MCB4304 MODULE 1 Recombinant DNA and PCR
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
What is recombinant DNA technology?
The use of in vitro molecular techniques to isolate and manipulate fragments of DNA.
What significant achievement occurred in the early 1970s at Stanford University?
Researchers constructed chimeric molecules called recombinant DNA molecules.
What does gene cloning refer to?
The technique of isolating and making many copies of a gene, usually using vectors.
What are the two kinds of DNA molecules involved in cloning experiments?
Chromosomal DNA (source of the DNA segment of interest) and Vector DNA (carrier for the DNA segment to be cloned).
What is the role of vector DNA in gene cloning?
Vector DNA serves as a carrier for the DNA segment that is to be cloned and can replicate independently of the host chromosomal DNA.
How can chromosomal DNA be obtained for cloning?
By obtaining cellular tissue from the organism of interest, breaking open the cells, and extracting and purifying DNA using biochemical techniques.
What is a host cell in the context of gene cloning?
The cell that harbors the vector.
What determines whether a vector can replicate in a particular host cell?
The sequence of the origin of replication.
What are the two natural sources from which commonly used vectors in gene cloning are derived?
Plasmids and viruses.
What are plasmids and their significance in gene cloning?
Naturally occurring plasmids often have selectable markers, typically genes conferring antibiotic resistance to the host cell.
How do viruses function as vectors in gene cloning?
Viruses infect living cells and propagate themselves by taking control of the host cell's machinery.
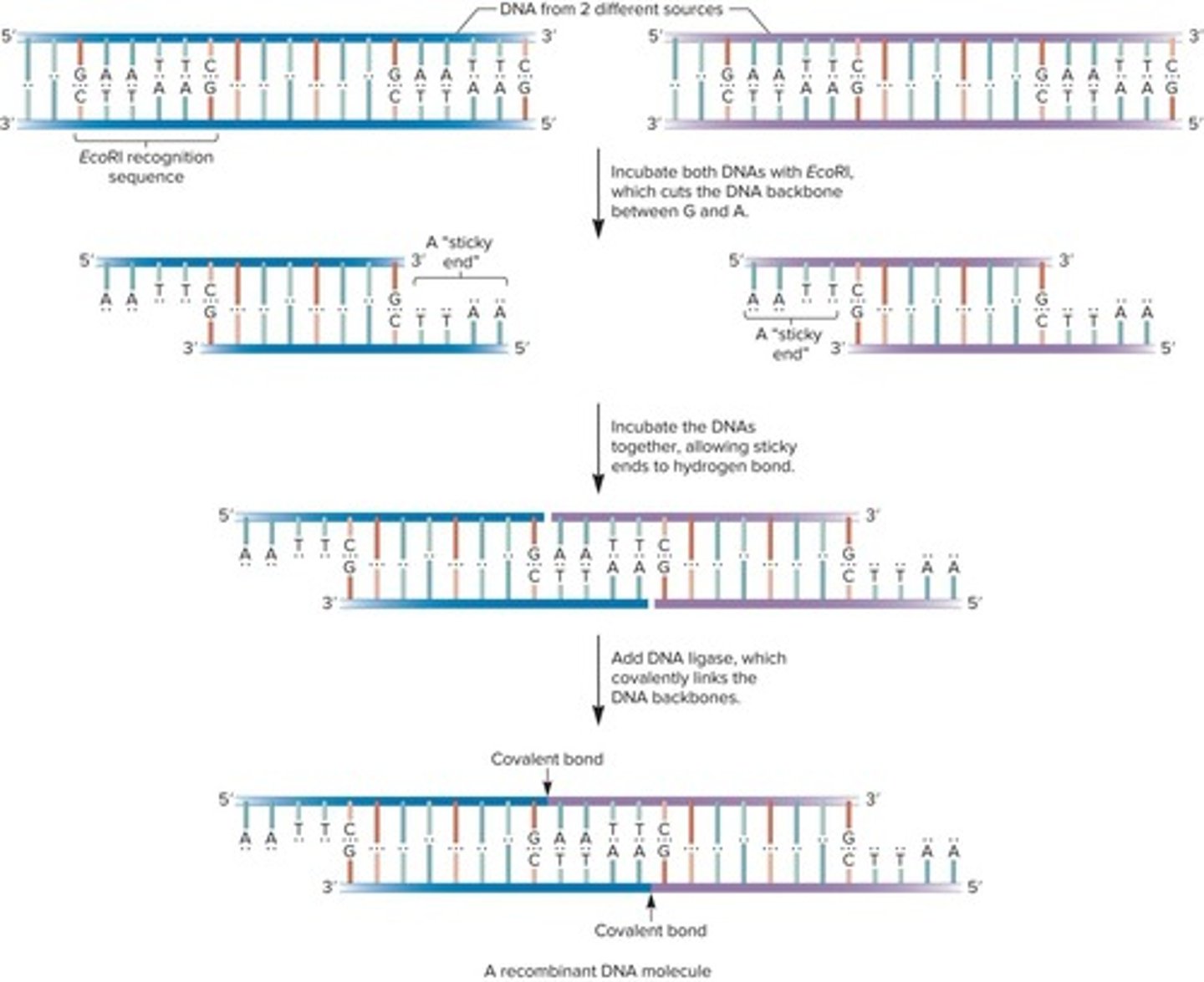
What are restriction enzymes?
Enzymes used to cut DNA into pieces, discovered in the 1960s and 1970s.
What is the function of restriction enzymes in molecular biology?
They bind to specific DNA sequences and cleave the DNA at two defined locations.
What is a recognition sequence in the context of restriction enzymes?
