Chapter 8: The Appendicular Skeleton
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
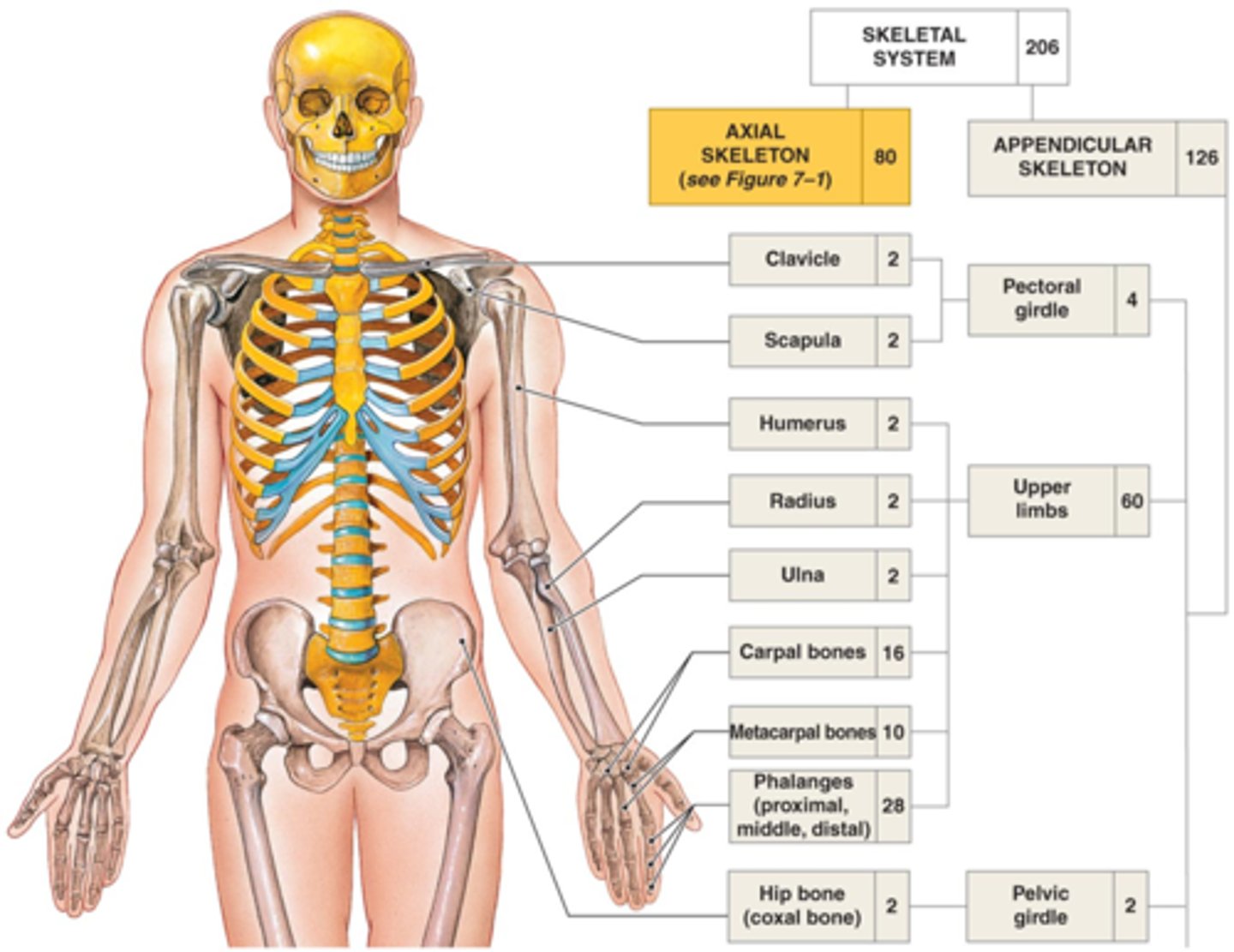
appendicular skeleton
126 bones in total
limb bones, pectoral girdle, and pelvic girdle
sternum (clavicle articulates with manubrium)
the only connection between the pectoral girdle and the axial skeleton is at the _____________
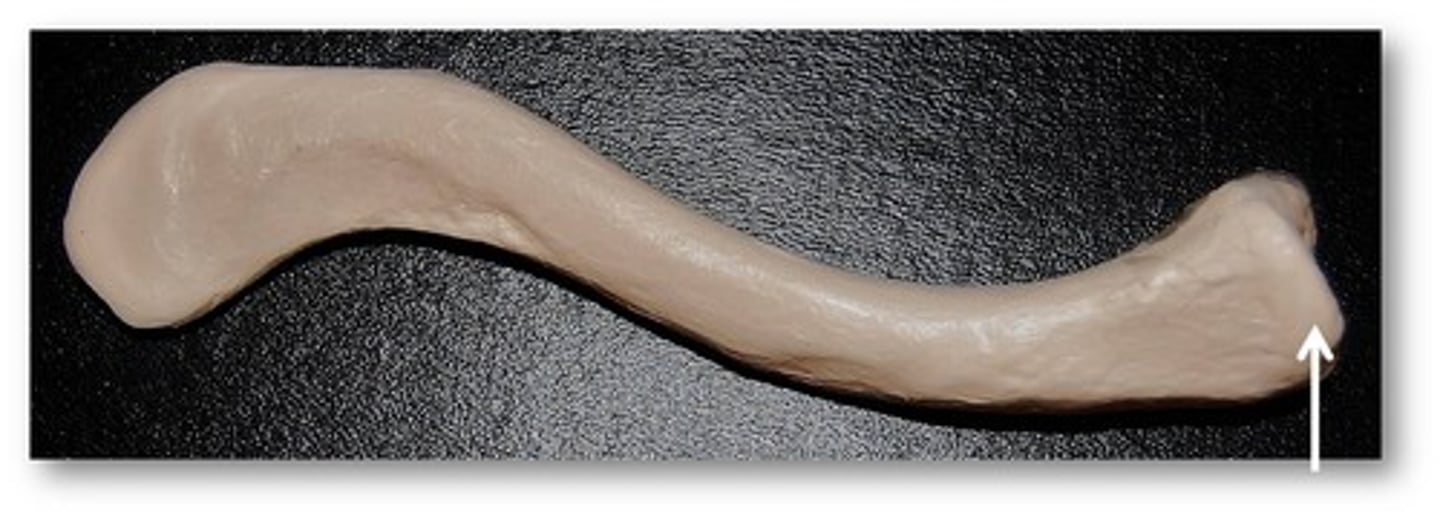
sternal end
Name this specific part of the clavicle. articulates with manubrium.
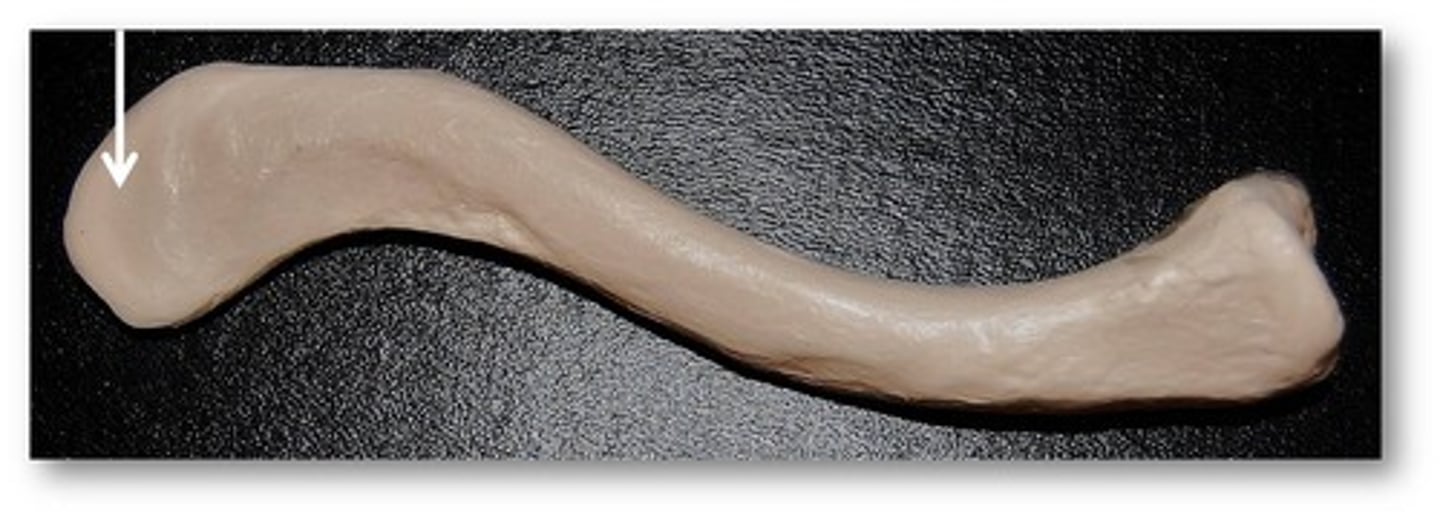
acromial end
Name this specific part of the clavicle. articulates with a process of the scapula.
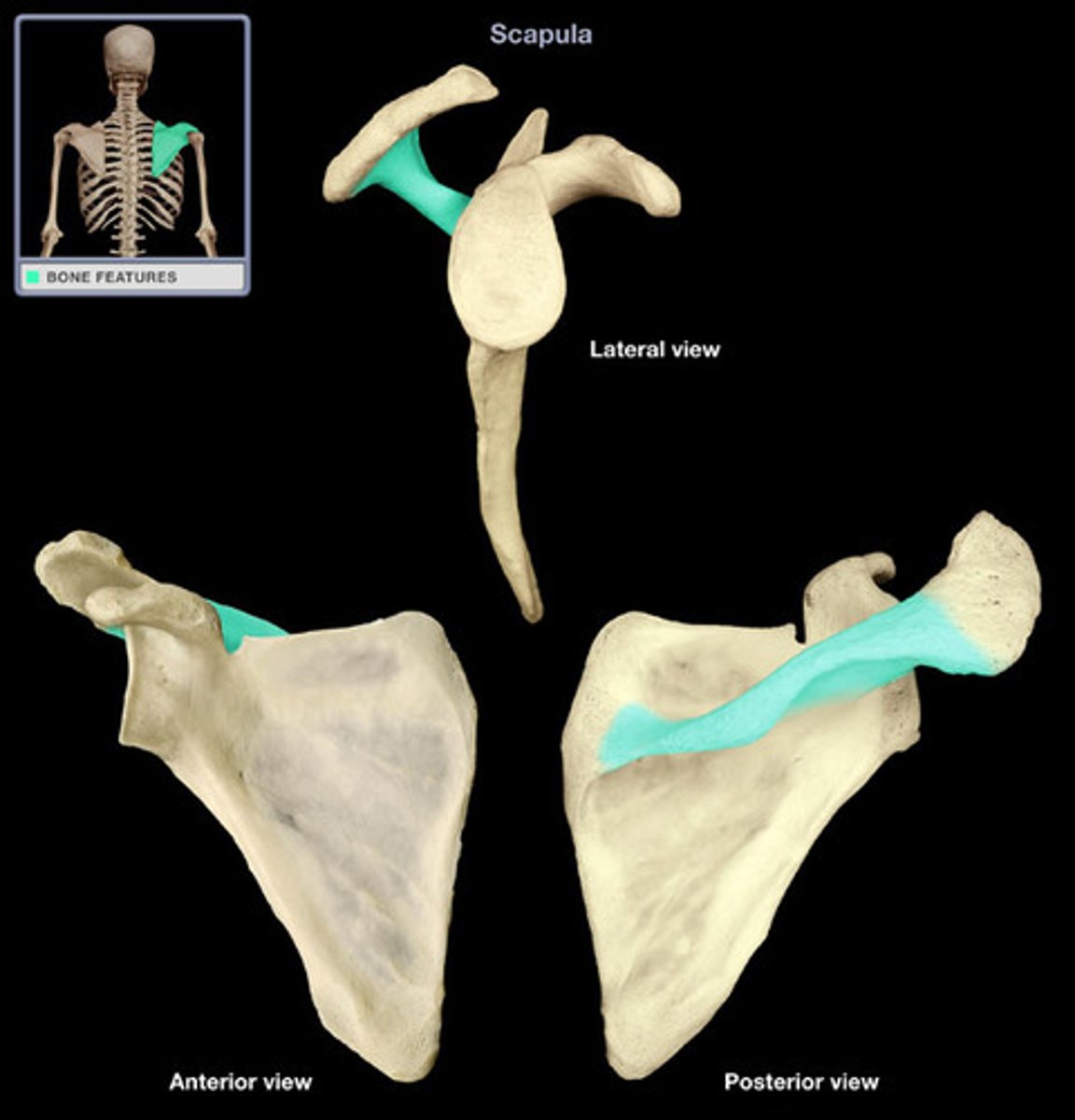
scapular borders
1. superior border
2. medial border (vertebral)
3. lateral border (axillary)
scapular angles
1. superior angle
2. inferior angle
3. lateral angle (head)
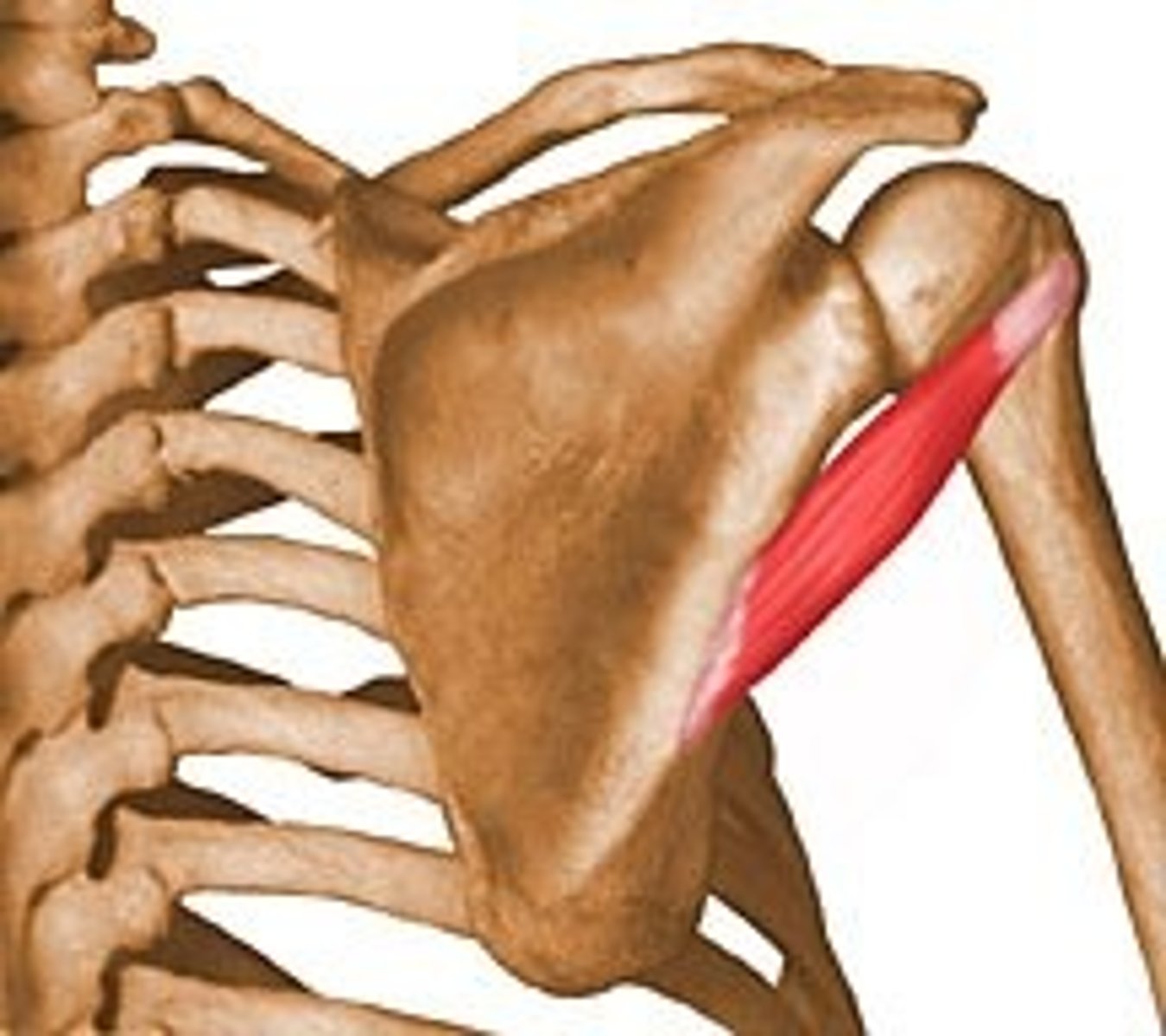
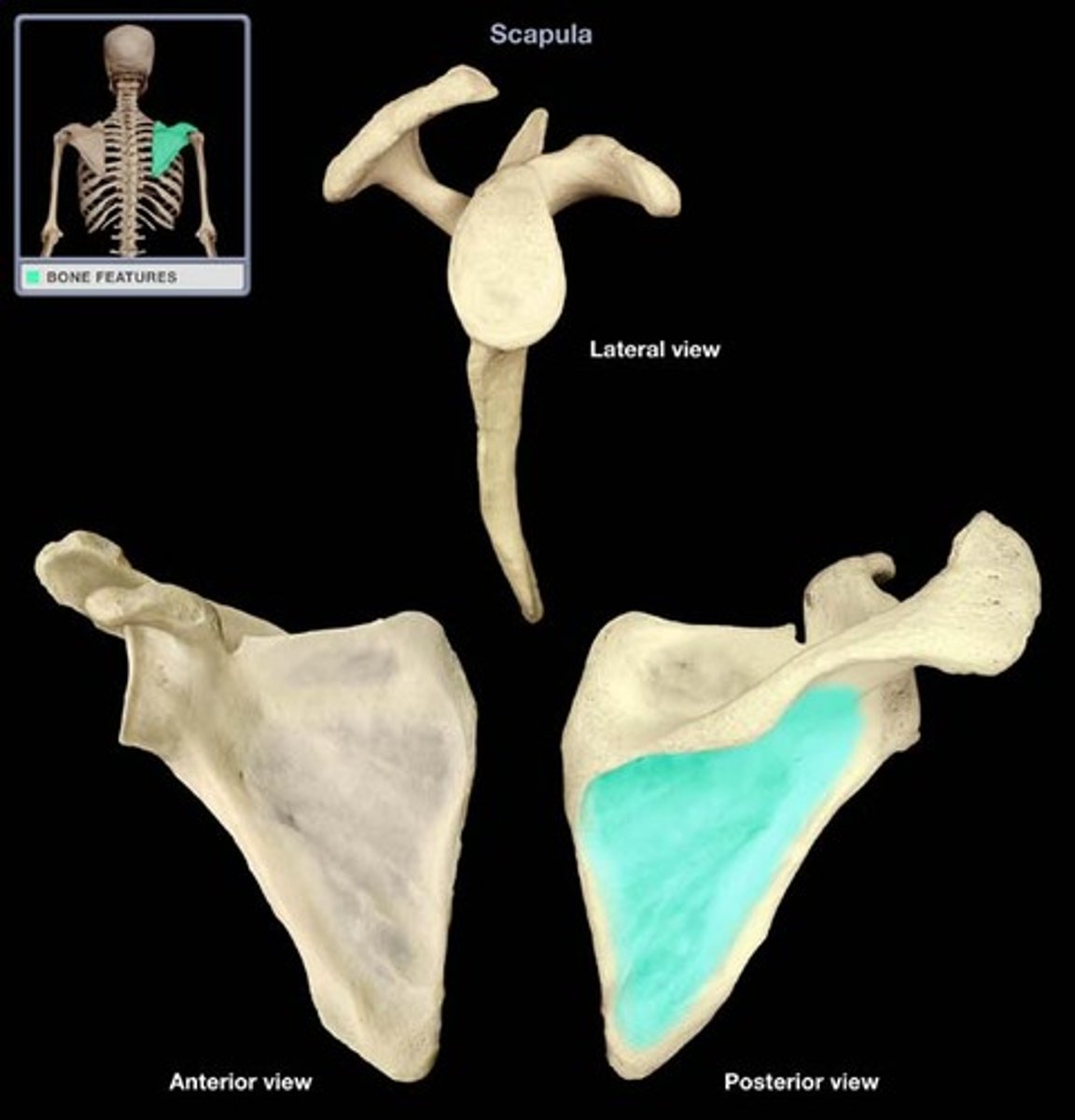
glenoid cavity
Name this specific part of the scapula.
Where the scapula articulates with the humerus.
The shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint).
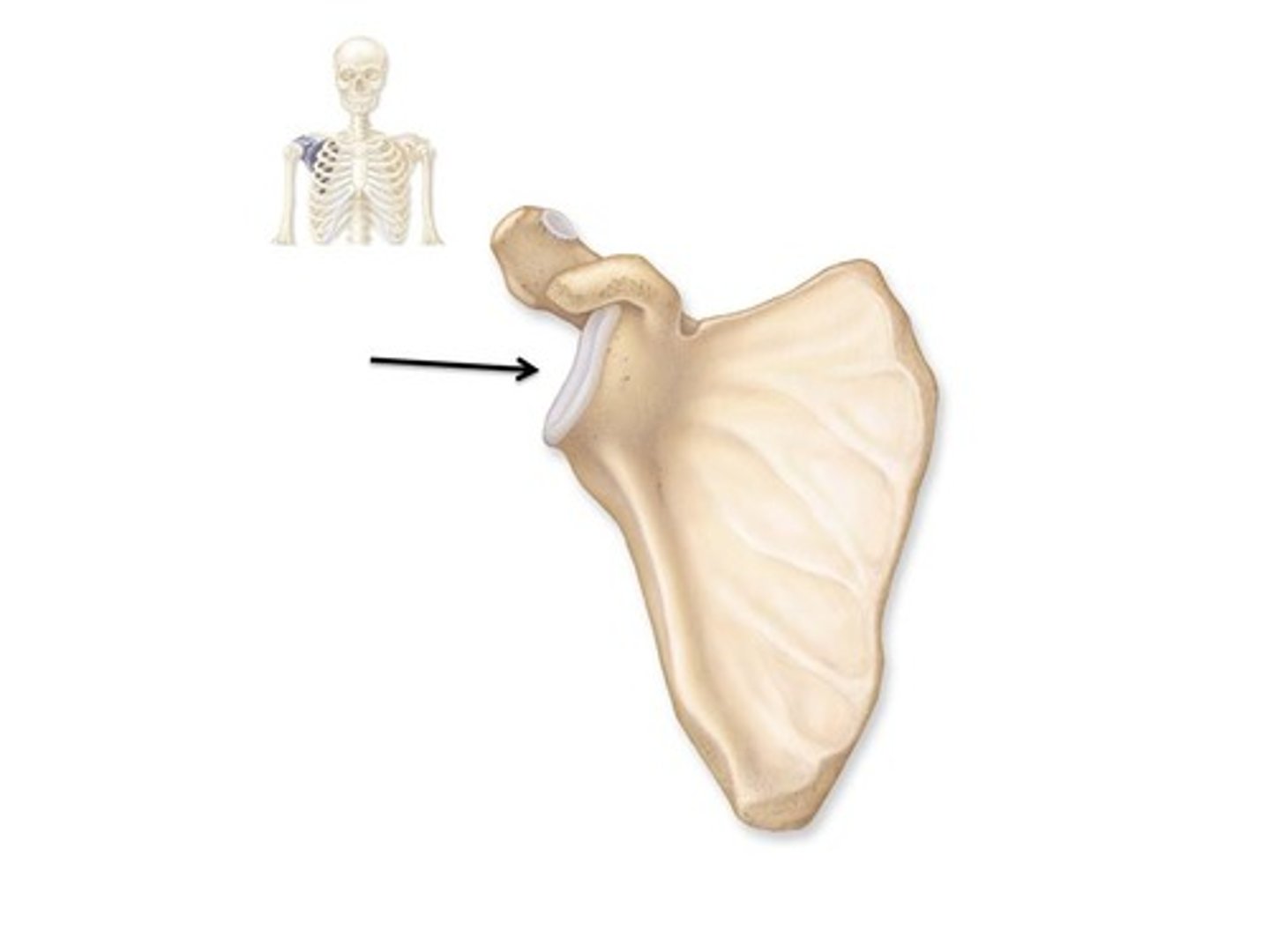
subscapular fossa
Name this specific part of the scapula.
Depression on anterior surface of scapula.
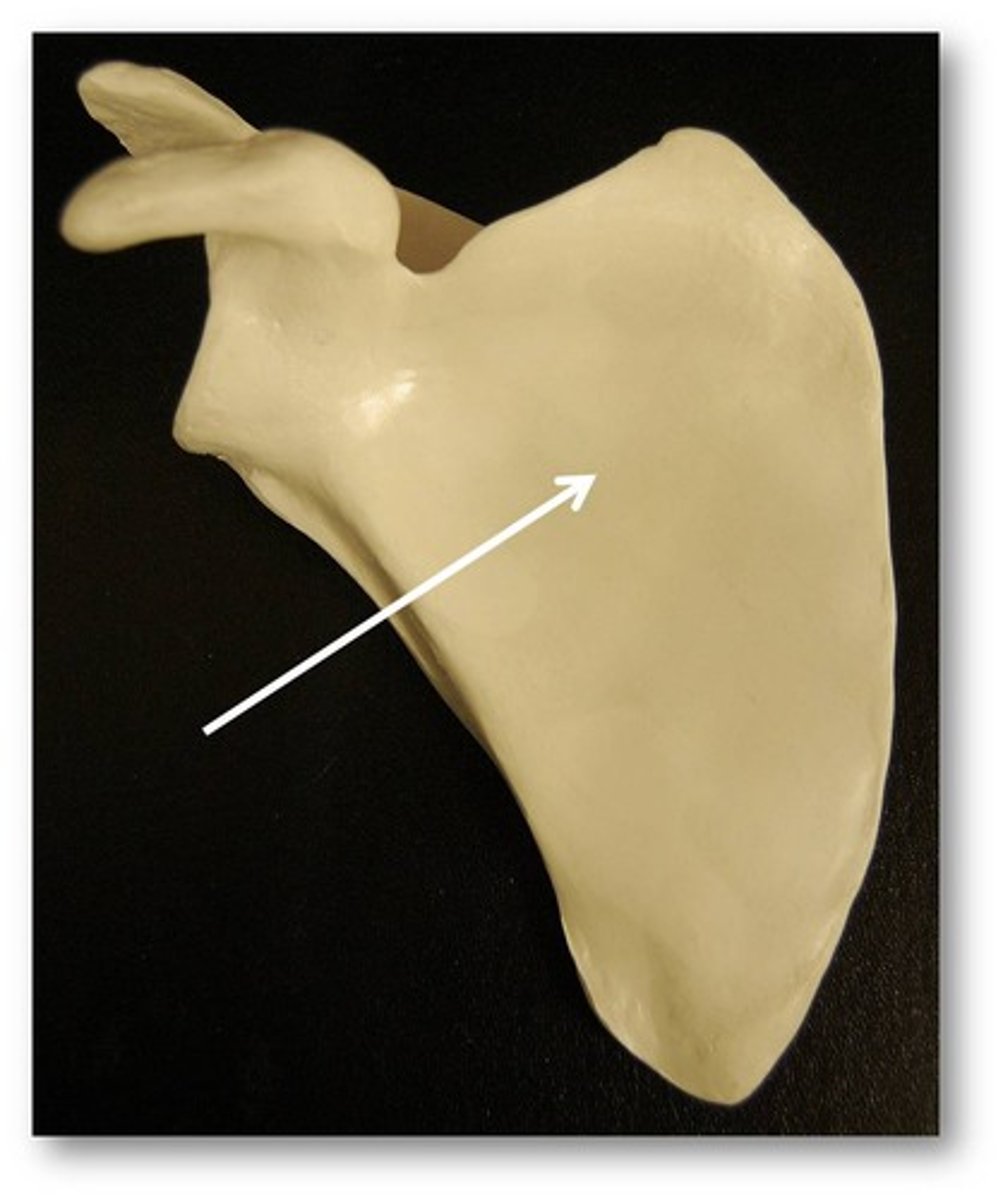
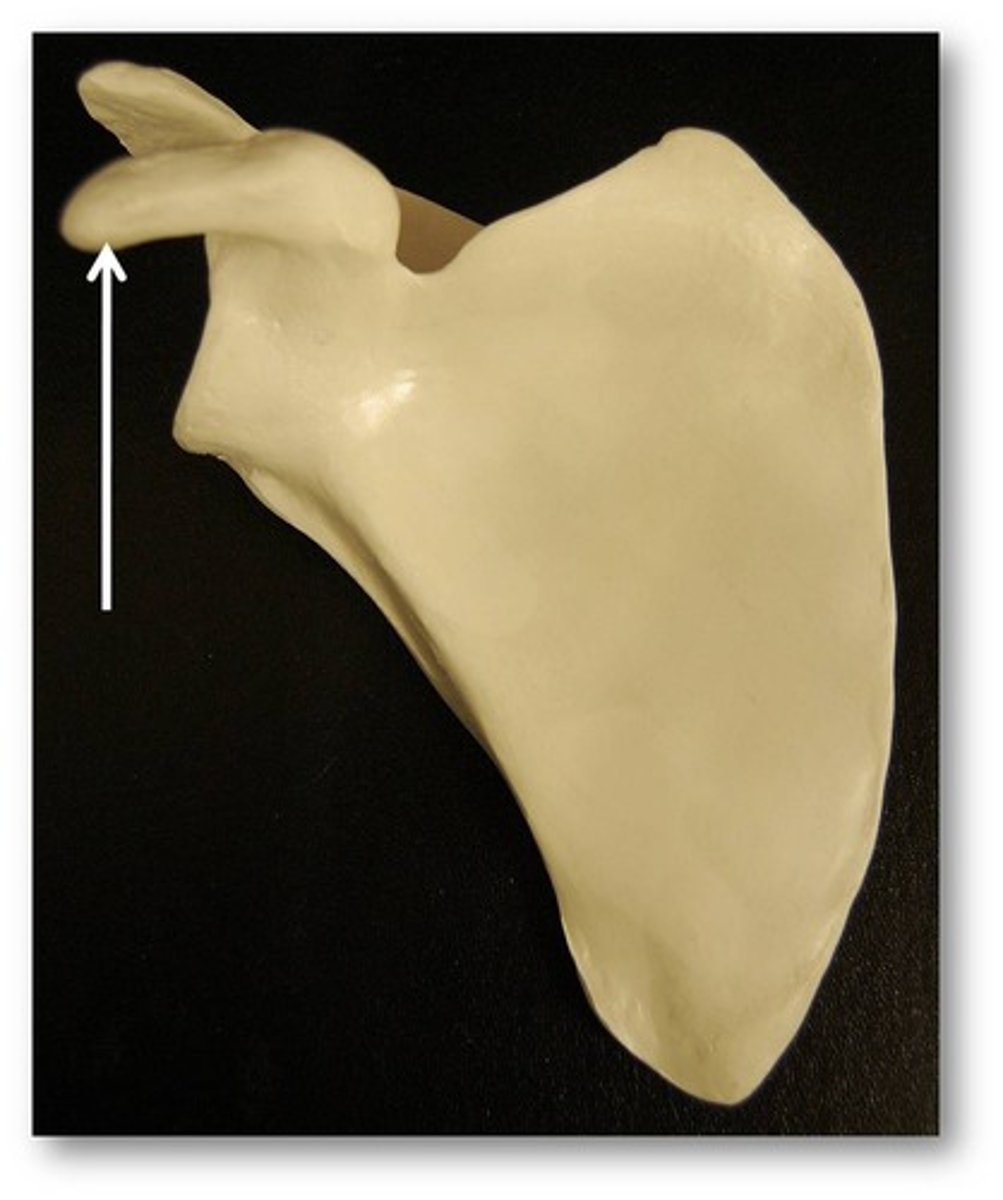
coracoid process
Name this specific part of the scapula.
Scapular process superior to the head of the humerus.
