NCLEX lectures major takeaways
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Hepatitis A
Transmission via food, all other hepatitis are blood and body fluid tranfer
ABG’s
ROME- respiratory opposite metabolic same.
If Ph low/high, everything low/high except potassium
Respiratory= underventilating- acidosis. overventilating- alkalosis
Default answer- metabolic acidosis
compensated- normal ph
uncompensated- normal pco2 or hco3
partial compensated- ph, paco2, hco3 all abnormal
Uppers- 5 & s/s, priority
caffeine
cocaine
PCP/LSD
Methamphetamines
Adderall
S/s- overdose makes everything go up, withdrawal (24 hr) makes everything go down
Priority- suctioning
Aminoglycosides- IM or IV
A Mean old Mysin- old mean infections- all have THRO throw out.
mysin- mice- monitor hearing, balnce tinnitus
ear- kidney shaped- nephrotoxicity- creatinine
Oral mycin- sterilizes the bowel
Trough and Peak (SubL, IV, IM)
Trough- always drawn 30 min before next dose
peak: always go with highest answer within range
subL- 5-10 min after dissolved
IV-15-30 min after finished bag
IM- 30-60 min
Calcium channel blockers/ Beta blockers: suffix, use, SE
end in “dipine” and “lol”
use: Antihypertensive, antianginal, antiatrialarrhythmia
SE: headache and hypotension (assess BP SBP >100)
Do not do any suctioning or clamping within an airway or chest tube for more then how many seconds
15-30
Congneital heart defects are Trouble
Trouble- all start with T
shunts blood R to L
B= blue cyanotic
Tet of fallot- remember PROVe
Transmission based precautions
Contact:
Use: anything enteric (GI,fecal, oral)
PPE: Private room, gown, gloves, disposable supply/ dedicated equipment
Droplet:
large particles
private room, mask, goggle, face shield, gloves, disposable supply/dedicated equipment
Airborne precautions: “Air MTV”
MMR, TB, Varicella
PPE: private room, goggle or face shield, respirator mask, gloves, door closed, negative airflow, disposable supply/dedicated equipment.
Order to take off- GGGM- alphabetical
Crutches, Canes
Crutches
6in away from foot, 2-3 finger from axillary fold, elbow 30 degrees
2 point gait- move crutch and opposite foot
3 point- two crutches and bad leg- 1 leg affected
4 point- everything separately
swing through- non-weight baring/ amputees
Up with the good down with the bad
Canes
hold cane on strong/ unaffected side, advance cane with opposite side for wide base of support
Psychiatric questions
psychotic?
no= therapeutic communication
yes, acknowledge feelings/reassure= functional (present reality, limits, enforce) demented/brain damage (redirect) or delirious/episodic/sudden (reassurance)
Give alone time to agitated patients
Know what phase you are in: pre-interaction, orientation, working, or termination.
Keep the patient talking and accept/ understand the patients feelings (scared, angry, sad, out of control) not what they said (don’t tell them how they should or shouldn’t feel)
No advice, guarantees, gifts, referring, yes/ no questions, slang, personal stories/feelings
If all else fails pick a question that examines your own feelings or establishs trust
Diabetes: types, insulin, hypoglycemia
S/S: PPP
DM1- lack of insulin
treat: Diet, insulin, exercise
DKA prone- Dehydration, ketones, kussmauls, high K, acidosis, acetone breath, anorexia. treat- insulin iv/ fluids
DM 2- insulin resistance- A1C >8
Treat:diet, oral hypoglycemic, activity
HHS/ HHNK prone: dehydration. insulin iv/fluids
Diabetes insipidus- not DM, brain injury low ADH> dehydration. Opposite= SIADH
Insulin: Onset, peak, duration
R= Regular- 1,2,4
N= Intermediate- 6,8,10,12
Lispro- 15,30,3
Glargine- long-acting insulin, 12 to 24hrs
Excercise=insulin
Regular insulin drawn into needle before intermediate
Hypoglycemia= drunk patient in shock
give carb, starch, protein, sugar
Drug toxicities toxic and normal value ranges
Values almost always toxic: >2 or >20
Normal values usually fall: .6-1.2 (lithium), 1-2 (dig) or 10-20 (theophylline, phenitoin)
Electrolytes
Kalemias do the same as the prefix (hypo or hyper), except for HR and urine output which go opposite
Calcemias do the opposite as the prefix (sedative)
Magnesemias do the opposite as the prefix (sedative)
hyponatremia= volume overload, hypernatremia= dehydration
Thyroids
Hyperthyroidism= hypermetabolism- weightloss, HR BP up, heat interolence
Hypothyroidism= hypometabolism- obesity, HR BP down, flat, cold intolerance.