A specific DNA sequence that is typically palindromic, meaning it reads the same in both directions on complementary strands.
Give an example of a recognition sequence for a restriction enzyme.
The EcoRI recognition sequence: 5′-GAATTC-3′ and 3′-CTTAAG-5′.
Who were the scientists credited with the discovery of restriction enzymes?
Werner Arber, Hamilton Smith, and Daniel Nathans.
What is the primary function of restriction enzymes in bacteria?
To protect bacterial cells from invasion by foreign DNA, particularly that of bacteriophages.
What is the significance of the era of gene cloning?
It has been fundamental to our understanding of gene structure and function.
What laboratory methods have advanced gene cloning since the early 1970s?
DNA sequencing, DNA probes, and expression of cloned genes.
What is the purpose of inserting chromosomal DNA into a vector?
To clone the DNA segment for further study or manipulation.
What is the importance of the New England Biolabs (NEB) Enzyme Finder Website?
It hosts a list of all commercially available restriction enzymes.
How many different restriction enzymes are currently available commercially?
Several hundred.
What is the recognition sequence for BamHI?
5′-GGATCC-3′ and 3′-CCTAGG-5′.
What organism produces the restriction enzyme BamHI?
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens.
What is the recognition sequence for Sau3AI?
5′-GATC-3′ and 3′-CTAG-5′.
What organism produces the restriction enzyme Sau3AI?
Staphylococcus aureus.
What are the two types of ends that restriction enzymes can generate?
Sticky ends and blunt ends.
What type of cut does the enzyme NaeI make?
Cuts in the middle of its recognition sequence.
What enzyme catalyzes the linking of DNA molecules with sticky or blunt ends?
DNA ligase.
What are 'sticky ends' in the context of restriction enzymes?
Short, single-stranded regions of DNA that can base-pair with complementary sequences.
What is the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)?
A method to copy a specific sequence of DNA without vectors and host cells.
