness
-identified events and describes underlying causes, suggests steps to prevent future vents
-first SEA published Feb 28, 1998
-goal SEA is to reduce freq of medical errors and other AEs
-SEA #39: Preventing Pediatric Med Errors
->published 2008
->pediatric risk factors for med errors
->strategies for preventing pediatric med errors
types of pediatric med errors
-10-fold errors are most common error during prescribing and preparation phase of med management system
-improper dose/quantity: 37.5%
-omission error: 19.9%
-unauthorized/wrong drug: 13.7%
-prescribing error: 9.4%
-other:
->wrong admin technique, wrong time, drug prepared incorrectly, wrong dosage form, wrong route
institute for safe med practices: best practice 11
-when compounding sterile preparations, perform independent verification to ensure that the proper ingredients (meds and diluents) are added
->incl confirmation of proper amt (volume) od each ingredient prior to its addition to final container
-at min, perform verification for all high-alert meds, pediatric/neonatal preparations, pharmacy-prepared source/bulk containers, products admin via high-risk routes of admin
6 rights of med admin
1. right pt (name and date of birth)
2. right med
3. right dose
4. right route and rate
5. right time and freq
6. right documentation
med safety challenges
-individualized dosing
-fluid overload
-commercially avail forms
-[ ] of med
-measurable volume
-complex calculations
->mg/kg/DAY, mg/kg/DOSE, BSA, mCg vs mg
pediatric risk factors for error
-developing renal, immune and hepatic organ systems
-wt based dosing (mg/kg, mg/m^2)
-maturational changes in PK parameters
-premature neonates to adolescents
-lack of pediatric dosage forms
-need to precise dose measurements and drug delivery
-lack of trained staff in pediatrics
-communication ability of pt
-lack of info or FDA approved labeling
-children DO NOT = little adults
altered PK in children1
-oral absorption:
->inc pH in neonates and young infants
->dec bioavail of weak acids and inc bioavail of weak bases
-distribution:
->inc body water to fat ratio compared to adults
->inc Vd of hydrophilic drugs and dec Vd of lipophilic drugs
-Metabolism:
->dec phase I and II enzyme activity
->dec hepatic metab
-Excretion:
->dec glomerular filtration and dec renal tubular absorption and secretion
->dec renal clearance
med safety measures in Peds/NICU
-syringe pumps
-barcode scanning
-peds specific standard [ ]
-peds specific entries in EMR
-dispense products as "ready to use" as possible
-pediatric and neonatal appropriate resources
-satellite pharmacies within specialized areas w/ peds/NICU focus
-pediatric and neonatal clinical pharmacy specialists
standardize 4 safety initiative
-consistent medication [ ]s for pts during transitions of care reduces potential for errors
-simplified ordering and fewer choices, which dec provider uncertainty
-accelerated manufacturing streamlines production and allows for formulation of premixed meds
-reduces operational variations, which enhances provider efficiency
overview of syringe pumps
-low vol infusion rates in small increments
->fluids, meds, blood products
-programmable pumps w/ library of standardized [ ] and built in guardrails
->attempts to program an infusion rate that falls outside the limits will alert user
->soft and hard limits
-ensure syringe and models are compatible w/ syringe pump
-use smallest syringe size necessary to delivery meds
->larger syringe at low rate can lead to delivery inaccuracies
-microbore tubing
->small priming volume
-smart pumps: syringe pump, bag pump, PCA pump, epidural pumps
medfusion syringe pump
-care area: PICU cont, PICU intermittent, NICU cont, peds chemo
-drug program
-dose rate
medfusion syringe pump: syringe sizes
-a 24 hr supply will be sent for all continuous infusions
->less than 0.05 mL/hr = 3 mL syringe
->0.05 ml/hr to <0.2 ml/hr = 5 ml syringe
-0.2 to <0.5 ml/hr = 20 ml syringe
->0.5 to 6 ml/hr = 50 ml syringe
-> >6ml/hr dispensed in a bag
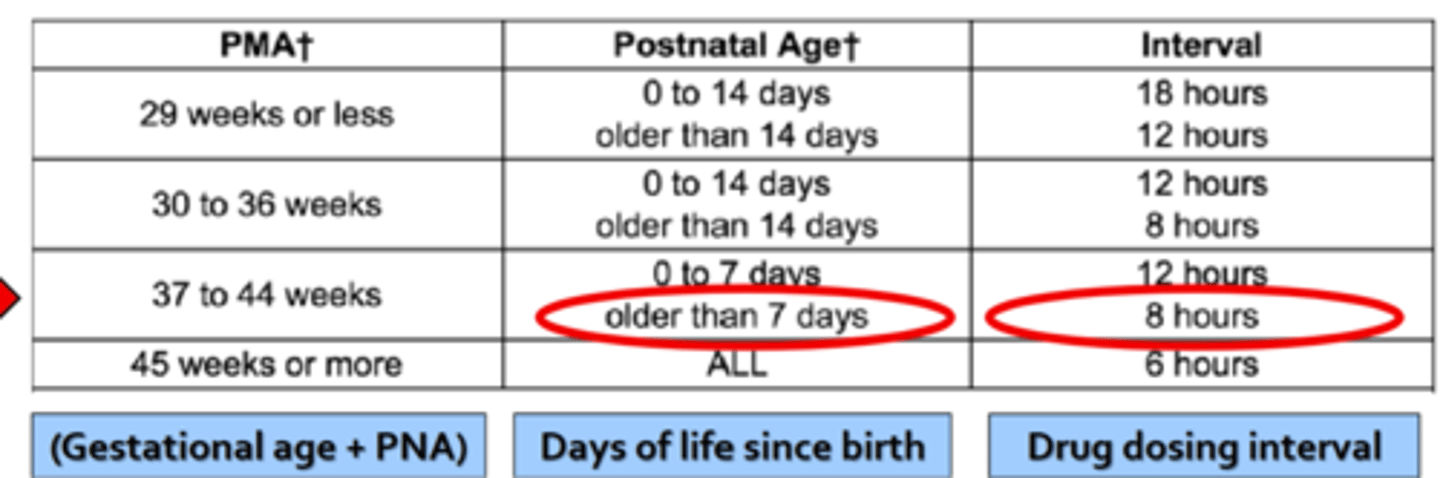
neonatal references and dosing
-most meds dosing/freq intervals based on postmenstrual age!!!