Anterior.
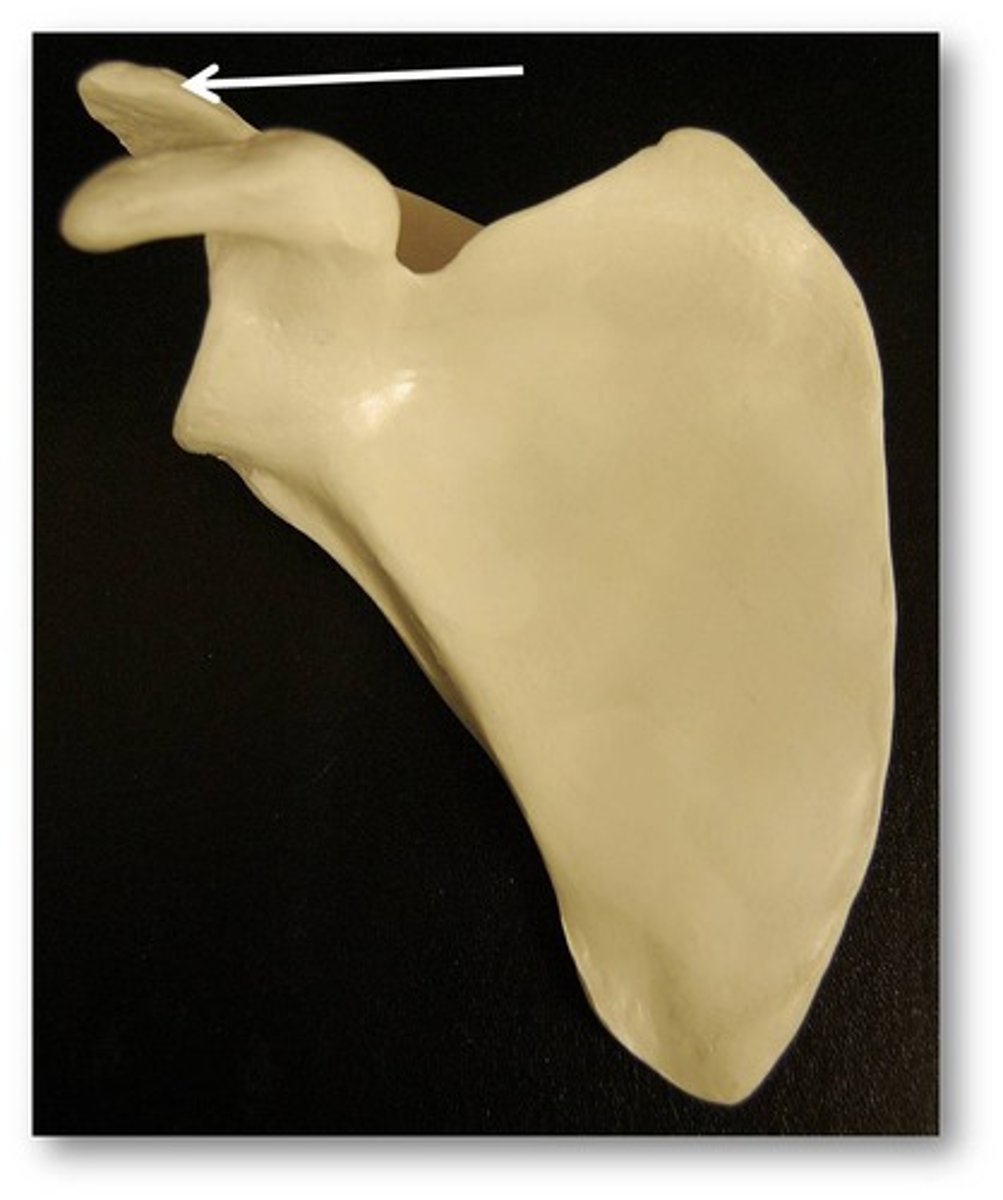
acromion
Name this specific part of the scapula.
Scapular process superior to the head of the humerus.
Posterior.
Articulates with clavicle at ACROMIOCLAVICULAR JOINT.
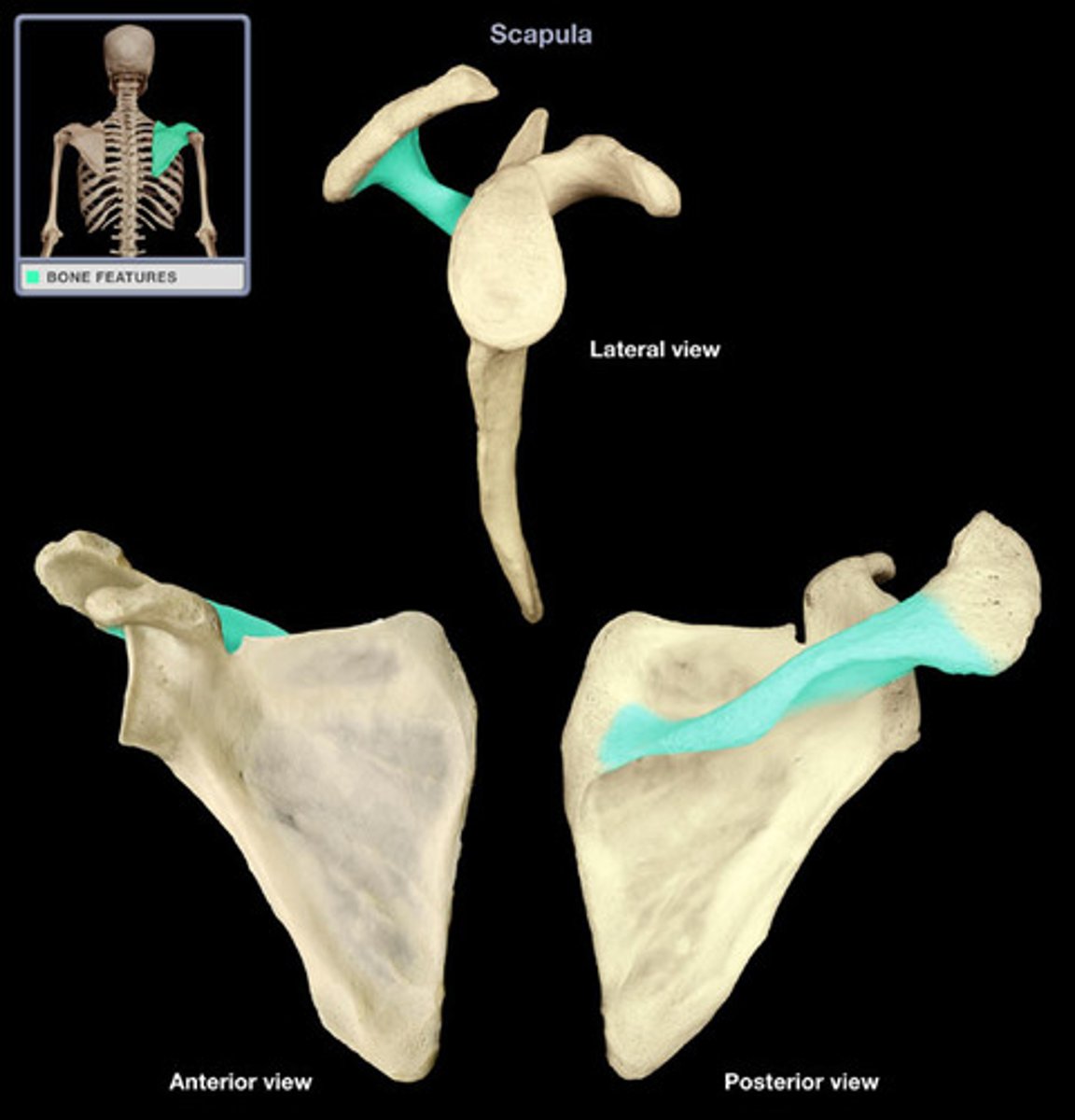
scapular spine
What structure is highlighted?
ridge that crosses the posterior surface of the scapular body which divides the posterior surface into two regions
supraspinous fossa
Name this specific area of the scapula.
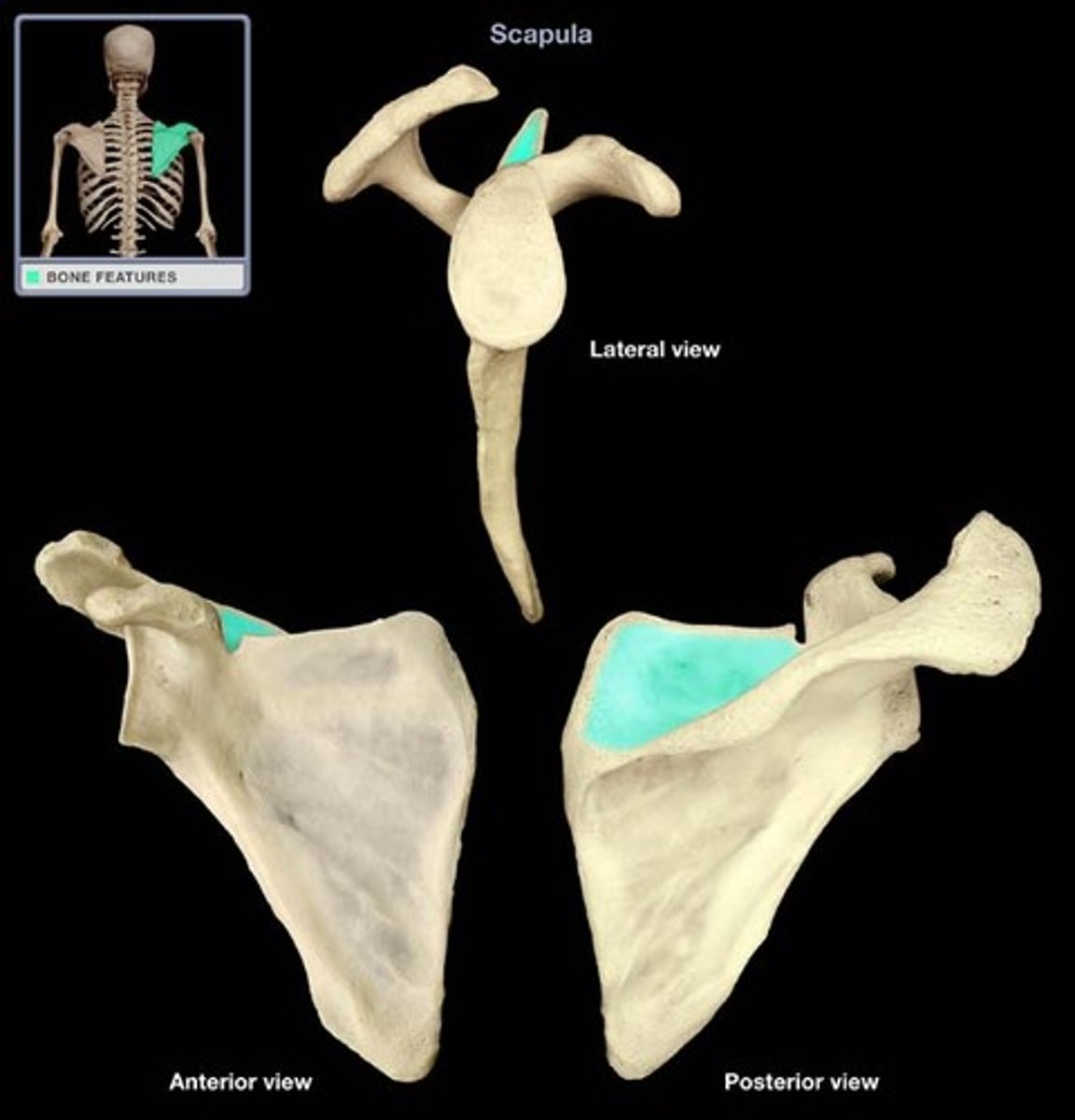
infraspinous fossa
Name this specific area of the scapula.
arm (brachium)
in anatomy, the upper limb from shoulder to elbow only
forearm (antebrachium)
in anatomy, the upper limb from elbow to wrist only
greater tubercle
Name this specific part of the humerus.
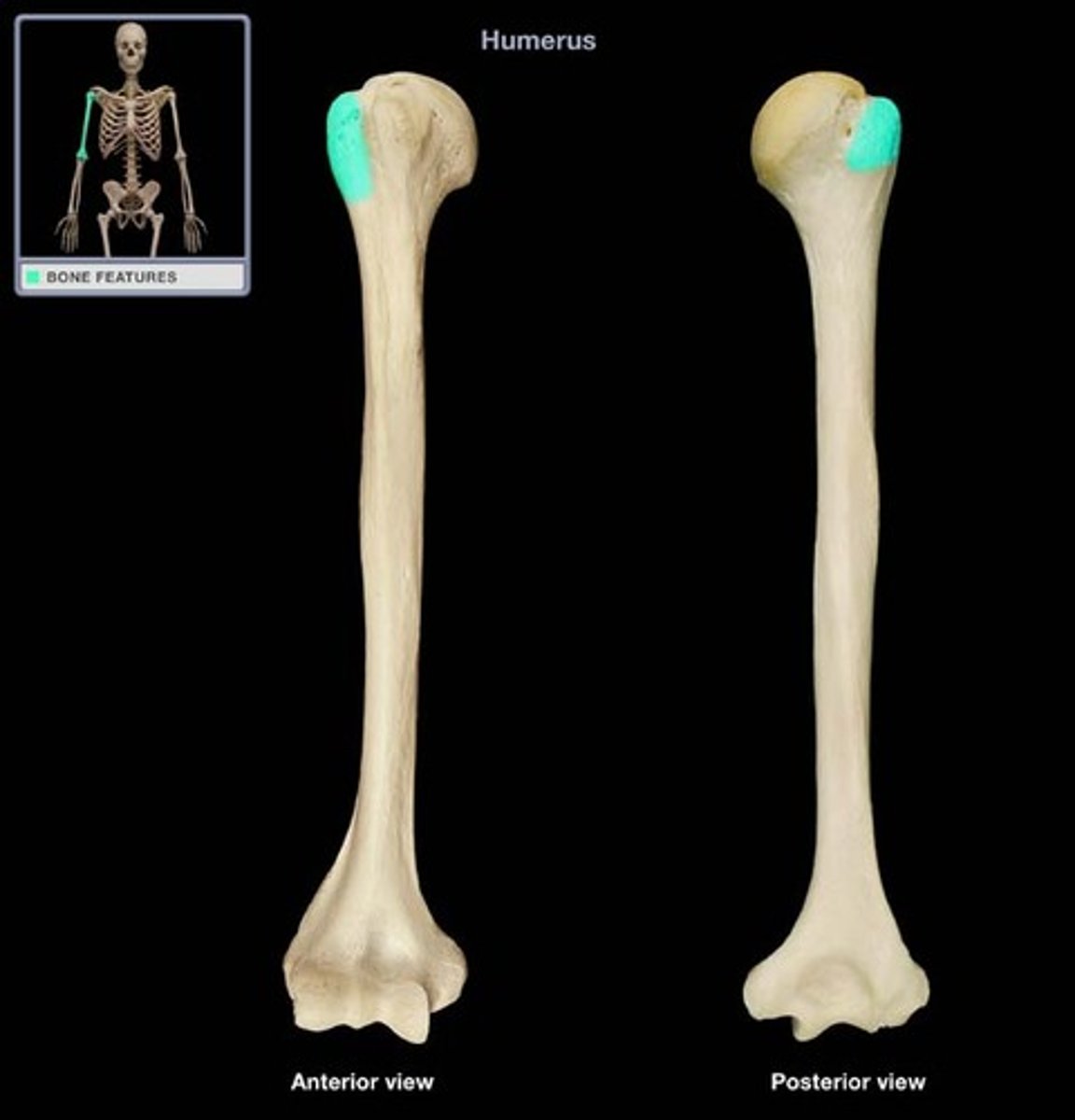
lesser tubercle
Name this specific part of the humerus.
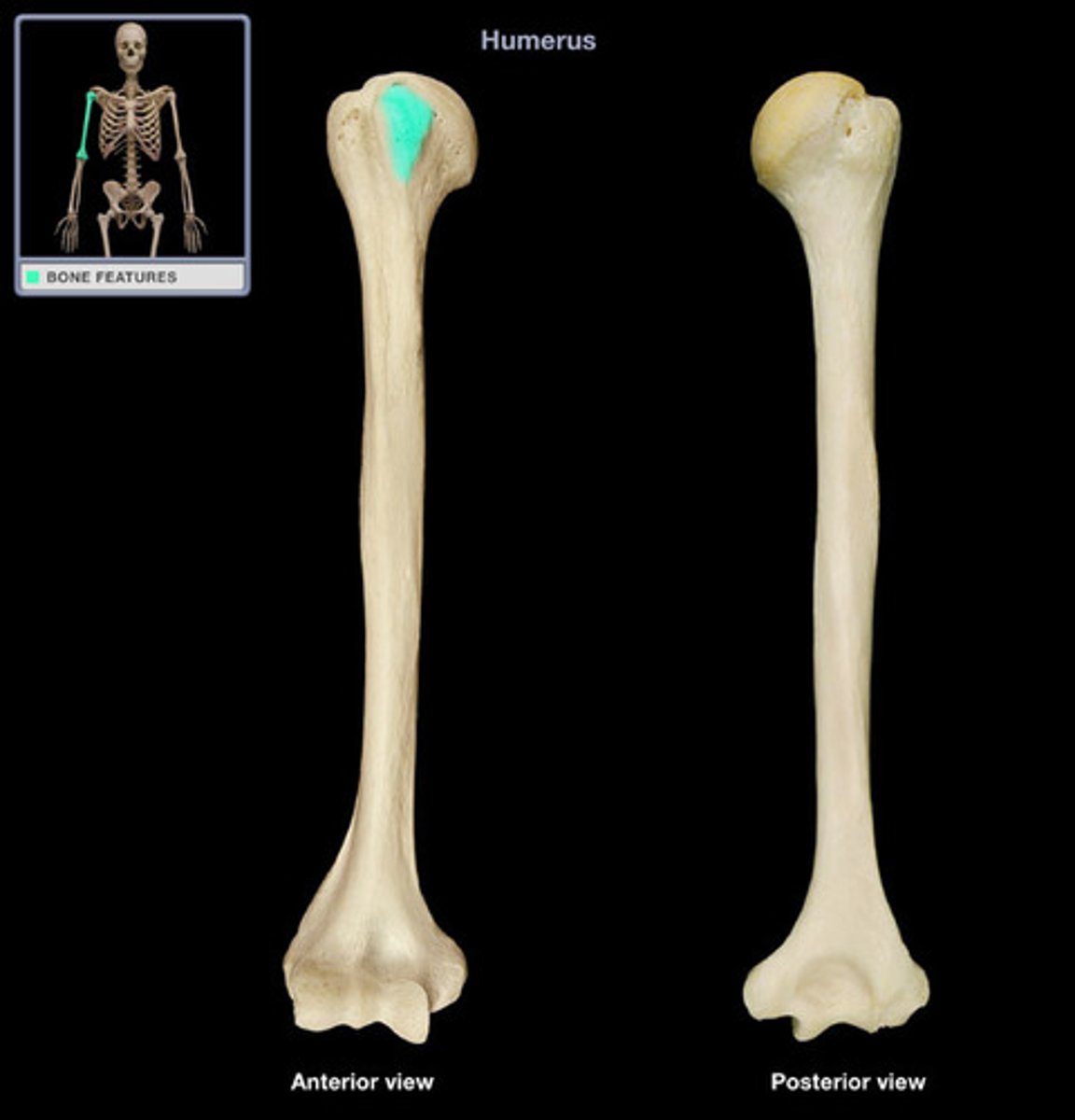
intertubercular groove (intertubercular sulcus)
separates the lesser tubercle from the greater one
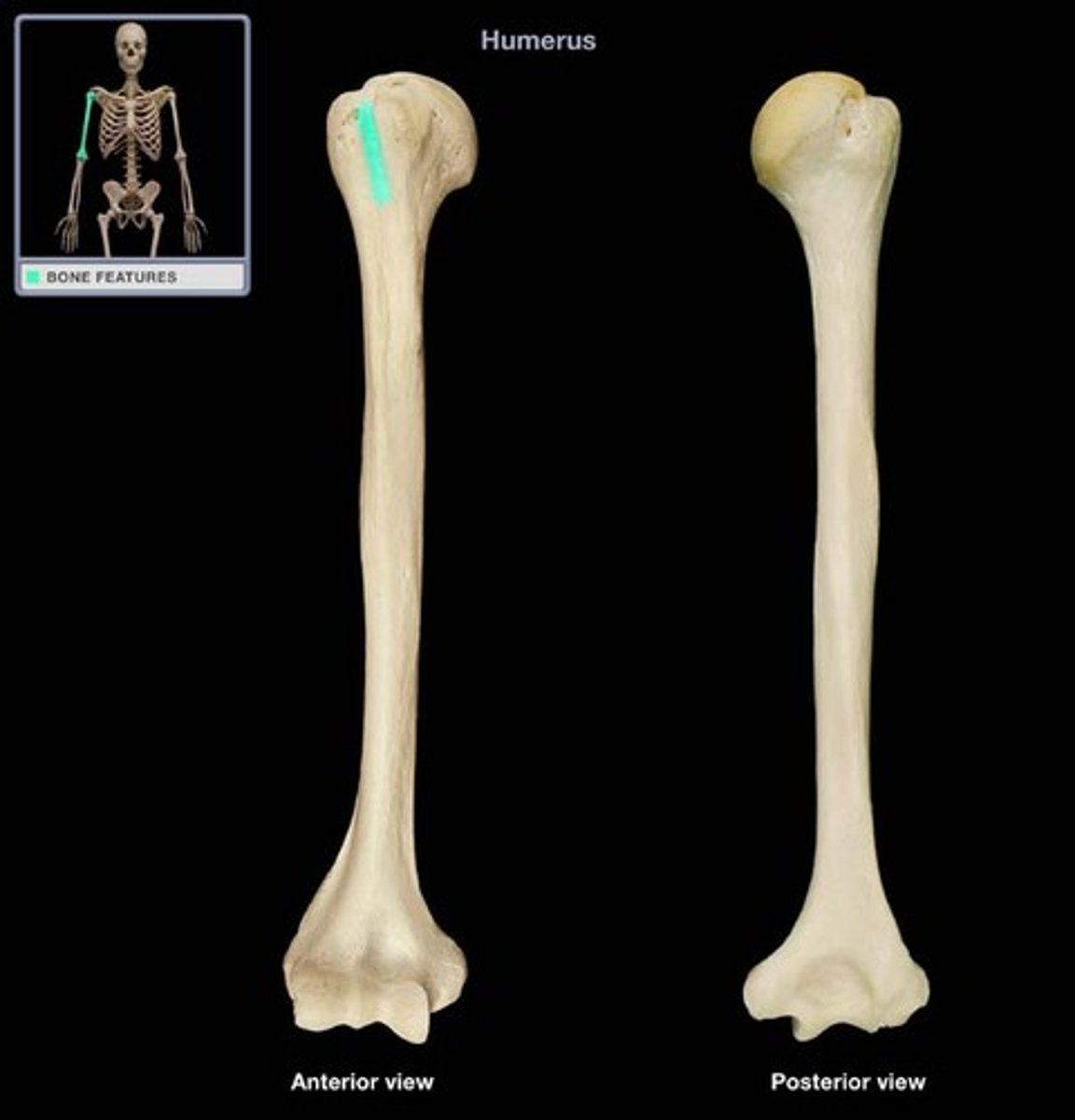
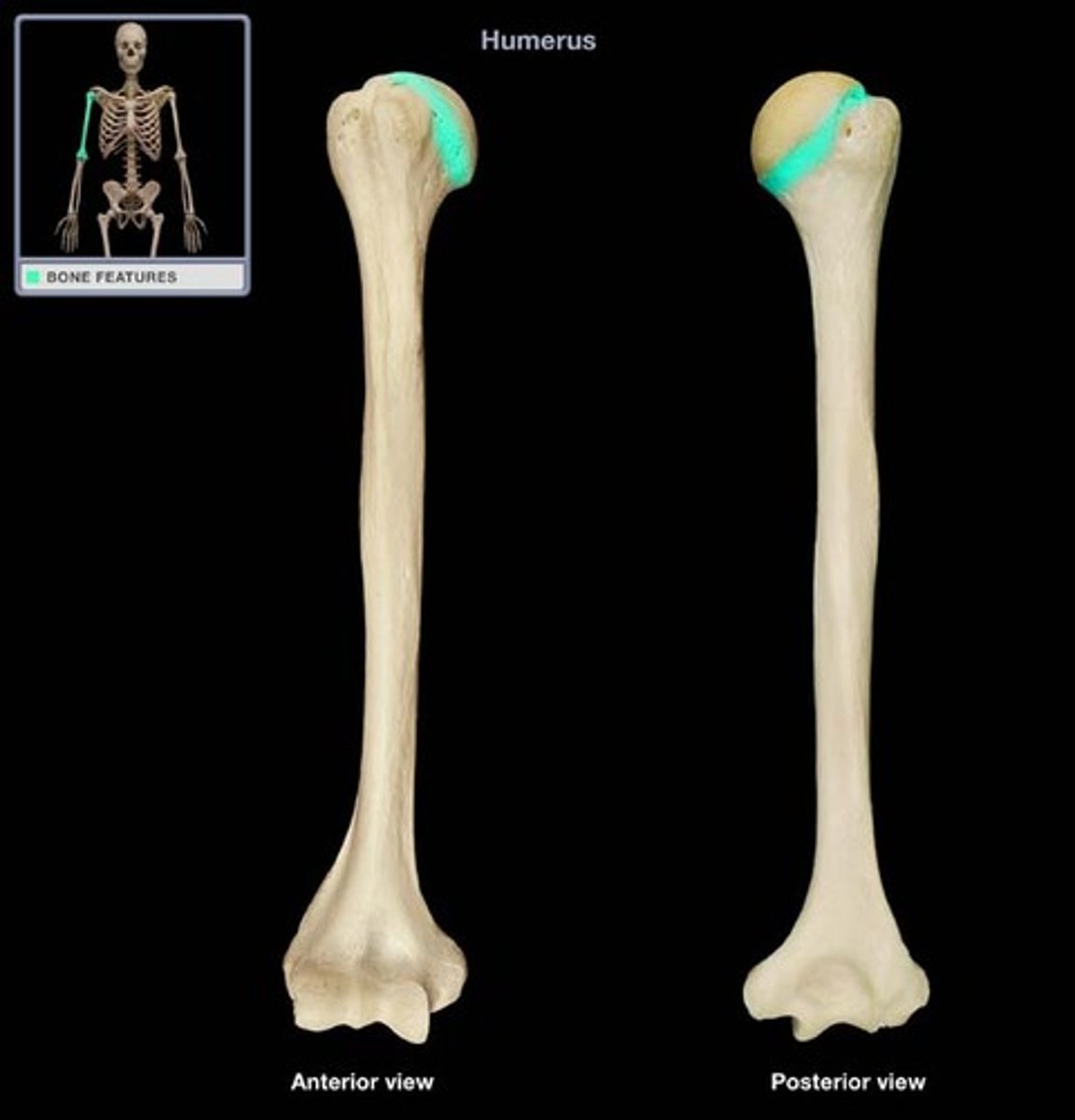
anatomical neck (humerus)
What structure is highlighted?
Lies between the two tubercles and the articular surface of the head
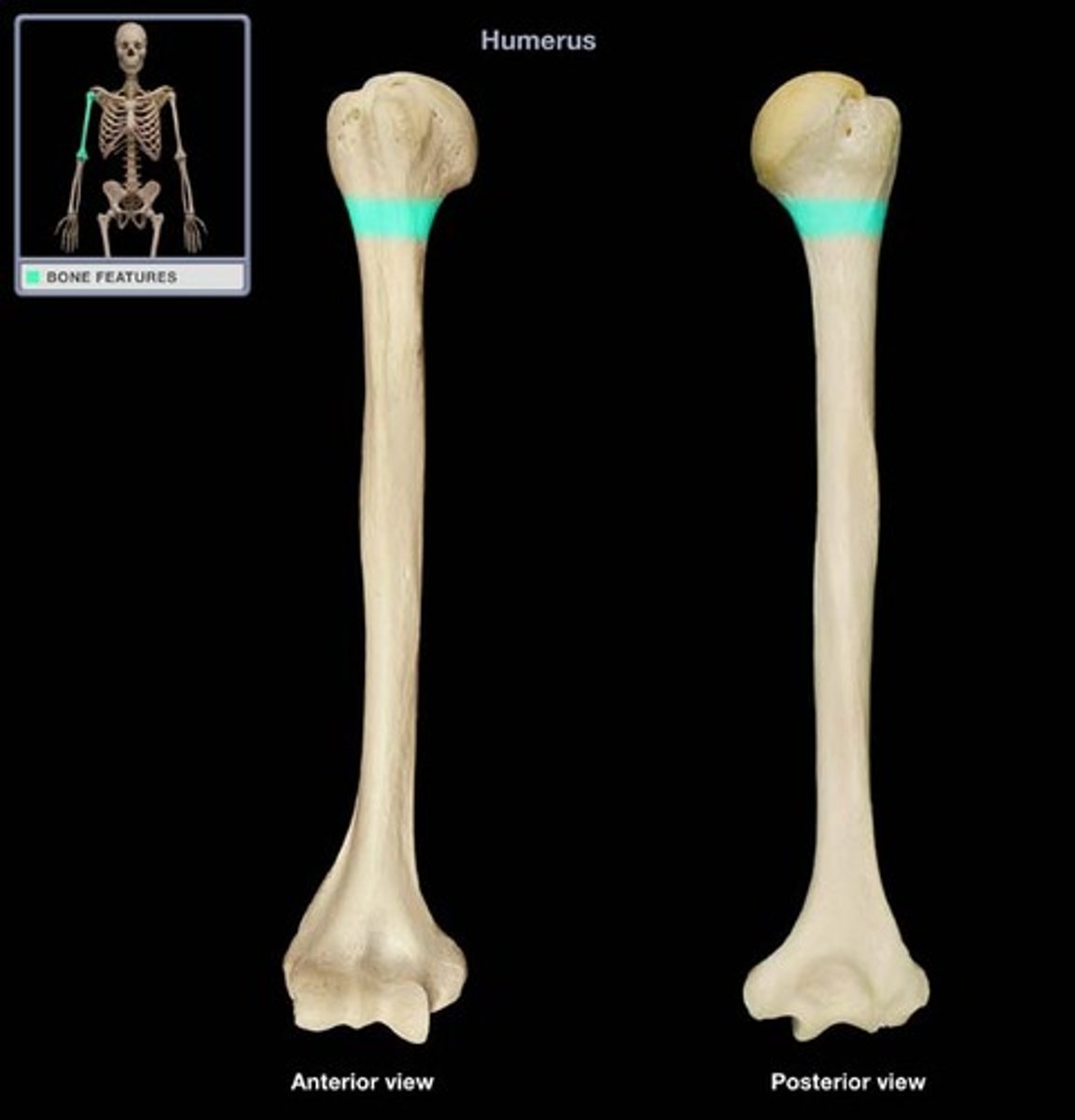
surgical neck (humerus)
What structure is highlighted?
corresponds to metaphysis of the growing bone...fractures typically occur here
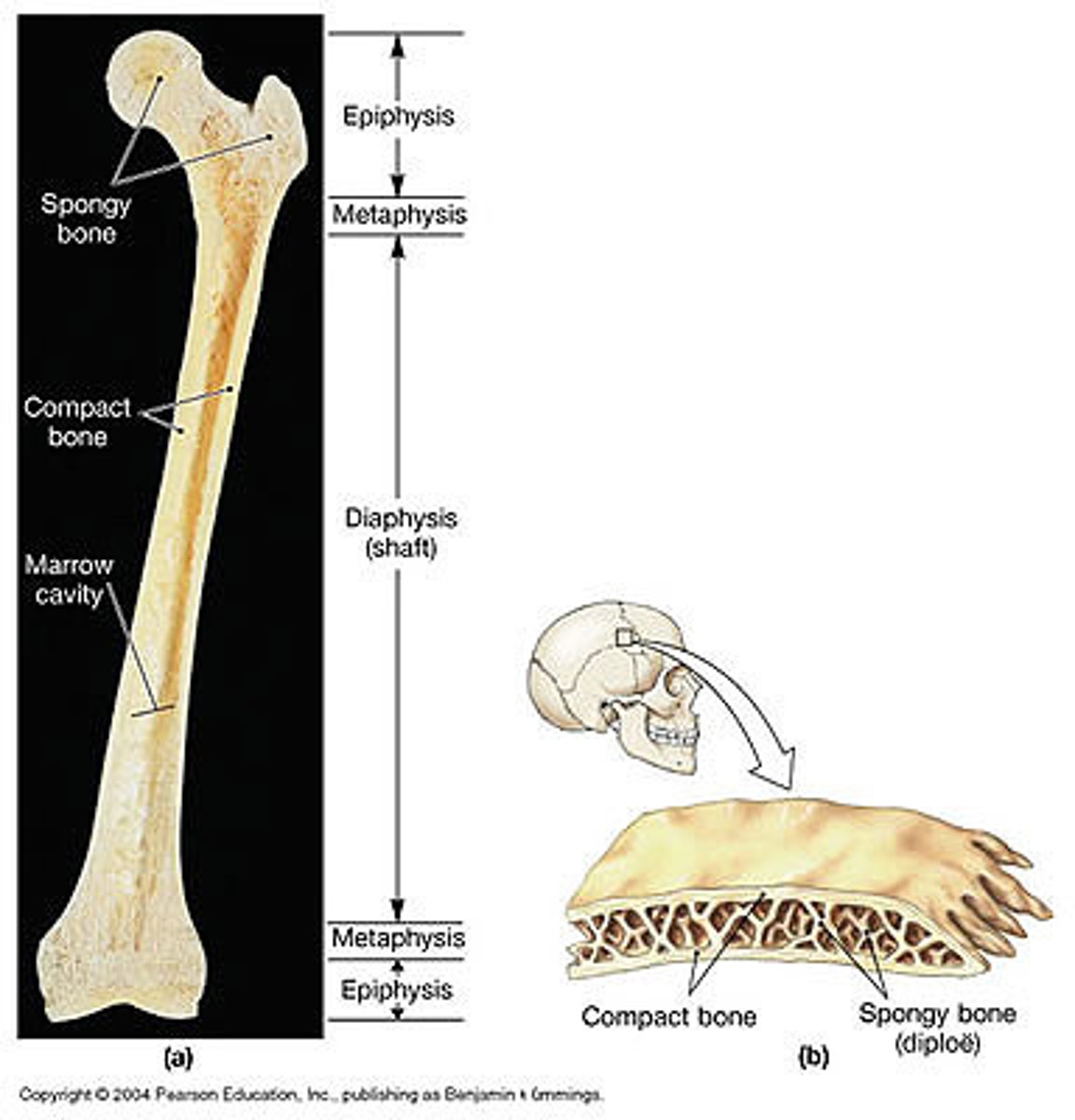
metaphysis
where diaphysis and epiphysis meet
deltoid tuberosity
Name this specific part of the humerus.