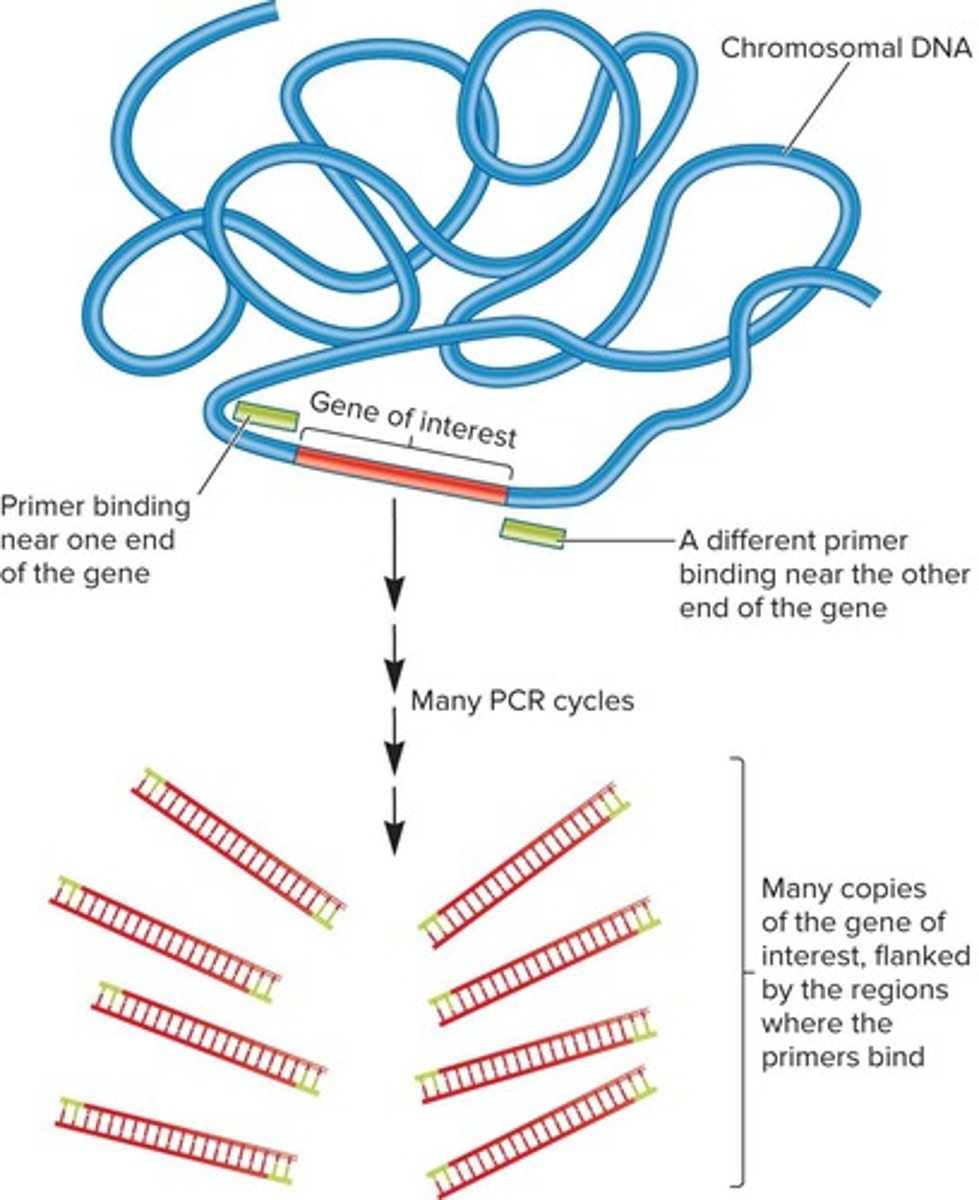
Who developed the Polymerase Chain Reaction and when?
Kary Mullis in 1985.
What is the starting material for PCR?
Template DNA, oligonucleotide primers, and deoxynucleoside triphosphates (dNTPs).
What is the function of oligonucleotide primers in PCR?
They are complementary to sequences at the ends of the DNA fragment to be amplified.
How long are oligonucleotide primers typically?
About 15 to 20 nucleotides long.
What do deoxynucleoside triphosphates (dNTPs) provide in PCR?
The precursors for DNA synthesis.
What is Taq polymerase and why is it important for PCR?
Taq polymerase is a DNA polymerase isolated from the bacterium Thermus aquaticus, and it is thermostable, making it necessary for PCR, which involves heating steps that inactivate most other DNA polymerases.
What are the three steps of a PCR cycle?
The three steps of a PCR cycle are denaturing, annealing, and synthesis.