-gestation age (conception)
-chronological age (after birth
-postmenstrual age = gestational + chronological age (first day of last menstrual period to current age)
gestational age
-completed wks, time elapsed btwn 1st day of last period and day of delivery
chronological age
-aka postnatal age, time elapsed after birth
-days of life
postmenstrual age
-expressed in wks, gestational age PLUS chronological age
dosing in neonates: NeoFax
concentration
-amt of drug in given volume
->mg/ml, mcg/ml, mEq/ml, g/ml
dilution
-[ ] of med is reduced
diluent
-solvent or liquid preparation used to reconstitute or further dilute med
reconstitution
-taking a powder form to a liquid form by adding liquid diluent
-usually sterile water for injection (SWFI) or NS
methods of delivery
-IV push
-IVPB bag
-IVPB syringe
-continuous infusion
-large volume IVF
IV push
-rapidly delivers one med thru line directly into bloodstream
-used for meds admin over short period of time (1-3 minutes)
-typically does not req further dilution
-easy for pharmacy to stock med cabinet
IV piggyback bag (IVPB)
-allows for delivery of med in a standard volume
->50ml, 100ml, 250 ml
->potassium chloride 10 mEq/100ml bags
->levetiracetam 1000mg/100ml bags
-may incl commercially avail products
->long shelf life (manufacturer dating)
-may also customize a pt-specific dose in a standard IV bag volume
->high dose methylprednisolone 30 mg/kg diluted in 250 ml NS
-ex: Magnesium PED 40 mg/ml
->2000 mg/50ml = 40mg/ml
-combo products = confusing
->ex: pip (3gm) + tazo (0.375g) = Zosyn (3.375 g)
->dosing is based on piperacillin content
->Zosyn PED 60mg/ml IV 3000mg Q6hrs
->3000/60 = 50 mL
->full bag of zosyn 3.375g
IV piggyback syringe
-preparation of doses in a syringe allows for enhanced ability to customize dose and volume
-allows for controlled drug delivery of an intermittent med over a set amt of time
->minutes to hrs
-extremely common for neonatal and pediatric dose that cannot be delivered w/ the commercially avail options
-can accurately deliver infusion rates <0.1 ml/hr
preparation of IVPB syringe
-original drug product
-pediatric stock soln
-dispense as final product
overview of continuous infusions
-certain meds may preferentially by admin via continuous infusion
->sedation/analgesia in critically ill children
->CV agents: vasopressors OR antihypertensives
->meds w/ short t1/2
-rates that are orders must incorporate unit of time
->mcg/kg/min
->mg/kg/hr
->units/kg/hr
ASHP principles for continuous infusions
-safety first: use commercial when possible
-try to limit to one concentration when possible
-consider operational dispensing aspects and steps incl waste
-consider concentration relative to fluid status
->use more concentrated when possible
dopamine case
look at lecture for problem and answers
rate of infusion (ml/hr)
rate = dose (mcg/kg/min) x wt (kg) x 60 min/hr divided by [ ] (mcg/ml)
overview of emergency med preparation
-some meds may need to be emergently prepped at bedside
->rapid response
->code white
->rapid sequence intubation
->emergent bedside procedure
-med typically for immediate use only (no extended expiration)
-med not used can discarded after 1 hr of reconstitution
preparation of adenosine
see lecture for example!!!
ICU adenosine algorithm
-pt wt less than 3kg
->MUST dilute adenosine following dilution instruction below, see BLUE label
-pt was >/ 3kg
->DO NOT dilute adenosine further
->use straight drug from viral, see GREEN label
excipients and preservatives
-Benzyl alcohol is common bacteriostatic preservative
->exposure in infants is assoc w/ neonatal gasping syndrome
->not to exceed 99 mg/kg/day of benzyl alcohol
->metabolic acidosis, respiratory distress, seizures
->hypotension, CV collapse
->death
-propylene glycol:
->CNS tox, hyperosmolarity, arrythmia, lactic acidosis
-ethanol
->neurotox, impaired brain development