Adrenal cortex disease
addisons disease= adrenal insufficiency= hyperpigmented= not adapt to stress (go into hypoglycemic shock). Treatment= ADD- a- SONE/ steroid.
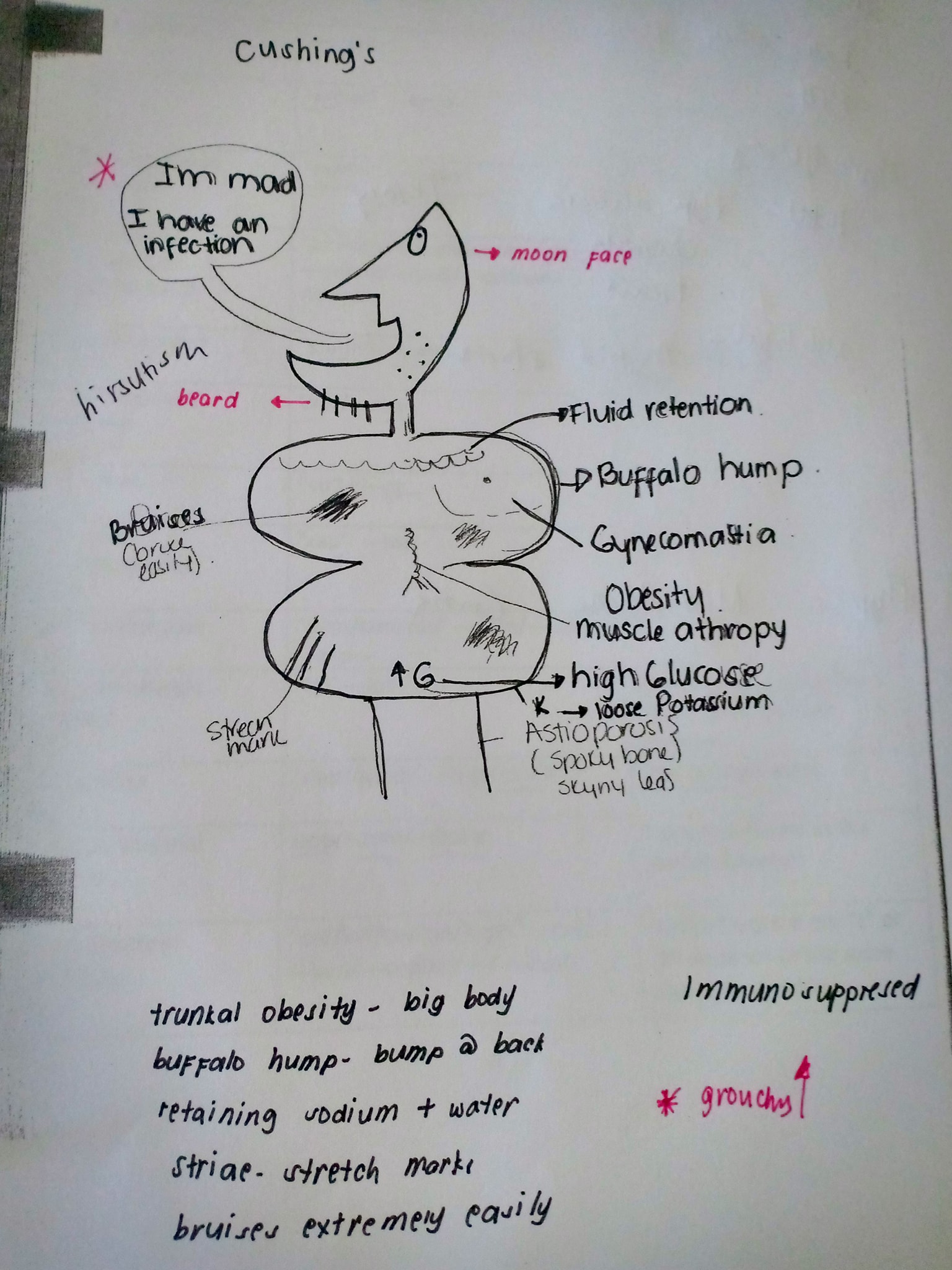
Cushings= adrenal oversecretion= cushy touchie= drawing of cushy man
Ericksons stages of development
Trust vs mistrust (birth- 1yr)- (piaget sensorimotor/ think present tense)
no small toys
rolling, smile, teeth, sitting
Reflexes (in order)= rooting/ sucking, pupillary, palmar, plantar, tonic neck, moro, supporting, stepping, babinski
Autonomy vs shame and doubt (1-3yr) (piaget sensorimotor/ present tense)
no small toys, can begin purposeful play
walking, running, playing
Gross motor skills- running, jumping, imitation play, parallel play
Initiative vs guilt (3-6yr) (piagets preoperational/ future tense)
fine motor- finger dexterity, drawing, dancing, cooperative play, highly imaginative, fantasy oriented
Industry vs inferiority (6-12yr) (piagets concrete operational/ cause and effect thinking)
concrete (3 C’s)= Creative, collective, compettive
identity vs Confusion (12-18yr) (piagets formal operational/ like an adult)
Peer group association
Intimacy vs isolation (18-40yr)
Generativity vs stagnation (40-65yr)
Integrity vs dispair (65<)
Hint: go with the answer that is normal, easier, and older child because growth and development is not standardized allow the child more time.
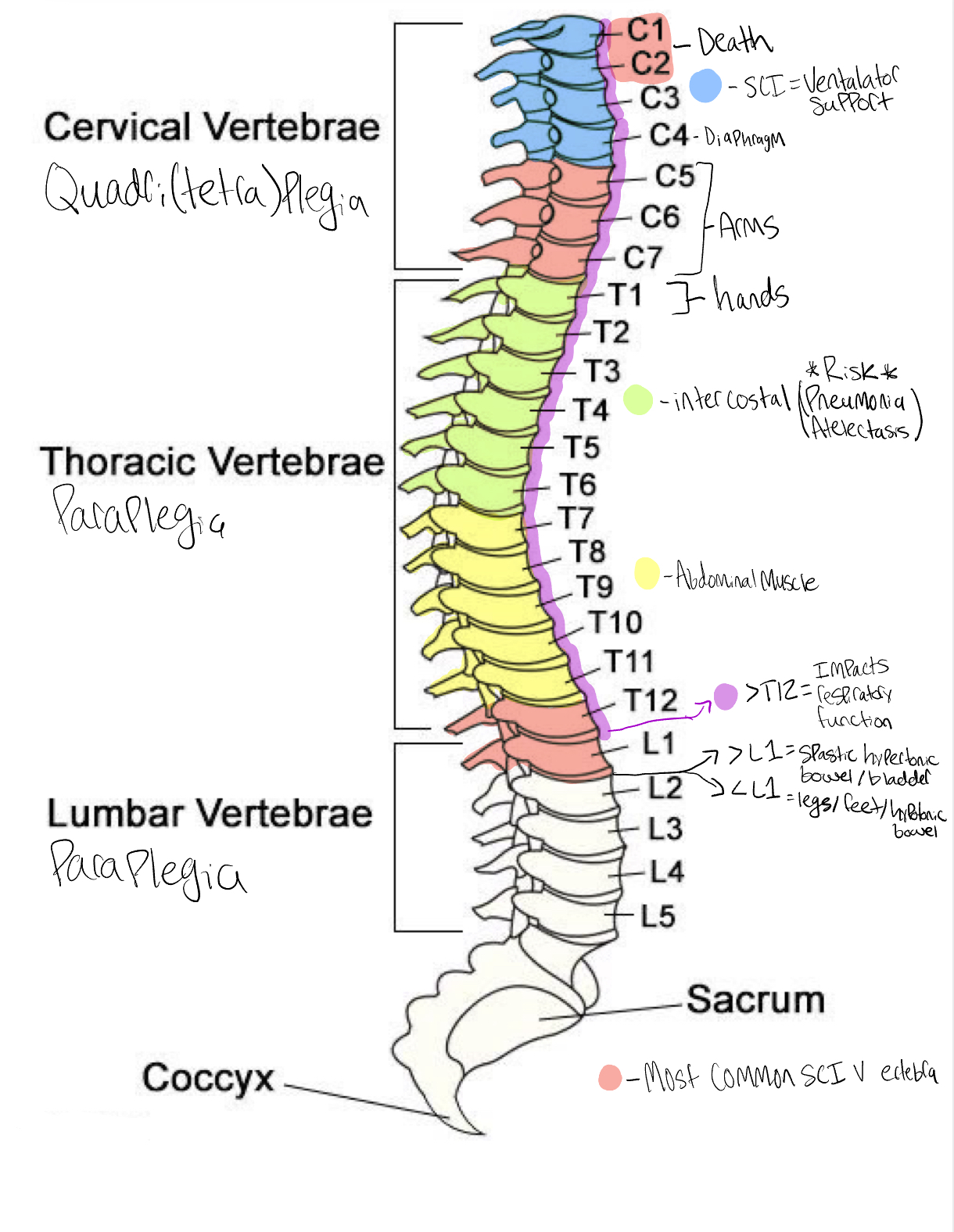
Vertebra