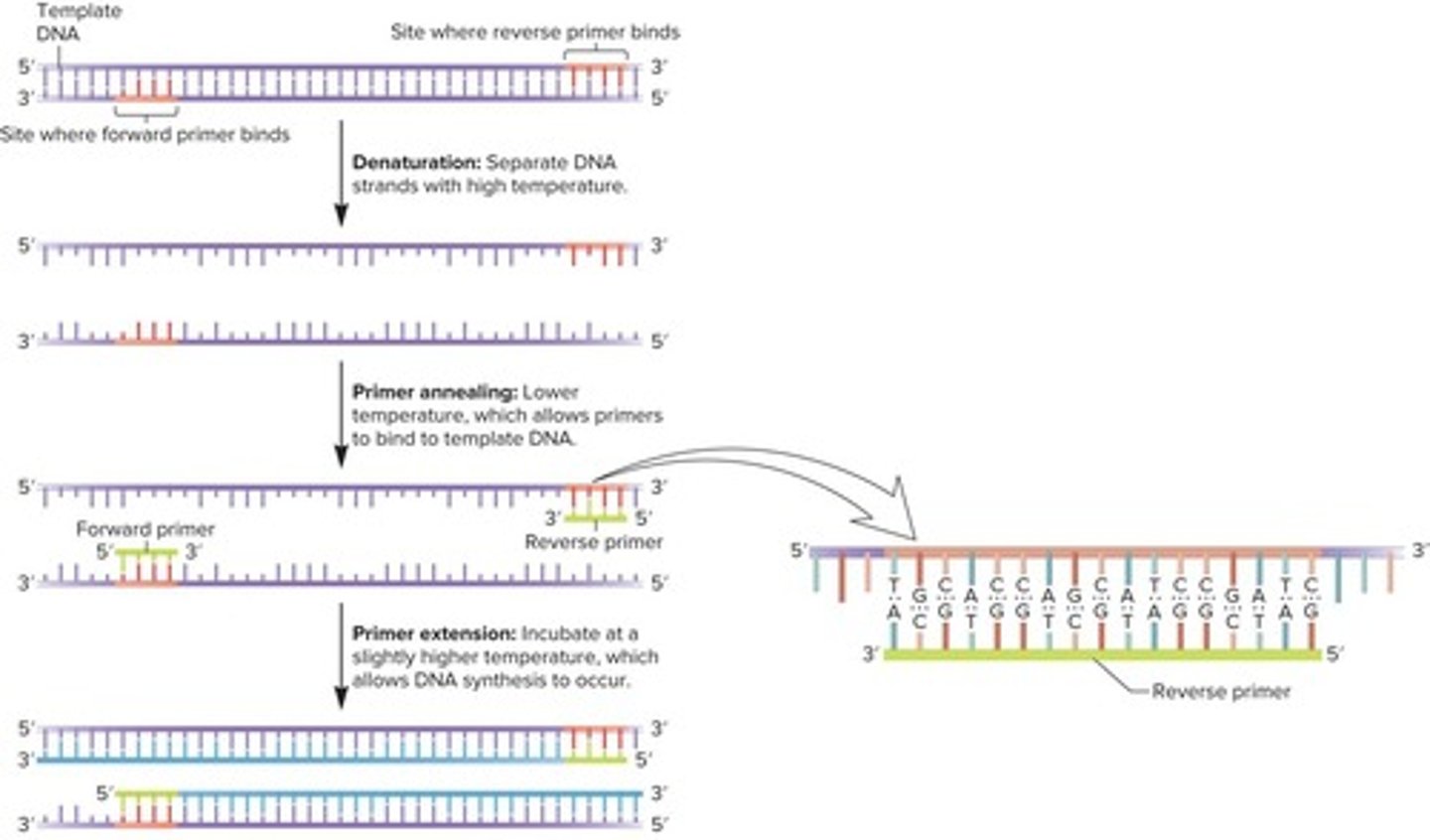
How many cycles are typically involved in a PCR run, and how long does it take?
A typical PCR run involves 20 to 30 cycles of replication and takes a few hours to complete.
What is the expected increase in target DNA sequence after 20 cycles of PCR?
After 20 cycles, a target DNA sequence will increase approximately 220-fold (around 1 million-fold).