Attachment point of deltoid muscle, on lateral surface of diaphysis
radial groove
Name this specific part of the humerus.
Marks the path of the radial nerve. On posterior surface.

epicondyles (humerus)
Processes that develop proximal to an articulation, provide additional surface area for muscle attachment.
In humerus, rough projections on either side (medial and lateral) of the distal end of the humerus that attach to the tendons of most forearm muscles.
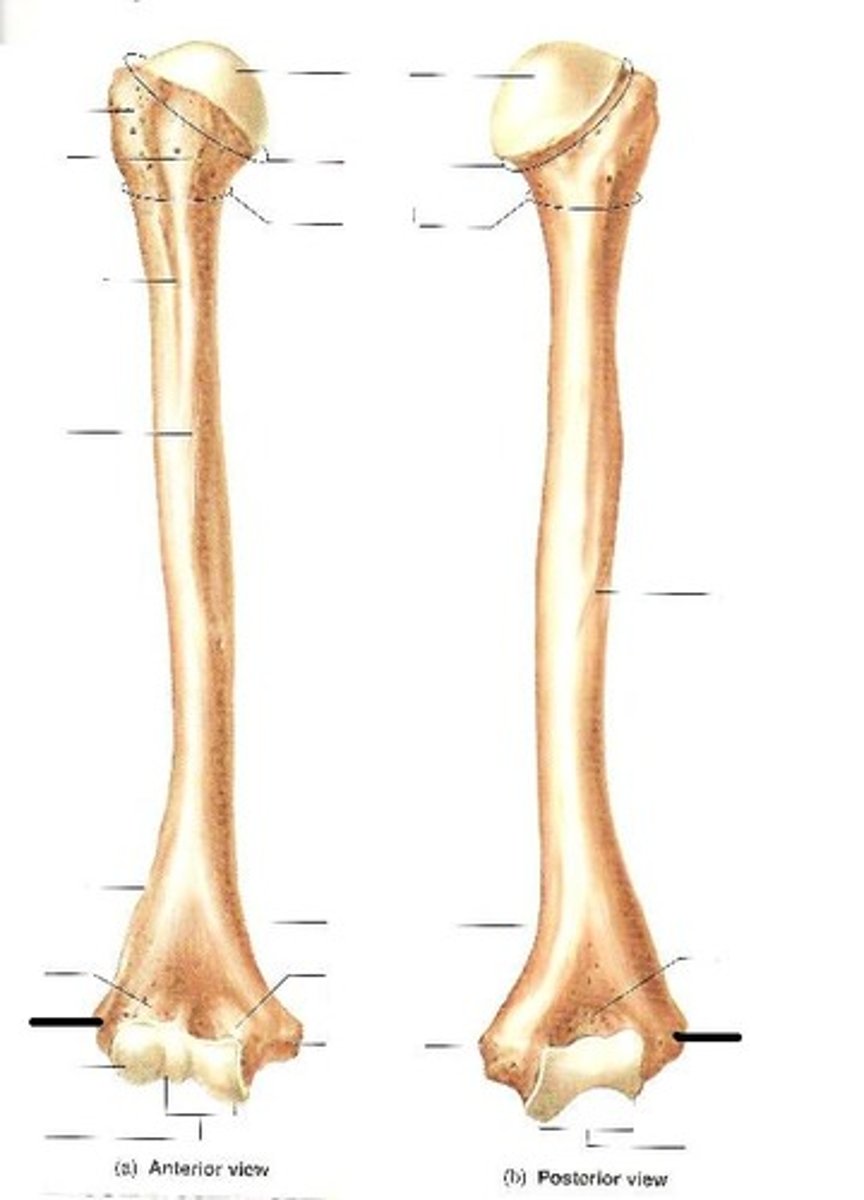
ulnar nerve
crosses the posterior surface of the medial epicondyle
AKA the "funny bone"
condyle (humerus)
articulates with the ulna and radius
has two articular faces the trochlea (spool-shaped, medial portion) and the capitulum (rounded, lateral portion)
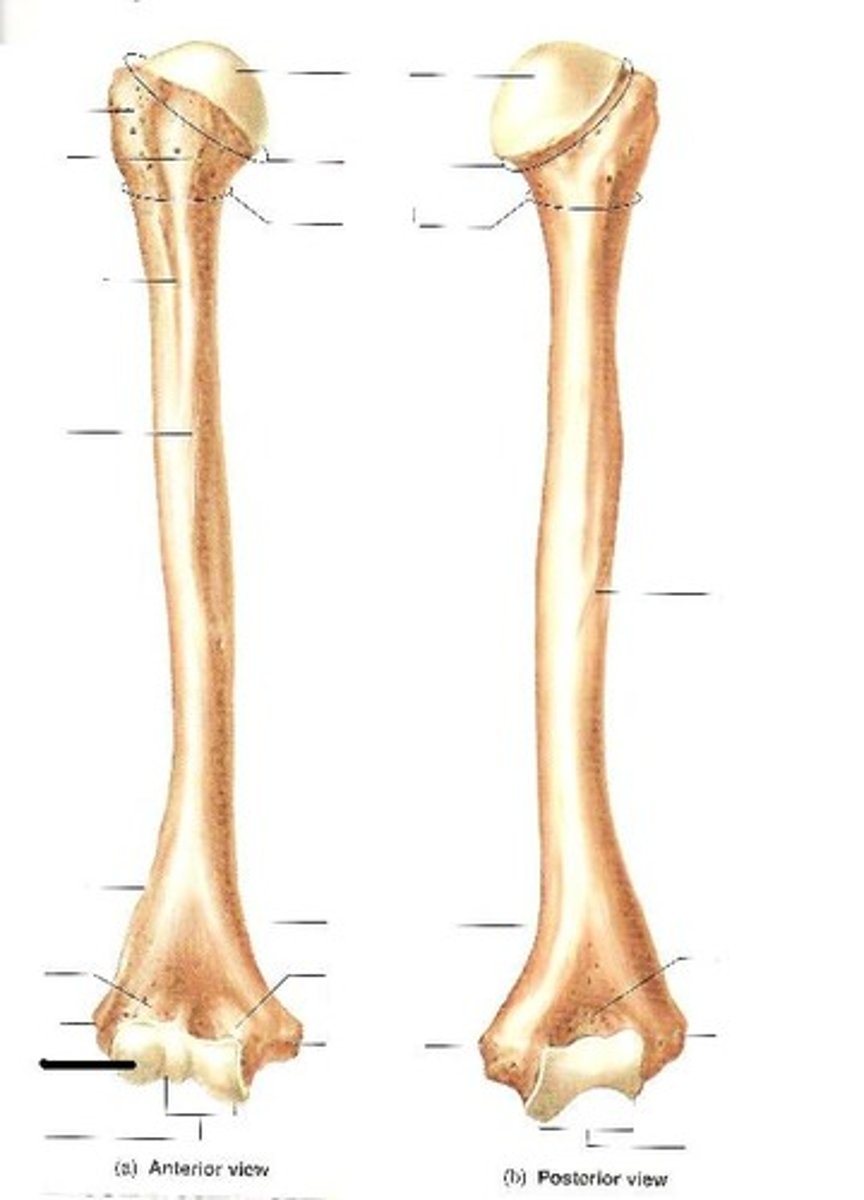
coronoid fossa (humerus)
anterior depression that receives the coronoid process of the ulna when forearm is flexed.
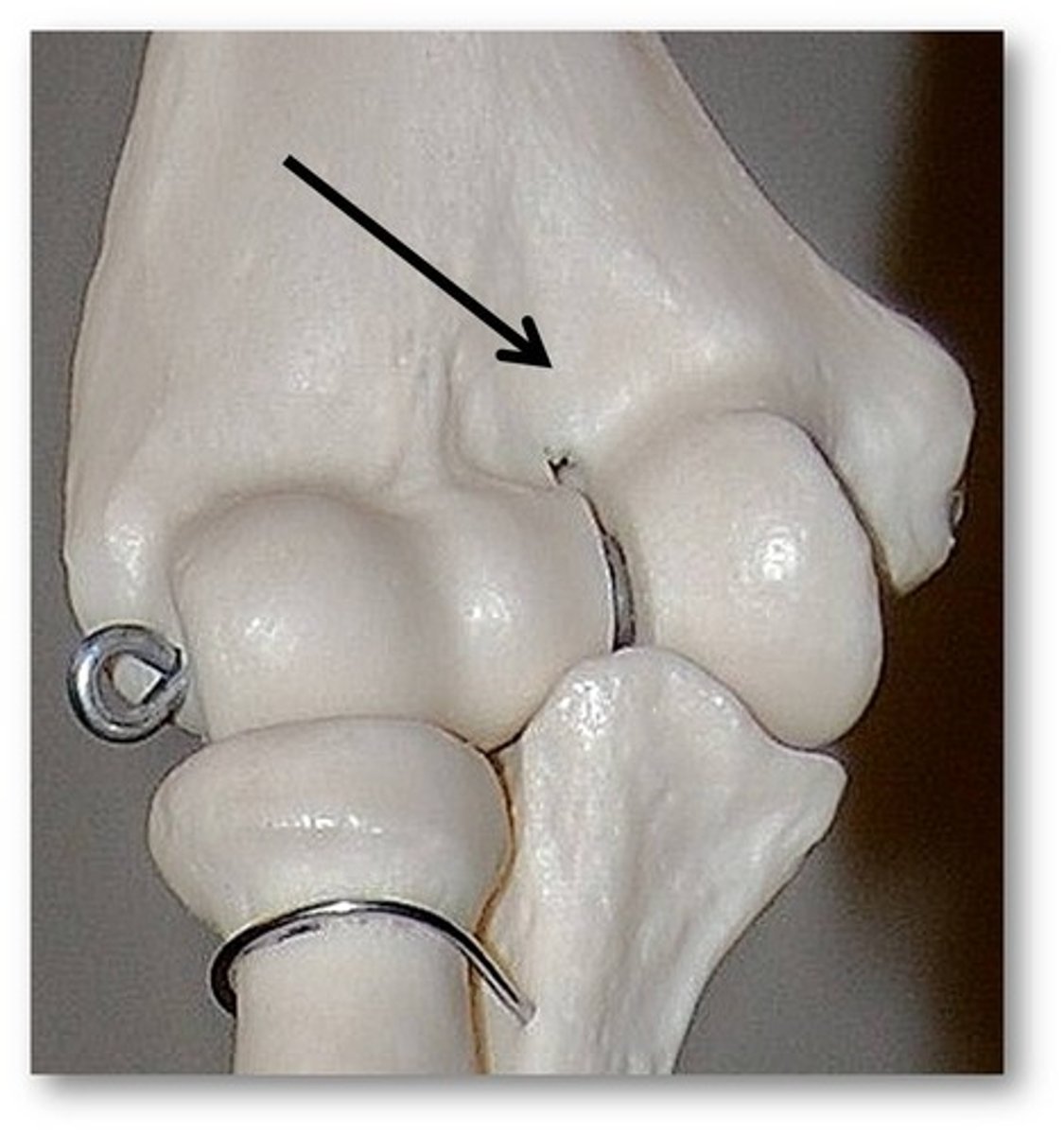
olecranon fossa (humerus)
large distal posterior depression that accommodates the olecranon of the ulna
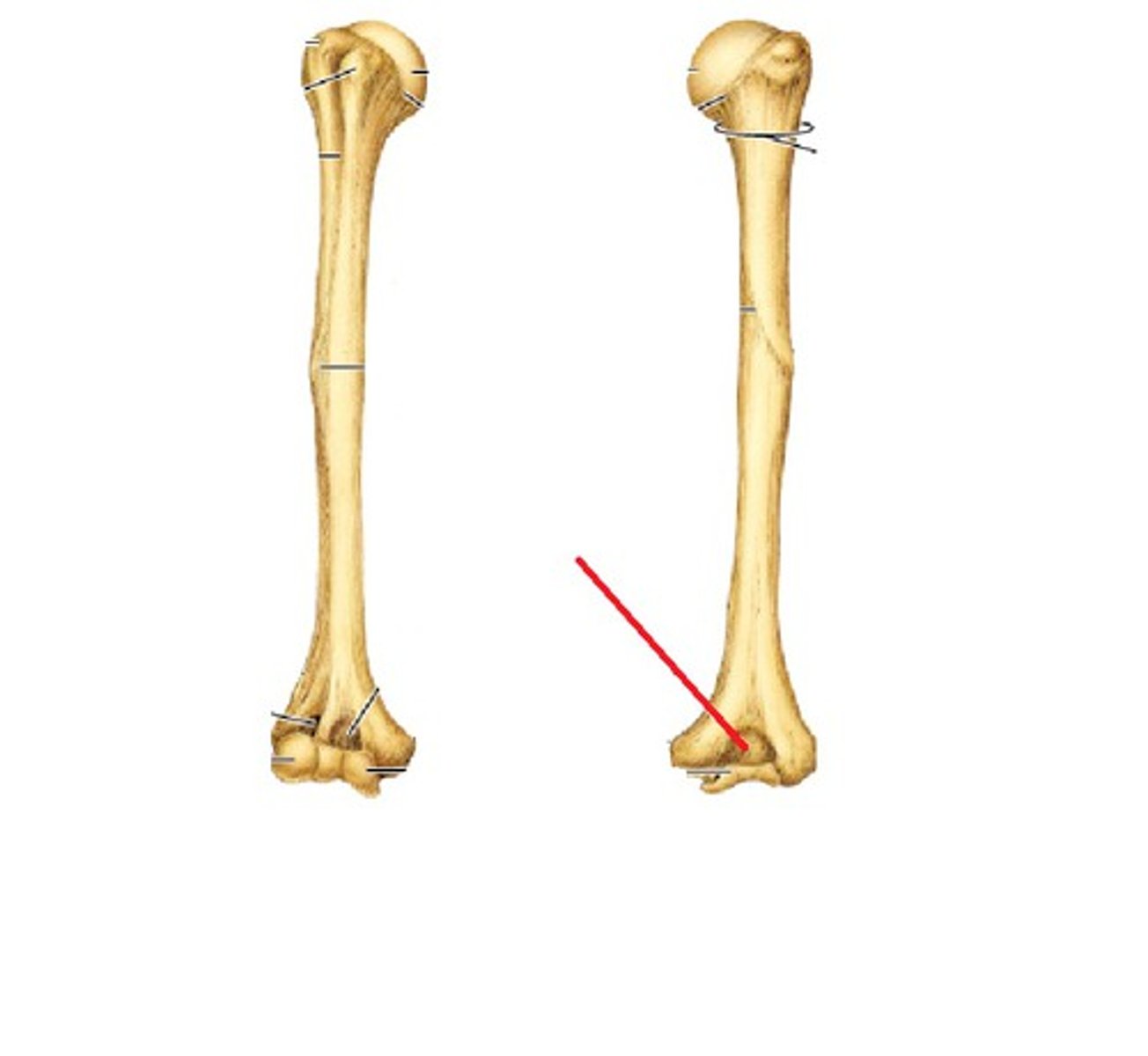
radial fossa (humerus)
anterior depression that receives the radial head with flexed forearm
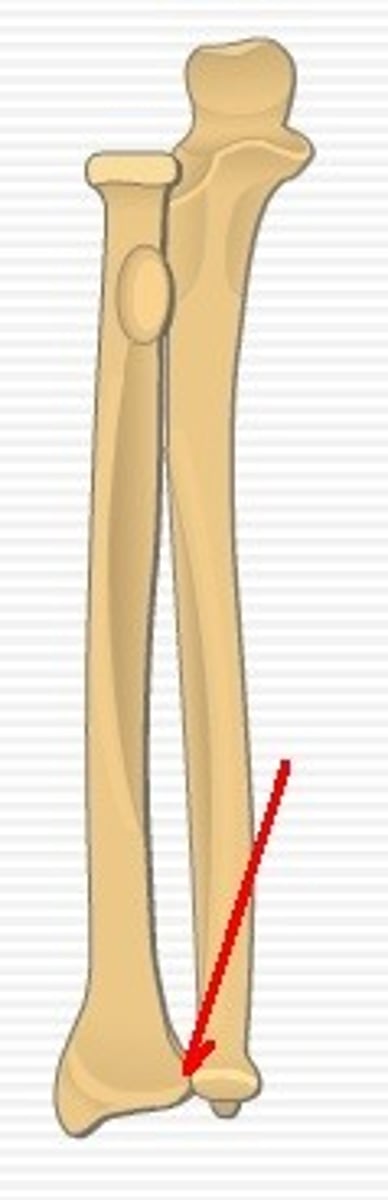
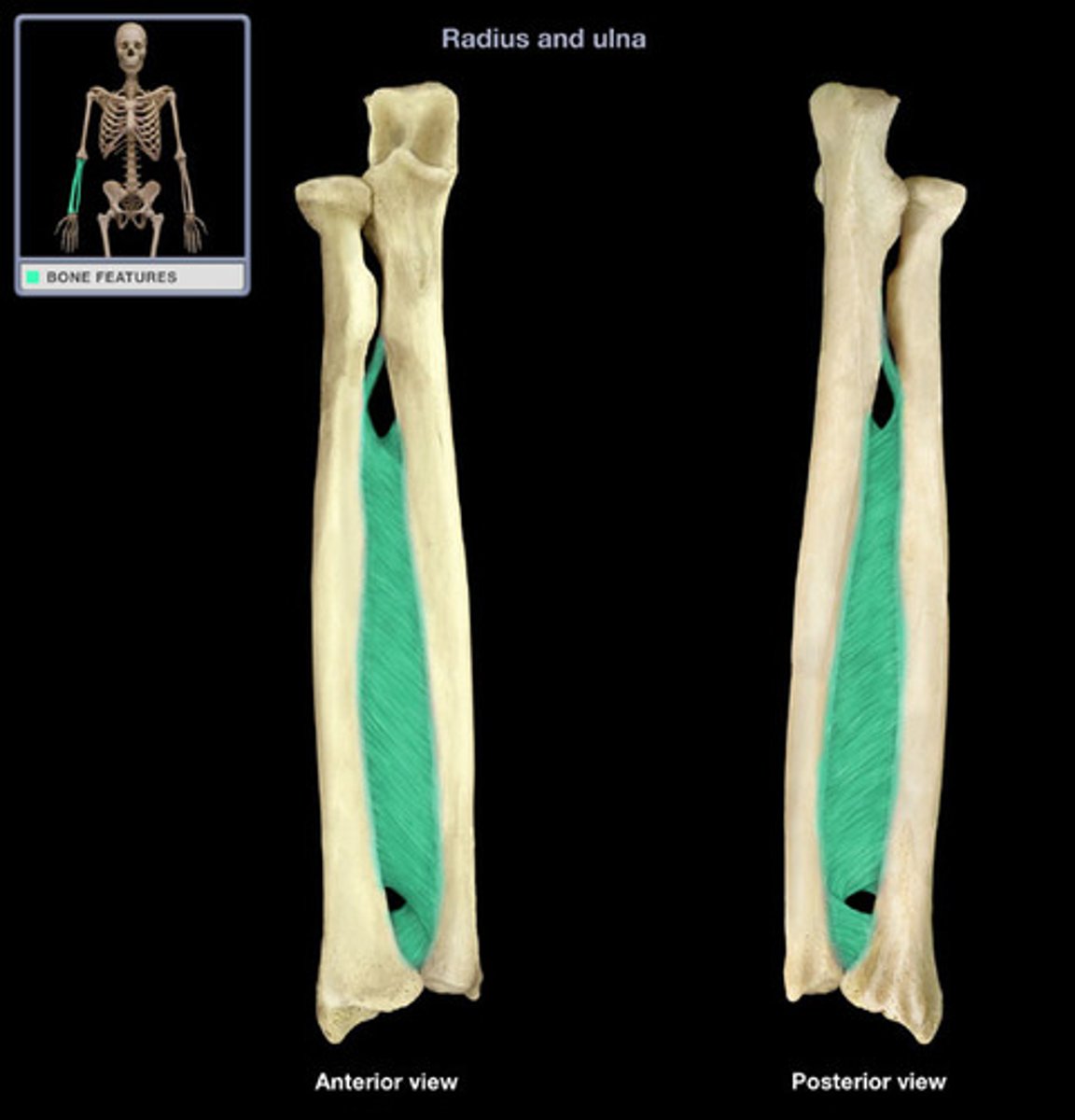
ulna
in the anatomical position, this antebrachial bone lies medially
radius
in the anatomical position, this antebrachial bone lies laterally
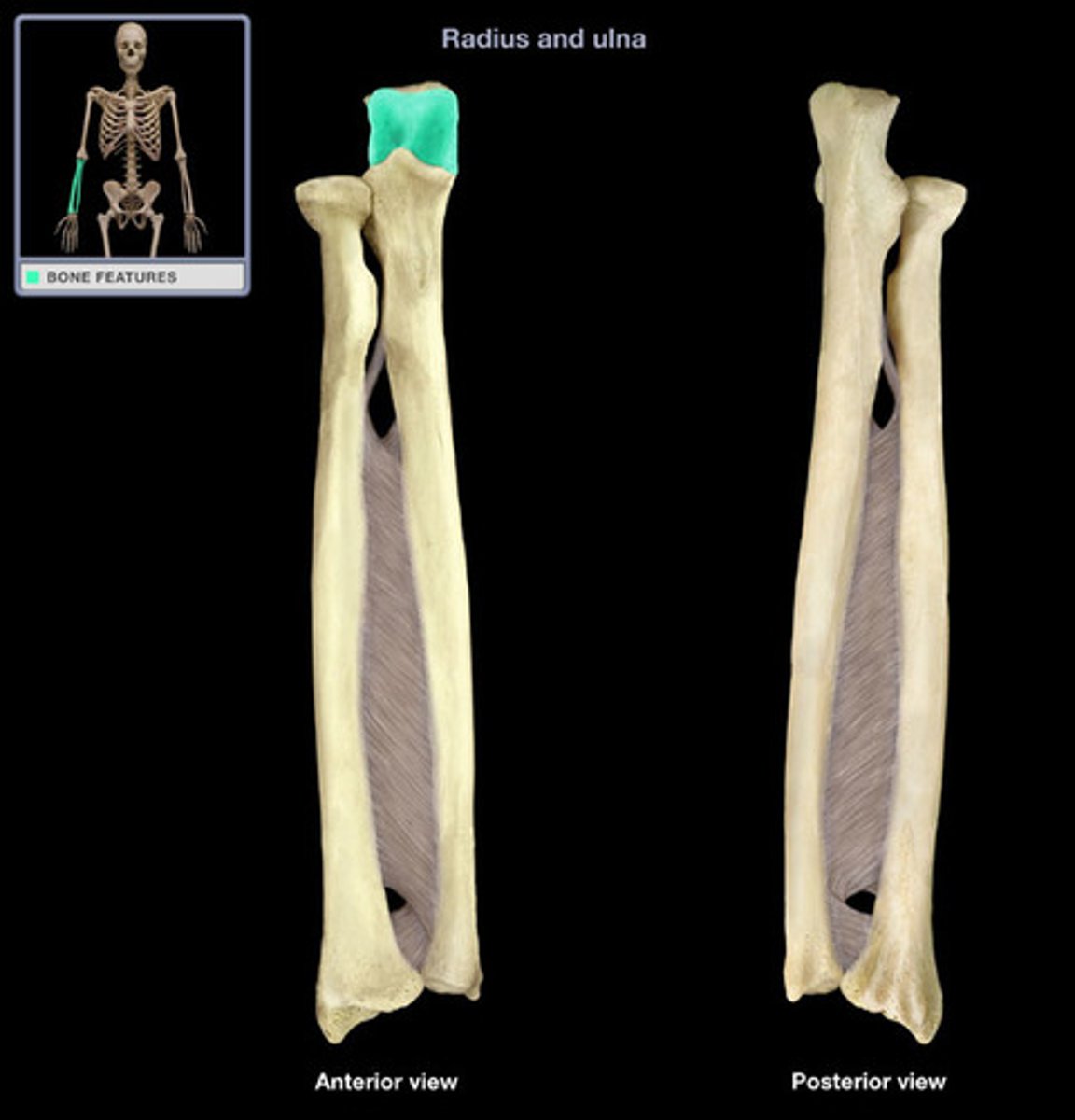
olecranon (ulna)
The superior end of the ulna, the point of the elbow

trochlear notch (ulna)
on the anterior surface of the ulna's proximal ephysis
articulates with trochlea of humerus
basically it's the anterior surface of the olecranon
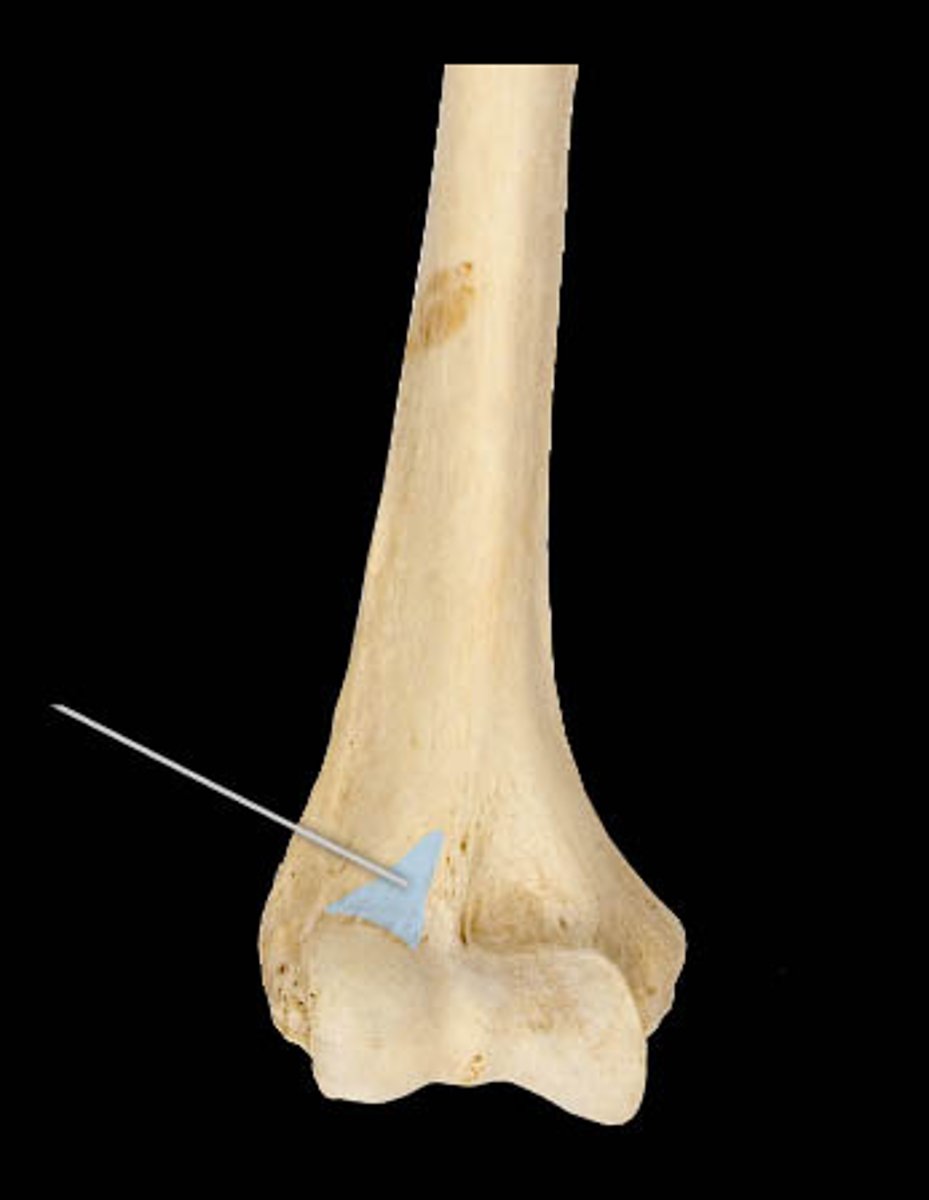
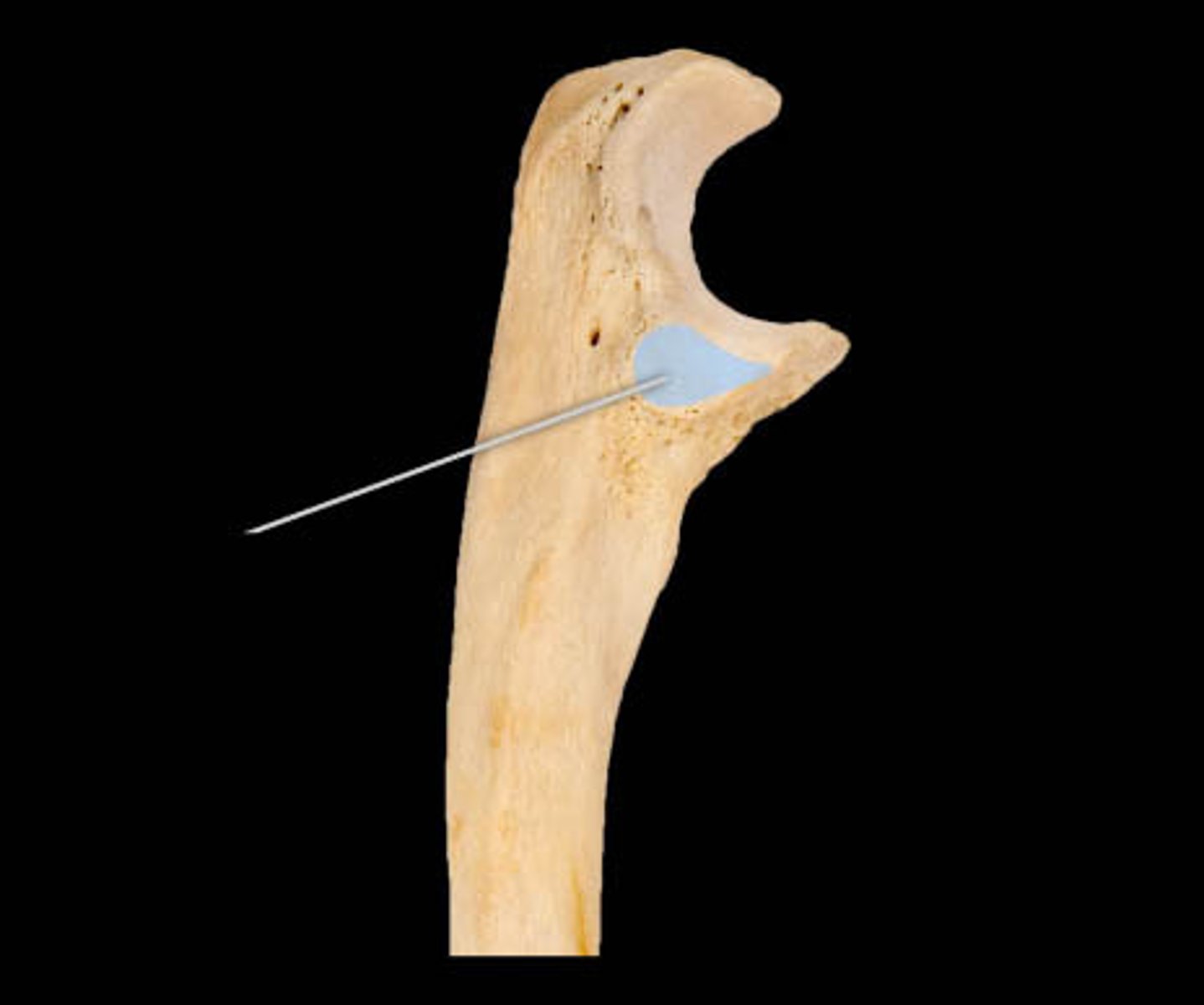
coronoid process (ulna)
name this part of the ulna
fits into the coronoid fossa of the humerus
flexion
Decreases the angle of a joint
extension
increases the angle of a joint
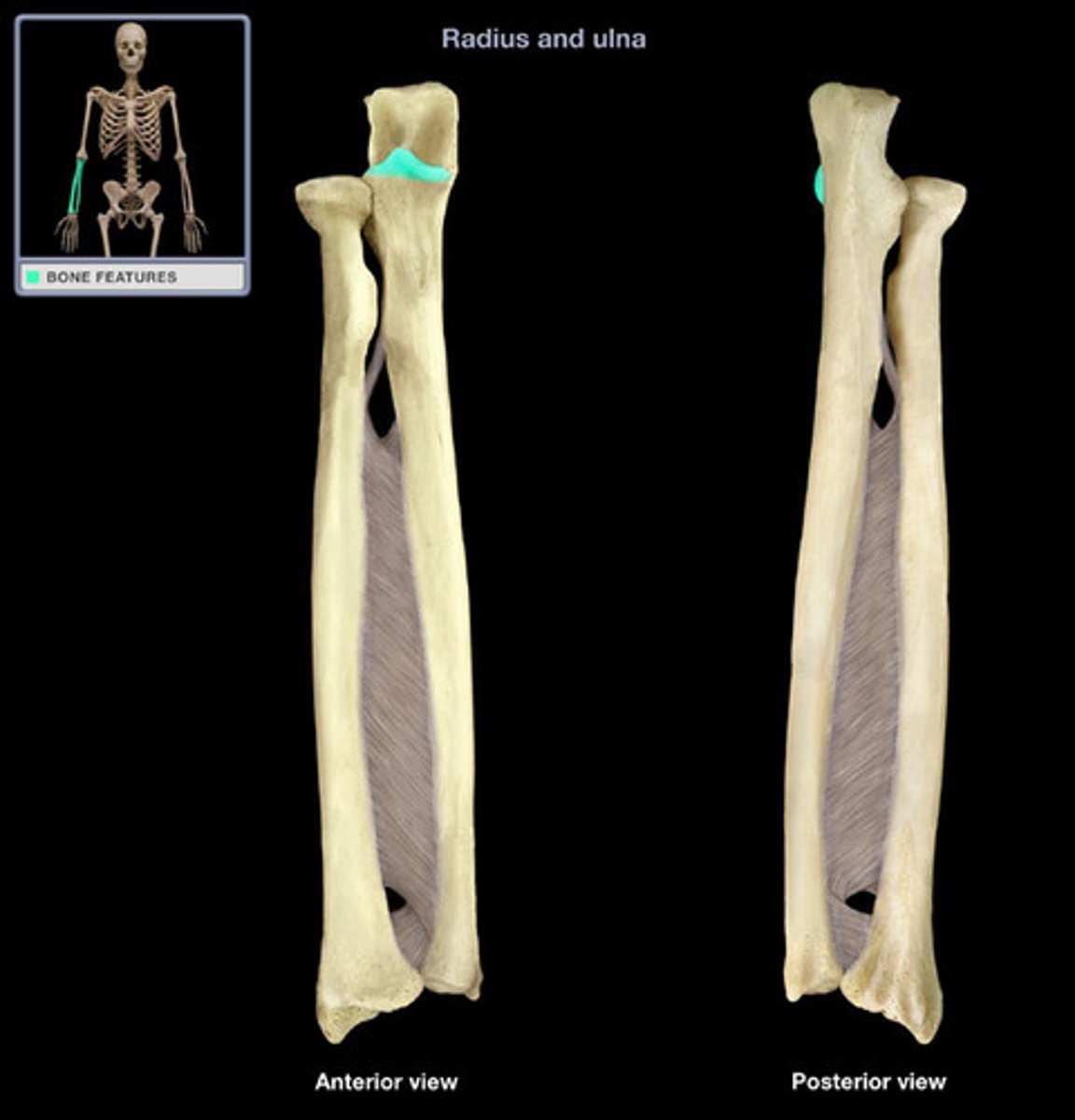
radial notch (ulna)
Name this specific part of the ulna.
