Bio E109 Midterm 1
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
6 Types of Connective Tissue
Blood - Least Rigid
Loose Connective Tissue
Cartilage
Dense Connective Tissue
Adipose
Bone - Most Rigid
What is the extracellular matrix consist up of in extracellular tissue?
ground substance and fibers
extracellular tissue are made up of
cells, ground substance, fibers
Blood
A type of connective tissue, composed of white blood cells, red blood cells, cell fragments (platelets), & liquid matrix (plasma)
Adipose Tissue
Connective Tissues that cushions and insulates, stores energy, has very little ground substance; no fibers
- adipocytes are the cells inside
Loose Connective Tissue
Connective Tissues that surrounds blood vessels & internal organs
What do Loose Connective Tissue have?
Collagen fibers: for tensile strength and support
Fibroblasts: secretes and maintains matrix in the connective tissue
Elastic Fibers (ability to recoil)
Ground substance: gelatinous in the cell
Cartilage
A type of connective tissue that’s elastic and absorbs shock
blood doesn’t reach the cartilage that well
What does Cartilage have?
Chondrocytes: produce & maintain matrix
Matrix: firm, but flexible, reinforced with collagen
Dense Connective Tissue
A type of connective tissue that consists of regular and irregular ones
- Made up of tendons, ligaments, muscles and nerve sheaths
What are regular dense connective tissues?
Tendons and ligaments: transmit force and stabilize joints.
Tendons connect muscles and bones
Ligaments connect only bones
What are irregular dense connective tissues?
Muscle and nerve sheaths
What do dense connective tissues have?
Collagen fibers: allows muscle to contract and pull on the tendon and store energy elastically
Fibroblasts: secretes and maintains matrix
Bone
A type of connective tissue that provides structural support, organ protection,
and creates movement
Epithelial Tissue
Tissue that has a protective outer layer and lines internal cavities and orgam which helps with protection, absorption, secretion, and filtration
Exchange Epithelia
in the lungs, lining of blood vessels (circulatory system)
there to provide exchange of materials
Transport Epithelia
found in the digestive system (the intestine & kidney) some exocrine glands
keeps the cell together so that the cells wanting to enter need other cells to pass through
Ciliated Epithelia
found in the nose, trachea, upper airways & female reproductive tract
moves around like a wave in a rhythmic and coordinated fashion, and moves particles around
Protective Epithelia
found in the skin & lining of cavities open to environment
Secretory Epithelia
cells that secrete chemicals such as mucus & hormones
Exocrine Epithelial Cells
the hollow center (lumen) makes an exocrine gland, that makes a duct that has a passageway for secretions to move to the surface
Endocrine Epithelial Cells
A slipped disc in the spine occurs when the cartilage between vertebrae is damaged. Which of the following statement is true about its healing?
Healing will be slow due to the lack of blood vessels, which limits nutrient delivery and repair processes
During digestion, epithelial cells of the small intestine increase the rate of glucose uptake into the blood. Which functional type of epithelium is responsible, and how does its structure support this function?
Transporting epithelium; polarized cells with microvilli and transport proteins move glucose efficiently
A Patient’s trachea is damaged after years of smoking. Which type of epithelium is most affected, and what is the physiological consequence of this damage.
Ciliated epithelium; particles and mucus are no longer effectively cleared from this airway
Which tissues rely on membrane dynamics to function
Epithelia, Nervous, Muscle
What motivates molecules & ions to move across a membrane?