What is the expected increase in target DNA sequence after 30 cycles of PCR?
After 30 cycles, a target DNA sequence will increase approximately 230-fold (around 1 billion-fold).
What is one application of PCR in genetics?
PCR can amplify a specific DNA segment from a complex mixture of other sequences, such as one gene out of an entire genome.
How does PCR amplify chromosomal DNA nonspecifically?
PCR can amplify chromosomal DNA nonspecifically by using a mixture of primers with many different random sequences that anneal randomly throughout the genome.
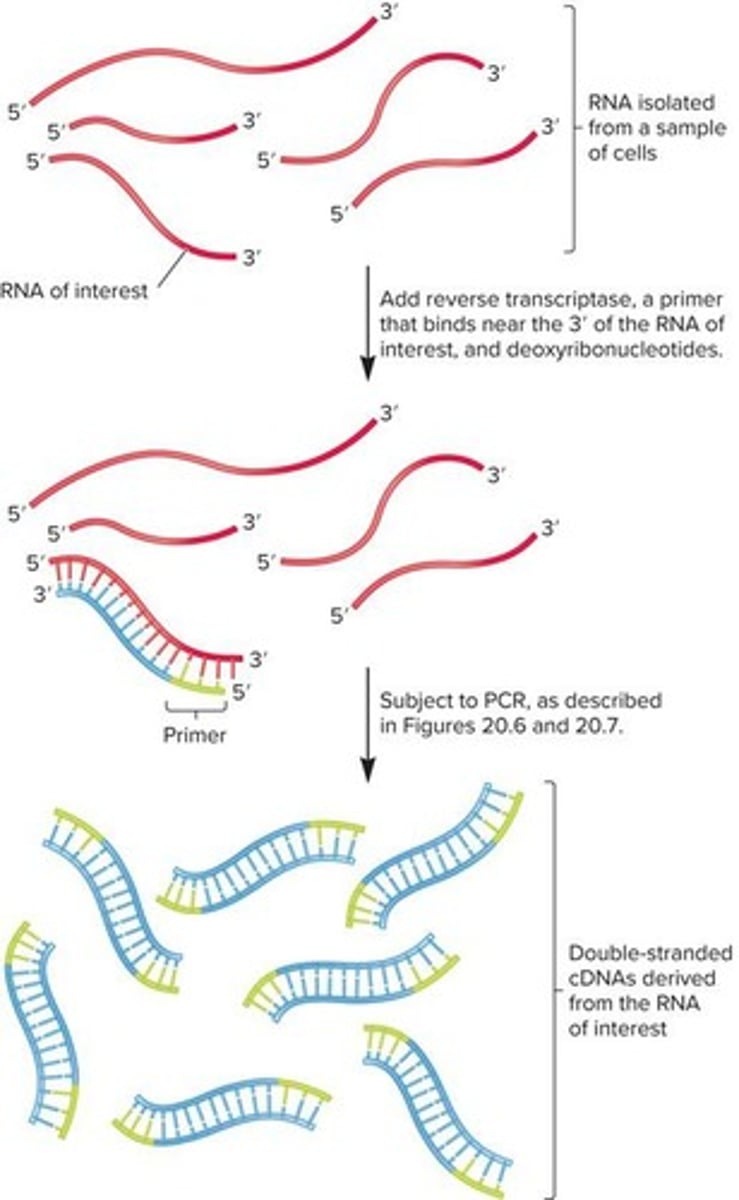
What is Reverse Transcriptase PCR (RT-PCR) used for?
RT-PCR is used to detect and quantify the amount of RNA in living cells.
What is the process of RT-PCR?
In RT-PCR, RNA is isolated, mixed with reverse transcriptase and a primer that anneals to the 3' end of the RNA, generating single-stranded cDNA that can be used as template DNA in conventional PCR.
What is quantitative PCR (qPCR) and how does it function?
qPCR is used to quantify the amount of a specific gene or mRNA in a sample in real time, using a thermocycler that measures changes in fluorescence emitted by detector molecules in the PCR reaction mix.