Articulates with the head of the radius at the RADIOULNAR joint
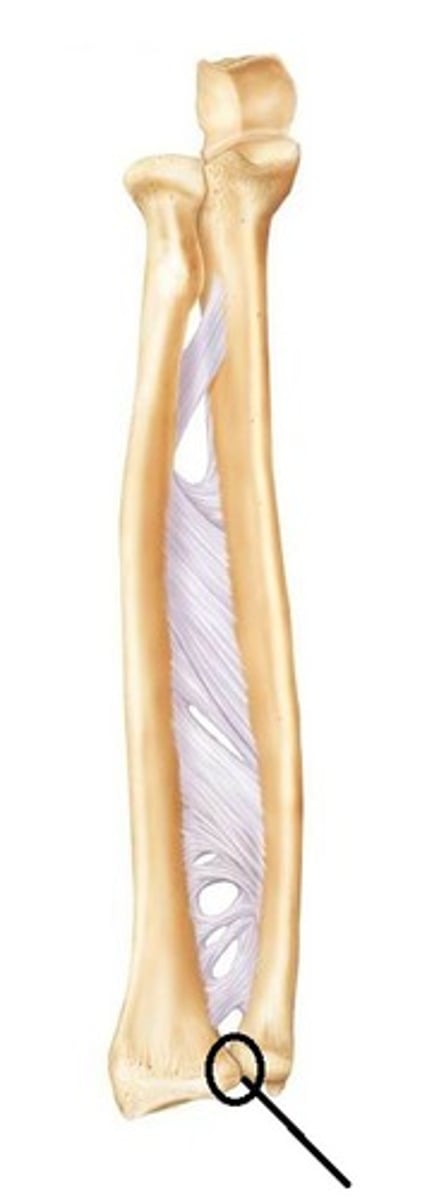
interossesous membrane (antebrachium)
fibrous sheet connecting the lateral margin of the ulna to the radius
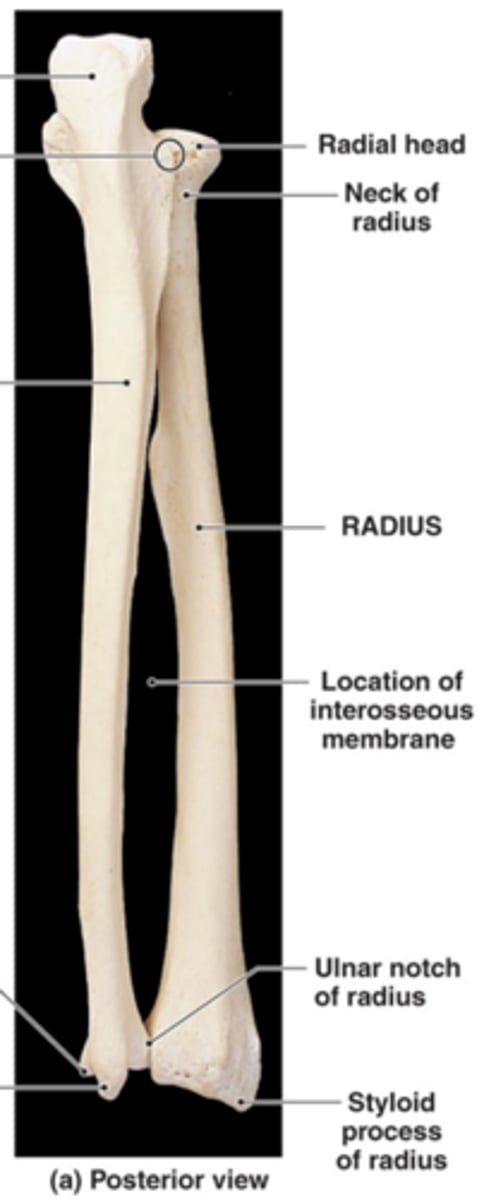
ulnar head
ulnar structure with a prominent styloid process
the ARTICULAR DISC attaches to the styloid process
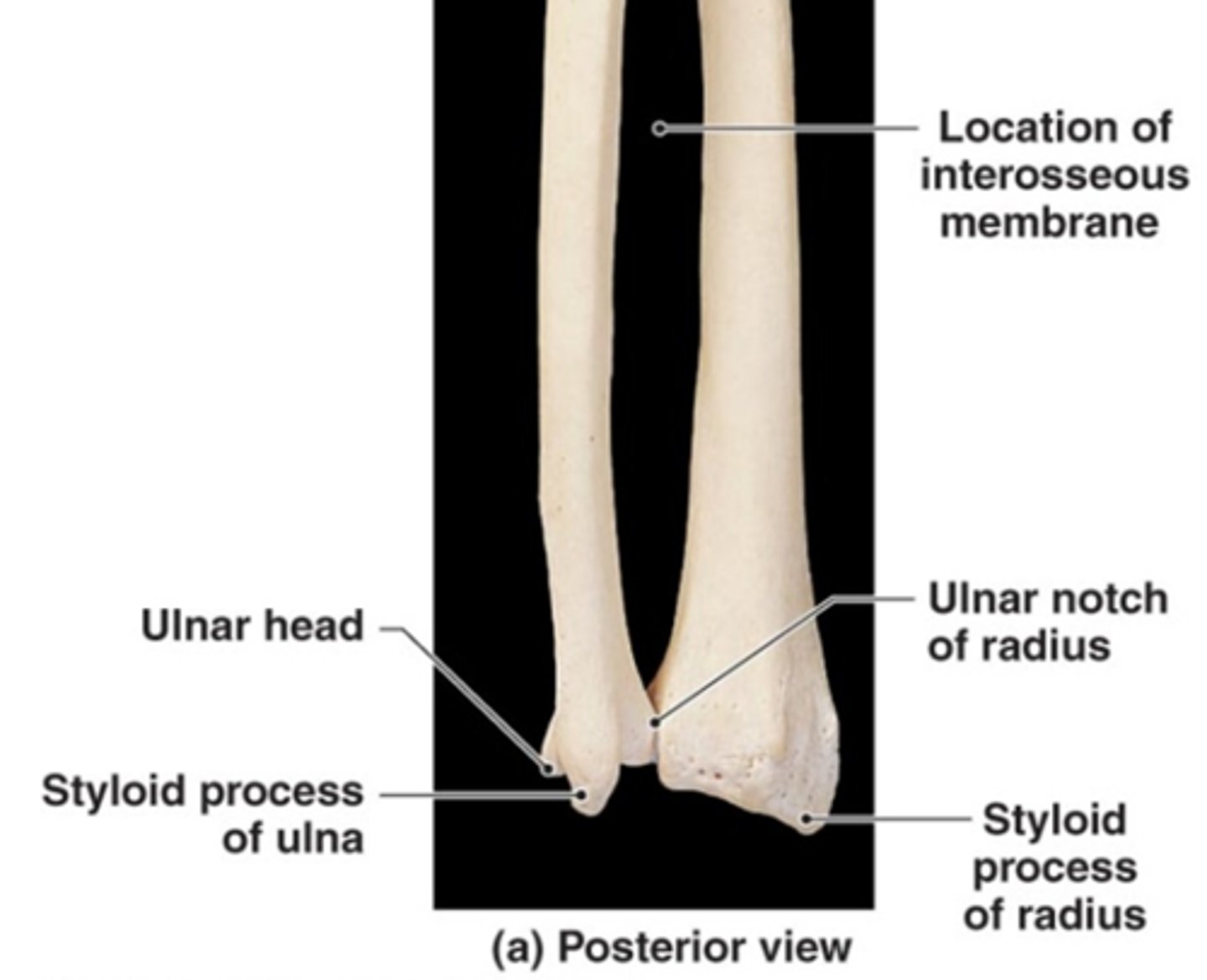
distal radioulnar joint
head of ulna articulates with ulnar notch of radius; joins ulna and radius distally

radial head
name this structure of the radius
articulates with capitulum of humerus
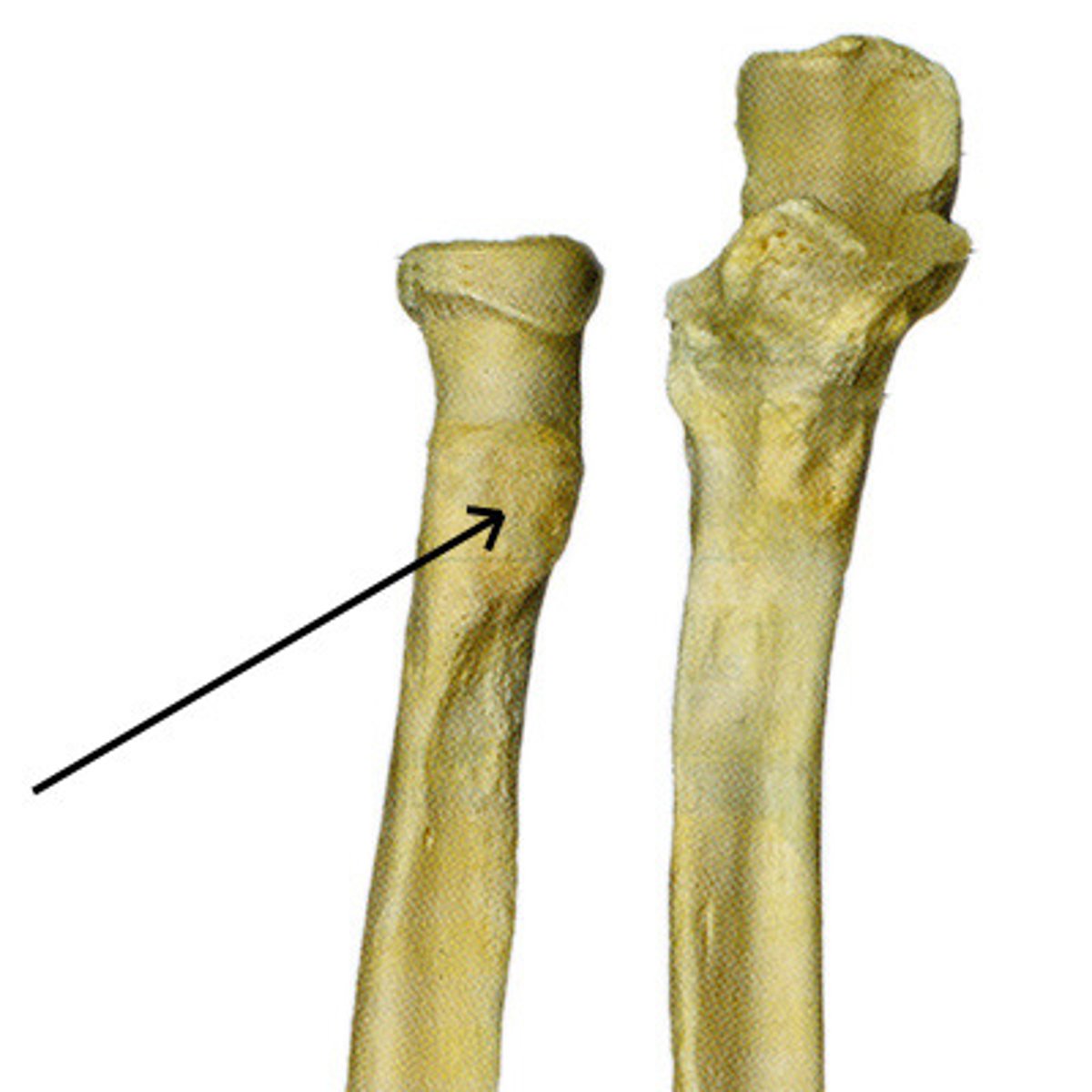
radial tuberosity
Name this specific part of the radius.
This tuberosity is an attachment site of the biceps brachii muscle
ulnar notch (radius)
articulates with the head of the ulna
medial surface of the distal end of the radius
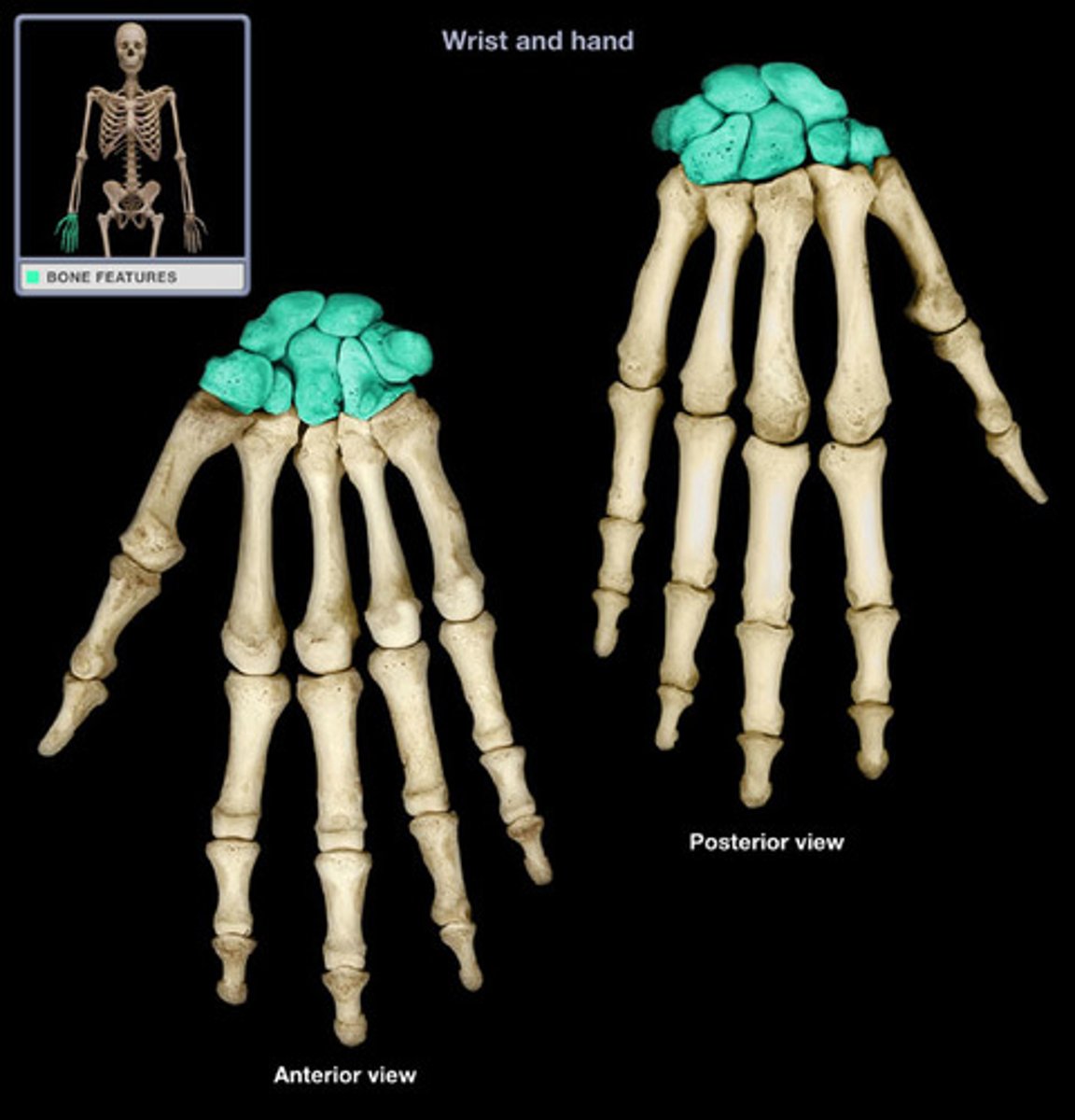
carpus
the eight carpal bones of the wrist, forms two rows
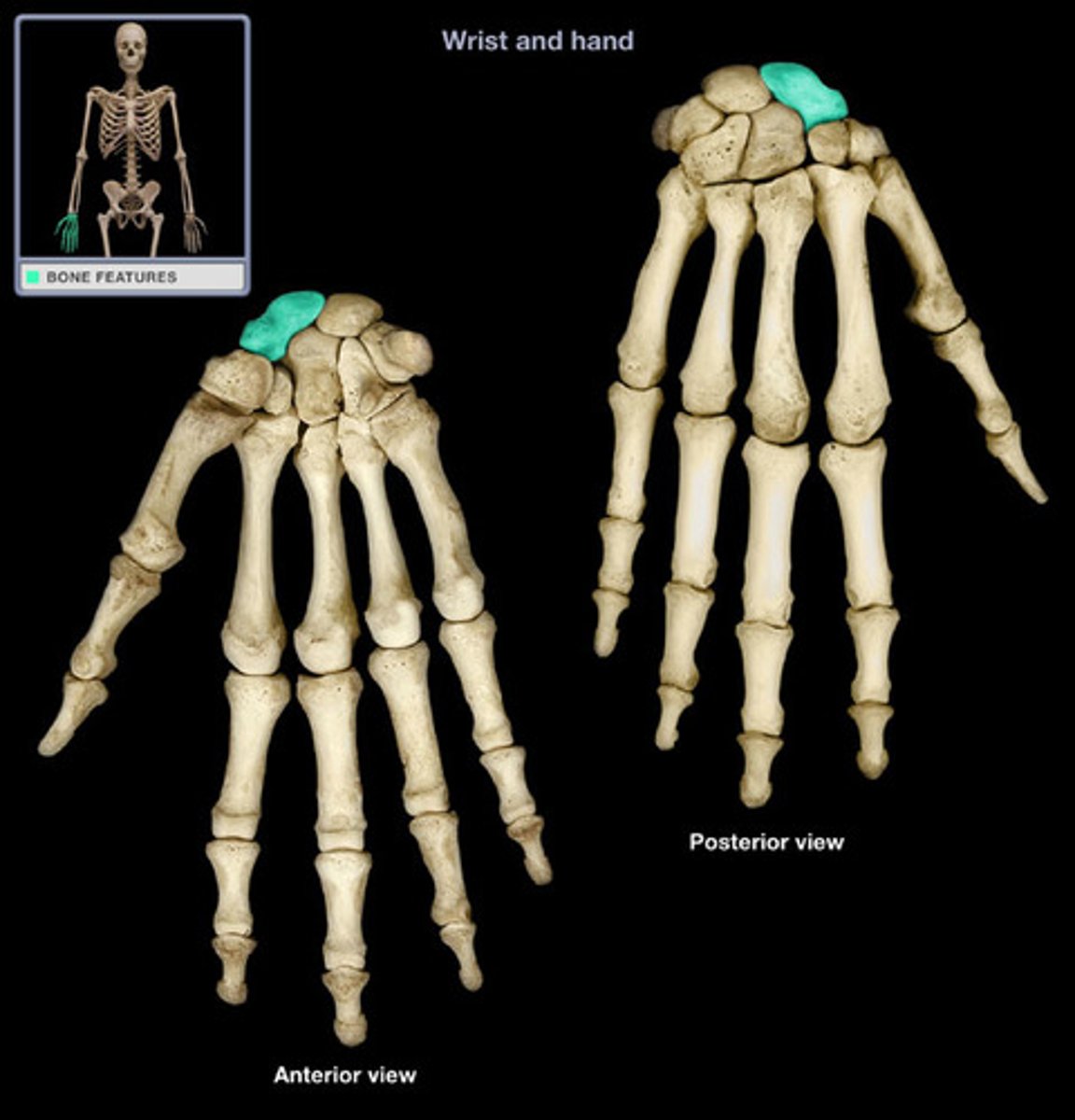
proximal carpal bones
the proximal row of carpal bones (SLTP) (SCALUTRIPI):
1. scaphoid
2. lunate
3. triquetrum
4. pisiform
distal carpal bones
the distal row of carpal bones (TTCH) (TRAPCAHA):
1. trapezium
2. trapezoid
3. capitate
4. hamate
scaphoid
"skaphe, boat"
name this proximal carpal bone
the lateral bone of the proximal row
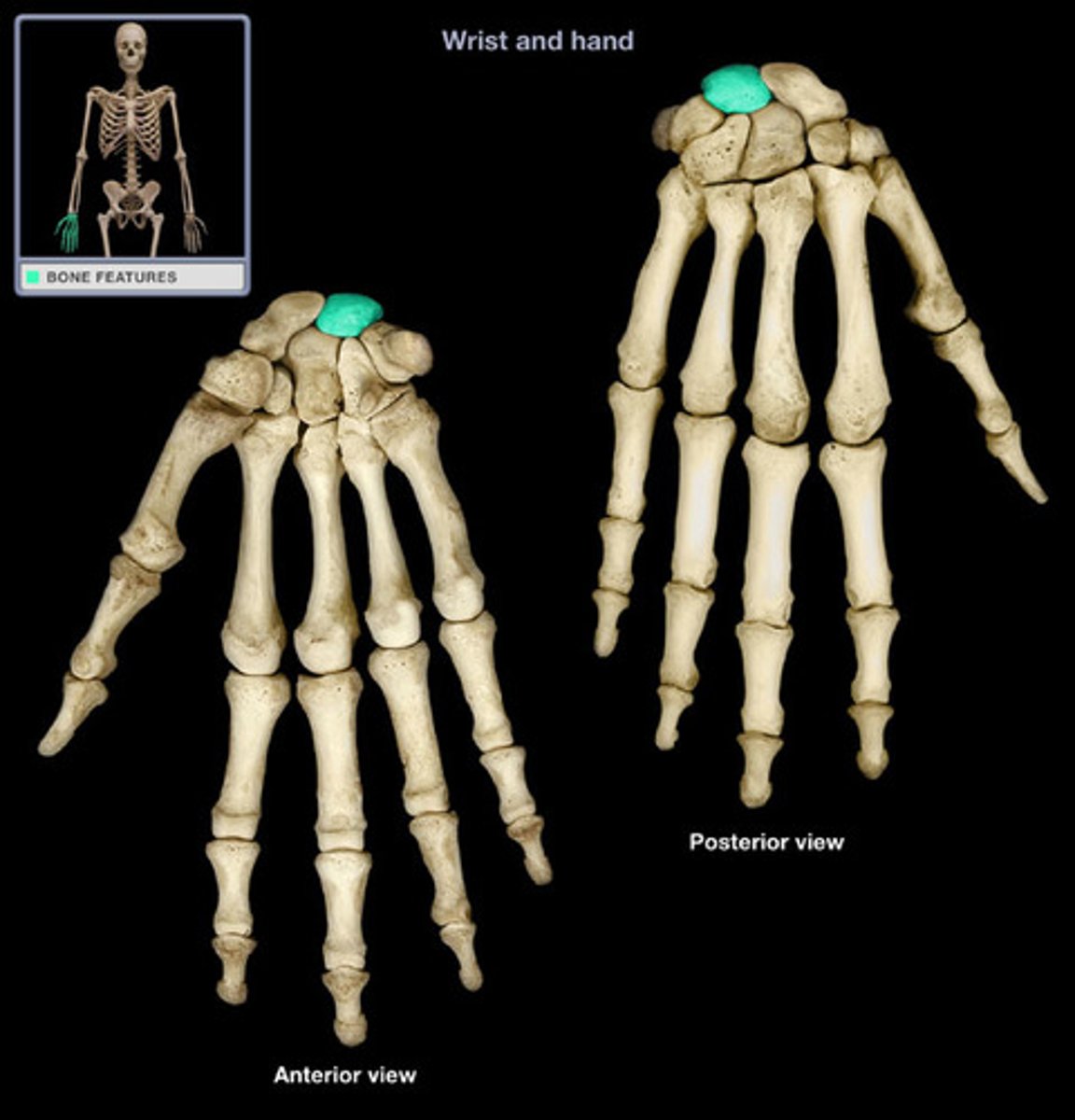
lunate
"luna, moon"
name this proximal carpal bone
the middle bone of the proximal row
triquetrum