lowest vertibra at which sensory or motor function are intact, above injured vertibra. Below the neurologic level there may be partial or complete loss of function or sensation.
S/S: conscious= acute pain to back or neck that may radiate along the injured nerve. Important to remember the absence of pain does not rule out a spinal cord injury. Respiratory dysfunction can be seen at multiple injury sites.
C1 & C2- Death
C4= diaphragm
>C4 = ventilator support
C5-C7= Arms
T1= Hands
T1-T6 = intercostal (pneumonia/ atelectsis risk)
T6-T12 = abdominal muscles
Anything >T12 = some impact on respiratory function
>L1= Spastic hypertonic bladder/bowel
<L1= lower legs/feet/ bowel bladder hypotonic
Med Calc values to remember
1kg=1000g
1g=1000mg
1mg=1000mcg
60mg=1grain
1kg=2.2lbs
1L=1000ml
30ml= 1oz
1lb=16oz
1cc=1ml
1tsp=5ml
1tbsp=15ml
1cup=8oz
BSA(m2)= √lbs x inches/ 3131
BSA (m2)= √kg X cm/ 3600
Pump rate=ml/hr
Due date= First day of last menstural period, add 7 days subtract 3 months
Ideal pregnancy weight gain= week gestation -9
ECG rate calculation= number of QRS x 10
Labs to remember
Creatinine/ BUN= 1 to 20 = Kidney function= Level A
Bicarb= 22-26= alk= level A
Hematocrit= 36-54= dehydration= level B
BNP= <100= CHF indicator= Level B
RBC= 4-6 million= level B
CVP: 2-8
Calcium: 8-10= level B
INR= 2-3 = Bleeding/warfarin= Level C
Hemoglobin= 12-18= bleeding/anemia= Level C (think puberty)
o2 sat= 93-100= level C if <90
Sodium= 135-145= Fluid indicator= level C if LOC change
WBC= 4,000-11,000= infection= level C (kids 4-11 always getting sick)