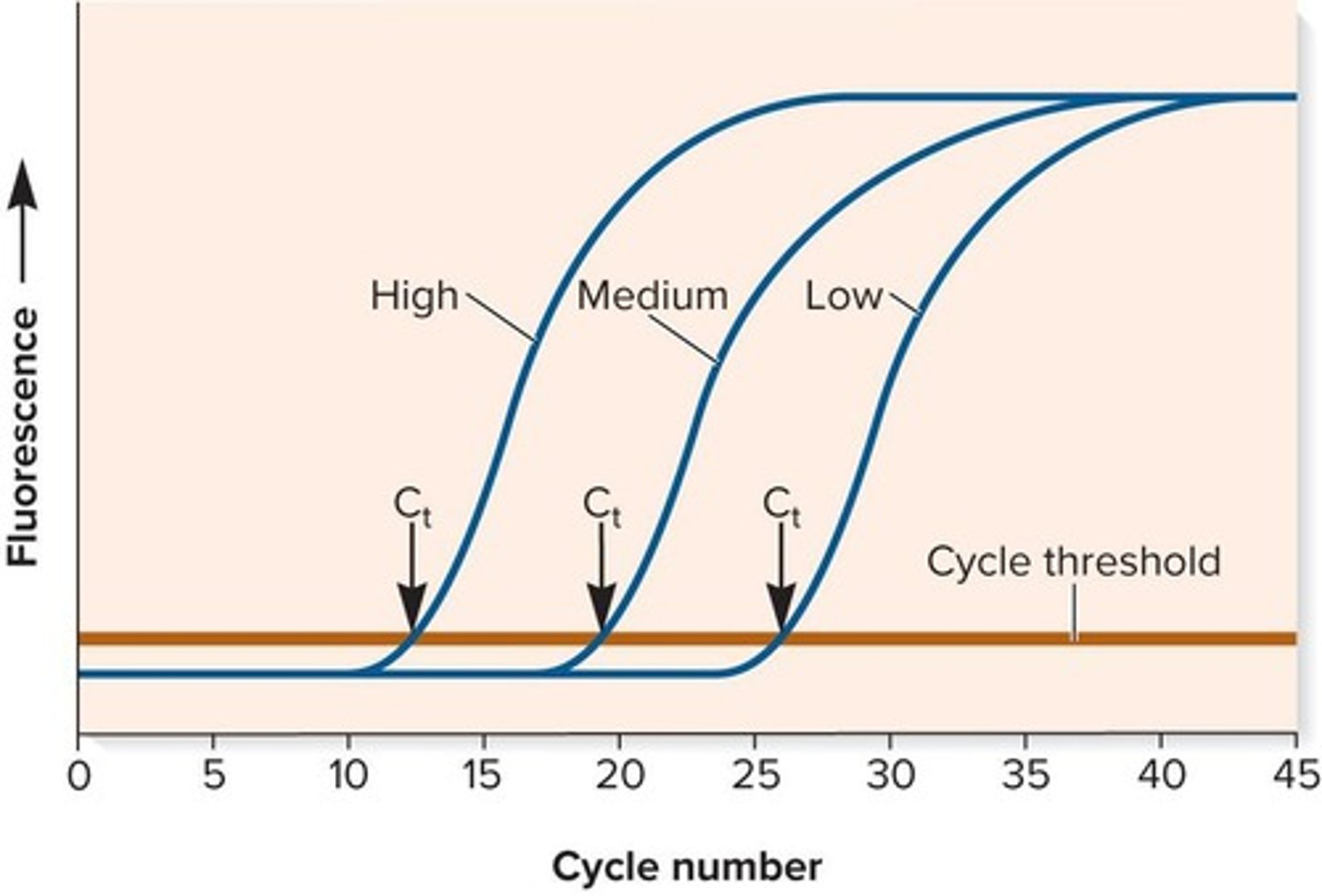
What does the Cycle Threshold (Ct) indicate in qPCR?
The Cycle Threshold (Ct) is reached when the accumulation of fluorescence is significantly greater than the background fluorescence, and it depends on the initial concentration of template DNA.
What are the phases of qPCR?
