Leukocoria & Childhood Tumors
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
persistent primary vitreous
Coat’s disease
ocular toxocarisis
ROP
retinal hamartoma
toxoplasmosis
posterior uveitis
cataracts
strabismus
anisometropia
high RE
retinoblastoma
what are the differentials for leukocoria?
toxocariasis
etiology: roundworms (infected dogs/cats), more common in warm climates
typically in children (avg age of onset: 8.1y)
typically unilateral signs:
floaters
pars planitis
chorioretinitis
vitritis
RD
peripheral granuloma w/ or w/o traction bands
retinal hamartoma
benign, non-cancerous tumor
many are thought to be congenital
consist of glial cells
combined or astrocytic
combined hamartoma
unilateral
if bilateral, associated w/ neurofibromatosis type 2
can be anywhere in retina
gray tumor
all involving RPE, retina, & vitreous
astrocytic hamartoma
composed of glial cells (mostly astrocytes)
lesions at/near optic disc (posterior pole)
pale, multinodular tumors
associated w/ tuberous sclerosis
tuberous sclerosis
uncommon genetic disorder that causes non-cancerous tumor development throughout the body
usually diagnosed in infancy
sx are related to secondary complications from tumors
retinoblastoma
primary malignant tumor of neuroectodermal origin arising from the nucleated layers of the retina
most common primary eye cancer of childhood
if left untreated, it grows to eventually fill the entire cavity of the eye & eventually spread extra ocularly
can metastasize via the ON or choroidal blood supply
save the child’s life
what is the primary tx goal for treating retinoblastoma?
save eye/vision
what is the secondary tx goal for treating retinoblastoma?
bilateral
what is the laterality of the hereditary/germline form of retinoblastoma?
unilateral
what is the laterality of the non-hereditary/somatic form of retinoblastoma?
10
only __% of germline cases of retinoblastoma have a +FHx
40
__% of retinoblastoma cases are hereditary/germline
60
__% of retinoblastoma cases are non-hereditary/somatic
5
__% of hereditary/germline cases of retinoblastoma develop another primary intracranial malignancy in childhood that are typically difficult to treat
30
__% of hereditary/germline cases of retinoblastoma will develop a non-ocular neoplasm by age 40
F
T/F: non-hereditary/somatic cases of retinoblastoma have a risk of passing it along to their children
T
T/F: non-hereditary/somatic cases of retinoblastoma have no predisposition to developing other forms of cancer later in life
2
2/3 of retinoblastoma tumors develop by __y of age
95
__% of retinoblastomas develop by 5y of age
13mo
the mean age of detection for bilateral retinoblastoma:
24mo
the mean age of detection for unilateral retinoblastoma:
endophytic
retinoblastoma tumor that grows toward the vitreous
exophytic
retinoblastoma tumor that grows from outer retina toward the choroid, causing elevation of the retina & possible serous detachment
mixed growth
type of retinoblastoma that is a combo of endophytic & exophytic growth, majority of cases
mixed growth
what type of growth pattern is majority of cases of retinoblastoma?
diffuse
type of retinoblastoma growth, only 1-2% of cases, tumor invades the retina & produces plaque-like thickening, difficult to dx
local therapy
IV or intra-arterial chemo
brachytherapy
external beam radiation
surgical enucleation
what are the tx options for retinoblastoma?
toxocariasis
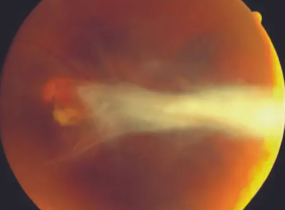
retinal astrocytic hamartoma
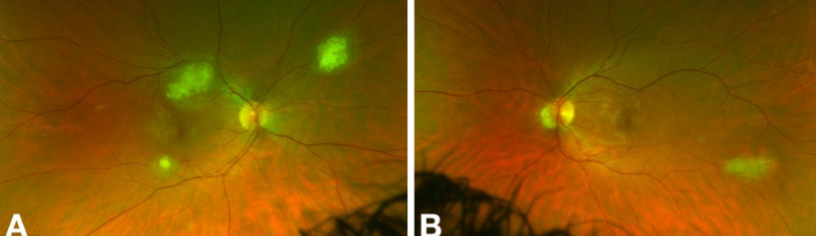
combined retinal hamartoma
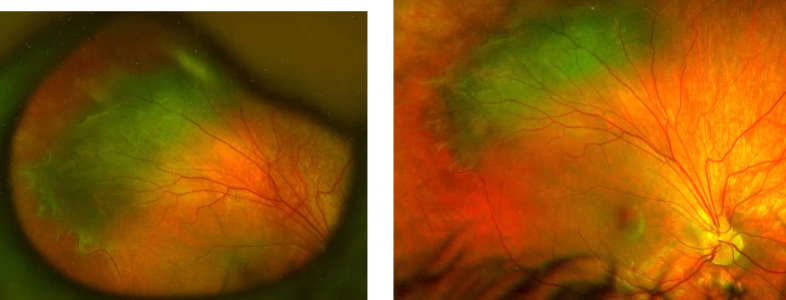
dermoid cyst
benign
formed when a piece of surface ectoderm is pinched off in bony suture line where the tissue will gradually form a cyst
lined w/ normal keratinizing stratified squamous epithelium w/ various adnexal structures in the wall
contents include: keratin, sebaceous secretions & hair
often attached to the bone at the frontozygomatic or frontonasal suture lines
smooth, painless, oval masses
palpable
only need removal if disrupting orbit/orbital structures
lipodermoid
benign
solid tumors that present subconjunctivally on the lateral bulbar surface over the LR muscle
can be removed if causing ocular discomfort or significant corneal astigmatism that isn’t manageable
conjunctival dermoid
benign
congenital
well circumscribed
usually inferotemporal
infantile hemangioma
benign
arise in infancy, stabilize, then spontaneous involution b/t the age of 1-8yo
can be multiple & involve the head & neck region
strawberry nevus
can cause ptosis, globe displacement, proptosis, strabismus, & astigmatism if extends into orbit
infantile hemangioma
what is the most common benign orbital tumor of childhood?