ANC= >500 = level C
CD4= >200= HIV AIDs indicator= Level C
pH= 7.35-7.45 = Acid or Alk= Level D
Co2= 45-35= Level D if 60
o2/ pao2= 78-100= oxygenation= level D if 60
Potassium= 3.5-5.3 = assess heart= Level D (number of bananas you buy from the store)
Platelet= 150,000-450,000= level D
Psych drugs
all cause low BP and weight changes
phenothiozines: Typical antipsychotics “zine”= Zany, major tranqulizers
S/S
A- anticholinergic (dry mouth)
B- blurred vision
C- constipation
D- drowsy
E- EPS (parkinson)
F-foto sensitivity
G- aGranulocytosis (low WBC)
Haloperidol: tranquilizers, first gen antipsychotic. only one can be given to pregnant women
A- anticholinergic
B- blurred vision
C- constipation
D- drowsiness
E- EPS
Foto sensitivity
aGranulocytosis
Fluoxetine: SSRI
A- anticholinergic
B- blurred vision
C- constipation
D- drowsiness
E- euphoria
I- insomnia
Tricyclic antidepressants- elavil, trofranil, aventyol, desyrel (they rhyme)
elavil mood
S/S:
A: antichholiinergic
B: blurred vision
C: constipation
D: drowsiness
E: euphoria
Benzodiazepines: minor tranquilizers “ZEP”
S/S
A- anticholinergic
B- blurred vision
C- constipation
D- drowsiness
Monamine Oxidase Inhibibitors: antidepresant- start with MAR,PAR, NAR. No foods with tyramine= hypertensive crisis
S/S
A- Anticholinergic
B- Blurred vision
C- constipation
D- drowsiness
Clozapine- atypical antipsychotic
Agranulocytosis= monitor WBC
Sertraline- SSRI antidepressant, no warfarin or st johns
I- insomnia
S- sweating
A- apprehensive