The phases of qPCR include: 1) Initial phase with no detectable fluorescence, 2) Exponential phase where product doubles with each cycle, 3) Linear phase when reagents are somewhat limiting, and 4) Plateau phase when reagents are used up.
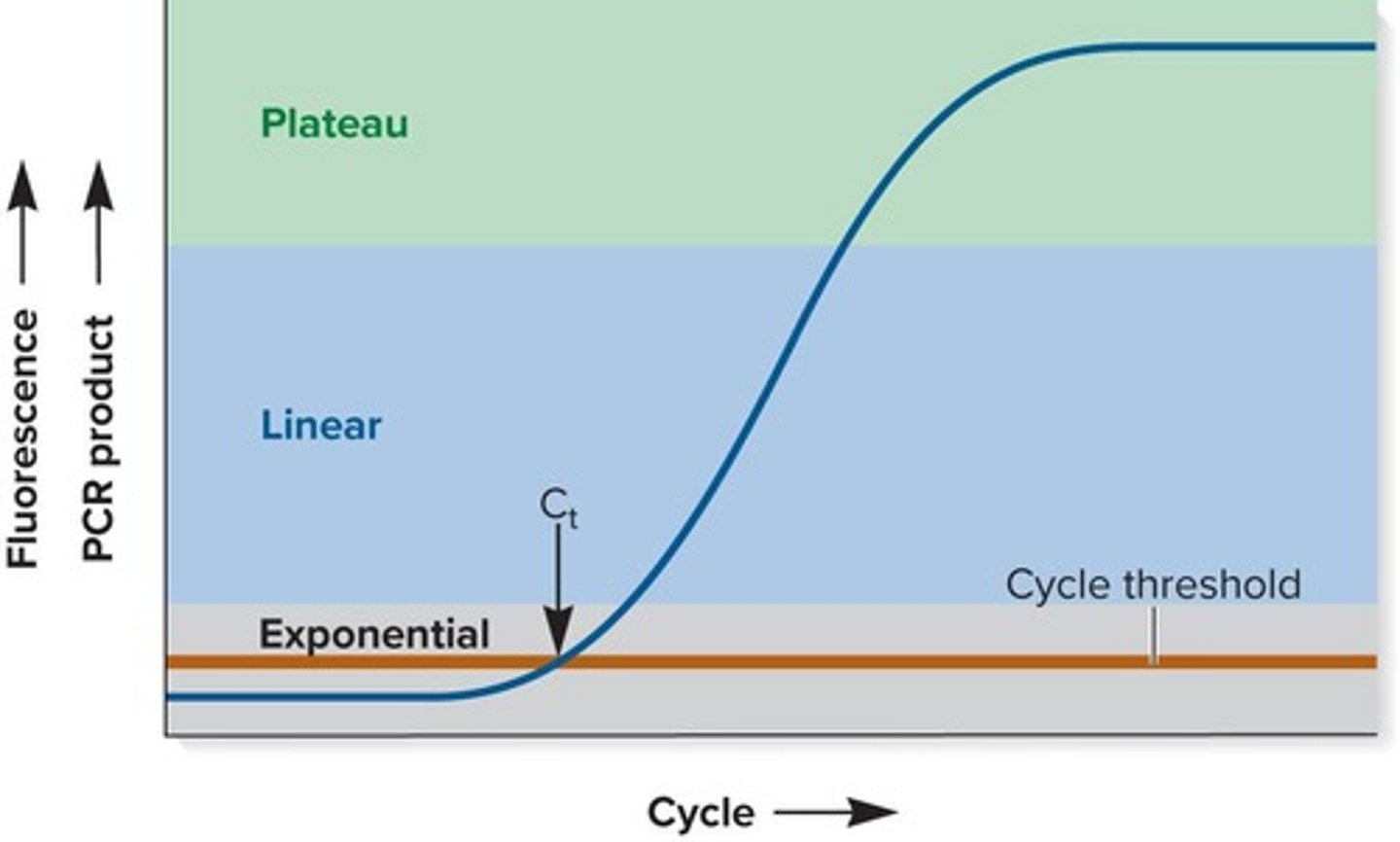
How can the concentration of an unknown amount of starting DNA be determined in qPCR?