"triquetrus, three-cornered"
name this proximal carpal bone
the pisiform sits anterior on this bone
the medial bone of the proximal row
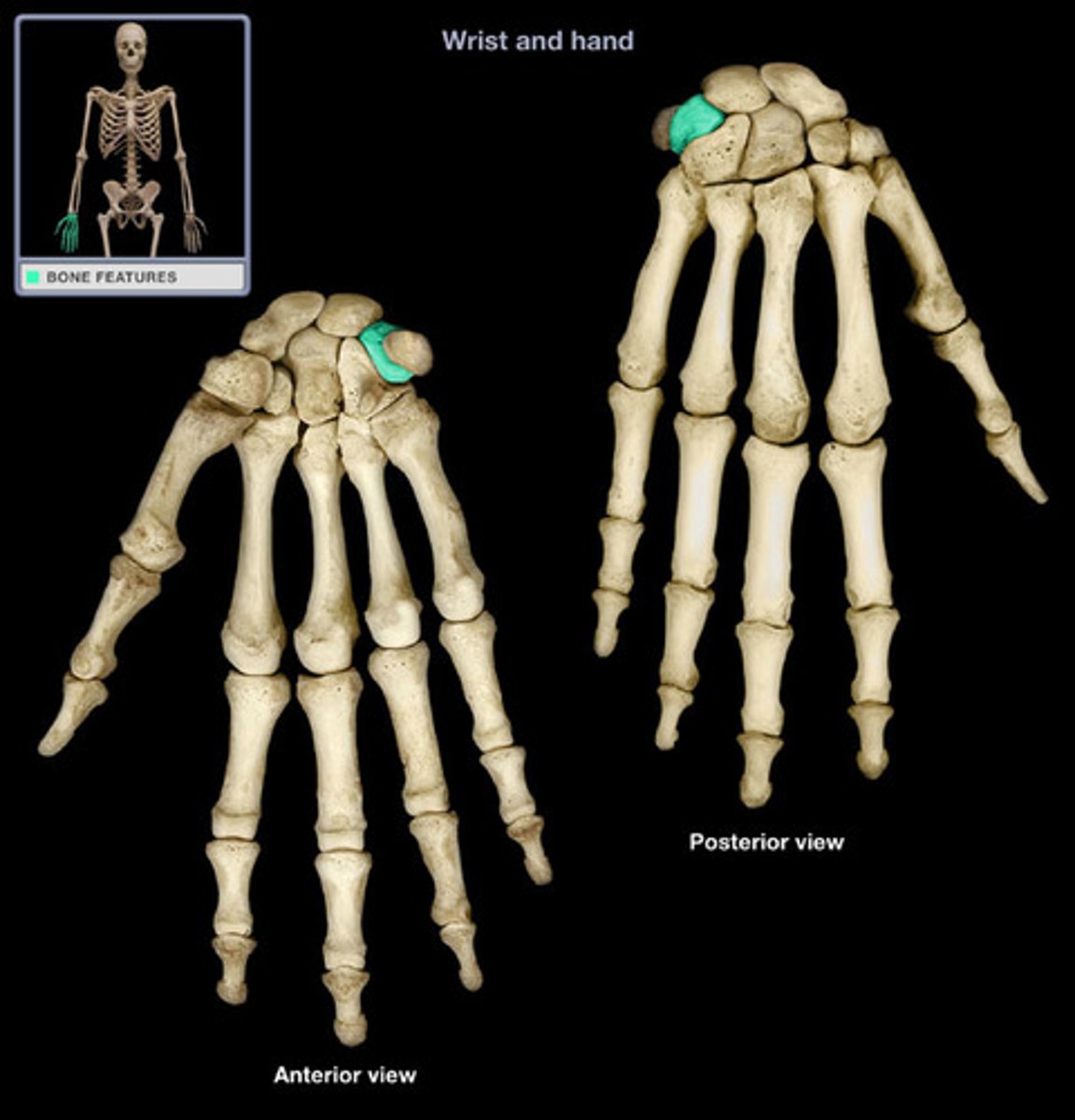
pisiform
"pisum, pea"
name this proximal carpal bone
sits anterior on the triquetrum
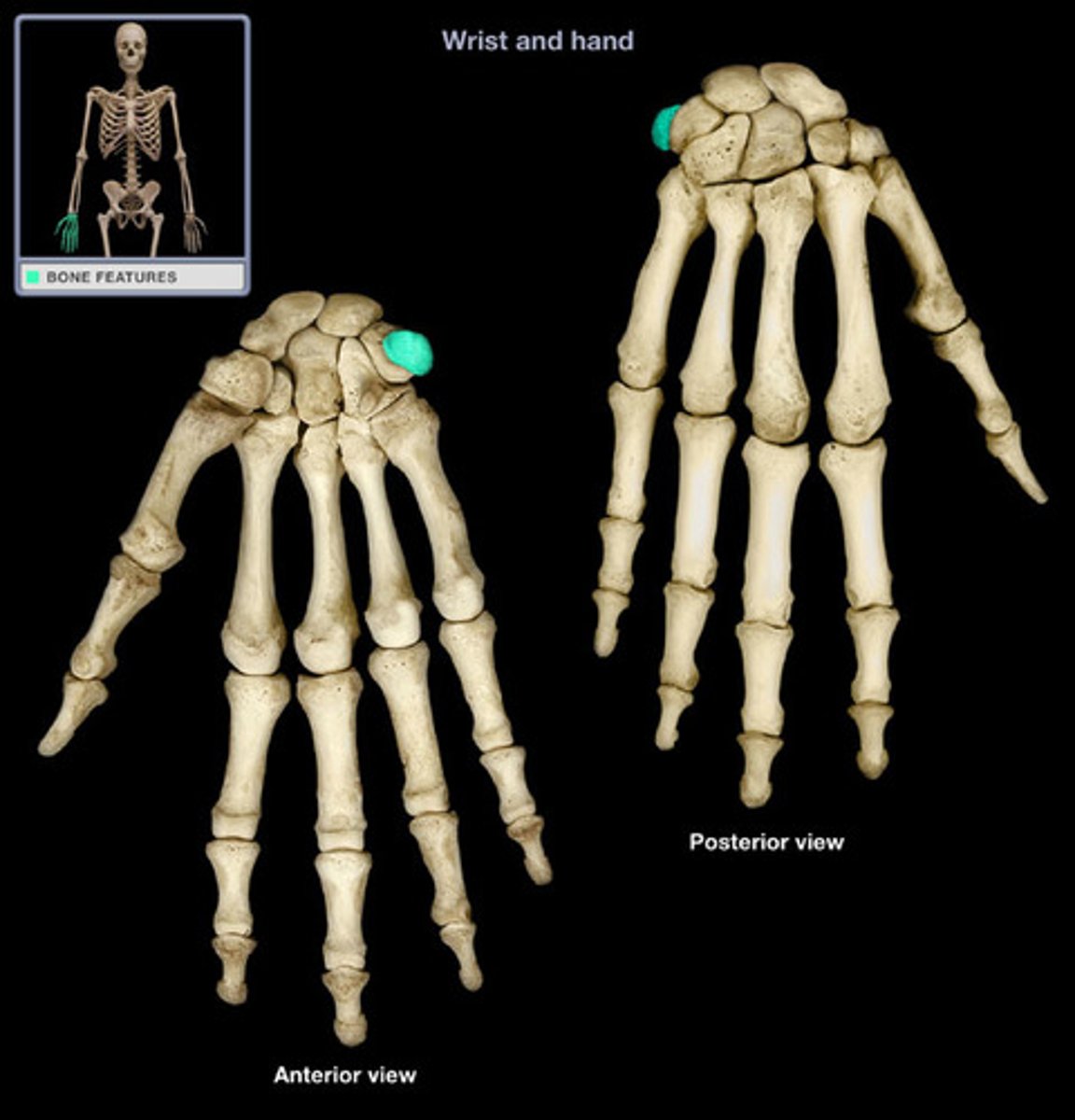
trapezium
"trapezion, four-sided"
name this distal carpal bone
the lateral bone of the distal row
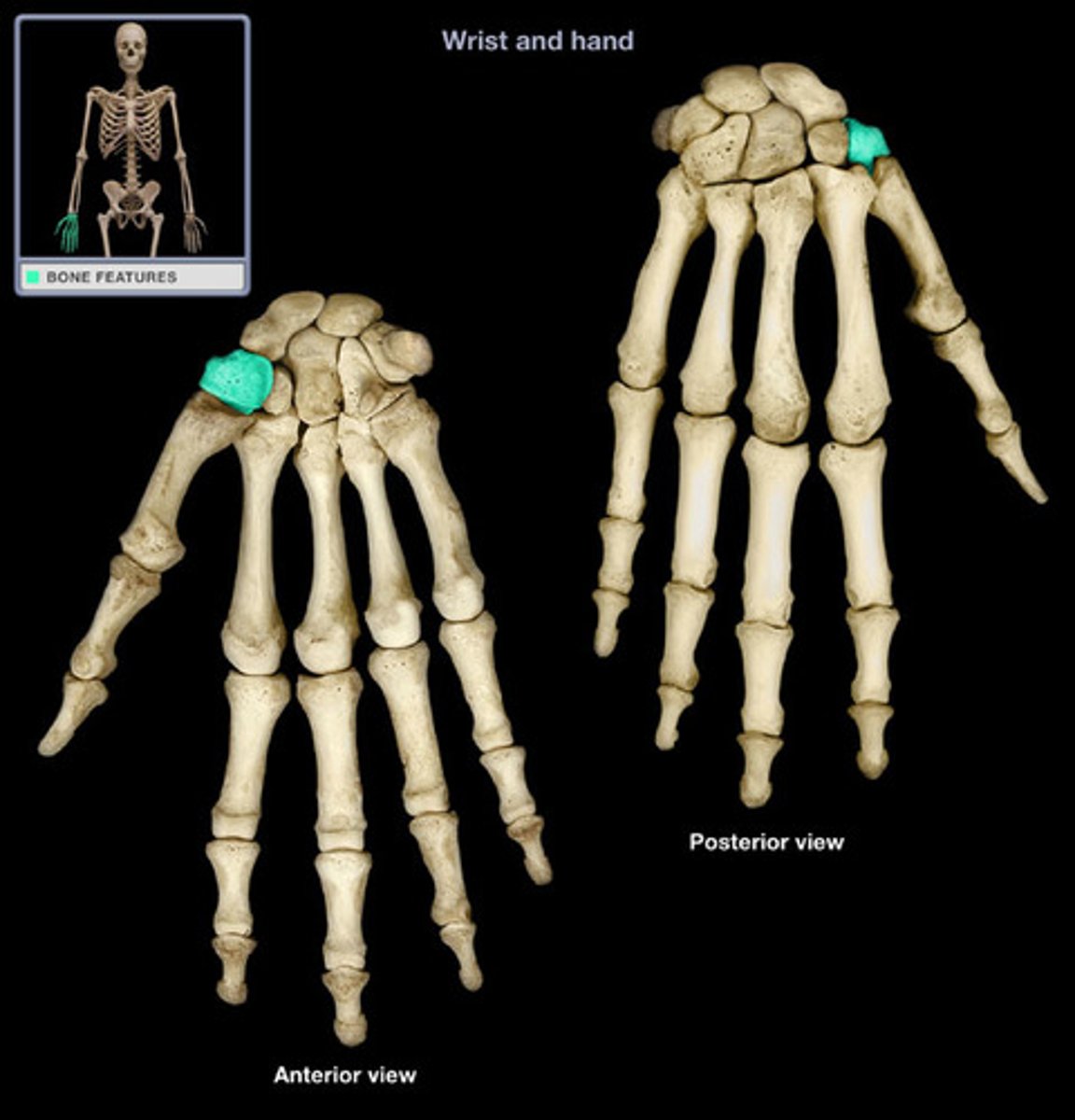
trapezoid
name this distal carpal bone
lies medial to the trapezium
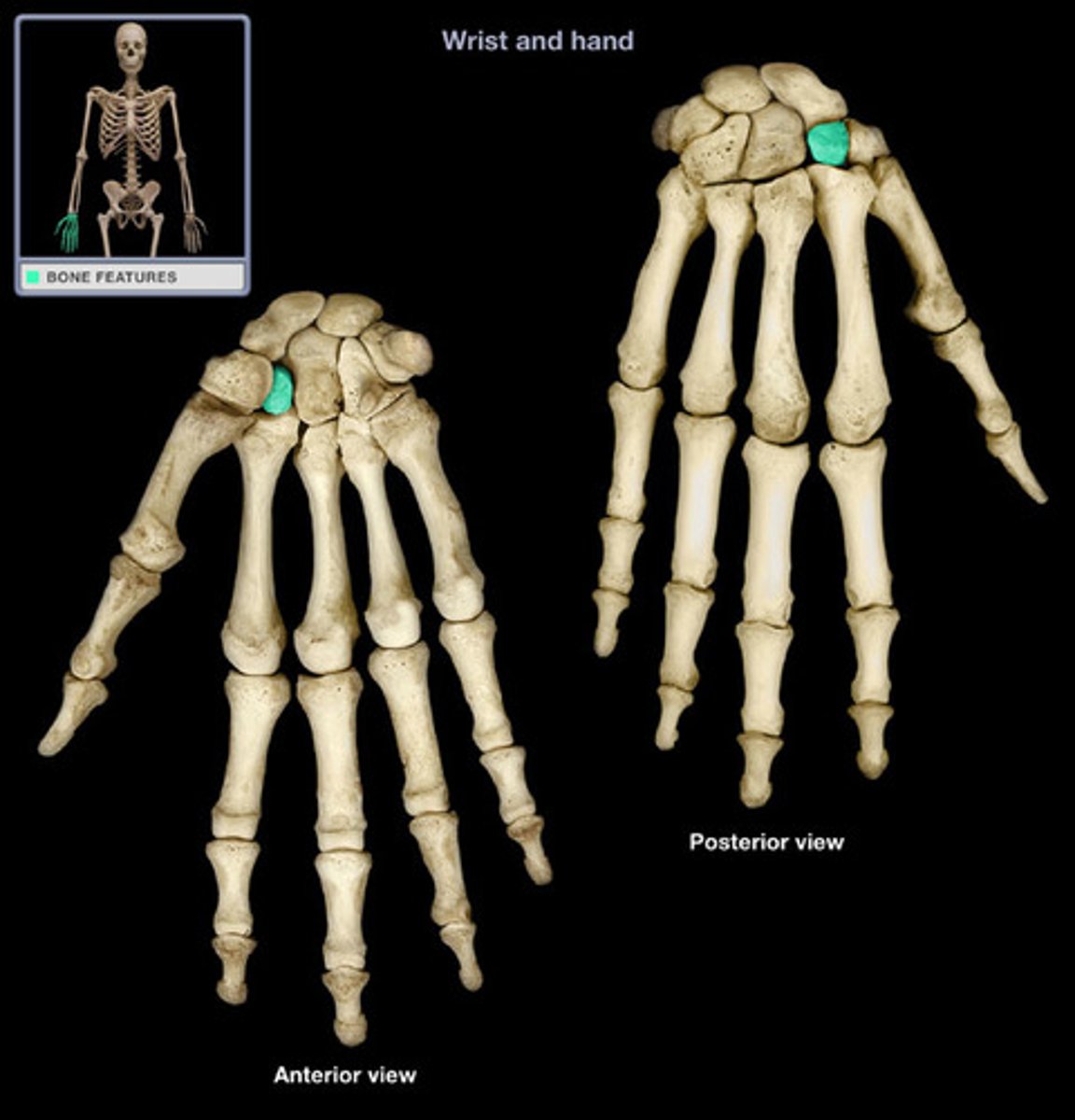
capitate
"caput, head"
name this distal carpal bone
largest carpal bone
sits between trapezoid and hamate
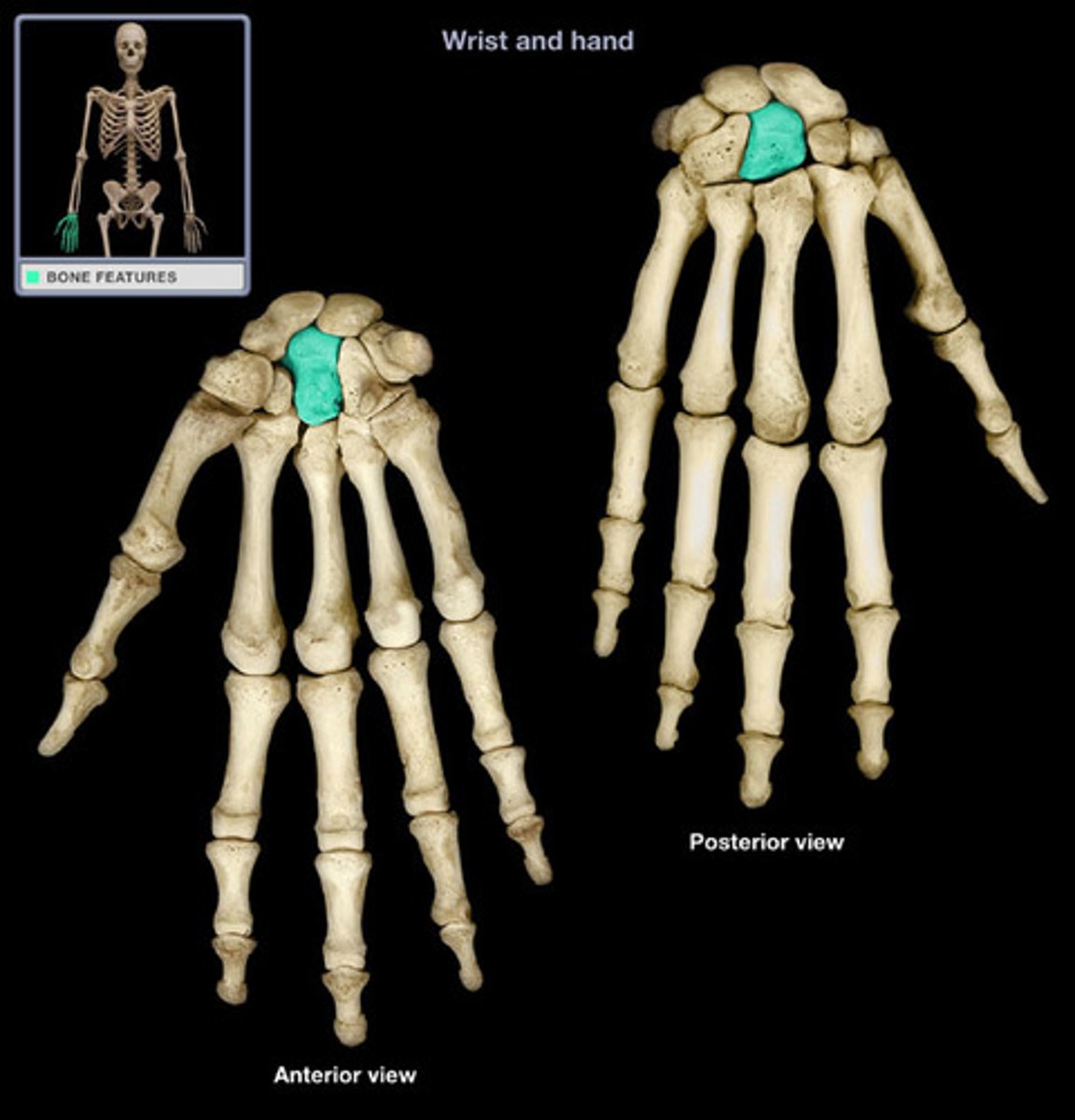
hamate
"hamatum, hooked"
name this distal carpal bone
the most medial distal carpal bone
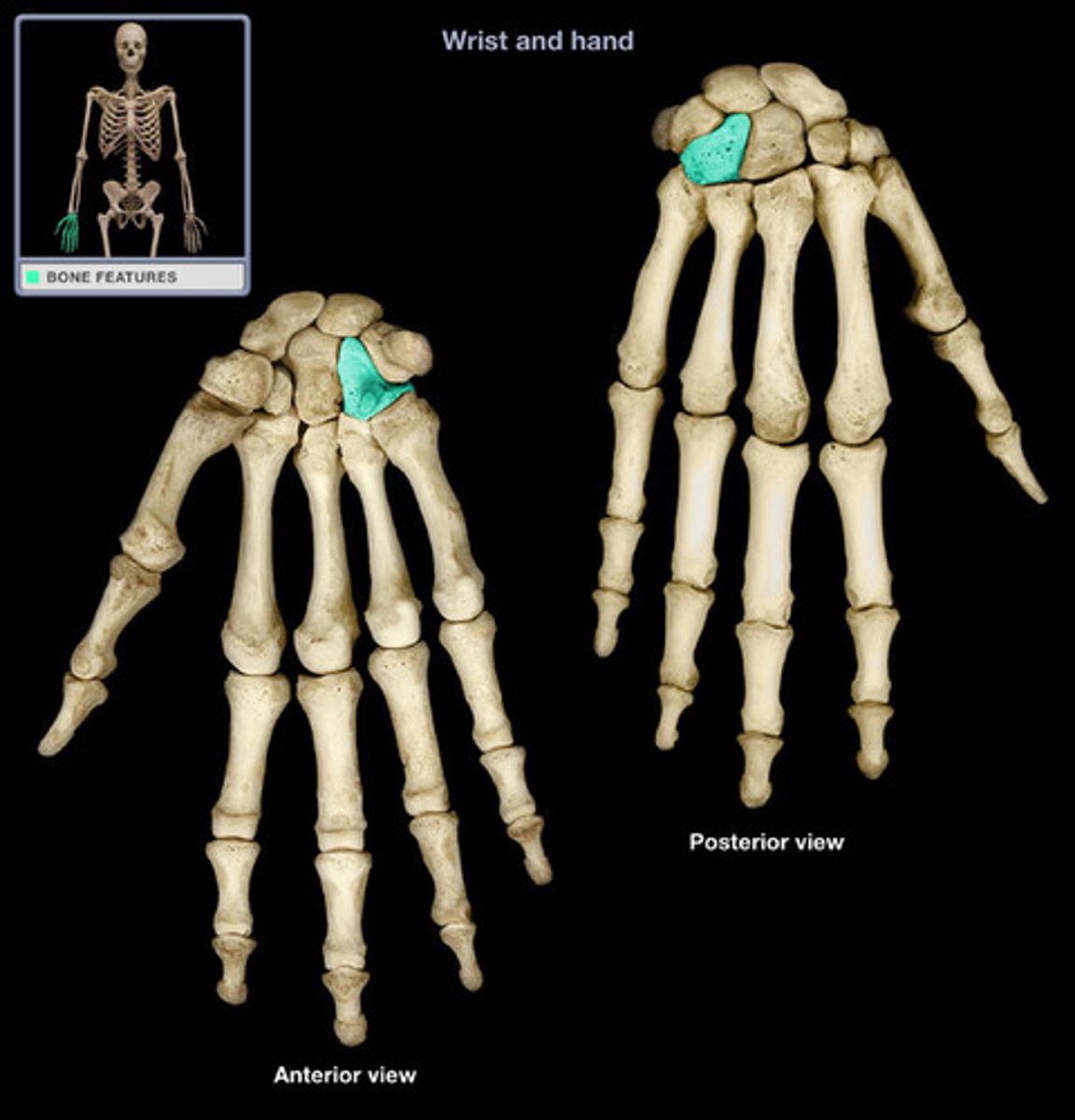
metacarpus
Bones of the palm of the hand; parts of the hand containing five bones between the carpus and phalanges.
Typically numbered with roman I-V
metacarpal I articulates with the pollex
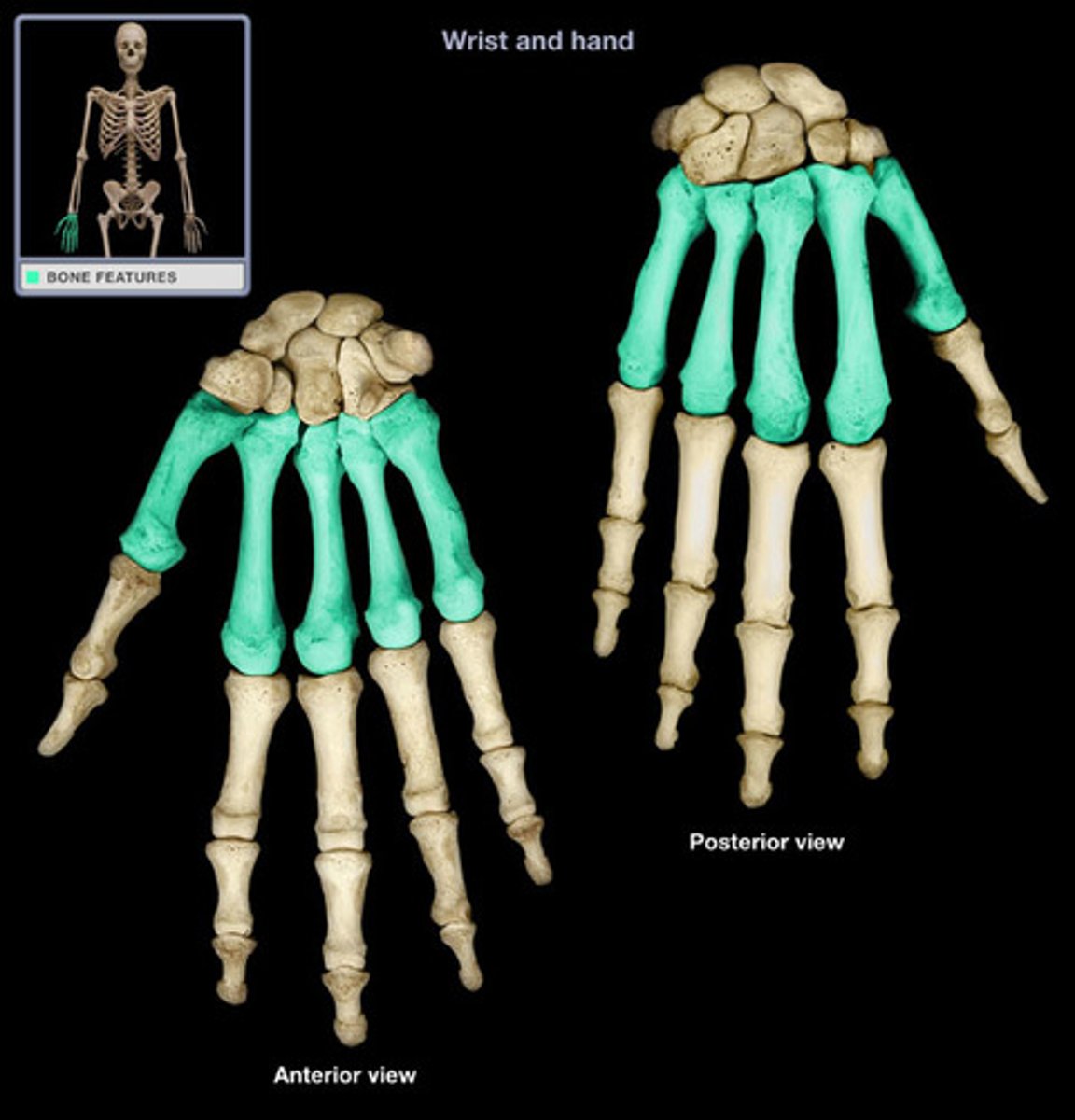
phalanges (hand)
finger bones (14 total)
pollex has 2 (medial and distal)
other phalanges have 3 (proximal, middle, and distal)
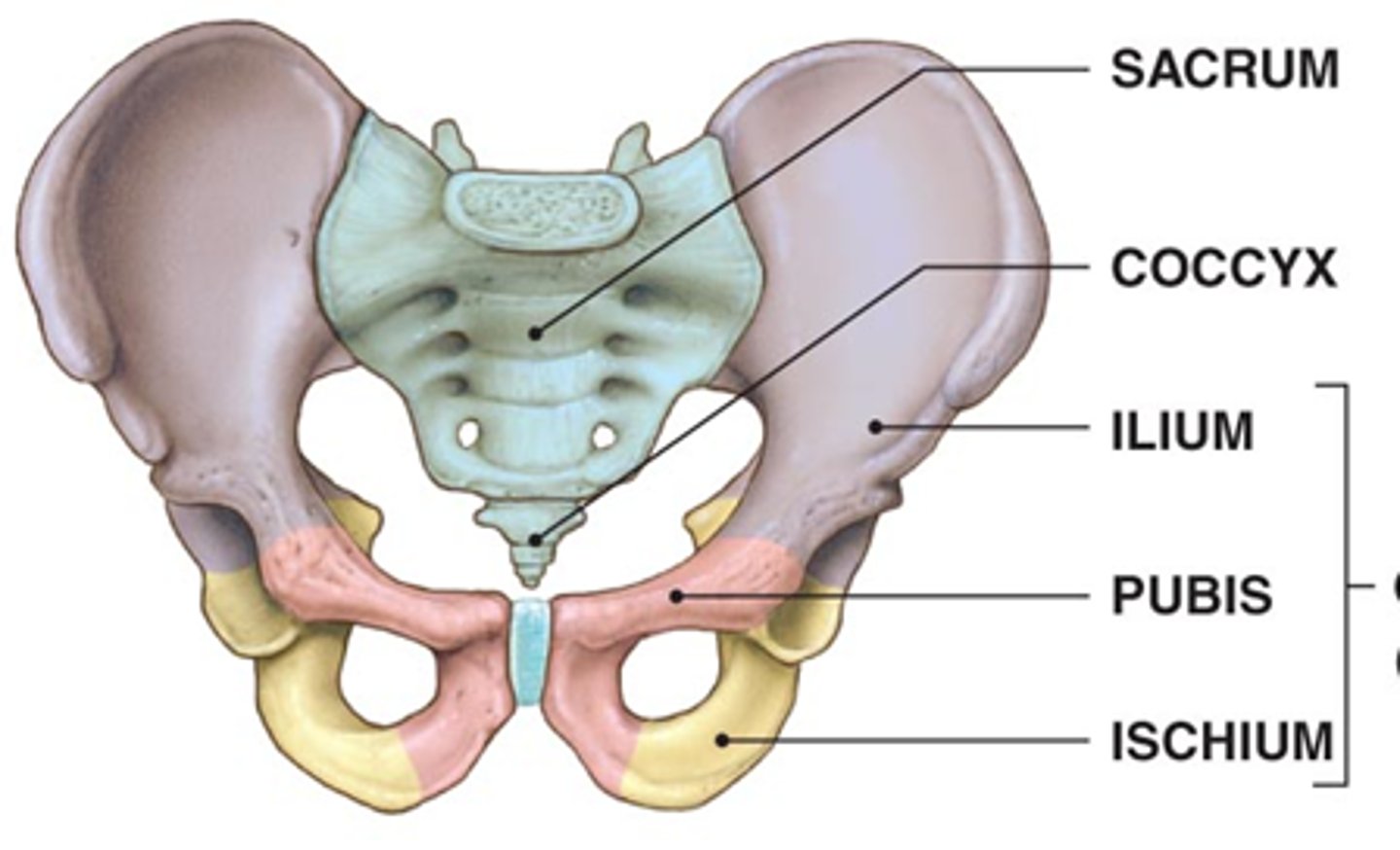
pelvic girdle
consists of 2 bones, the paired hip bones (coxal bones)
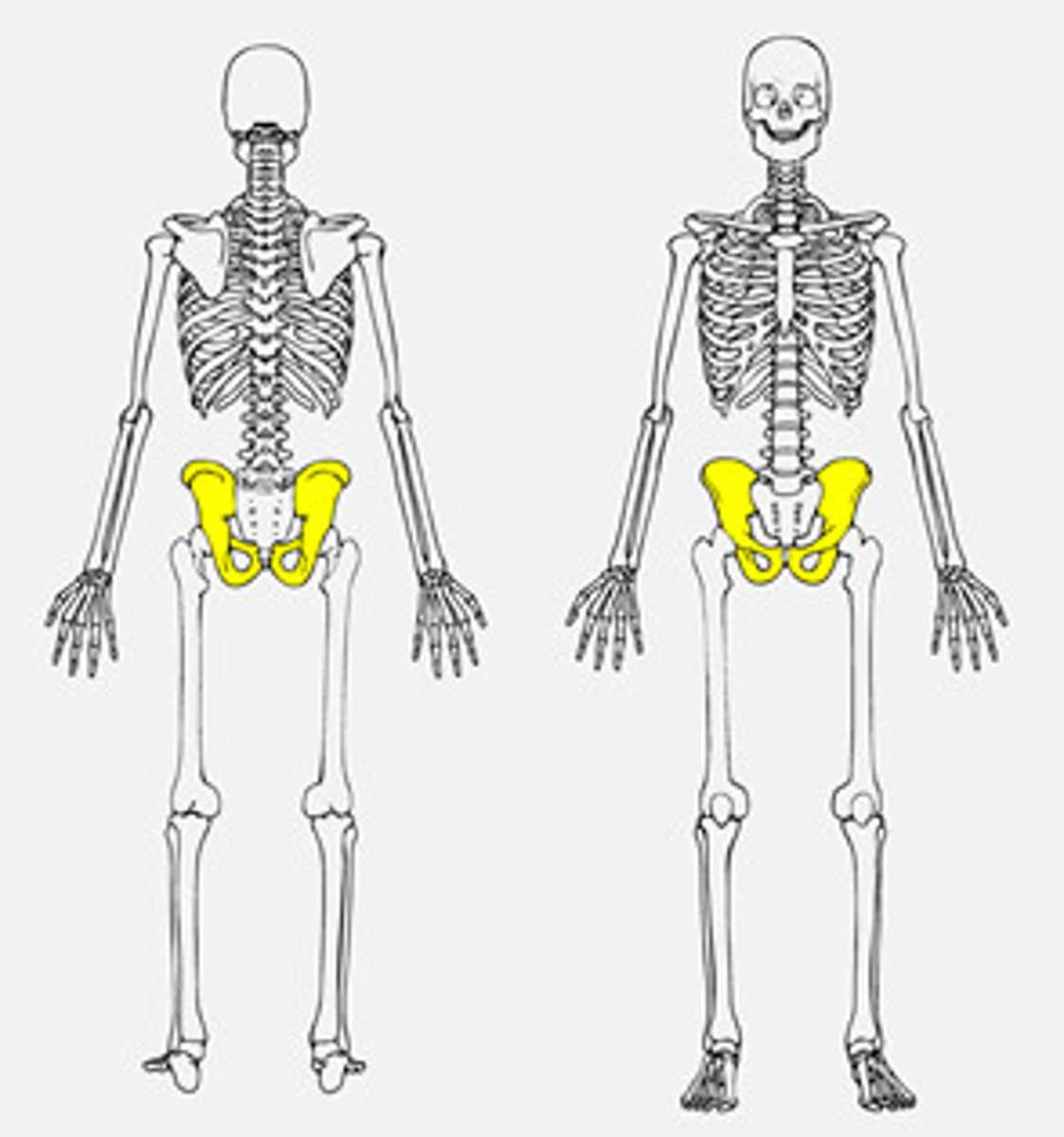
coxal bone
consists of 3 fused bones
1. ilium
2. ischium
3. pubis
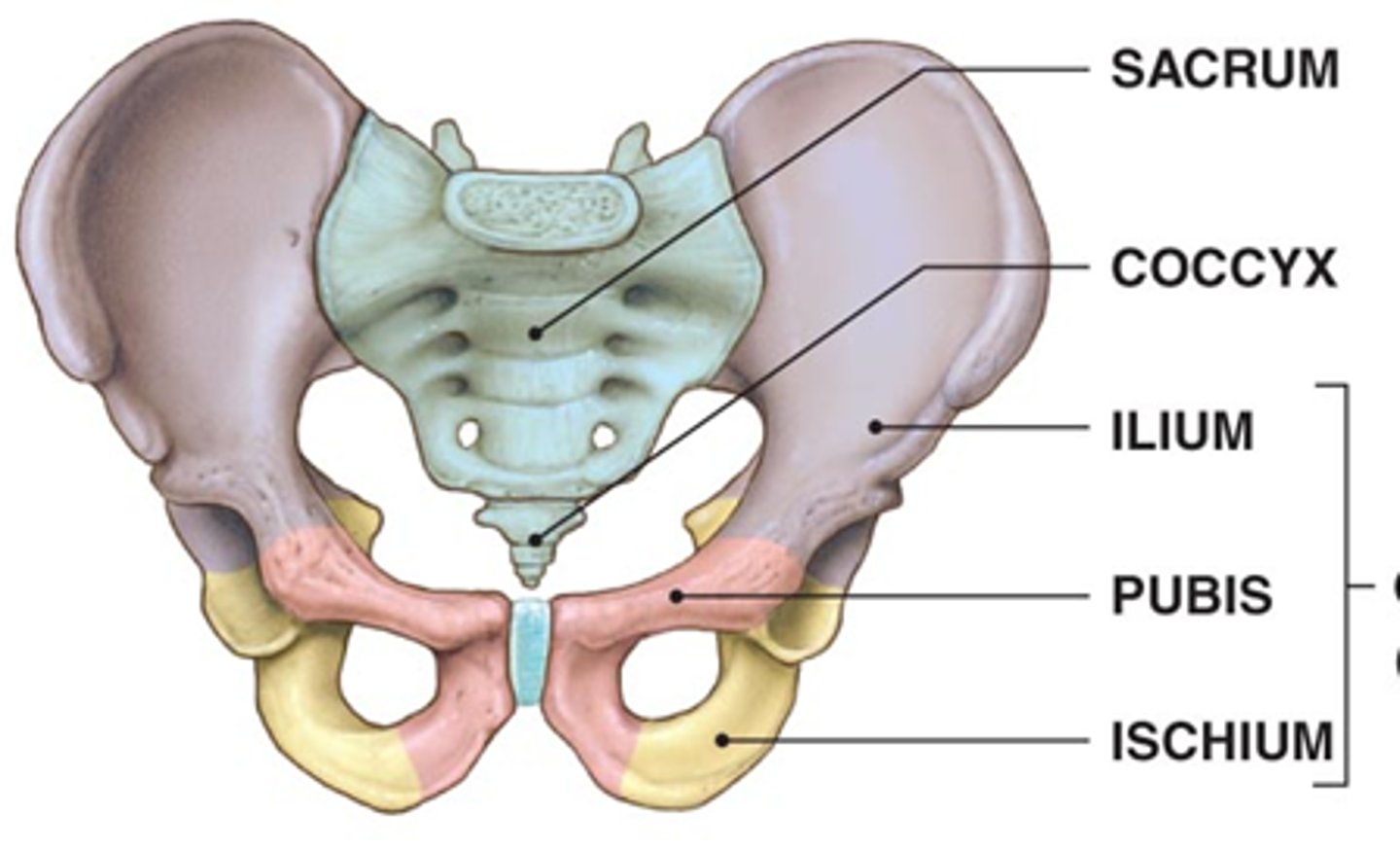
ilium
Name this specific region of the pelvic bone.