D- dizzyness
Headache
Lithium: Bipolar
3 P’s: peeing (polyuria), pooping (diarrhea), paresthesia (electrolyte imbalance)
Labor and delivery
Normal fetal heart rate= 120-160
Late & variable decelerations= very bad
Fundus (height should= day postpartum): boggy= massage. displaced= catheterize it
Lochia- Rubra, serosa, alba. Excessive is peripad compeletely saturated in 15 minutes
baby heads (non-issues)= Cephlaohematoma (C) vs caput succedaneum (CS)- CS crosses sutures caput symmetrical
Hint: Always pick check fetal heart rate when in doubt
needles for injection
IM= 21 guage 1 inch long needle, 90 degree angle
SubQ= 25 guage, 0.5 inche needle, 45 degree angle
Heparin vs warfarin
Heparin= IV subQ. works immediately. cannot be given for more then 3 weeks. Antidote protamine sulfate. Labs: PTT. can be used during pregnancy
Warfarin= PO. takes a few days to work. given life long. antidote= vitamin K (no leafy greens). labs: PT/INR
Muscle relaxants
Baclofen and cyclobenzaparine
S/E= fatigue and drowsiness, muscle weakness. No operating machinery.
Priority questions mark K: 4 questions
Diagnosis: high/low priority. Acute?
Modifying phrase: high/low priority, expected/ unexpected?
Stable or unstable? <12 hours post op/anesthesia, new s/s/ diagnosis, 24hr since admit or hemorrhage, fever >105, hypoglycemia, and pulseless or breathless.
Organ of modifying phrase: Brain, lungs, heart, liver, kidney, pancreas
LPN Jobs
Take care of stable patients and perform routine tasks, administer IM meds.