Chemical Diffusion, Colloid Osmotic Pressure, and Electromotive Force
Chemical Diffusion
Speed depends on temperature, mass, & molecular interactions
The bigger the gradient, the higher the rate of expansion
Center doesn’t move & the edges expand towards low concentration over time
Does chemical diffusion work best at fast at small scales or slow at large scales
It works best at fast and small scales
time is proportional to distance²
Fick’s Law
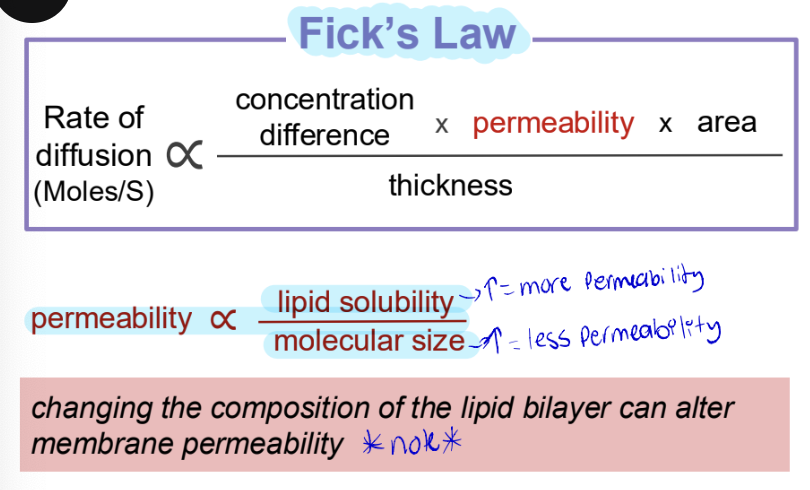
Colloid Osmotic Pressure
Osmotic pressure exerited by plasma proteins that pull water back into the blood vessels
Electromotive Force
If ions attract or repel each other based on the charge
membranes can be permeable to a particular ion or molecule
diffusion AND the electromotive force act on ions
final concentrations are determined by permeability & electrochemical gradients
Which property of tendons most directly contributes to their ability to transmit force from muscle to bone?
Their wavy “crimped” fiber arrangement straightens under tension to provide tensile strength
Which statement best explains the role of tight junctions in transport epithelia?
They prevent movement of solutes through the paracellular space, forcing substances to cross cells instead
A Researcher is comparing oxygen diffusion across the alveolar-capillary membrane in two different samples:
Sample 1 (healthy lung): Alveolar surface area = 2cm², membrane thickness = 1 mm
Sample 2 (diseased lung)Alveolar surface area = 4cm², membrane thickness = 2 mm
Both samples have the same permeability and concentration gradient. Which statement best describes the relative rates of oxygen diffusion?
Diffusion rates are equal
A cell membrane is permeable to both K+ and Na-. Inside the cell, K+ concentration is much higher than outside, while Na- concentration is much higher outside than inside. The interior of the cell is negatively charged relative to its exterior. Which statement best explains how these forces determine the resting membrane potential?
K+ tends to diffuse outside the cell, but the negative charge inside pulls the K+ in, so that movement balances the two forces
Na- tends to diffuse into the cell, but the negative charge inside pulls the Na- inward, so both forces act in the same direction
Both diffusion and electrical forces act in the same direction for Na, but opposite directions for K+
Carrier Proteins
Transmembrane transport proteins that change shape to move molecules across the membrane - like a revolving door because of its specificity, competition, and saturation
Molecular Flux
rate at which the molecules can cross the membrane
Primary Active Transport
Na+ K+ ATPase: Uses ATP to move Na+ & K+ against chemical (concentration) gradients
Channel Proteins
Specific to Potassium (K+) - Use facilitated diffusion to move molecules through a water filled opening - like a regular door
Facilitated Diffusion
K+ pore or “leak” channel: no energy required
Desmosome
Provides structure, and anchoring between cells
Tight Junction
Molecule that keeps the epithelia closed
Apical Surface
wavy part of the cell that increases surface area
What are the physical requirements to move across a membrane?
1. Diffusion
2. Protein-mediated
3. Vesicle
What are the energy requirements to move across a membrane?
Primary Active Transport, Secondary Active Transport, and Facilitated diffusion
Secondary Active Transport
Na+ glucose symporter: uses Na+ gradient to transport glucose
What motivates molecules & ions to move across a membrane?
Chemical Diffusion, Colloid Osmotic Pressure, and Electromotive force
Which of the following statements about epithelial tissue are true?
They regulate exchange of material between the internal and external environments, help protect the internal environment, transport epithelia activity and selectively regulate the exchange of materials, and transport epithelia line the hollow tubes of the digestive system and the kidney
Liver cells can convert glycogen to glucose. If intracellular [Glu] is greater than extracellular [Clu], in whhat direction will these GLUT transporters carry glucose?
Out of the cell, with the concentration gradient
Which of the following correctly distinguishes carrier proteins from channel proteins?
Channel proteins are used only in active transport, while carrier proteins are used only in passive transport.
The Na+ glucose symporter (same direction) uses the energy stored in the Na+ concentration gradient to transport glucose across the cell membrane. What does the term “symporter” indicate about this protein?
It uses the Na+ gradient to move glucose in the same direction across the membrane.