articulates with the sacrum
ischium
Name this specific region of the pelvic bone.
lies posterior to the anterior projecting pubis
pubis
Name this specific region of the pelvic bone.
the two hip bones articulate with each other via the pubic symphysis (between the two pubises)
projects anterior to the posterior angled ischium
acetabelum
concave socket on the lateral surface of each hip bone, articulates with the head of the femur
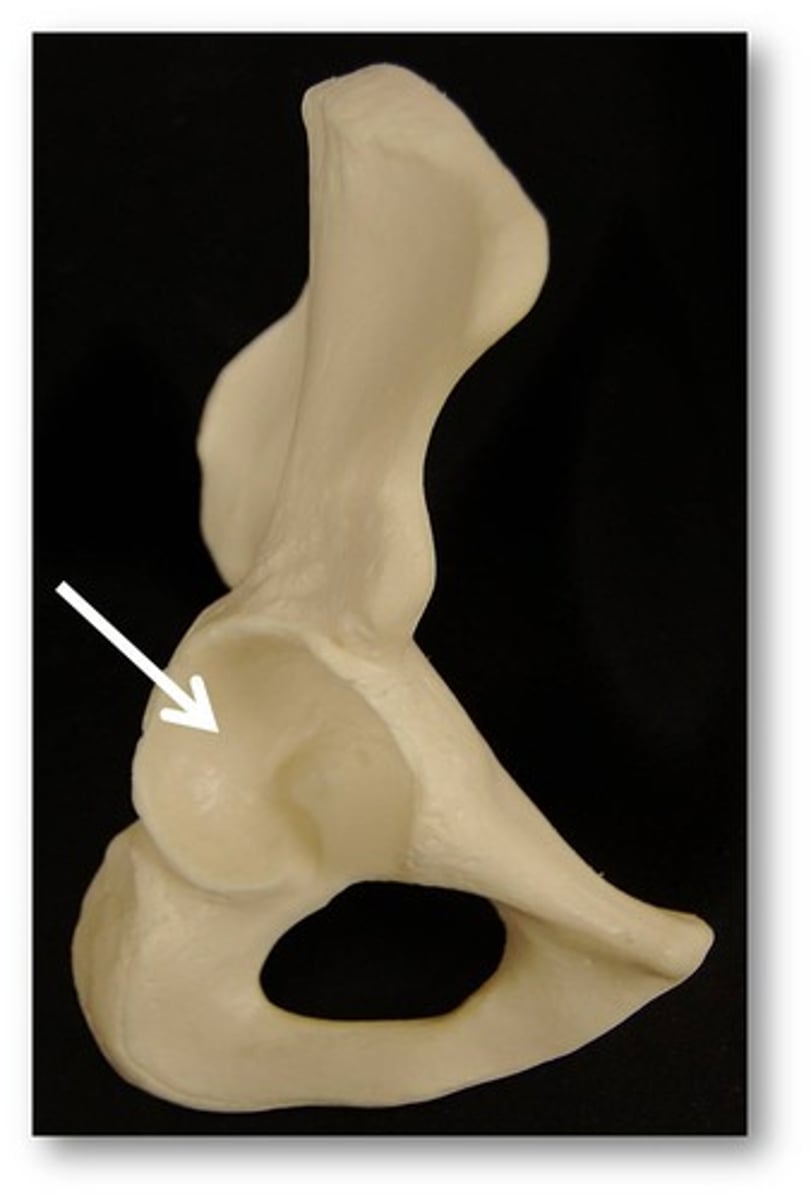
lunate surface
smooth, cup shaped articular surface of the acetabelum
greater sciatic notch
allows blood vessels and the large sciatic nerve to pass from the pelvis posteriorly into the thigh
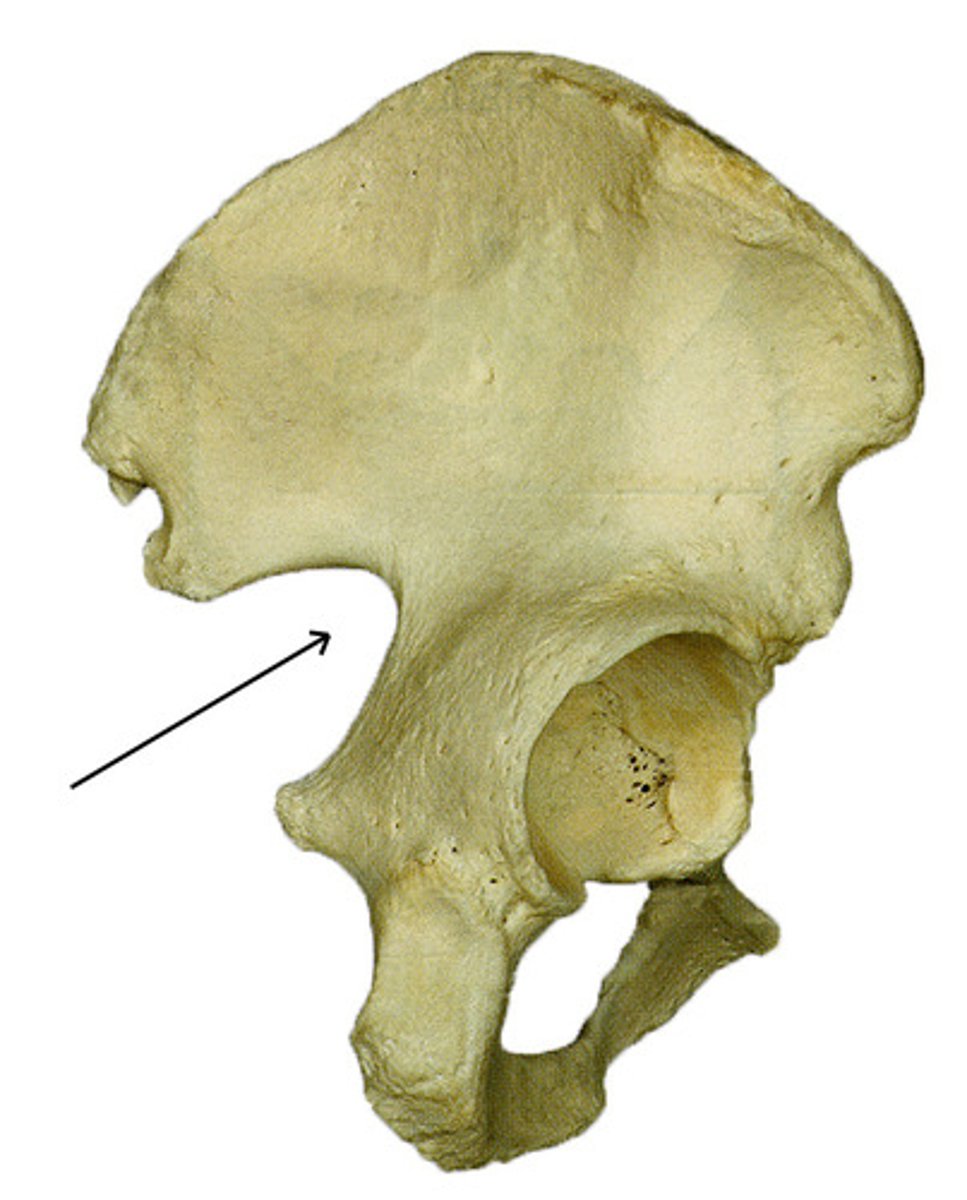
ischial spine
located superior to the ischial tuberosity and projects medially into the pelvic cavity
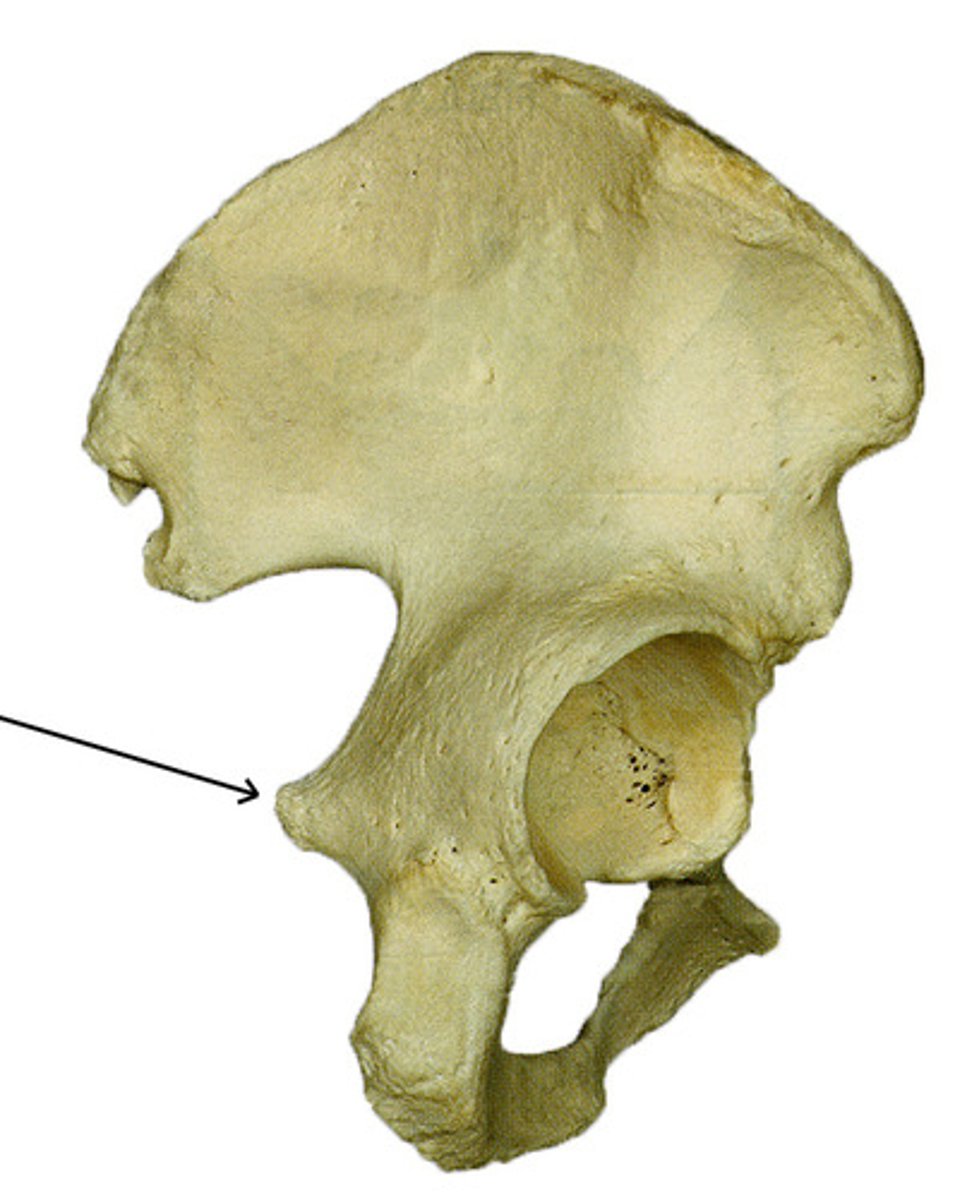
ischial ramus
narrow portion of the ischium that articulates with the inferior ramus of the pubis
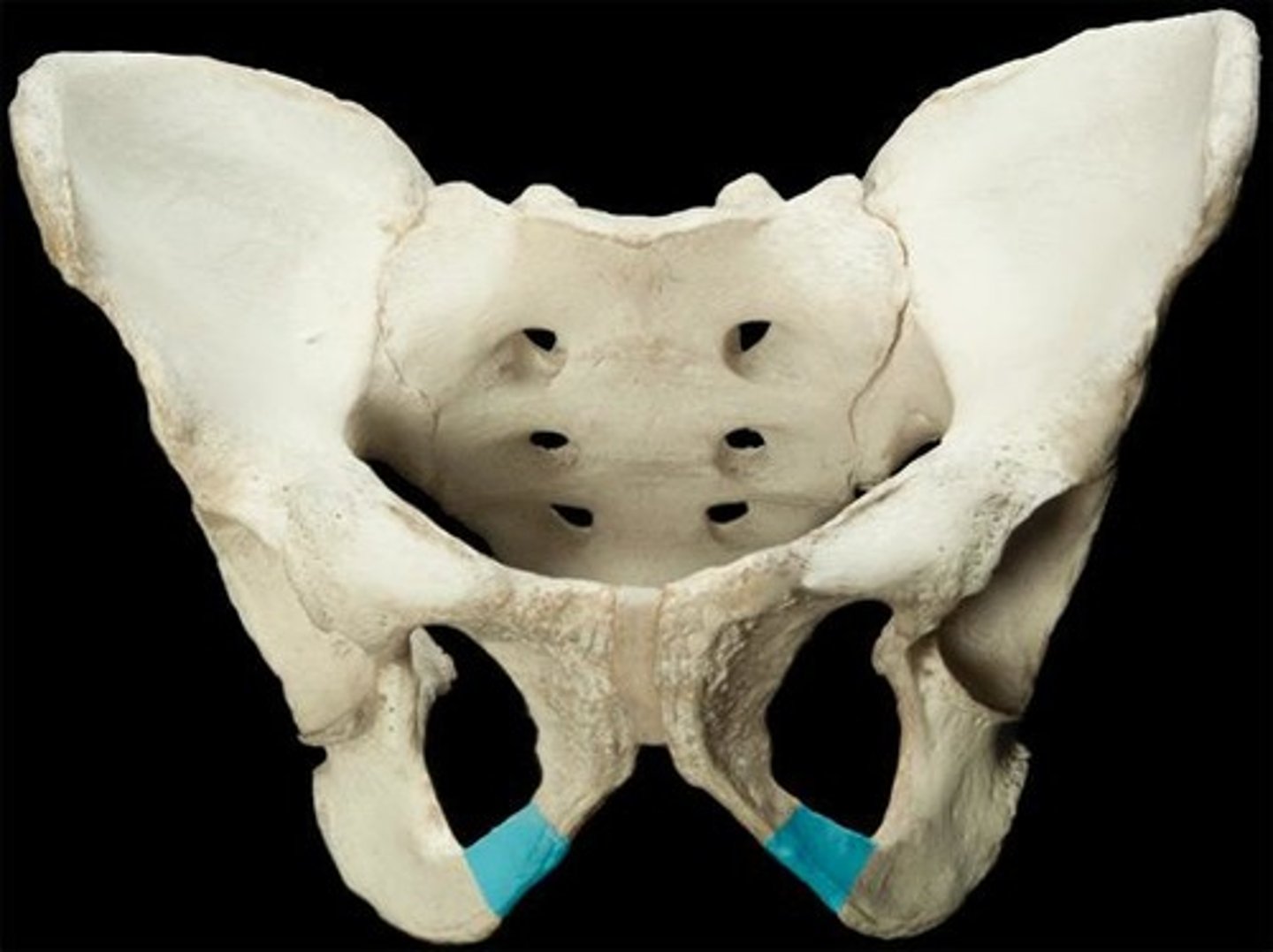
superior ramus (pubis)
Name this specific region of the pelvic bone.
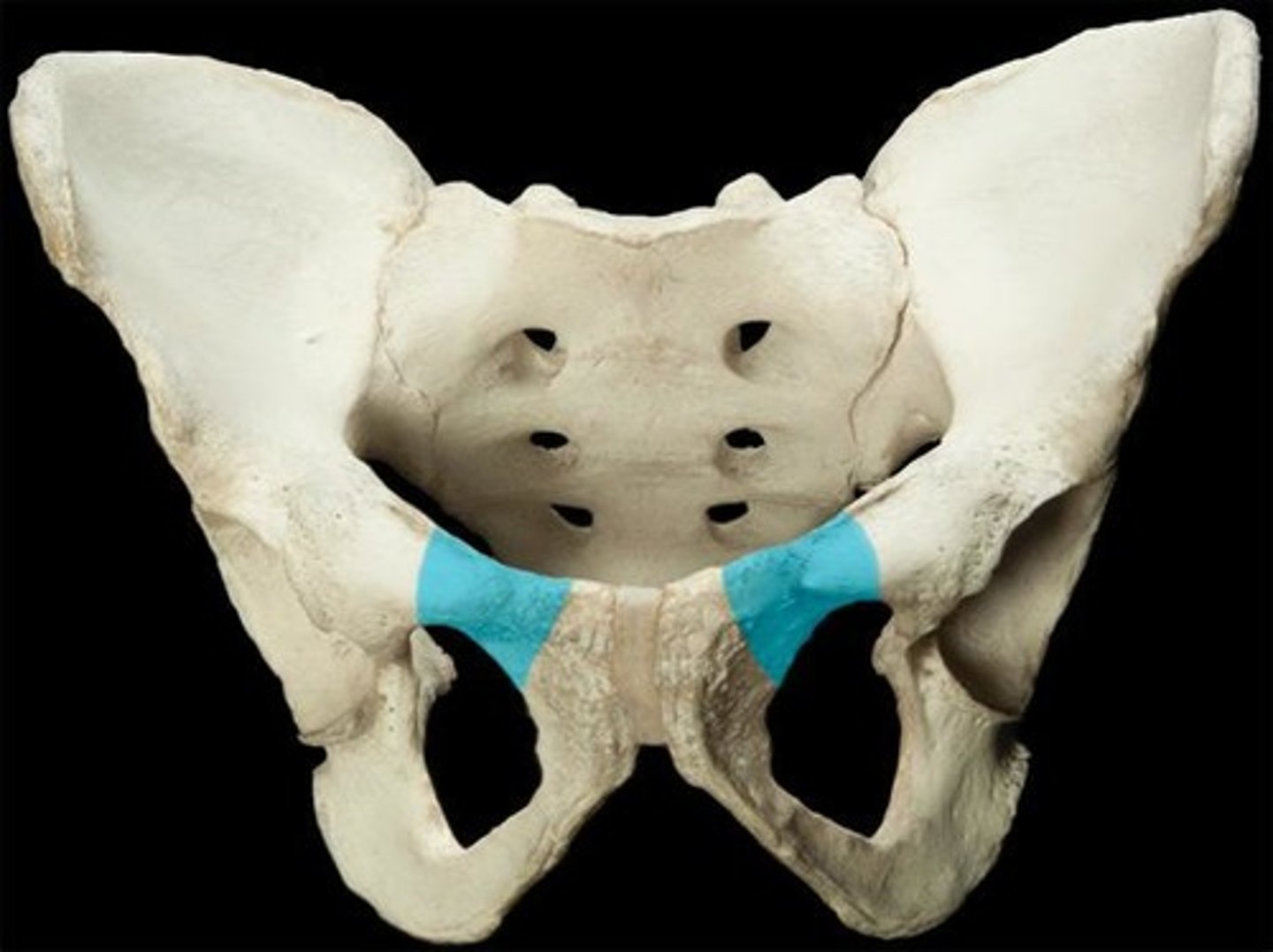
inferior ramus
located between ischial ramus and superior ramus
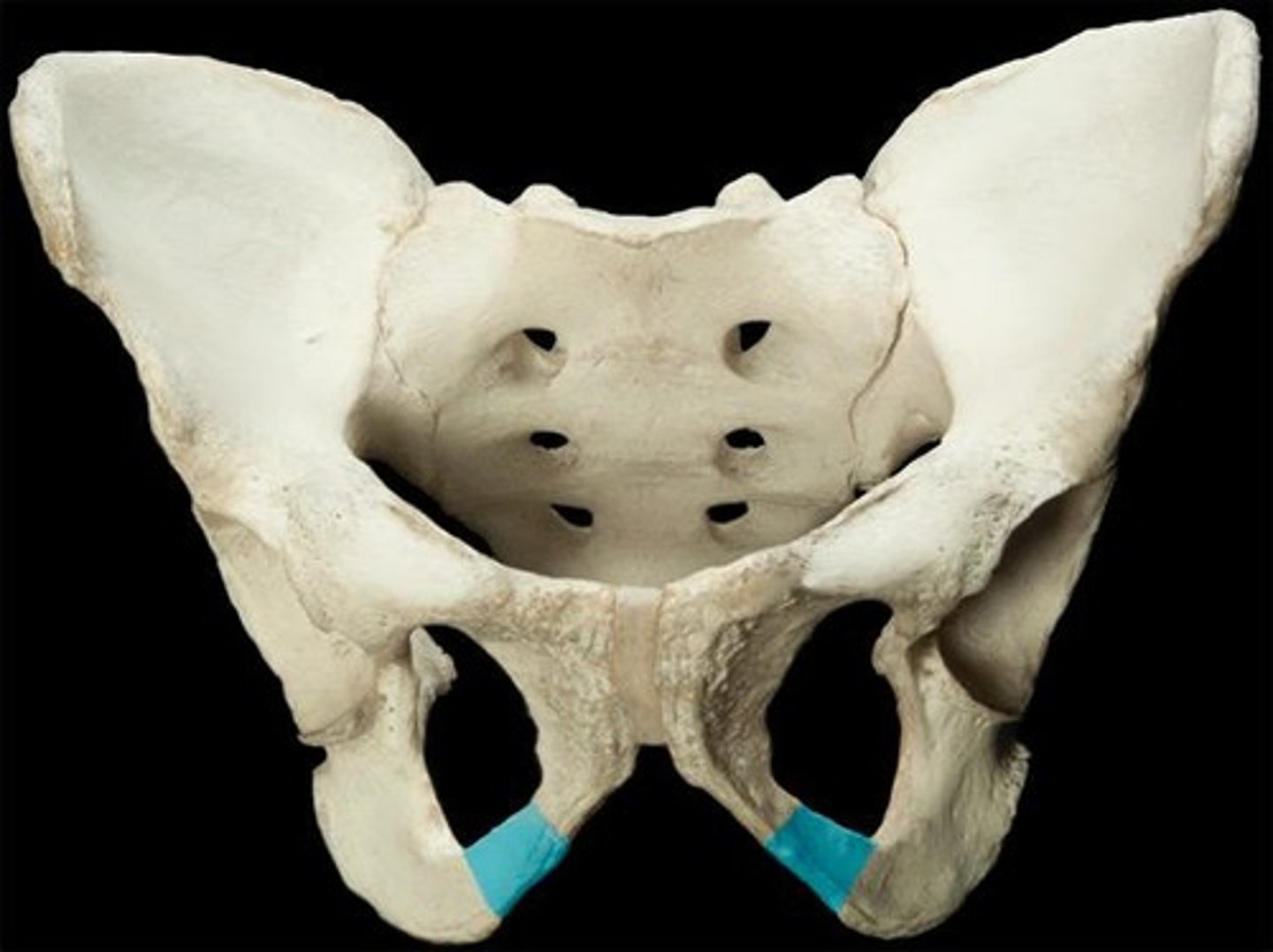
obturator foramen
opening in hip bone formed by the pubic and ischial rami
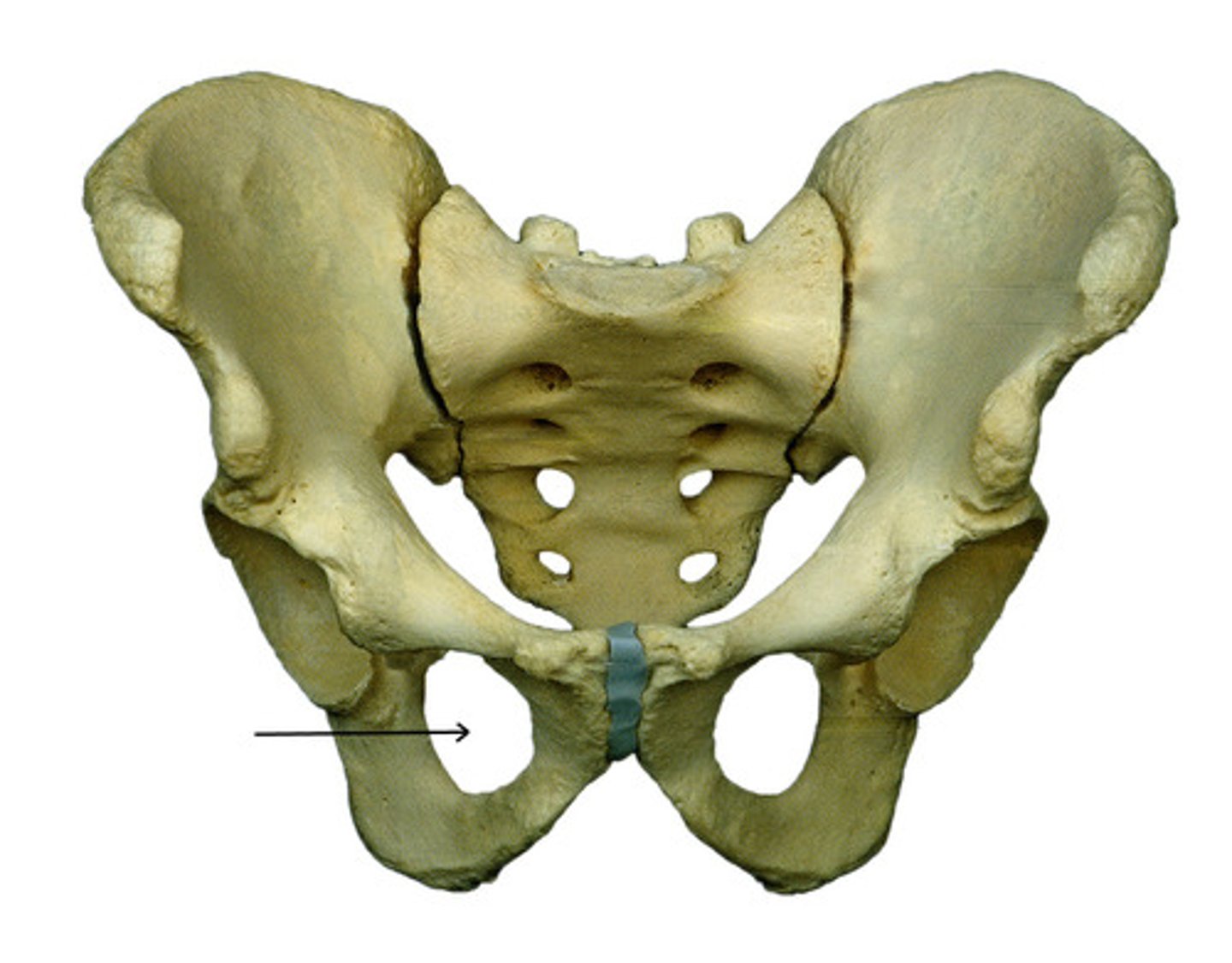
sacroiliac joint
The connection point between the pelvis and the vertebral column.
The ilium articulates with the sacrum.