The concentration can be determined by comparing the Ct with known standards or by adding a known amount of DNA and amplifying another gene in the sample.
What does qPCR data show at high, medium, and low concentrations of starting template DNA?
qPCR data shows different fluorescence levels corresponding to high, medium, and low concentrations of starting template DNA, indicating the amount of PCR product produced.
What is the role of chromosomal DNA in gene cloning?
It serves as the source of the DNA segment of interest.
What is the function of vector DNA in gene cloning?
It serves as the carrier for the DNA segment that is to be cloned and can replicate independently of the host chromosomal DNA.
What is a plasmid?
A naturally occurring circular DNA molecule that can carry selectable markers, such as antibiotic resistance genes.
How do viruses function in gene cloning?
They infect living cells and propagate themselves by taking control of the host cell's machinery.
What is the recognition sequence for EcoRI?
5′-GAATTC-3′ and 3′-CTTAAG-5′.
What are recognition sequences typically characterized by?
They are usually palindromic, meaning they read the same in the opposite direction in the complementary strand.
What is the purpose of the New England Biolabs (NEB) Enzyme Finder Website?
To list all commercially available restriction enzymes.
What is the significance of gene cloning in science?
It has been fundamental to our understanding of gene structure and function.
What advances have enabled gene cloning to become widely used?
DNA sequencing, DNA probes, and expression of cloned genes.
What happens when a vector is replicated inside a host cell?
The DNA that it carries is also replicated.
What are the two types of ends generated by restriction enzymes?
Sticky ends and blunt ends.
How does NaeI cut DNA?
It cuts in the middle of its recognition sequence.
What is the role of DNA ligase in DNA manipulation?
It covalently links the sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA molecules with sticky or blunt ends.
What are 'sticky ends' in DNA?
Short, single-stranded regions of DNA that can base-pair with complementary sequences.
Who developed PCR and when?
Kary Mullis in 1985.
What is required to perform PCR?
Knowledge of the gene of interest to have the sequence of 2 short primers.
What do deoxynucleoside triphosphates (dNTPs) provide for PCR?
They provide the precursors for DNA synthesis.
How many cycles are typically involved in a PCR run?
A typical PCR run involves 20 to 30 cycles of replication.
What is the purpose of PCR?
PCR is used to amplify a specific DNA segment from a complex mixture of other sequences, such as one gene out of an entire genome.
What is the purpose of Reverse Transcriptase PCR (RT-PCR)?
RT-PCR is used to detect and quantitate the amount of RNA in living cells.
Why is RT-PCR considered extraordinarily sensitive?
RT-PCR can detect the expression of small amounts of RNA in a single cell.
What is Quantitative PCR (qPCR) used for?
qPCR is used to quantitate the amount of a specific gene or mRNA in a sample in real time.
How does a thermocycler measure changes in qPCR?
A thermocycler measures changes in fluorescence emitted by detector molecules in the PCR reaction mix.
How can the concentration of an unknown amount of starting DNA (or RNA) be determined in qPCR?
The concentration can be determined by comparing the Ct with known standards.
What happens to the PCR product during the exponential phase of qPCR?
During the exponential phase, the PCR product doubles with every cycle.
What is the significance of fluorescence in qPCR?
Fluorescence detected by the thermocycler increases in proportion to the amount of PCR product produced.
What is the role of primers in PCR?
Primers anneal to specific sequences of DNA to initiate the synthesis of new DNA strands during PCR.
What is the importance of using a thermocycler in PCR?
A thermocycler allows for precise temperature control necessary for the denaturing, annealing, and synthesis steps of PCR.
What is the difference between specific and nonspecific amplification in PCR?
Specific amplification targets a particular DNA segment, while nonspecific amplification uses a mixture of primers to amplify many sequences throughout the genome.
What is a common application of PCR in forensic science?
PCR is used to amplify very small DNA samples, such as those obtained from crime scenes.
What is the role of reverse transcriptase in RT-PCR?
Reverse transcriptase synthesizes complementary DNA (cDNA) from RNA, allowing for the amplification of RNA sequences.