Can not: IV meds/ transfusions/ lines, no care planning or teaching. Can’t do any first and lasts in patient care.
CANNOT DO ASSESSMENTS/ interpret data
UAP jobs
Can: vitals, creams, I&O’s, Accu-checks,
ADLs, reinforce teaching for stable patients
Can’t: meds, assessments
RN jobs
Do: always do first and last in patient care, IV meds/lines/ transfusions, teaching, discharge, meds, assessments, unstable patients
Don’ts: educate on surgical procedure/ give results of procedure outside of RN duties without prompt by doctor, give/ do orders
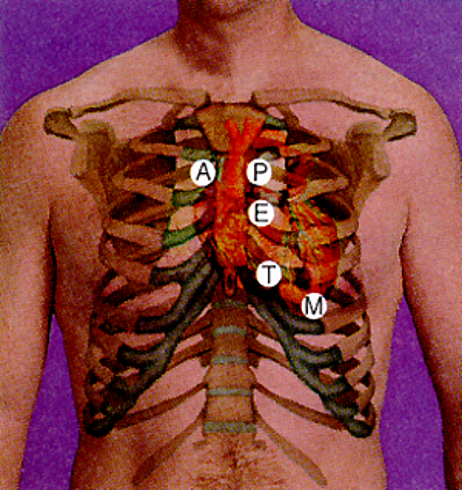
auscultation over heart valves
A- aortic valve- 2nd intercostal right sternal border
P- Pulmonic valve- 2nd intercostal left sternal border
E- Erb point- 3rd intercostal left sternal border
T- Tricuspid valve- 4th intercostal space left sternal border
M- mitral valve- 5th intercostal space midclavicular line
Meds & SE to know
Amlodipine- CCC, antihypertensive, SE: edema
Furosemide- diuretic, Monitor BP and K+
Albuterol- bronchodialator, SE: tachycardia
Lisinopril/ losartan- ACE and ARB, used HF HTN, SE: cough
Pantoprazole- PPI, Gerd, take first thing in the morning, long term increases fracture risk
Levothyroxine- hypothyroidism, give first thing in morning
If allergic to pennicilin don’t give a cephlasporin
Parkinsons drugs- end in “ine and ole” plus levodopa carbidopa
Hint: if you don’t know the SE pick a SE in the same body system as where the med is working, or PO pick GI side effect.
Rights to med admin
My- Medication
Parents- Patient
Drove- Dose
Right- route
To- time
DQ- documentation
Gillian barre & ALS & huntingtons disease
both cause muscle weakness and paralysis
ALS- Attacks upper and lower nervous system
GBS- attacks the peripheral nervous system
swallowing, drooling, difficulty chewing is always a red flag sign
Huntingtons- neuromuscular disease that is genetically inherited and involuntary movement
Vaccines
there are no vaccines given under a month appart except for the hep b booster
if a diagnostic test ends in -gram
It is a dye test
Meaning no metformin
need an empty bowel
client may feel hot flushed and nauseas from the dye
encourage fluids after
Health promotion and maintence must knows
menarche- first menstrual period
Fundal height/ listening for baby: 20 weeks= at the umbilicus+ 1cm per week. <20 symphysis pubis.
Always go with autosomal recessive (25%)
TORCH (toxoplasmosis other= syphilis varicella/shingles Group b strep, hep A & B, AIDS, Rubella, ytomegalovirus, herpes2)- diseases that transfer to baby C section necessary
Remember LOA and ROA- for baby heart sounds pre-birth
Birthing plan: airway, Apgar, clamp cord, warmth, id band, medication (eye drops and K+).
Orange juice with prenatal vitamins/iron
Early decels: uniform, onset begins before peak of contraction, quick to baseline
Late decels: begins at after/ during peak of the contraction, slow return to baseline
Variable decels- transient all over the place at anytime, slow/ low baseline