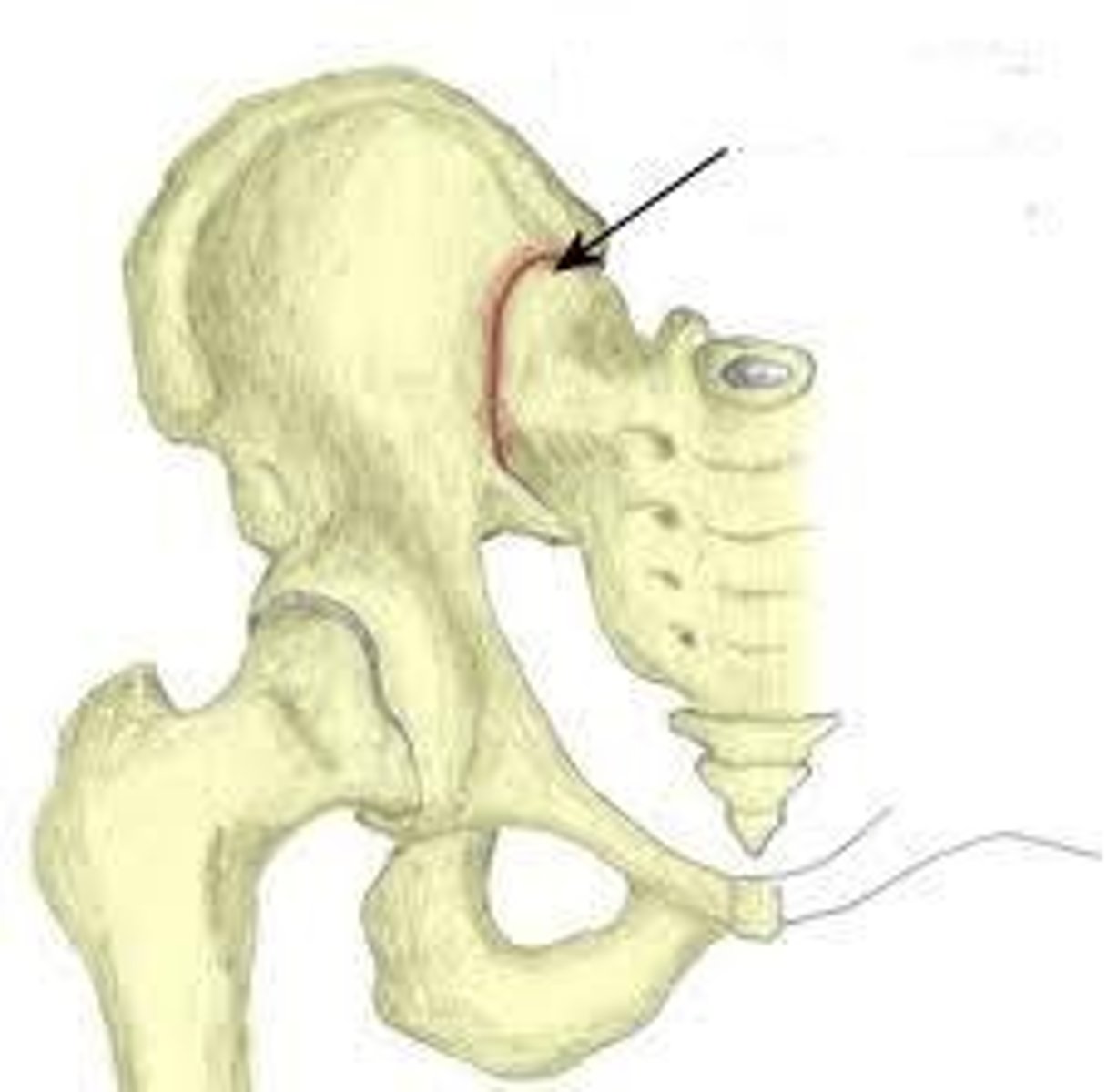
arcuate line
Name this specific region of the pelvic bone.
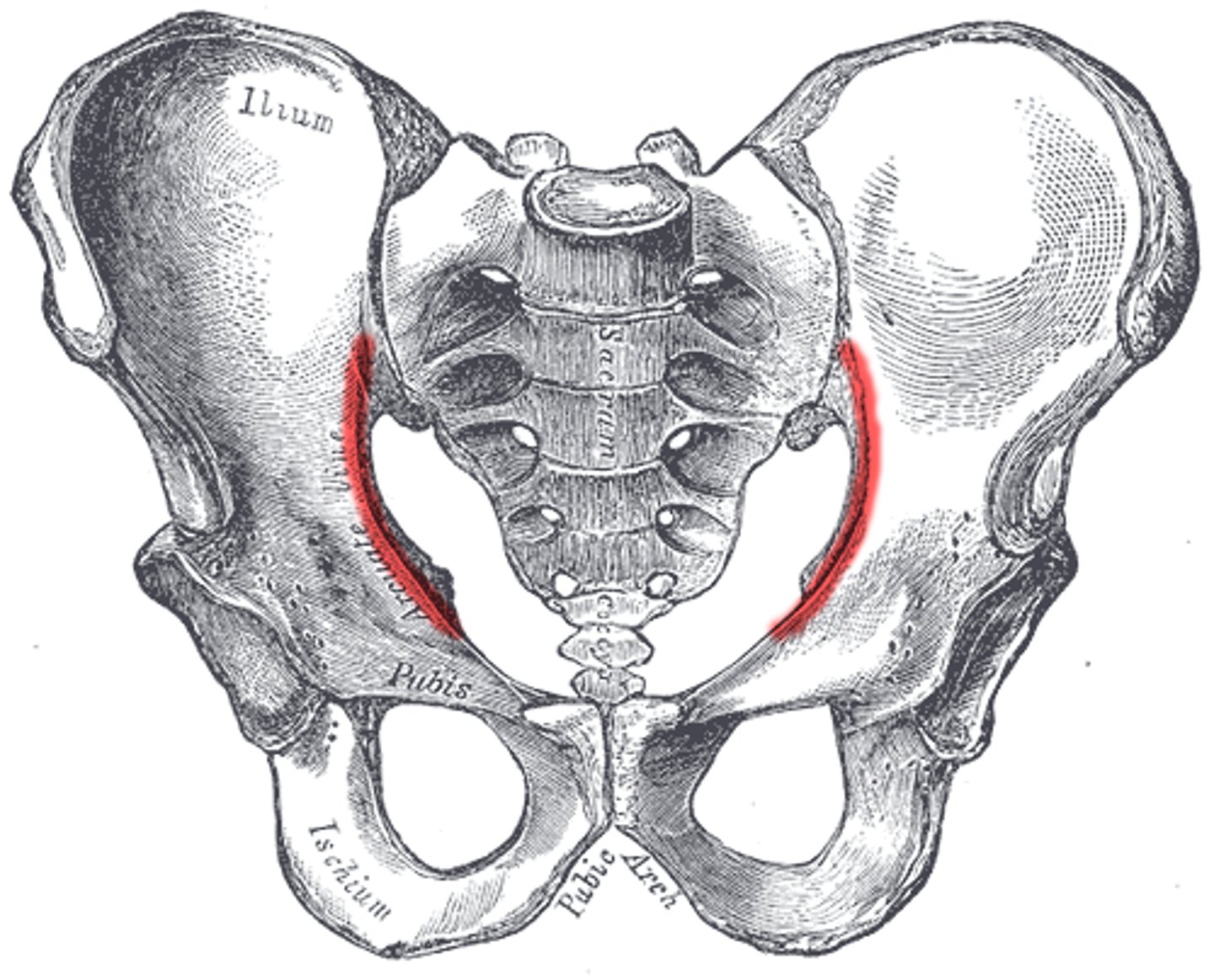
true pelvis (lesser pelvis)
surrounded by bone and lies inferior to flaring parts of the ilia; passage for infant at birth in women
encloses the pelvic cavity
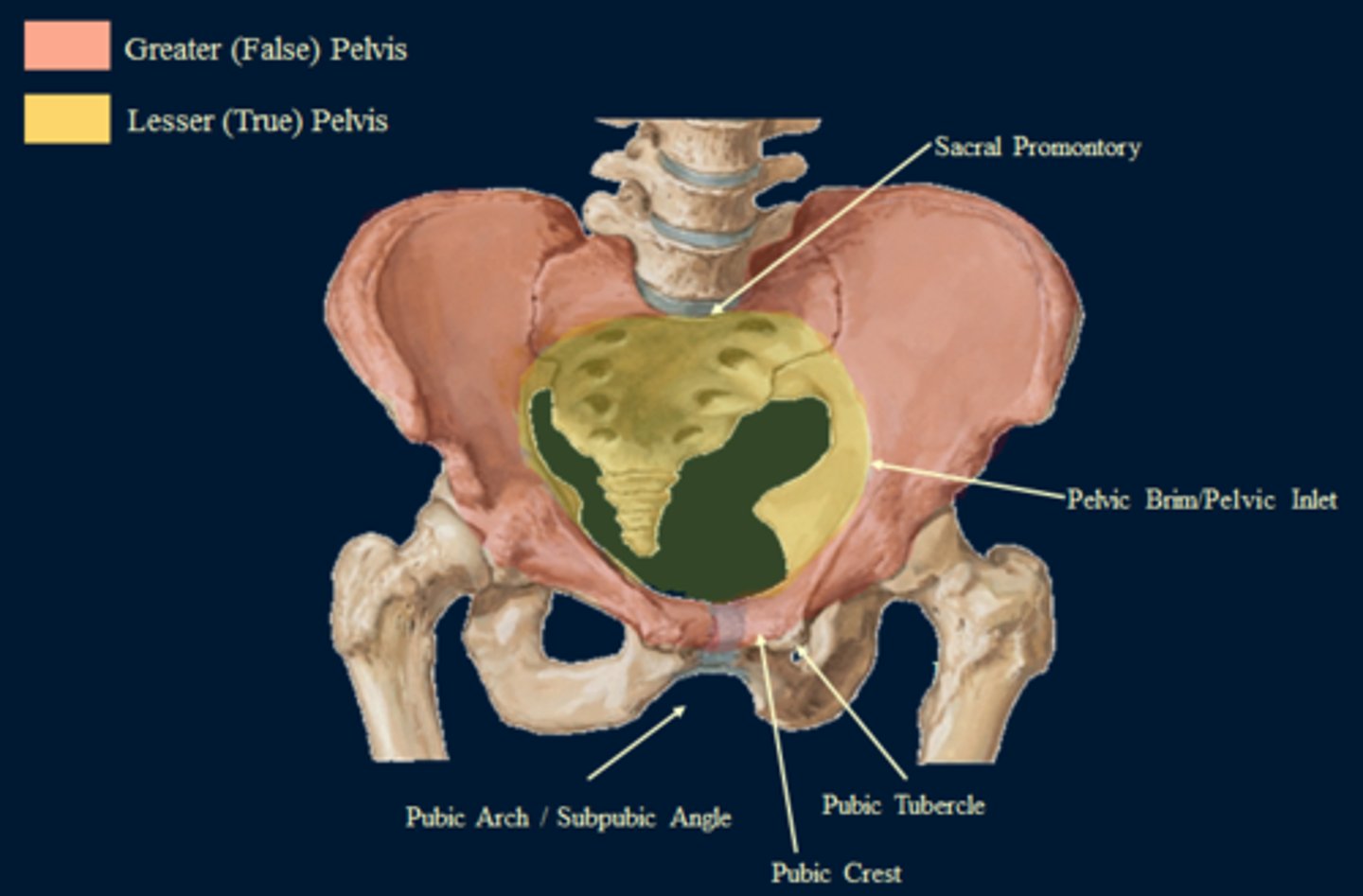
false pelvis (greater pelvis)
superior to the true pelvis; it is the area medial to the flaring portions of the ilia
the blades of the ilium superior to the arcuate line
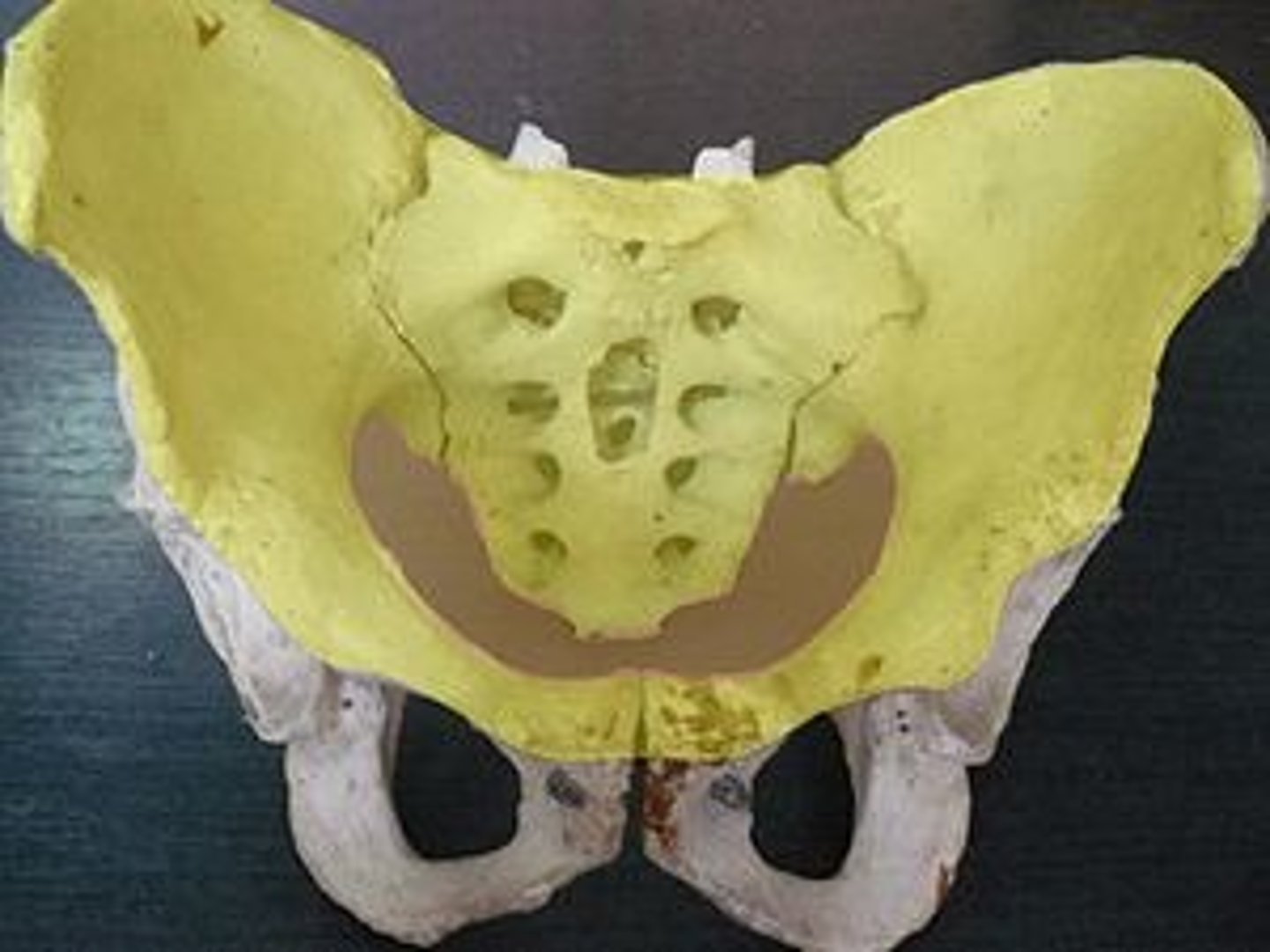
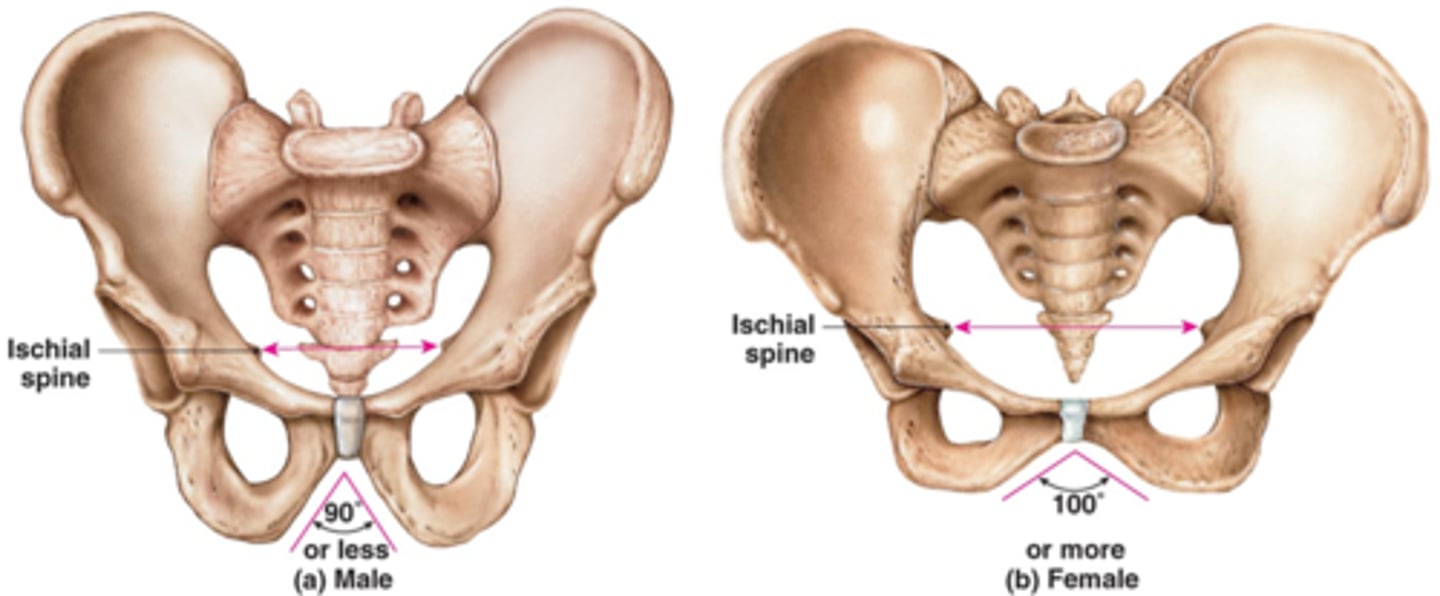
female vs. male (pelvis)
female has wider hips - broader false pelvis
female has wider pelvic brim
pubic arch is obtuse (u-shaped) in female, acute (v-shaped) in males
true pelvis is shallower and wider in female
female has a wider pelvic outlet
Female pelvis- smoother & lighter
Less prominent muscle & ligament attachments
Modifications for childbearing
enlarged pelvic outlet, broad pubic angle
less curvature of sacrum and coccyx
wide, circular pelvic inlet
lower limb
1. femur
2. patella
3. tibia
4. fibula
5. foot
leg
distal portion of the lower extremity
thigh
The proximal portion of the lower extremity; the portion lying between the hip joint and knee.
femur
thigh bone; longest and heaviest bone in the body
articulates with the pelvis at the acetabelum
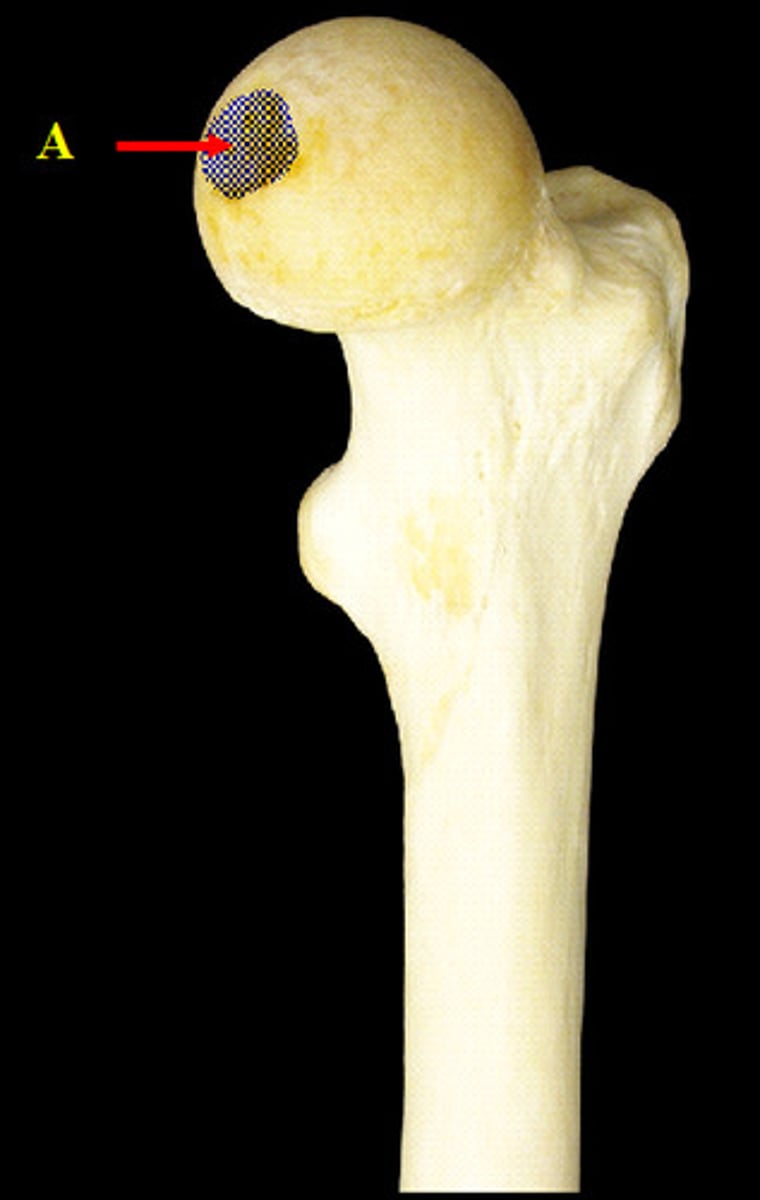
fovea capitis (femur)
pit in the head of a femur, where the femur articulates with the acetabelum
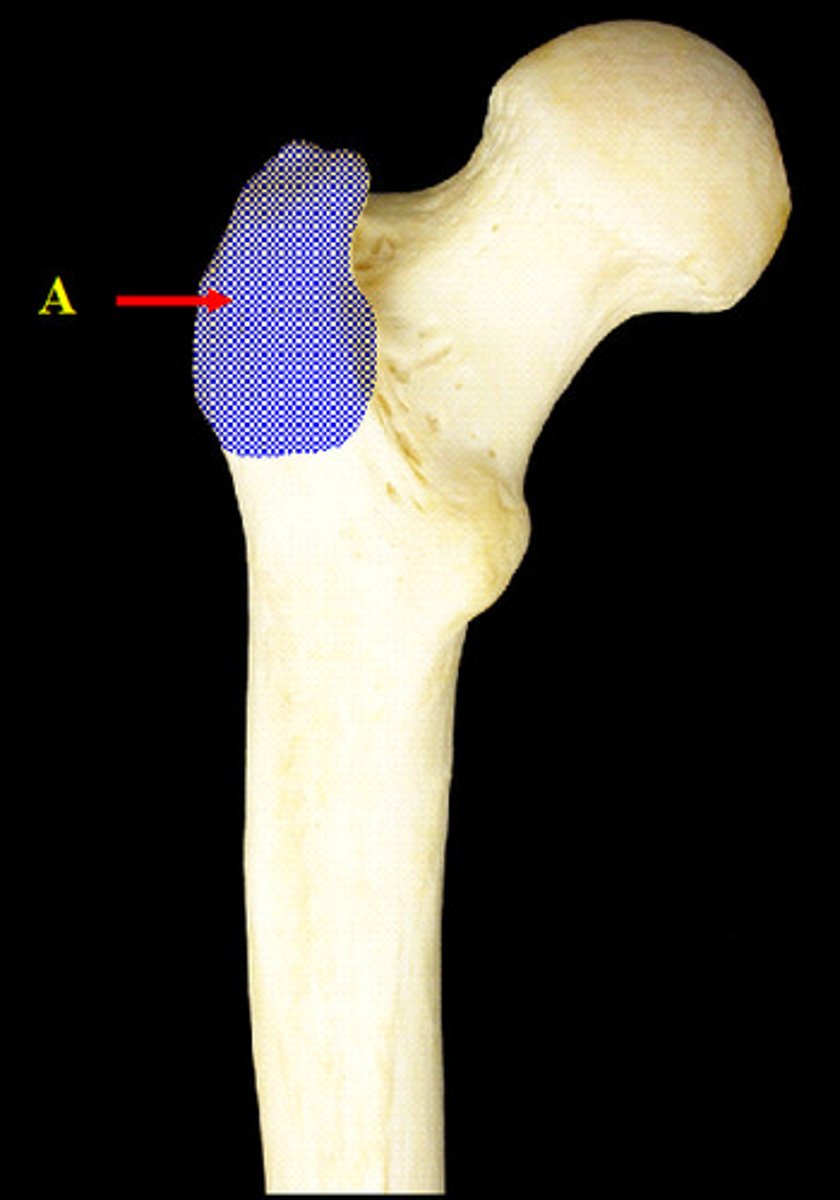
trochanters (femur)
greater and lesser on proximal shaft; Greater lateral to neck and larger, Lesser inferior and posterior to neck; Attachments for muscles that fasten lower extremites to hip; Greater/muscles form bulge that is seen as widest part of hips
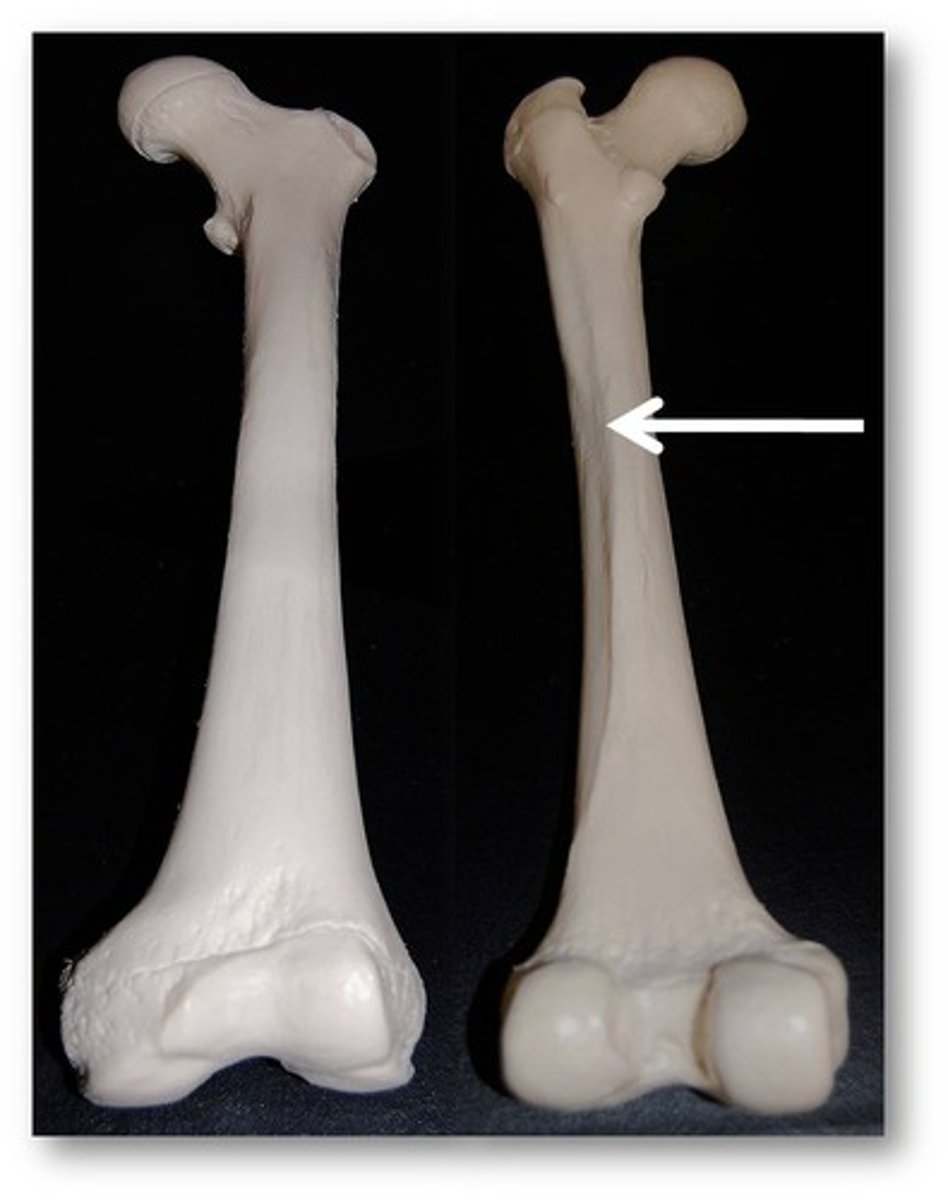
linea aspera
Name this specific part of the femur.