lymphangioma
benign
typically diffuse unencapsulated choristomatous primitive vascular tumors that infiltrate the normal tissues of the lid & orbit & become apparent in the 1st decade
thought to be a combined vascular malformation w/ both the venous & lymphatic components
multilobular, involve conjunctiva, lids, orbit, scalp & sinuses
most commonly in superior & inferior nasal orbit
rarely spread intracranially
highly variable progression
typically progress until mid-adolescence & then stabilize
don’t regress
can induce ptosis, proptosis, ON compression, induced astigmatism, & strabismus
can surgically debulk but cannot excise completely
optic nerve glioma
benign
most common sign: optic nerve pallor
also can get proptosis & EOM restrictions
can occur anywhere along the ON or hypothalamus
associated w/ neurofibromatosis type 1
surgical excision can be considered if it progresses into the optic canal to protect the chiasm or to reduce extreme proptosis
optic nerve glioma
what is the most common pediatric optic nerve tumor?
rhabdomyosarcoma
malignant
94% survival rate
secondary malignant neoplasms occur
avg age of onset: 8-10yo
arises from undifferentiated pluripotent mesenchymal cells of the orbit
characteristically develops superior nasally in the orbit, displacing the eye down & out
quick growing
tx:
chemo
radiation
surgery
rhabdomyosarcoma
what is the most common primary malignant tumor in children?
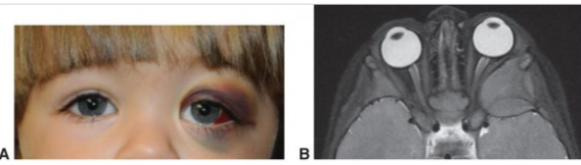
neuroblastoma
arises from the adrenal medulla in infants & young children
originated in abdomen in most
10% of pediatric cancers
90% occur in kids under 5 but can occur up to age 20
orbital involvement occurs as a metastasis from elsewhere
poor prognosis if orbital involvement
common ocular signs: periorbital redness (raccoon eyes)
dermoid cyst
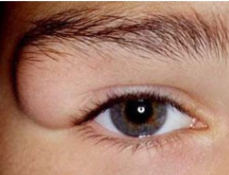
limbal dermoid
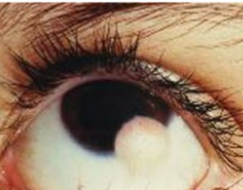
infantile hemangioma
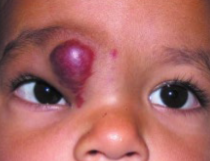
infantile hemangioma
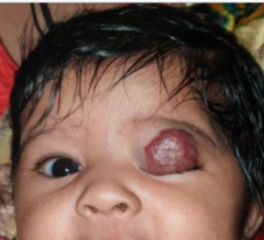
lymphangioma
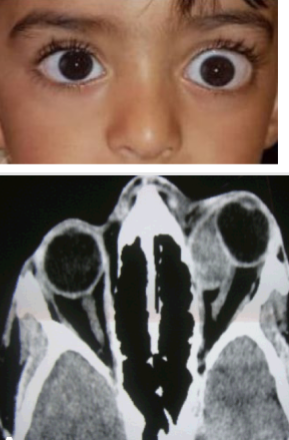
optic nerve glioma
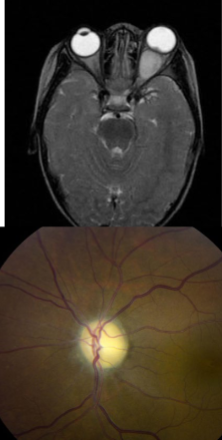
rhabdomyosarcoma
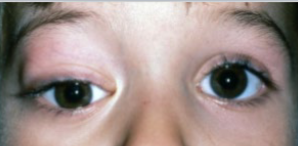
neuroblastoma
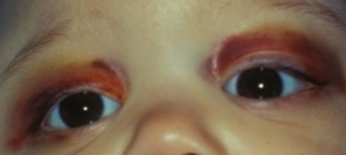
neuroblastoma