rough ridge that runs along posterior of femur
attachment site for hip muscles
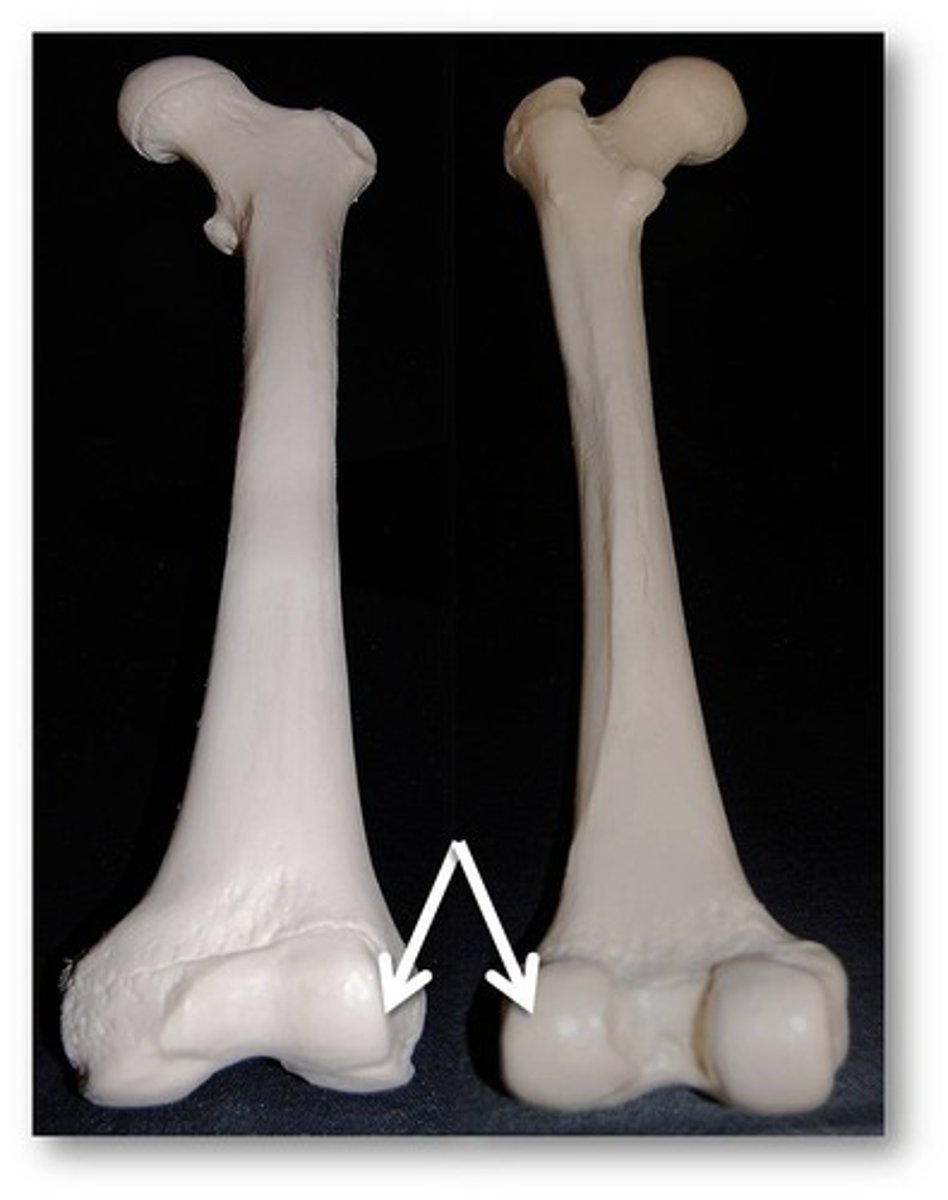
epicondyles (femur)
medial and lateral; located proximally to condyles; ligament attachment;
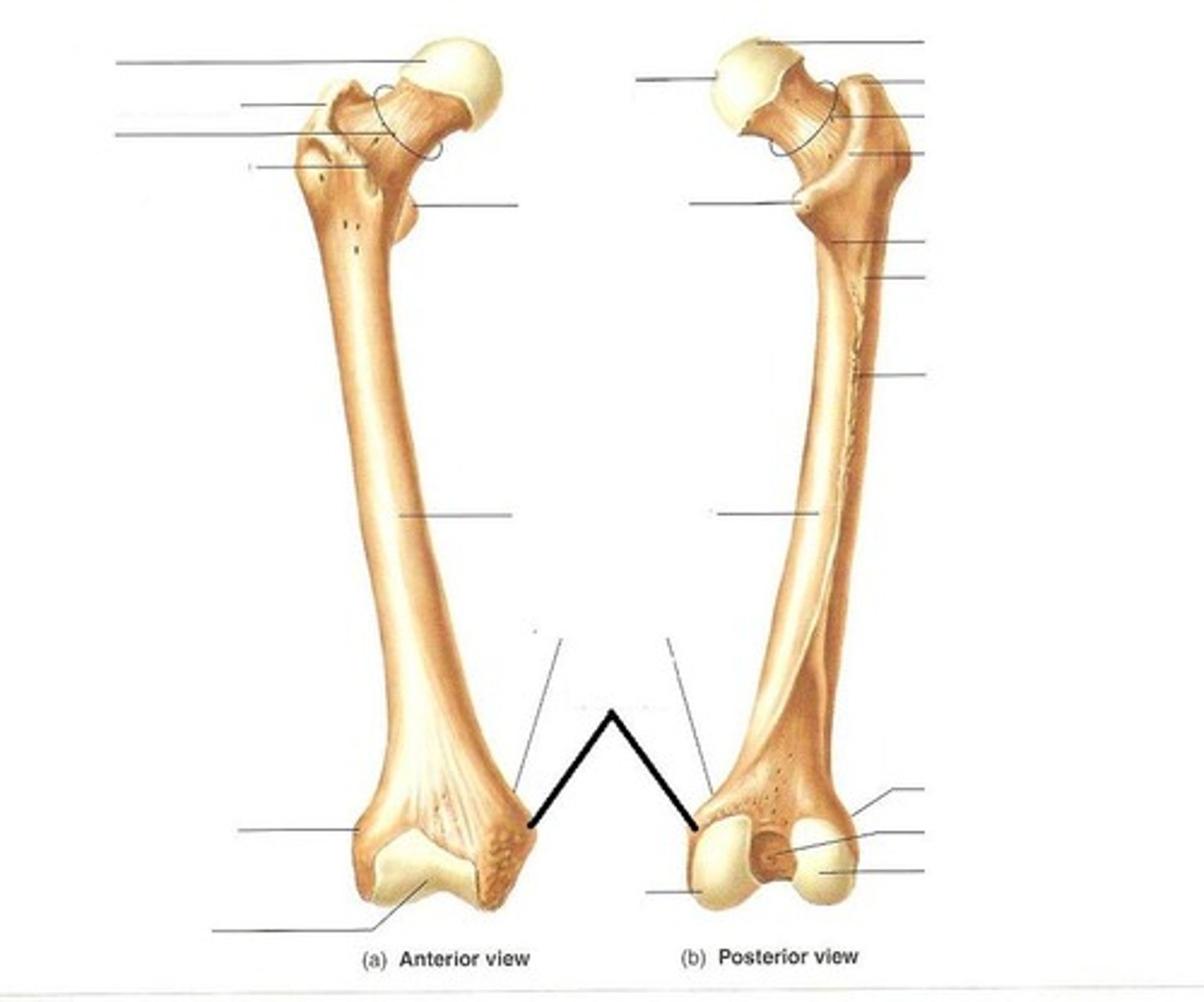
condyles (femur)
medial and lateral; located inferior to epicondyles of femur; part of the knee joint
patella
large, sesamoid bone that forms within the tendon of the quadriceps femoris
direction of movement is superior-inferior (up and down)
patellar base
Broad, superior portion (round side) of patella
patellar apex
Pointed inferior part of patella
Rough surface is point of attachment for patellar tendon
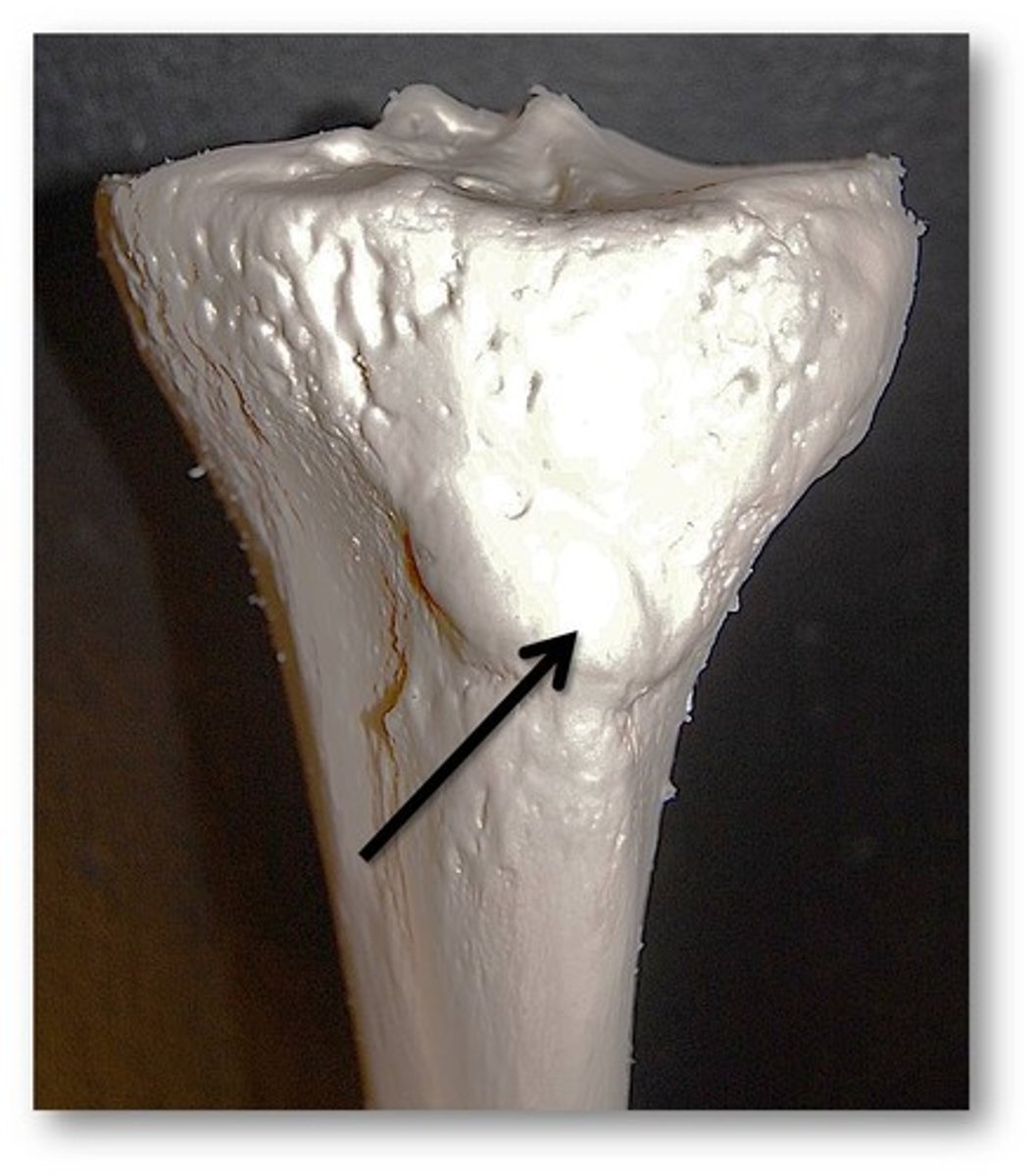
tibia
"shinbone"; large medial bone of the leg
tibial tuberosity
Name this specific part of the tibia.
fibula
calf bone; does not transfer weight to ankle and foot
does not articulate with femur
but it is an important site for muscle attachments that move the foot and toes
interosseous membrane of leg
sheet of dense connective tissue that unites the shafts of the tibia and fibula bones
lateral malleolus
distal end of fibula; a fibular process that extends lateral to the ankle joint
gives lateral stability to the ankle

medial malleolus
distal process on medial tibial surface, gives the ankle medial support
tarsus
ankle; consists of 7 tarsal bones
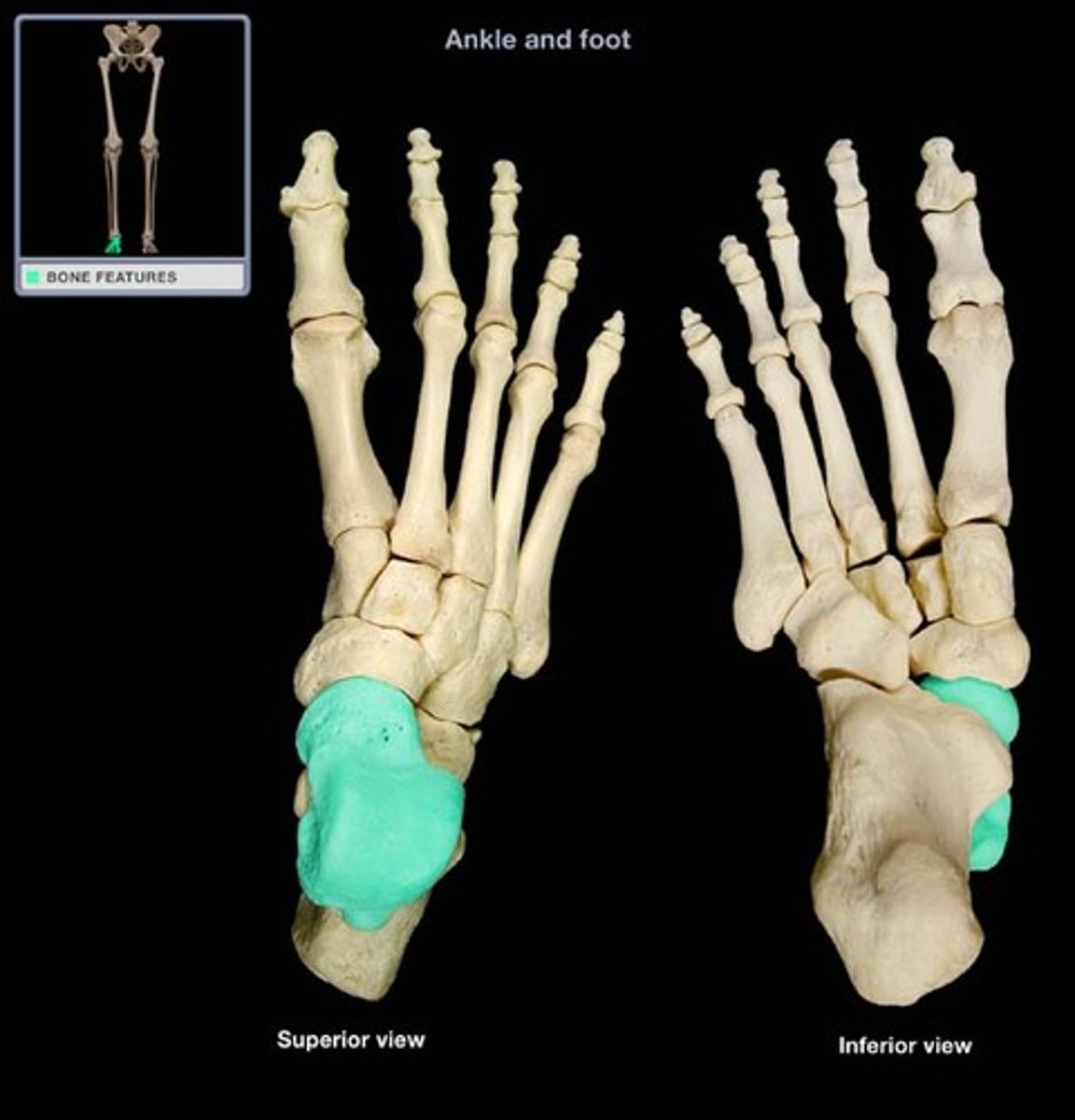
talus
Name this specific bone of the foot.
articulates with the tibia across the trochlea
calcaneus
heel bone
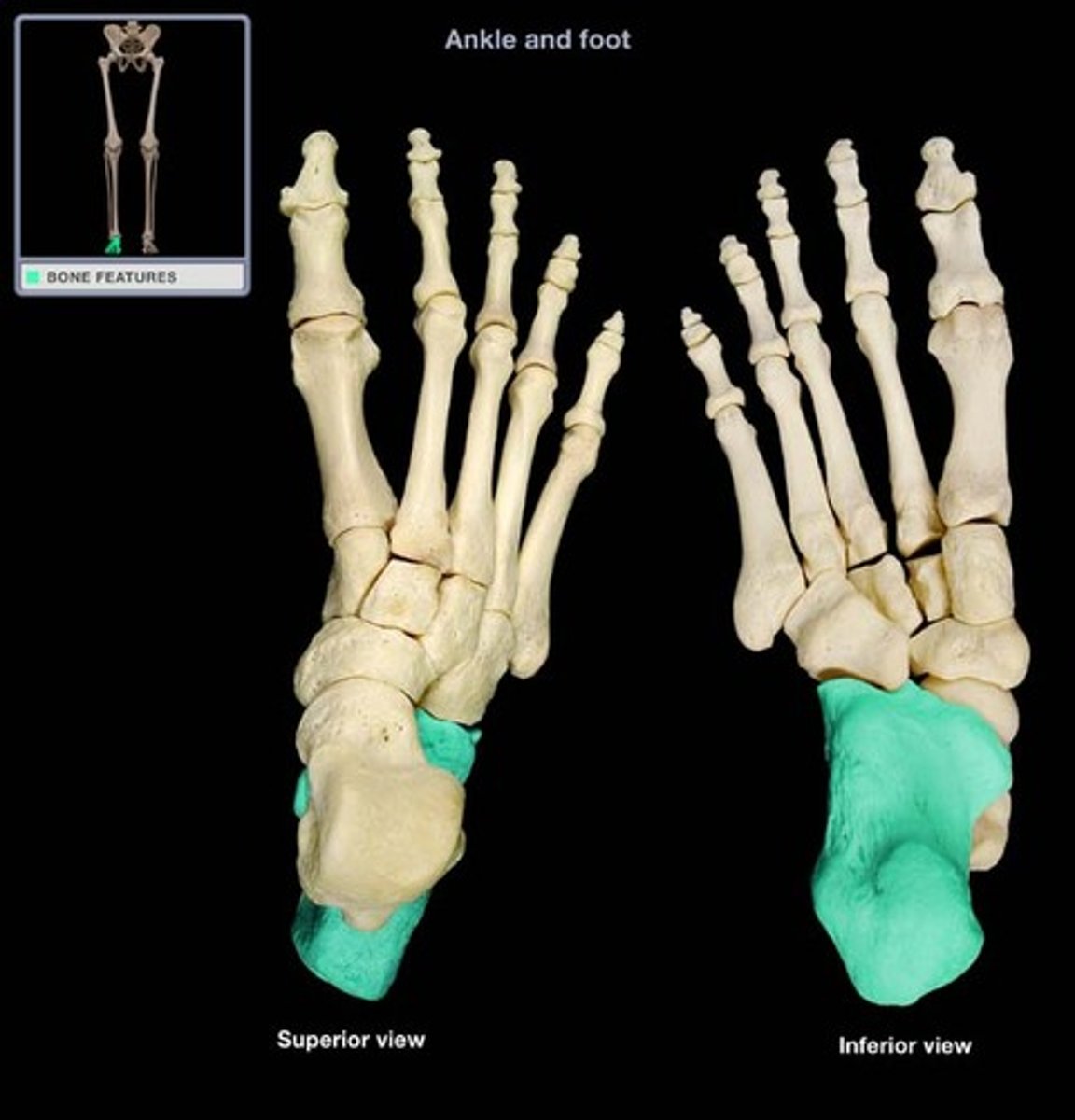
calcaneal tendon
achilles tendon, attaches at posterior of calcaneus
cuboid
Name this specific bone of the foot.
anterior to the calcaneus
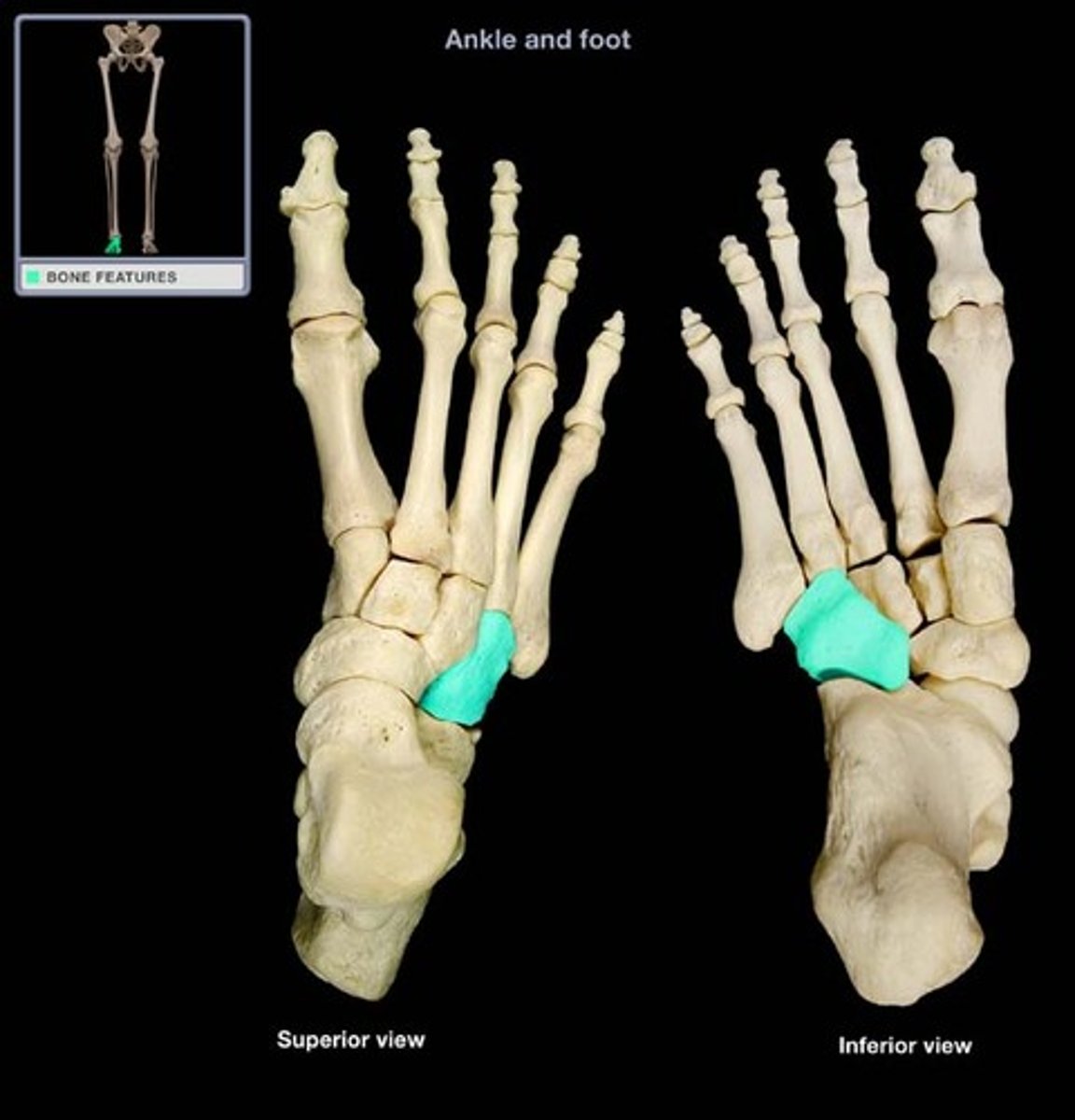
navicular
Name this specific bone of the foot.
anterior to the talus
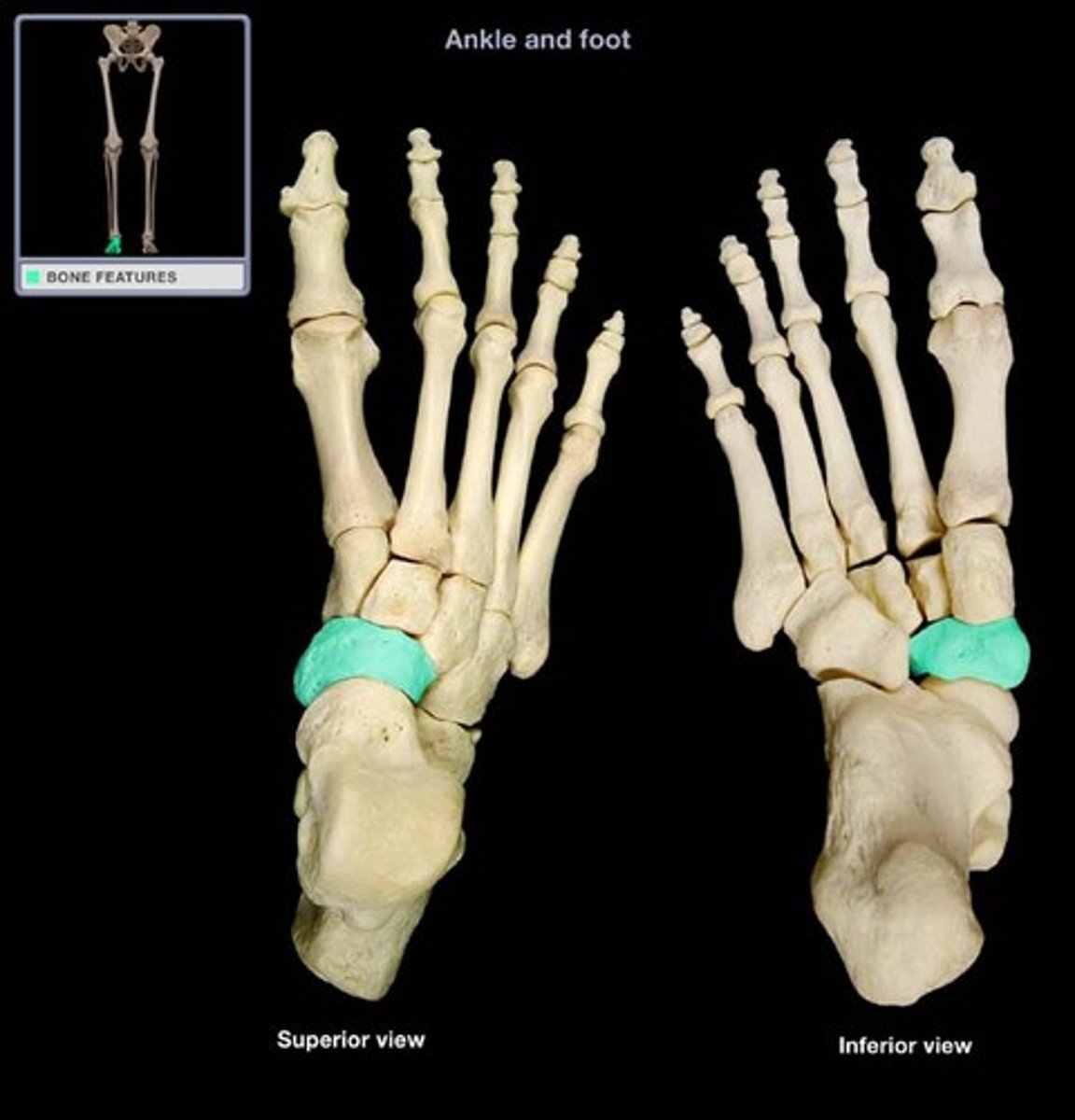
cuneiform bones
row of three bones distal to the calcaneus/talus
medial, intermediate, lateral
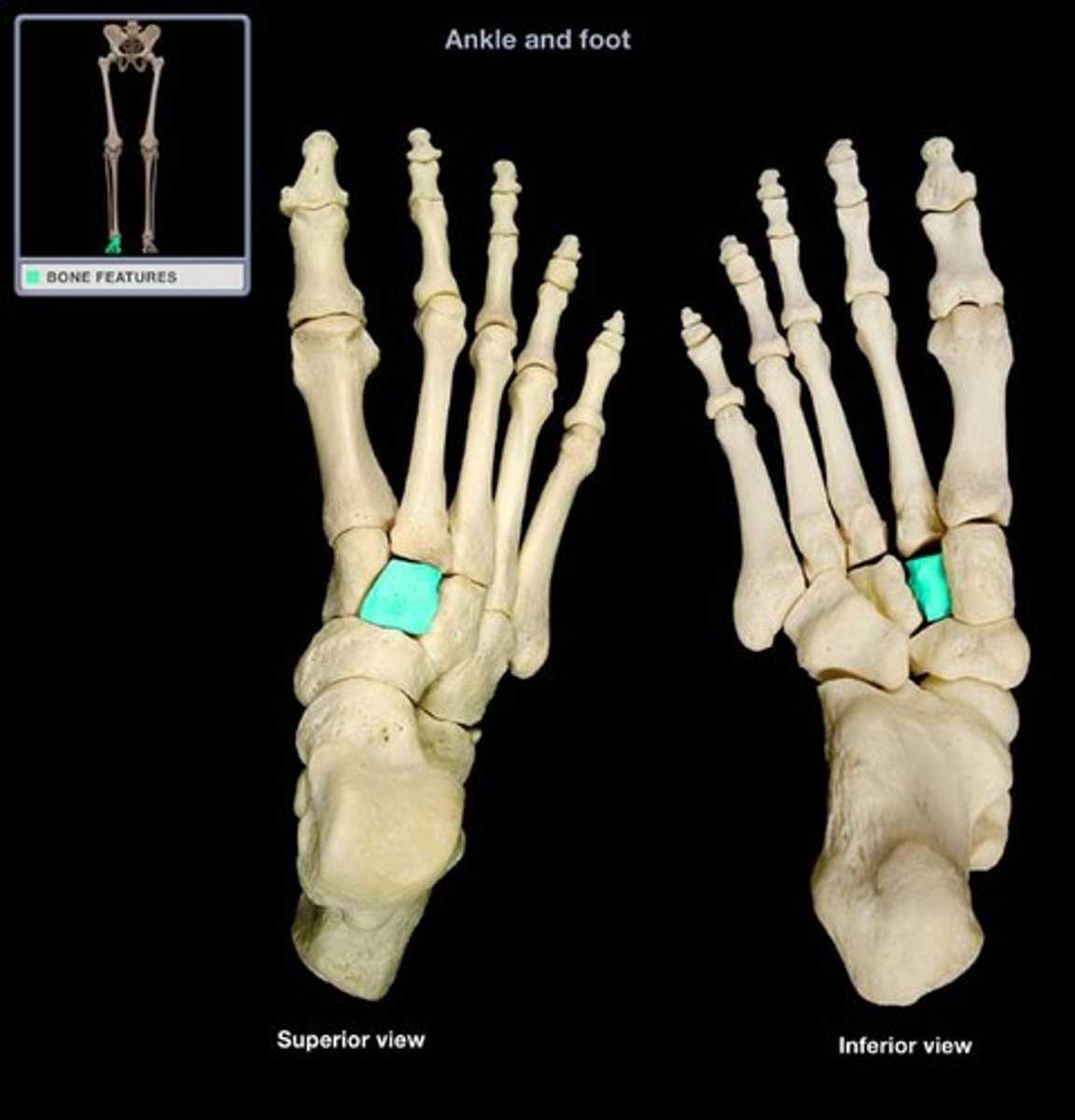
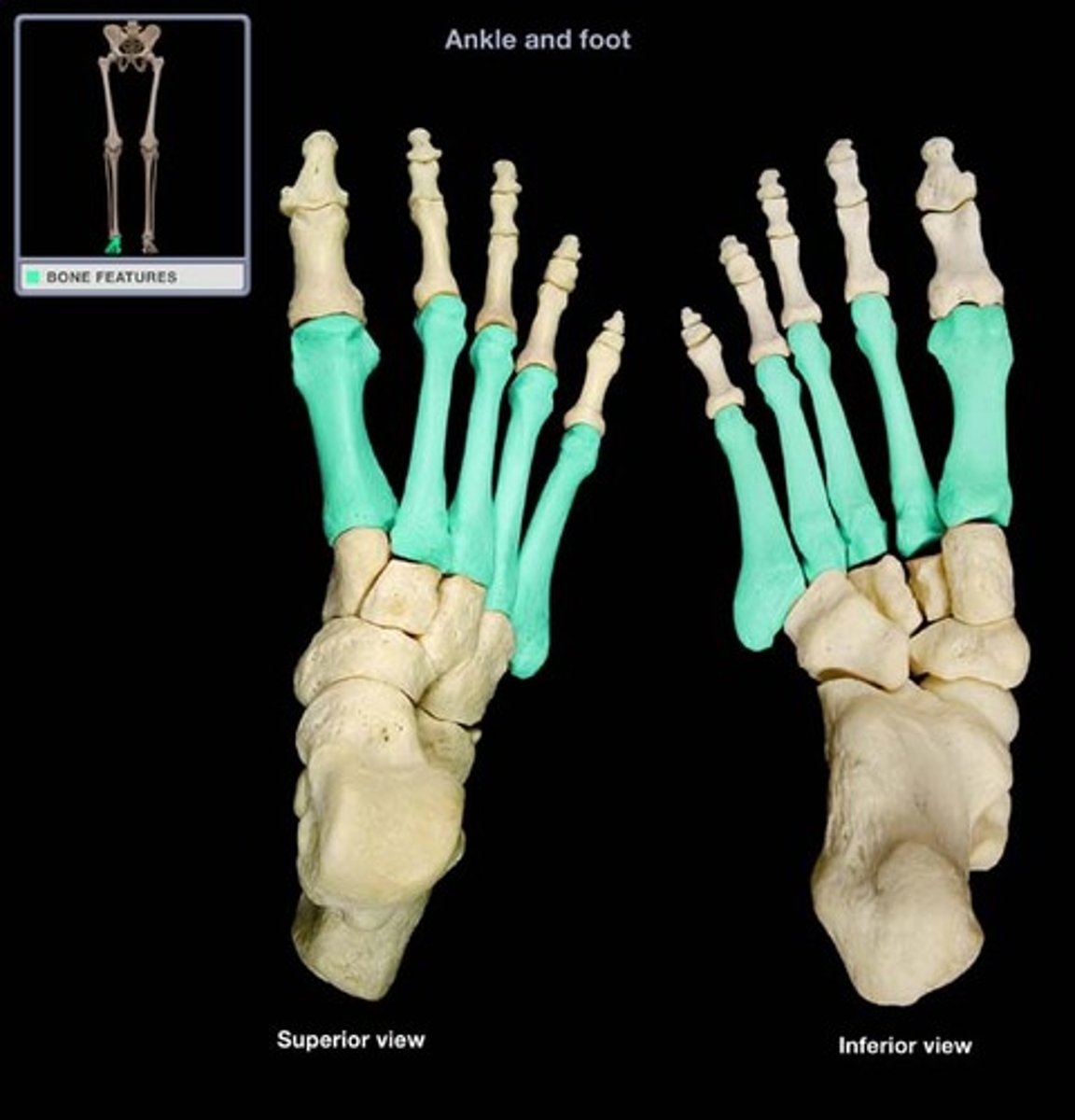
metatarsus (metatarsal bones)
5 long bones that form the distal portion of the foot
identified by roman I-V
metatarsals I-III articulate with cuneiforms
metatarsals IV-V articulate with cuboid
metatarsal I is most medial